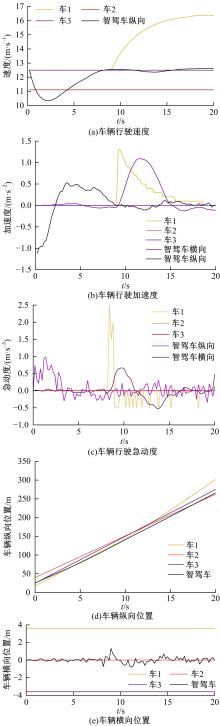
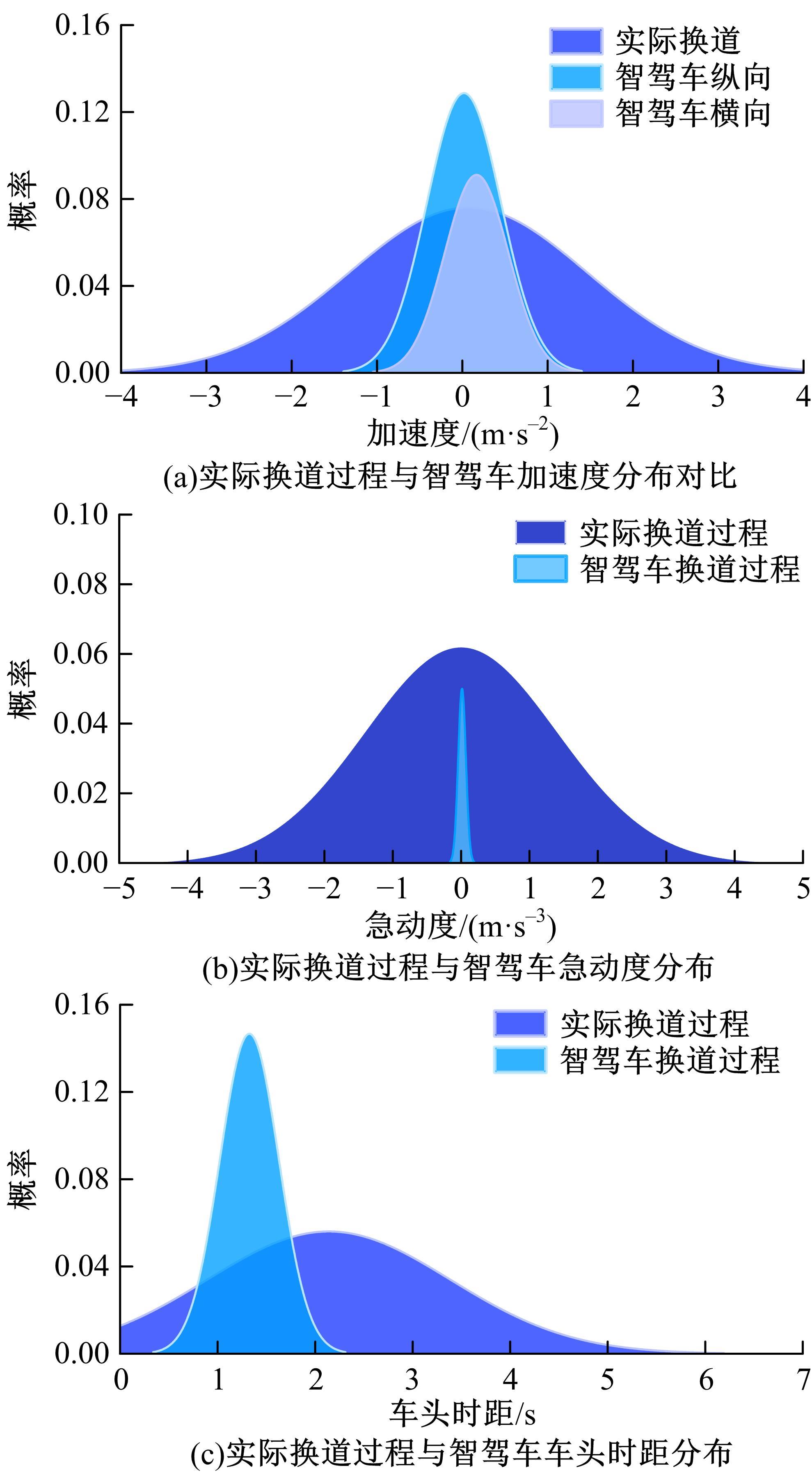
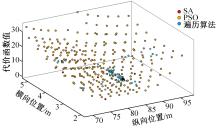
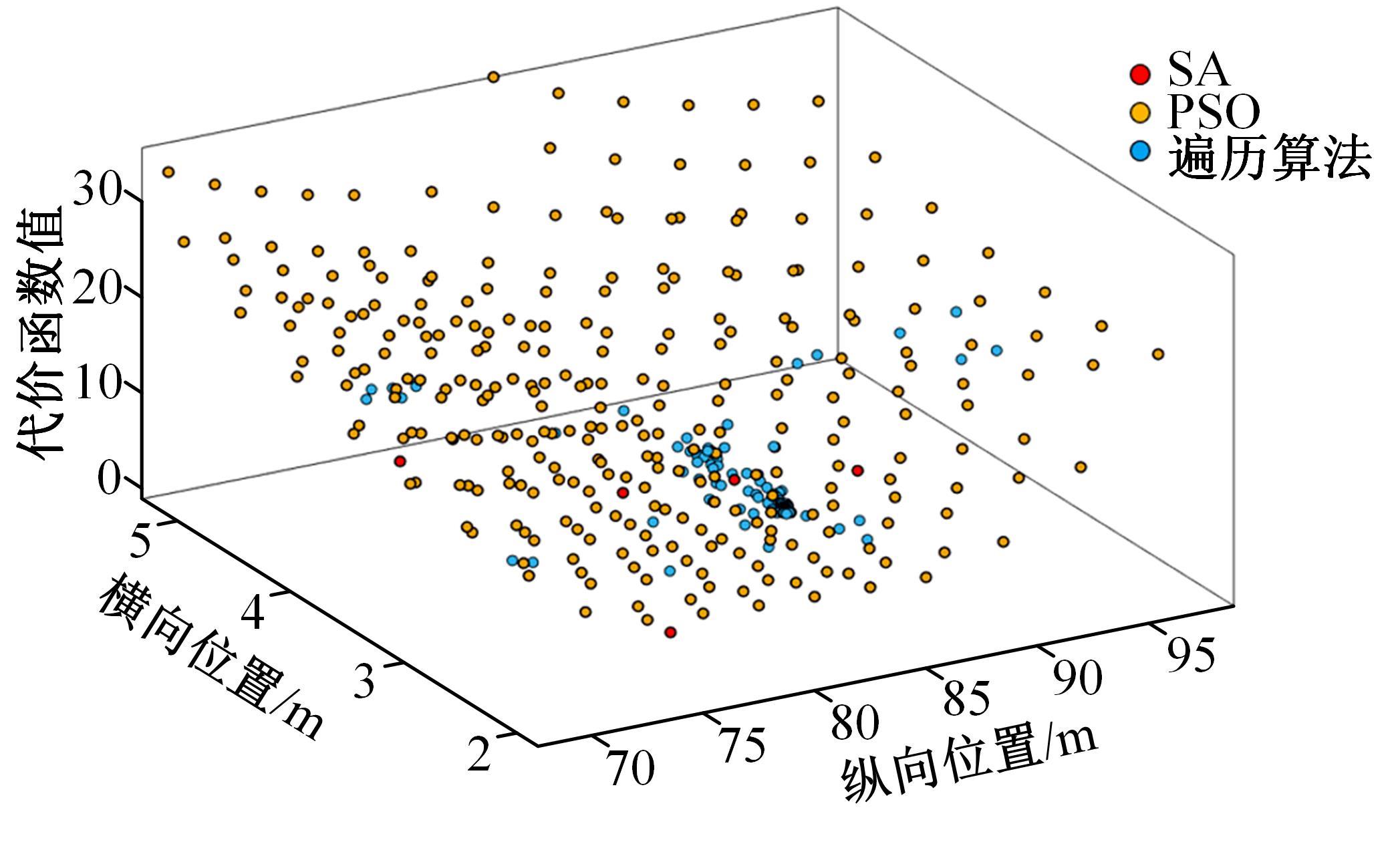
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (3): 746-757.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20220560
Integrated lane⁃changing model of decision making and motion planning for autonomous vehicles
Xue XIAO1( ),Ke-ping LI1,Bo PENG2,Man-wei CHANG1
),Ke-ping LI1,Bo PENG2,Man-wei CHANG1
- 1.Key Laboratory of Road and Traffic Engineering,Ministry of Education,Tongji University,Shanghai 201804,China
2.College of Transportation,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
CLC Number:
- U491.2
| 1 | Hang P, Lv C, Huang C, et al. An integrated framework of decision making and motion planning for autonomous vehicles considering social behaviors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(12): 14458-14469. |
| 2 | Lu Y, Xu X, Zhang X, et al. Hierarchical reinforcement learning for autonomous decision making and motion planning of intelligent vehicles[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 209776-209789. |
| 3 | Lee N, Choi W, Vernaza P, et al. Desire: distant future prediction in dynamic scenes with interacting agents[C]∥2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, America, 2017: 2156-2174. |
| 4 | Xu W, Pan J, Wei J, et al. Motion planning under uncertainty for on-road autonomous driving[C]∥2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Hong Kong, China, 2014: 2507-2512. |
| 5 | Schmerling E, Leung K, Vollprecht W, et al. Multimodal probabilistic model-based planning for human-robot interaction[C]∥2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, Australia, 2018: 1-9. |
| 6 | Gindele T, Brechtel S, Dillmann R. Learning driver behavior models from traffic observations for decision making and planning[J]. IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Magazine, 2015, 7(1): 69-79. |
| 7 | Schulz J, Hubmann C, Löchner J, et al. Interaction-aware probabilistic behavior prediction in urban environments[C]∥2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 2018: 3999-4006. |
| 8 | Althoff M, Mergel A. Comparison of markov chain abstraction and monte carlo simulation for the safety assessment of autonomous cars[J]. IEEE Transaction on Intelligent Transportation System, 2011, 12(4): 1237-1247. |
| 9 | Kamrani M, Srinivasan A R, Chakraborty S, et al. Applying markov decision process to understand driving decisions using basic safety messages data[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2020, 115: 1-16. |
| 10 | Vallon C, Ercan Z, Carvalho A, et al. A machine learning approach for personalized autonomous lane change initiation and control[C]∥2017 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Los Angeles, America, 2017: 1590-1595. |
| 11 | Lenz D, Diehl F, Le M T, et al. Deep neural networks for Markovian interactive scene prediction in highway scenarios[C]∥Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, Los Angeles, America, 2017: 685-692. |
| 12 | Xie D F, Fang Z, Jia B, et al. A data-driven lane-changing model based on deep learning[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2019, 106(2019): 41-60. |
| 13 | Morton J, Wheeler T A, Kochenderfer M J. Analysis of recurrent neural networks for probabilistic modeling of driver behavior[J]. IEEE Transaction on Intelligent Transportation System, 2017, 18(5): 1289-1298. |
| 14 | Yu H T, Tseng H E, Langari R, et al. A human-like game theory-based controller for automatic lane changing[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2018, 88(5): 140-158. |
| 15 | 胡益恺, 庄瀚洋, 王春香, 等. 基于主从博弈的智能车汇流场景决策方法[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2021, 55(8): 1027-1034. |
| Hu Yi-kai, Zhuang Han-yang, Wang Chun-xiang, et al. Stackelberg-game-based intelligent vehicle decision method for merging scenarios[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2021, 55(8):1027-1034. | |
| 16 | Kang K, Rakha H A. A repeated game freeway lane changing model[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(6):1554-1588. |
| 17 | Hang P, Lv C, Huang C, et al. An integrated framework of decision making and motion planning for autonomous vehicles considering social behaviors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(12): 14458-14469. |
| 18 | Katrakazas C, Quddus M, Chen W H, et al. Real-time motion planning methods for autonomous on-road driving: state-of-the-art and future research directions[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2015, 60: 416-442. |
| 19 | Gonzalez D, Pérez J, Milanes V, et al. A review of motion planning techniques for automated vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2016, 17(4): 1135-1145. |
| 20 | Lim W, Lee S, Sunwoo M, et al. Hybrid trajectory planning for autonomous driving in on-road dynamic scenarios[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2019, 22(1): 341-355. |
| 21 | Xu W D, Wei J Q, Dolan J M, et al. A real-time motion planner with trajectory optimization for autonomous vehicles[C]∥2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, St Paul, America, 2012: 2061-2067. |
| 22 | Ziegler J, Bender P, Dang T, et al. Trajectory planning for Bertha-A local continuous method[C]∥Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, Michigan, America, 2014: 450-457. |
| 23 | Jiang Y, Jin X, Xiong Y, et al. A dynamic motion planning framework for autonomous driving in urban environments[C]∥In Proceedings of the 2020 39th Chinese Control Conference, Shenyang, China, 2020: 5429-5435. |
| 24 | Liao X, Zhao X, Wu G, et al. A game theory based ramp merging strategy for connected and automated vehicles in the mixed traffic: a Unity-SUMO integrated platform[DB/OL]. [2022-01-27]. |
| 25 | Zhou D, Ma Z, Sun J. Autonomous vehicles turning motion planning in multi-interaction area of mixed-flow intersections[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2020, 5(2): 204-216. |
| 26 | Chu K, Lee M, Sunwoo M. Local path planning for off-road autonomous driving with avoidance of static obstacles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2012, 13(4): 1599-1616. |
| 27 | Werling M, Kammel S, Ziegler J, et al. Optimal trajectories for time-critical street scenarios using discretized terminal manifolds[J]. International Journal of Robotics Research, 2012, 31(3): 346-359. |
| 28 | 陈华根, 吴健生, 王家林,等. 模拟退火算法机理研究[J]. 同济大学学报:自然科学版, 2004, 32(6): 802-805. |
| Chen Hua-gen, Wu Jian-sheng, Wang Jia-lin, et al. Mechanism study of simulated annealing algorithm[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2004, 32(6): 802-805. | |
| 29 | Kirkpatrick S, Gelatt C D, Vecchi M P. Optimization by simulated annealing[J]. Science, 1983, 220(4598): 671-680. |
| 30 | 唐俊. PSO算法原理及应用[J]. 计算机技术与发展, 2010, 20(2): 213-216. |
| Tang Jun. Principle and application of PSO algorithm[J]. Computer Technology and Development, 2010, 20(2): 213-216. | |
| 31 | Qiao F, Rahman R, Li Q, et al. Safe and environment-friendly forward collision warning messages in the advance warning area of a construction zone[J]. International Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems Research, 2017, 15: 166-179. |
| 32 | Vishal M, Christos K, Constantinos A. Prediction of lane-changing maneuvers with automatic labeling and deep learning[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2020, 2674(7): 336-347. |
| [1] | Jing WANG,Feng WAN,Chun-jiao DONG,Chun-fu SHAO. Modelling on catchment area and attraction intensity of urban rail transit stations [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(2): 439-447. |
| [2] | Min MA,Da-wei HU,Lan SHU,Zhuang-lin MA. Resilience assessment and recovery strategy on urban rail transit network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(2): 396-404. |
| [3] | Song FANG,Jian-xiao MA,Gen LI,Ling-hong SHEN,Chu-bo XU. Traffic risk analysis of moving work zone on right lane of city expressway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1786-1791. |
| [4] | Song-xue GAI,Xiao-qing ZENG,Xiao-yuan YUE,Zi-hao YUAN. Parking guidance model based on user and system bi⁃level optimization algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1344-1352. |
| [5] | Hong-feng XU,Hong-jin CHEN,Dong ZHANG,Qian-hui LU,Na AN,Xian-cai Geng. Fully⁃actuated signal timing technique for isolated signalized intersections in connected vehicle environment [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1324-1336. |
| [6] | Xian-yan KUANG,Zi-ru CHEN. Dynamic game comity behavior at pedestrians′ crossing on unsignal-controlled roads based on cellular automata [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(4): 837-846. |
| [7] | Guo-zhu CHENG,Qiu-yue SUN,Yue-bo LIU,Ji-long CHEN. Cut⁃in behavior model based on game theoretic approach on urban roads [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(12): 2839-2844. |
| [8] | Heng-yan PAN,Wen-hui ZHANG,Bao-yu HU,Zun-yan LIU,Yong-gang WANG,Xiao ZHANG. Construction and robustness analysis of urban weighted subway⁃bus composite network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(11): 2582-2591. |
| [9] | Zhuang-lin MA,Shan-shan CUI,Da-wei HU. Urban residents' low⁃carbon travel intention after implementation of driving restriction policy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(11): 2607-2617. |
| [10] | Jing-xian WU,Hua-peng SHEN,Yin HAN,Min YANG. Residents' commuting time model under the nonlinear impact of urban built environment [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(11): 2568-2573. |
| [11] | Jie MA,Jia-jun HUANG,Jun TIAN,Yang-hui DONG. Simulation modeling of pedestrian target decision⁃making in evacuation process in transfer corridors of subway stations [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(11): 2600-2606. |
| [12] | Da-yi QU,Kai-xian HEI,Hai-bing GUO,Yan-feng JIA,Tao WANG. Game behavior and model of lane-changing on the internet of vehicles environment [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(1): 101-109. |
| [13] | Feng XUE,Chuan-lei HE,Qian HUANG,Jian LUO. Coordination degree of multimodal rail transit network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(6): 2040-2050. |
| [14] | Xiang-jun YU,Yuan-hui HUAI,Zong-wei YAO,Zhong-chao SUN,An YU. Key technologies in autonomous vehicle for engineering [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(4): 1153-1168. |
| [15] | Yao-rong CHENG,Qian YANG,Guo-hua ZHENG. Tractor scheduling optimization of drop and pull transport in large⁃scale manufacturing enterprises considering carbon emission [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 893-899. |
|
||