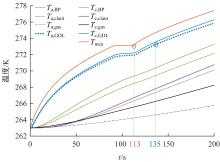
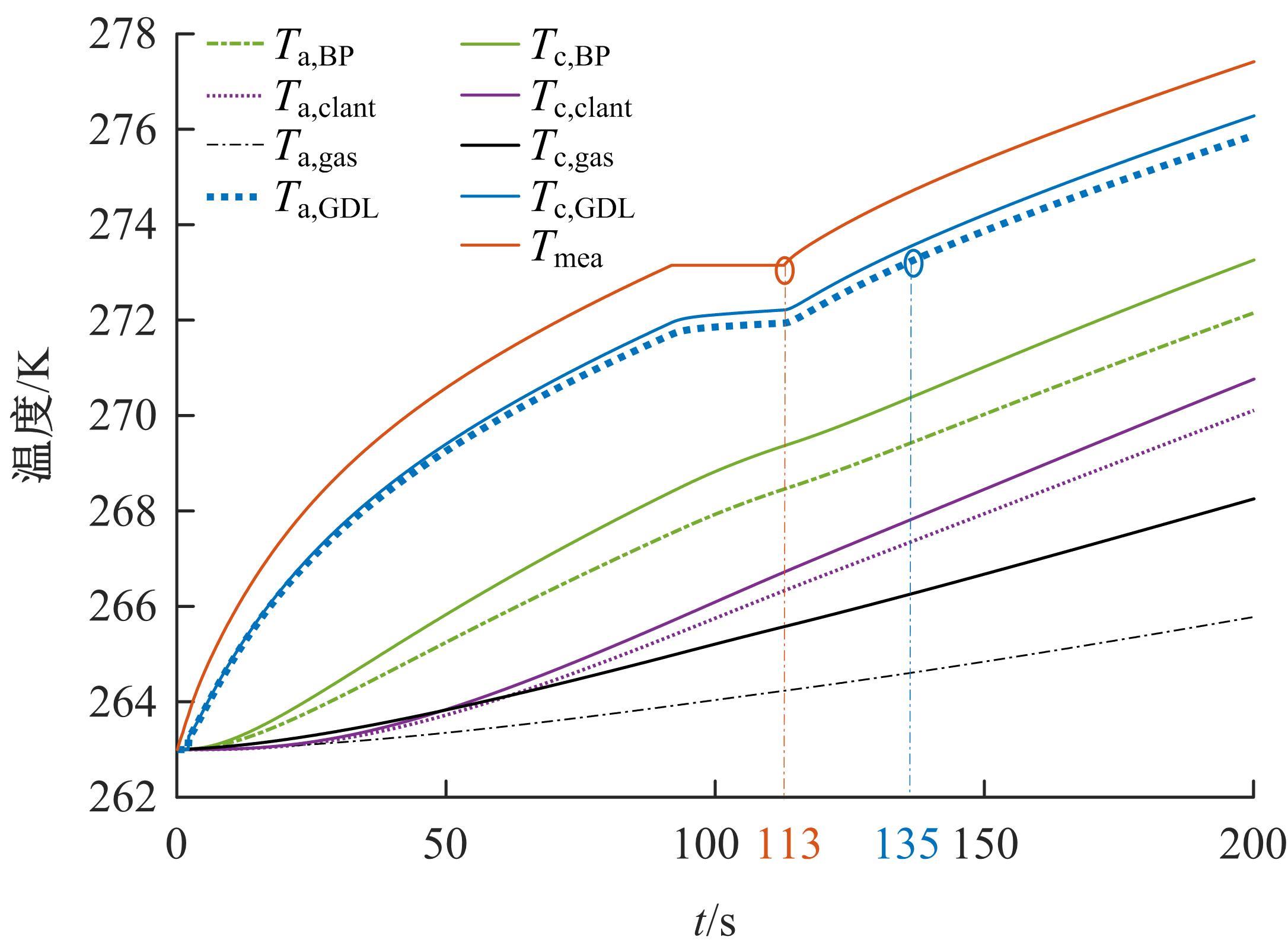
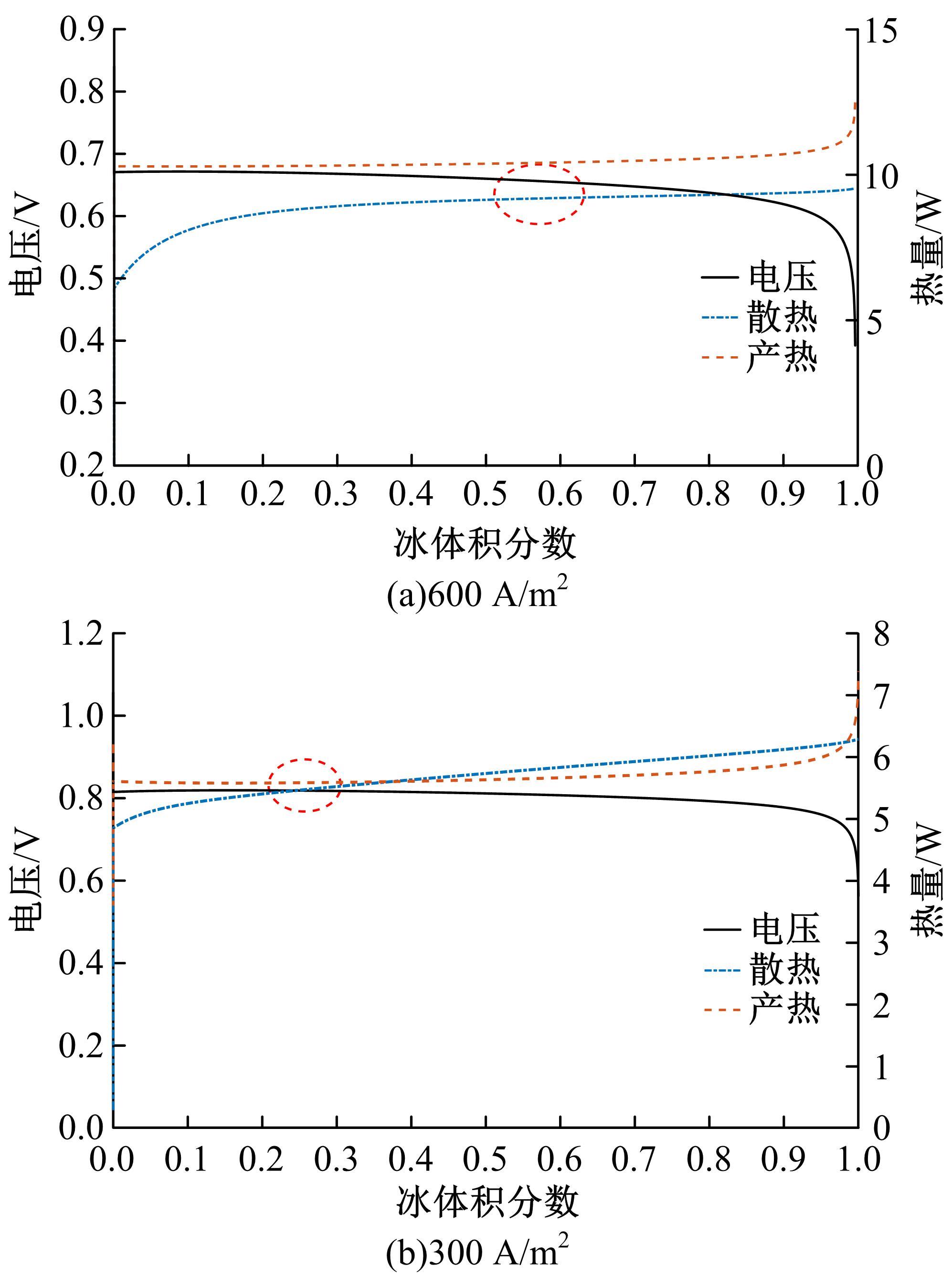
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (9): 2139-2146.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20220100
Hydrothermal characteristics of proton exchange membrane fuel cell start⁃up at low temperature
Qi-ming CAO( ),Hai-tao MIN,Wei-yi SUN(
),Hai-tao MIN,Wei-yi SUN( ),Yuan-bin YU,Jun-yu JIANG
),Yuan-bin YU,Jun-yu JIANG
- State Key Laboratory of Automotive Simulation and Control,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
CLC Number:
- TM911.4
| 1 | Wang Jun-ye. Theory and practice of flow field designs for fuel cell scaling-up: a critical review[J]. Applied Energy, 2015, 157: 640-663. |
| 2 | Jiao Kui, Li Xian-guo. Effects of various operating and initial conditions on cold start performance of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2009, 34(19): 8171-8184. |
| 3 | Meng Hua. A PEM fuel cell model for cold-start simulations[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2008, 178(1): 141-150. |
| 4 | Yao Lei, Peng Jie, Zhang Jian-bo, et al. Numerical investigation of cold-start behavior of polymer electrolyte fuel cells in the presence of super-cooled water[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(32): 15505-15520. |
| 5 | Amamou A, Kandidayeni M, Macias A, et al. Efficient model selection for real-time adaptive cold start strategy of a fuel cell system on vehicular applications[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(38): 19664-19675. |
| 6 | Du Qing, Jia Bin, Luo Yue-qi, et al. Maximum power cold start mode of proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39(16): 8390-8400. |
| 7 | Luo Yue-qi, Jiao Kui, Jia Bin. Elucidating the constant power, current and voltage cold start modes of proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. Int J Heat Mass Tran, 2014, 77: 489-500. |
| 8 | Jiang F M, Wang C Y, Chen K S. Current ramping: a strategy for rapid start-up of PEMFCs from subfreezing environment[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2010, 157(3): B342-B347. |
| 9 | Jiang H L, Xu L F, Struchtrup H, et al. Modeling of fuel cell cold start and dimension reduction simplification method[J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2020, 167(4): No. 044501. |
| 10 | Tajiri K, Tabuchi Y, Kagami F, et al. Effects of operating and design parameters on PEFC cold start[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2007, 165(1): 279-286. |
| 11 | Schießwohl E, von Unwerth T, Seyfried F, et al. Experimental investigation of parameters influencing the freeze start ability of a fuel cell system[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2009, 193(1): 107-115. |
| 12 | Min Hai-tao, Cao Qi-ming, Yu Yuan-bin, et al. A cold start mode of proton exchange membrane fuel cell based on current control[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(8): 5507-5520. |
| [1] | Ji-zong LIU,Xiao-ping WU,Wei-hua KONG. Parameter configuration of fuel cell hybrid system for tram based on fish swarm optimization algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2004-2013. |
| [2] | Ke-yong WANG,Da-tong BAO,Su ZHOU. Data-driven online adaptive diagnosis algorithm towards vehicle fuel cell fault diagnosis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2107-2118. |
| [3] | Zi-rong YANG,Yan LI,Xue-feng JI,Fang LIU,Dong HAO. Sensitivity analysis of operating parameters for proton exchange membrane fuel cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 1971-1981. |
| [4] | Yun-feng HU,Tong YU,Hui-ce YANG,Yao SUN. Optimal control method of fuel cell start⁃up in low temperature environment [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2034-2043. |
| [5] | Jing DU,Hong-hui ZHAO,Yu-peng WANG,Tian-wei DING,Kai WEI,Kai WANG,Ling-hai HAN. Purge strategy optimization and verification of PEM fuel cell engine based on AMESim simulation model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2069-2076. |
| [6] | Chong ZHANG,Yun-feng HU,Xun GONG,Yao SUN. Design of model⁃free adaptive sliding mode controller for cathode flow of fuel cell [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2085-2095. |
| [7] | Hai-lin KUI,Ze-zhao WANG,Jia-zhen ZHANG,Yang LIU. Transmission ratio and energy management strategy of fuel cell vehicle based on AVL⁃Cruise [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2119-2129. |
| [8] | Pei ZHANG,Zhi-wei WANG,Chang-qing DU,Fu-wu YAN,Chi-hua LU. Oxygen excess ratio control method of proton exchange membrane fuel cell air system for vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 1996-2003. |
| [9] | Feng-xiang CHEN,Jun-yu ZHANG,Feng-lai PEI,Ming-tao HOU,Qi-peng LI,Pei-qing LI,Yang-yang WANG,Wei-dong ZHANG. Modeling and selection scheme of proton exchange membrane fuel cell hydrogen supply system [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 1982-1995. |
| [10] | Zhen-ning LIU,Ke JIANG,Tao-tao ZHAO,Wen-xuan FAN,Guo-long LU. Development and experimental of high⁃power proton exchange membrane fuel cell test system [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2025-2033. |
| [11] | Xun-cheng CHI,Zhong-jun HOU,Wei WEI,Zeng-gang XIA,Lin-lin ZHUANG,Rong GUO. Review of model⁃based anode gas concentration estimation techniques of proton exchange membrane fuel cell system [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 1957-1970. |
| [12] | Yao-wang PEI,Feng-xiang CHEN,Zhe HU,Shuang ZHAI,Feng-lai PEI,Wei-dong ZHANG,Jie-ran JIAO. Temperature control of proton exchange membrane fuel cell thermal management system based on adaptive LQR control [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2014-2024. |
| [13] | Heng ZHANG,Zhi-gang ZHAN,Ben CHEN,Pang-chieh SUI,Mu PAN. Anisotropic transport properties of gas diffusion layer based on pore⁃scale model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2055-2062. |
| [14] | Feng-xiang CHEN,Qi WU,Yuan-song LI,Tian-de MO,Yu LI,Li-ping HUANG,Jian-hong SU,Wei-dong ZHANG. Matching,simulation and optimization for 2.5 ton fuel cell/battery hybrid forklift [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2044-2054. |
| [15] | Xiao-hua WU,Zhong-wei YU,Zhang-ling ZHU,Xin-mei GAO. Fuzzy energy management strategy of fuel cell buses [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2077-2084. |
|
||