Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (12): 2839-2844.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210404
Previous Articles Next Articles
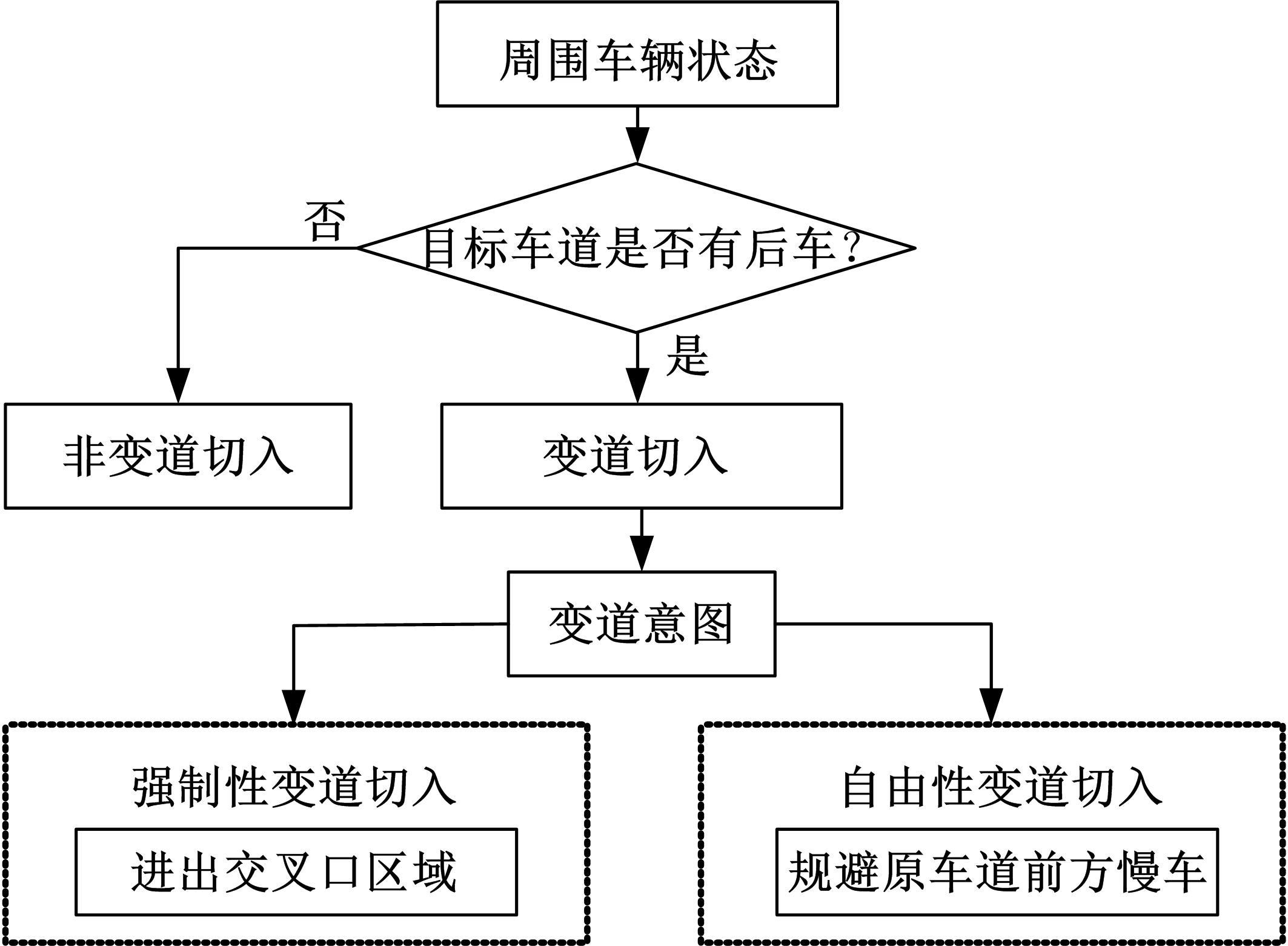
Cut⁃in behavior model based on game theoretic approach on urban roads
Guo-zhu CHENG1( ),Qiu-yue SUN1,Yue-bo LIU2(
),Qiu-yue SUN1,Yue-bo LIU2( ),Ji-long CHEN1
),Ji-long CHEN1
- 1.School of Traffic and Transportation,Northeast Forestry University,Harbin 150040,China
2.School of Computer Science and Engineering,Jilin University of Architecture and Technology,Changchun 130114,China
CLC Number:
- U491
| 1 | 王雪松,杨敏明. 基于自然驾驶数据的变道切入行为分析[J]. 同济大学学报:自然科学版,2018, 46(8): 1057-1063. |
| Wang Xue-song, Yang Min-ming. Cut-in behavior analyses based on naturalistic driving data[J]. Journal of Tongji University(Natural Science), 2018, 46(8):1057-1063. | |
| 2 | Talebpour A, Mahmassani H S. Influence of connected and autonomous vehicles on traffic flow stability and throughput[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2016, 71: 143-163. |
| 3 | Ali Y, Zheng Z, Haque M M. Connectivity's impact on mandatory lane-changing behaviour: Evidences from a driving simulator study[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2018, 93: 292-309. |
| 4 | Talebpour A, Mahmassani H S, Hamdar S H. Modeling lane-changing behavior in a connected environment: a game theory approach[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2015, 59: 216-232. |
| 5 | Liu H X, Xin W P, Adams Z M, et al. A game theoretical approach for modeling merging and yielding behavior at freeway on-ramp section[C]∥Transportation and Traffic Theory, London, England,2007:196-211. |
| 6 | Wang M, Hoogendoorn S P, Daamen W, et al. Game theoretic approach for predictive lane-changing and car-following control[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2015, 58: 73-92. |
| 7 | Kang K, Rakha H A. Game theoretical approach to model decision making for merging maneuvers at freeway on-ramps[J]. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2017, 2623(1): 19-28. |
| 8 | Ali Y, Zheng Z, Haque M M, et al. A game theory-based approach for modelling mandatory lane-changing behaviour in a connected environment[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2019, 106: 220-242. |
| 9 | Lin D, Li L, Jabari S E. Pay to change lanes: a cooperative lane-changing strategy for connected/automated driving[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2019, 105: 550-564. |
| 10 | Nakata M, Yamauchi A, Tanimoto J, et al. Dilemma game structure hidden in traffic flow at a bottleneck due to a 2 into 1 lane junction[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2010, 389(23): 5353-5361. |
| 11 | Hidas P. Modelling vehicle interactions in microscopic simulation of merging and weaving[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2005, 13(1): 37-62. |
| 12 | Arbis D, Dixit V V. Game theoretic model for lane changing: incorporating conflict risks[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2019, 125: 158-164. |
| 13 | Montanino M, Punzo V. Making NGSIM data usable for studies on traffic flow theory[J]. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2013, 2390(1): 99-111. |
| 14 | 蔺湘然. 基于NGSIM数据的车道级车辆换道策略研究[J]. 综合运输,2019, 41(4): 120-126. |
| Lin Xiang-ran. Lane-level vehicle lane change strategy based on NGSIM data[J]. China Transportation Review,2019, 41(4): 120-126. | |
| 15 | 曾小华,宋美洁,宋大凤,等. 基于车联网信息的公交客车行驶工况数据处理方法[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2021, 51(5): 1692-1699. |
| Zeng Xiao-hua, Song Mei-jie, Song Da-feng, et al. Data processing method of bus driving condition based on internet of vehicles information[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(5): 1692-1699. |
| [1] | Jing WANG,Feng WAN,Chun-jiao DONG,Chun-fu SHAO. Modelling on catchment area and attraction intensity of urban rail transit stations [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(2): 439-447. |
| [2] | Min MA,Da-wei HU,Lan SHU,Zhuang-lin MA. Resilience assessment and recovery strategy on urban rail transit network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(2): 396-404. |
| [3] | Song FANG,Jian-xiao MA,Gen LI,Ling-hong SHEN,Chu-bo XU. Traffic risk analysis of moving work zone on right lane of city expressway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1786-1791. |
| [4] | Song-xue GAI,Xiao-qing ZENG,Xiao-yuan YUE,Zi-hao YUAN. Parking guidance model based on user and system bi⁃level optimization algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1344-1352. |
| [5] | Hong-feng XU,Hong-jin CHEN,Dong ZHANG,Qian-hui LU,Na AN,Xian-cai Geng. Fully⁃actuated signal timing technique for isolated signalized intersections in connected vehicle environment [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1324-1336. |
| [6] | Jie MA,Jia-jun HUANG,Jun TIAN,Yang-hui DONG. Simulation modeling of pedestrian target decision⁃making in evacuation process in transfer corridors of subway stations [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(11): 2600-2606. |
| [7] | Heng-yan PAN,Wen-hui ZHANG,Bao-yu HU,Zun-yan LIU,Yong-gang WANG,Xiao ZHANG. Construction and robustness analysis of urban weighted subway⁃bus composite network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(11): 2582-2591. |
| [8] | Zhuang-lin MA,Shan-shan CUI,Da-wei HU. Urban residents' low⁃carbon travel intention after implementation of driving restriction policy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(11): 2607-2617. |
| [9] | Jing-xian WU,Hua-peng SHEN,Yin HAN,Min YANG. Residents' commuting time model under the nonlinear impact of urban built environment [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(11): 2568-2573. |
| [10] | Feng XUE,Chuan-lei HE,Qian HUANG,Jian LUO. Coordination degree of multimodal rail transit network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(6): 2040-2050. |
| [11] | Bo PENG,Yuan-yuan ZHANG,Yu-ting WANG,Ju TANG,Ji-ming XIE. Automatic traffic state recognition from videos based on auto⁃encoder and classifiers [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 886-892. |
| [12] | Dian-hai WANG,Xin-yi SHEN,Xiao-qin LUO,Sheng JIN. Offset optimization with minimum average vehicle delay [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 511-523. |
| [13] | Xian-min SONG,Ming-ye ZHANG,Zhen-jian LI,Xin WANG,Ya-nan ZHANG. Setting of dynamic bus lane and its simulation analysis and evaluation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(5): 1677-1686. |
| [14] | Hong-fei JIA,Xin-ru DING,Li-li YANG. Bi-level programming model for optimization design of tidal lane [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 535-542. |
| [15] | Chao-ying YIN,Chun-fu SHAO,Xiao-quan WANG,Zhi-hua XIONG. Influence of built environment on commuting mode choice considering spatial heterogeneity [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 543-548. |
|