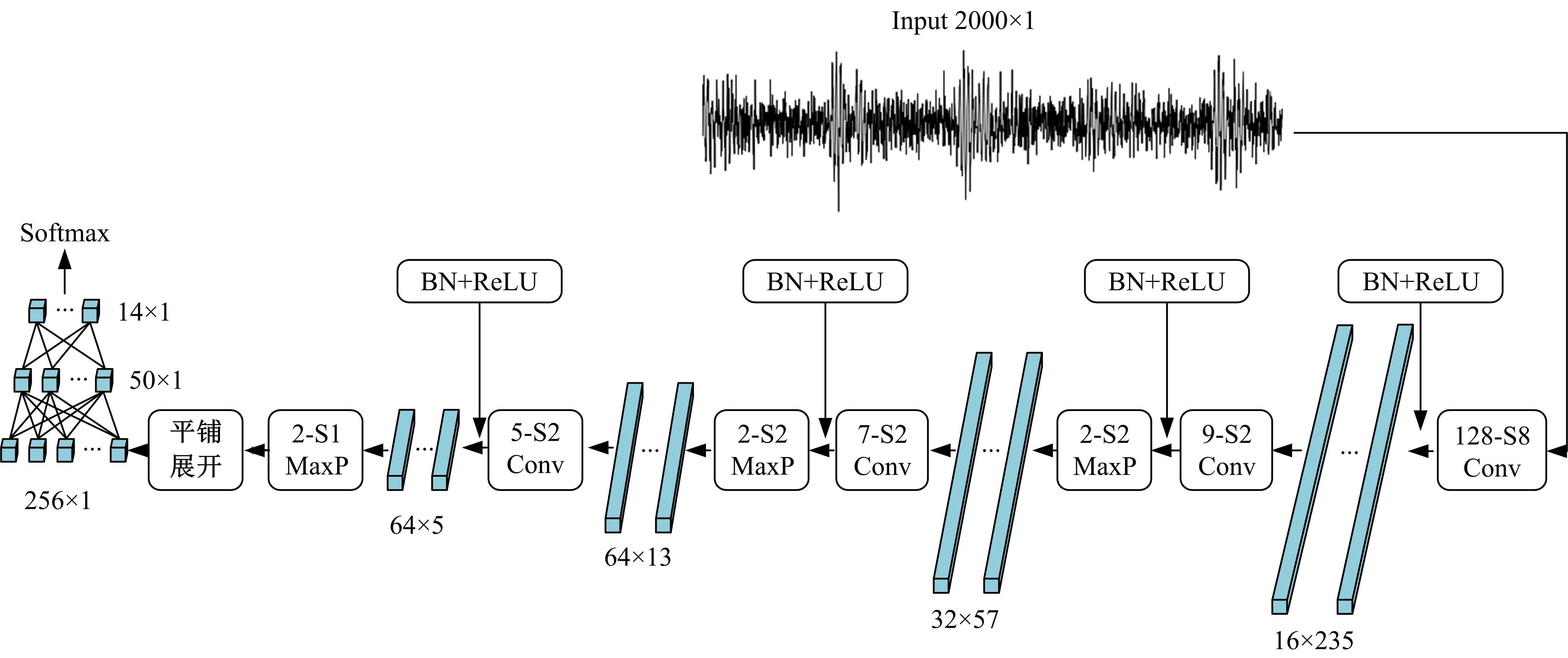
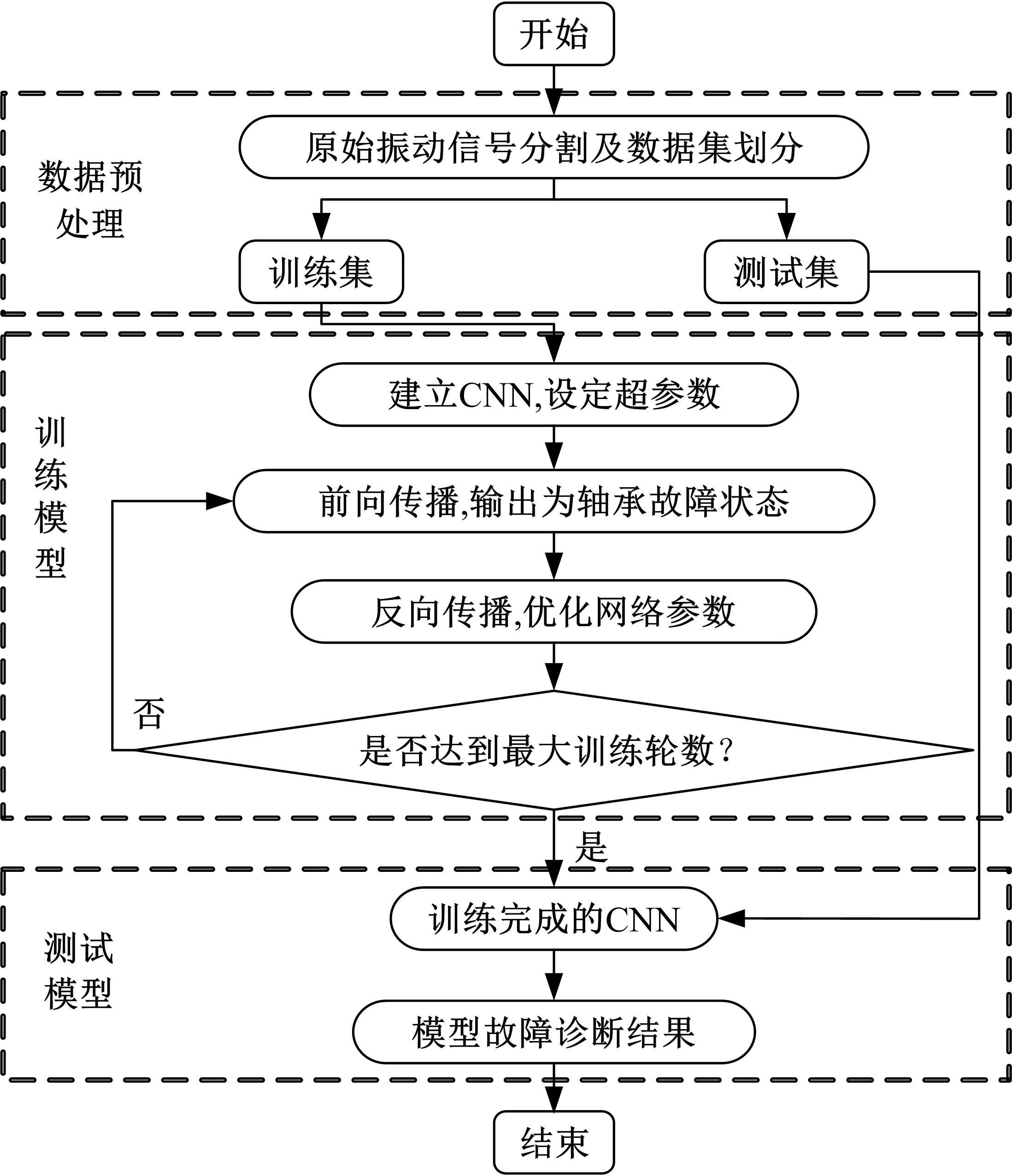
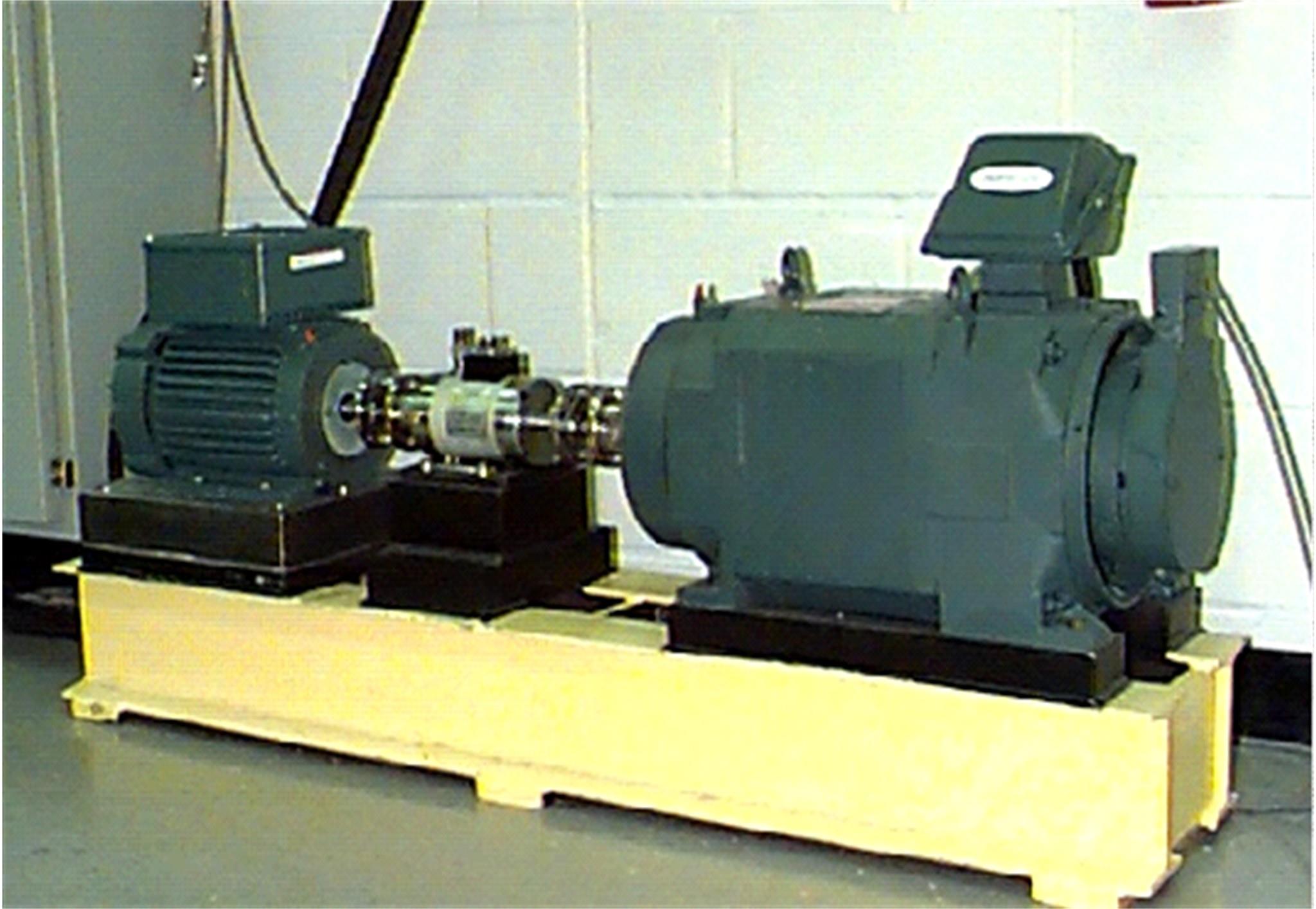
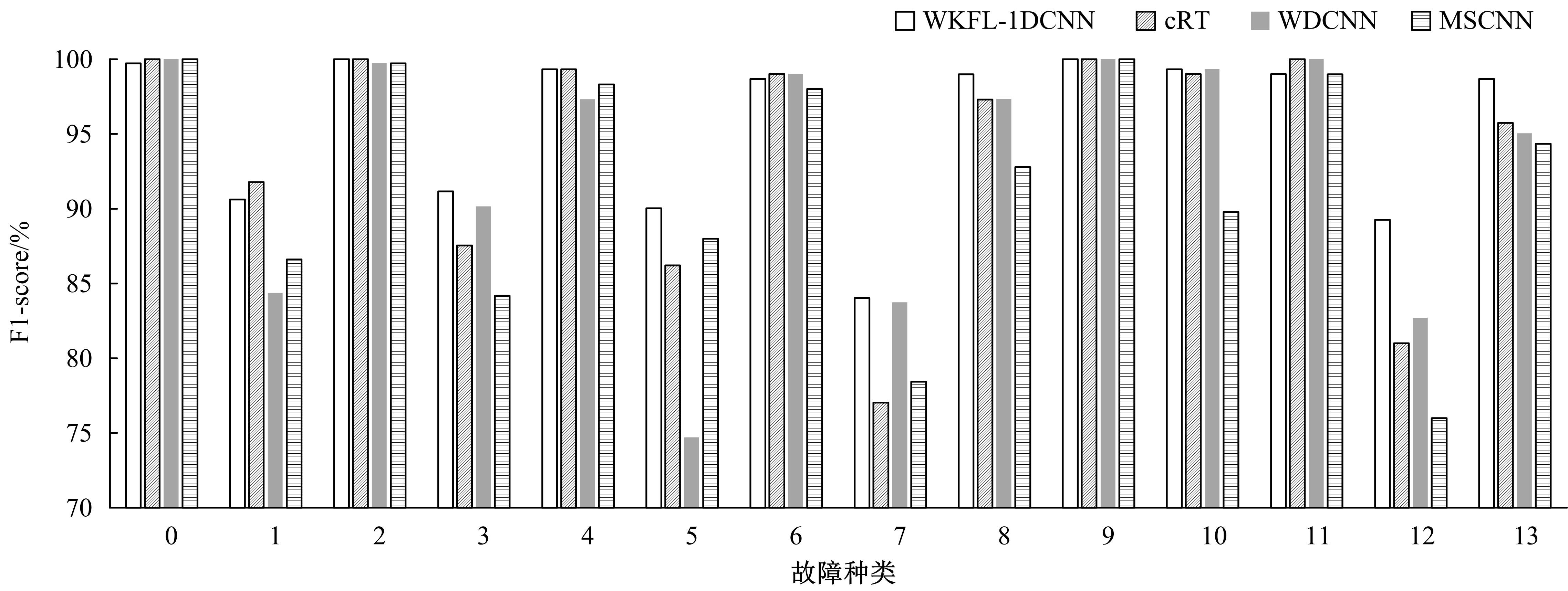
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (11): 2523-2531.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210374
Bearing fault diagnosis method under unbalanced data distribution
Jie CAO1,2,3( ),Zhi-Dong HE1,Ping YU1,3(
),Zhi-Dong HE1,Ping YU1,3( ),Jin-hua WANG1,3,4
),Jin-hua WANG1,3,4
- 1.College of Electrical & Information Engineering,Lanzhou University of Technology,Lanzhou 730050,China
2.Engineering Research Center of Urban Railway Transportation of Gansu Province,Lanzhou 730050,China
3.Engineering Research Center of Manufacturing Information of Gansu Province,Lanzhou 730050,China
4.National Experimental Teaching Center of Electrical and Control Engineering,Lanzhou University of Technology,Lanzhou 730050,China
CLC Number:
- TP277
| 1 | Tang D H, Hee J K. A survey on deep learning based bearing fault diagnosis[J]. Neurocomputing, 2019, 335: 327-335. |
| 2 | Szegedy C, Ioffe S, Vanhoucke V, et al. Inception-v 4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning[J/OL]. (2020-08-23). |
| 3 | Mikolov T, Karafiát M, Burget L, et al. Recurrent neural network based language model[C]∥Interspeech, Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, Makuhari, Japan, 2015: 1045-1048. |
| 4 | 钟辉, 康恒, 吕颖达, 等. 基于注意力卷积神经网络的图像篡改定位算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(5): 1838-1844. |
| Zhong Hui, Kang Heng, Ying-da Lyu, et al. Image manipulation localization algorithm based on channel attention convolutional neural networks[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(5): 1838-1844. | |
| 5 | Xia M, Li T, Liu L Z, et al. Intelligent fault diagnosis approach with unsupervised feature learning by stacked denoising autoencoder[J]. IET Science, Measurement & Technology, 2017, 11(6): 687-695. |
| 6 | Zhang W, Li C H, Peng G L, et al. A deep convolutional neural network with new training methods for bearing fault diagnosis under noisy environment and different working load[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2018, 100: 439-453. |
| 7 | Shao H, Jiang H, Zhao H, et al. An enhancement deep feature fusion method for rotating machinery fault diagnosis[J].Knowledge-Based Systems, 2017, 119: 200-220. |
| 8 | Levent E. Bearing fault detection by one-dimensional convolutional neural networks[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2017,2017: 1-9. |
| 9 | Pan J, Zi Y Y, Chen J L, et al. LiftingNet: a novel deep learning network with layerwise feature learning from noisy mechanical data for fault classification[J]. IEEE Trans Ind Electron, 2018, 65(6): 4973-4982. |
| 10 | 陈晓雷, 孙永峰, 李策, 等.基于卷积神经网络和双向长短期记忆的稳定抗噪声滚动轴承故障诊断[J].吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(2): 296-309. |
| Chen Xiao-lei, Sun Yong-feng, Li Ce, et al. Stable anti-noise fault diagnosis of rolling bearing based on CNN-BiLSTM[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(2): 296-309. | |
| 11 | Eren L, Ince T, Kiranyaz S. A generic intelligent bearing fault diagnosis system using compact adaptive 1D CNN classifier[J]. Signal Process Syst, 2019, 91(2): 179-189. |
| 12 | 邓飞跃, 吕浩洋, 顾晓辉, 等. 基于轻量化神经网络Shuffle-SENet的高速动车组轴箱轴承故障诊断方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(2):474-482. |
| Deng Fei-yue, Hao-yang Lyu, Gu Xiao-hui, et al. Fault diagnosis of high-speed train axle bearing based on a lightweight neural network Shuffle-SENet[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(2): 474-482. | |
| 13 | Wang X, Mao D X, Li X D. Bearing fault diagnosis based on vibro-acoustic data fusion and 1D-CNN network[J]. Measurement, 2021, 173(6): 108518. |
| 14 | Lessmeier C, Kimotho J K, Zimmer D, et al. Condition monitoring of bearing damage in electromechanical drive systems by using motor current signals of electric motors: a benchmark data set for data-driven classification[C]∥European Conference of the Prognostics and Health Management Society, Bilbao, Spain, 2016:1-17. |
| 15 | Jia F, Lei Y, Lu N, et al. Deep normalized convolutional neural network for imbalanced fault classification of machinery and its understanding via visualization[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2018, 110: 349-367. |
| 16 | Huang S Z, Tang J, Dai J Y, et al. 1DCNN fault diagnosis based on cubic spline interpolation pooling[J]. Shock and Vibration, 2020(2/3): 1-13. |
| 17 | Kang B Y, Xie S N, Marcus R, et al. Decoupling representation and classifier for long-tailed recognition[J/OL]. [2020-10-21]. |
| 18 | Cao K D, Wei C, Adrien G, et al. Learning imbalanced datasets with label-distribution-aware margin loss[J/OL]. [2020-06-18]. 0/arXiv.1906.07413 |
| 19 | Cui Y, Jia M L, Lin T Y, et al. Class-balanced loss based on effective number of samples[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 9268-9277. |
| 20 | 张明德, 卢建华, 马婧华. 基于多尺度卷积策略CNN的滚动轴承故障诊断[J]. 重庆理工大学学报:自然科学, 2020, 34(6): 102-110. |
| Zhang Ming-de, Lu Jian-hua, Ma Jing-hua. Fault diagnosis of rolling bearing based on multi-scale convolution strategy CNN[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology(Natural Science), 2020, 34(6): 102-110. | |
| 21 | Sergey I, Christian S. Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[J/OL]. [2020-08-11]. 8550/arXiv.1502.03167 |
| 22 |
Bjorck J, Gomes C, Selman B. Understanding batch normalization[J/OL]. [2020-06-01]. / 10.48550/arXiv.1806.02375
doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1806.02375 |
| 23 | Kingma D P, Ba J. Adam: a method for stochastic optimization[J/OL]. [2020-12-22]. |
| 24 | Zhang W, Peng G L, Li C H, et al. A new deep learning model for fault diagnosis with good anti-noise and domain adaptation ability on raw vibration signals[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(3): 425-445. |
| 25 | Jiang G Q, He H B, Yan J, et al. Multiscale convolutional neural networks for fault diagnosis of wind turbine gearbox[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(4): 3196-3207. |
| [1] | Xuan-jing SHEN,Xue-feng ZHANG,Yu WANG,Yu-bo JIN. Multi⁃focus image fusion algorithm based on pixel⁃level convolutional neural network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1857-1864. |
| [2] | Ming-hua GAO,Can YANG. Traffic target detection method based on improved convolution neural network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1353-1361. |
| [3] | Huai-jiang YANG,Er-shuai WANG,Yong-xin SUI,Feng YAN,Yue ZHOU. Simplified residual structure and fast deep residual networks [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1413-1421. |
| [4] | Xue-zhi WANG,Qing-liang LI,Wen-hui LI. Spatio⁃temporal model of soil moisture prediction integrated with transfer learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(3): 675-683. |
| [5] | Xiang-jun LI,Jie-ying TU,Zhi-bin ZHAO. Validity classification of melting curve based on multi⁃scale fusion convolutional neural network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(3): 633-639. |
| [6] | Xian-tong LI,Wei QUAN,Hua WANG,Peng-cheng SUN,Peng-jin AN,Yong-xing MAN. Route travel time prediction on deep learning model through spatiotemporal features [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(3): 557-563. |
| [7] | Jie CAO,Jia-lin MA,Dai-lin HUANG,Ping YU. A fault diagnosis method based on multi Markov transition field [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(2): 491-496. |
| [8] | Wei LUO,Bo LU,Fei CHEN,Teng MA. Fault diagnosis method of NC turret based on PSO⁃SVM and time sequence [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(2): 392-399. |
| [9] | Wen-zhi GAO,Yan-jun WANG,Xin-wei WANG,Pan ZHANG,Yong LI,Yang DONG. Real⁃time diagnosis for misfire fault of diesel engine based on convolutional neural network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(2): 417-424. |
| [10] | Jin-hua WANG,Jia-wei HU,Jie CAO,Tao HUANG. Multi⁃fault diagnosis of rolling bearing based on adaptive variational modal decomposition and integrated extreme learning machine [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(2): 318-328. |
| [11] | Shao-jiang DONG,Peng ZHU,Xue-wu PEI,Yang LI,Xiao-lin HU. Fault diagnosis of rolling bearing under variable operating conditions based on subdomain adaptation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(2): 288-295. |
| [12] | Fei-yue DENG, LYUHao-yang,Xiao-hui GU,Ru-jiang HAO. Fault diagnosis of high⁃speed train axle bearing based on a lightweight neural network Shuffle⁃SENet [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(2): 474-482. |
| [13] | Long ZHANG,Tian-peng XU,Chao-bing WANG,Jian-yu YI,Can-zhuang ZHEN. Gearbox fault diagnosis baed on convolutional gated recurrent network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(2): 368-376. |
| [14] | Xiao⁃lei CHEN,Yong⁃feng SUN,Ce LI,Dong⁃mei LIN. Stable anti⁃noise fault diagnosis of rolling bearing based on CNN⁃BiLSTM [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(2): 296-309. |
| [15] | Fei CHEN,Zheng YANG,Zhi-cheng ZHANG,Wei LUO. Fault diagnosis method of rotating machinery for unlabeled data [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(11): 2514-2522. |
|
||