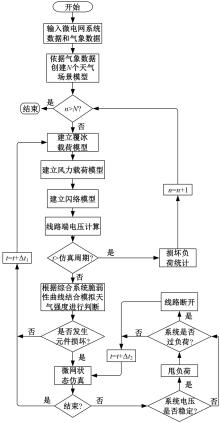
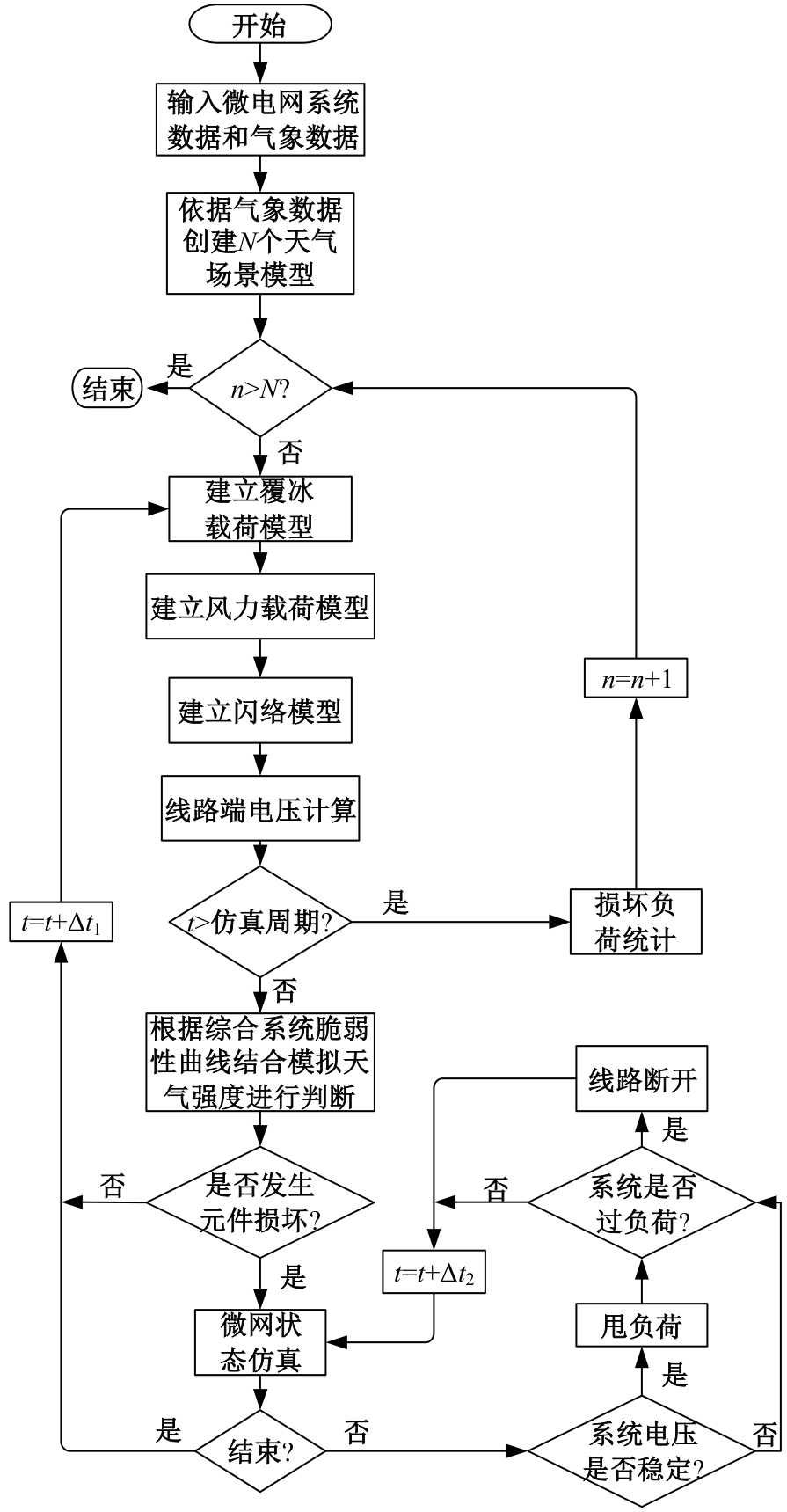
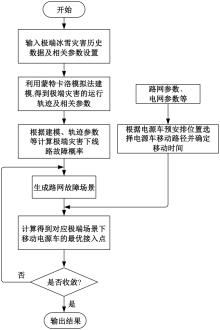
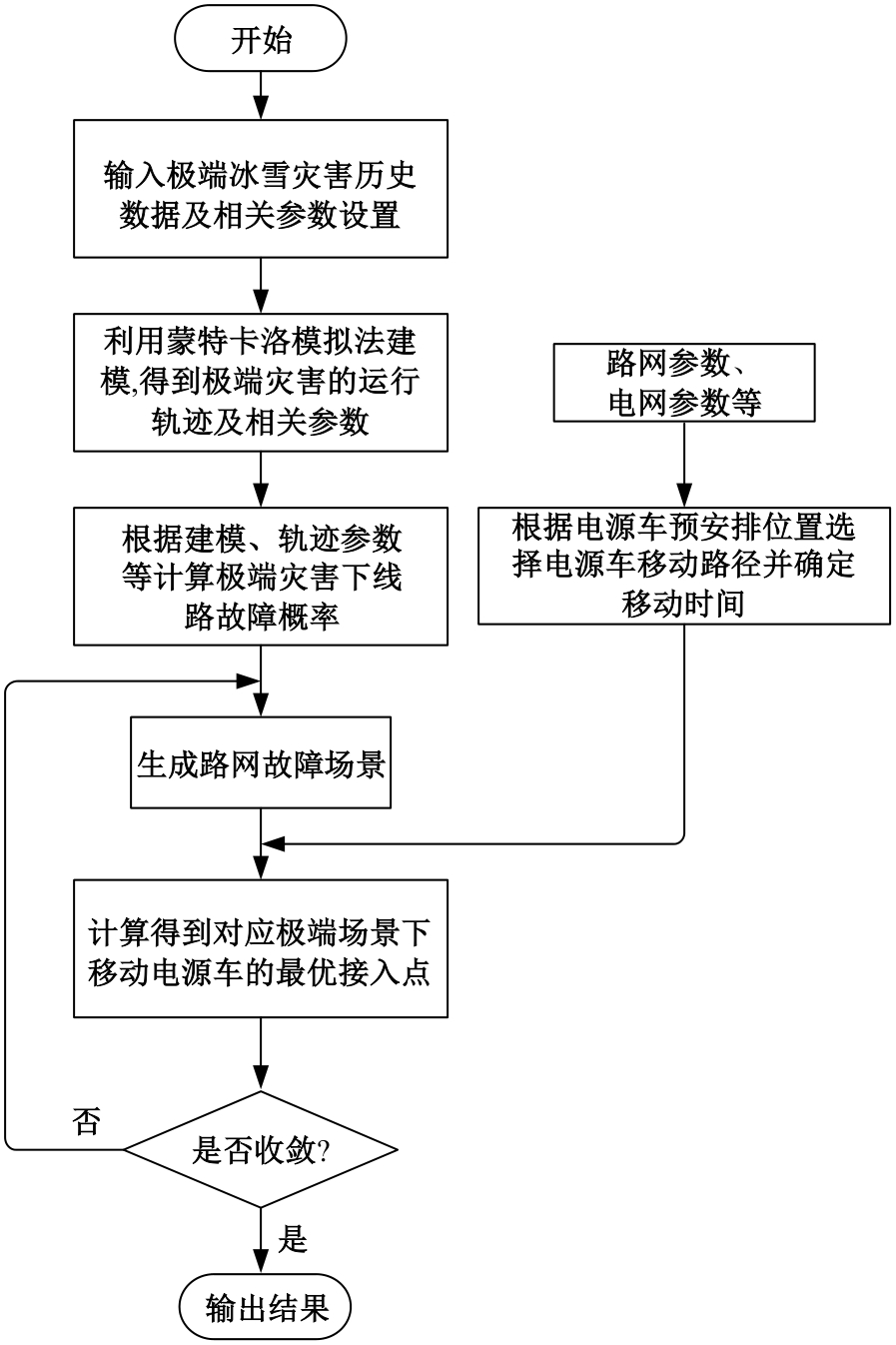
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (11): 3623-3631.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20240224
Optimal scheduling of mobile power vehicles for highway self-consistent energy systems in extreme weather conditions
Yan-bo LI1( ),Miao-yang LIU2,Kai YANG3,Yun-rui ZHANG1,Hao-nan LYU1,Qiu-cai WANG2(
),Miao-yang LIU2,Kai YANG3,Yun-rui ZHANG1,Hao-nan LYU1,Qiu-cai WANG2( )
)
- 1.School of Energy and Electrical Engineering,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064 China
2.School of Electronic and Control Engineering,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
3.Shandong Traffic Planning Design Institute Group Co. ,Ltd. ,Jinan 250101,China
CLC Number:
- U491.8
| [1] | 刘洋, 刘吉成. 基于大数据与粒子群的清洁能源协同优化调度方法[J].吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2023, 53(5): 1443-1448. |
| Liu Yang, Liu Ji-cheng. Collaborative optimization scheduling method of clean energy based on big data and particle swarm optimization[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1443-1448. | |
| [2] | 朱晓荣, 司羽. 考虑物理-信息-交通网耦合的配电网多时段动态供电恢复策略[J]. 电工技术学报,2023, 38(12): 3306-3320. |
| Zhu Xiao-rong, Si Yu. Multi-period dynamic power supply restoration strategy considering physical-cyber-traffic network coupling[J].Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2023, 38(12): 3306-3320. | |
| [3] | 卢志刚, 高启明, 赵号, 等. 配电网多故障抢修中应急电源车的优化调度[J]. 太阳能学报, 2020, 41(10):82-92. |
| Lu Zhi-gang, Gao Qi-ming, Zhao Hao, et al. Optimal dispatching of emergency power supply vehicle in multi fault repair of distribution network[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2020, 41(10): 82-92. | |
| [4] | 王钰山, 邓晖, 王旭, 等. 考虑台风时空演变的配电网移动储能优化配置与运行策略[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2022, 46(9): 42-51. |
| Wang Yu-shan, Deng Hui, Wang Xu, et al. Optimal configuration and operation strategy of mobile energy storge in distribution network considering spatial-temporal evolution of typhoon[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2022, 46(9): 42-51. | |
| [5] | Zhang Q Z, Wang Z Y, Ma S S, et al. Stochastic pre-event preparation for enhancing resilience of distribution systems[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2021, 152: 111636. |
| [6] | Lei S B, Chen C, Zhou H, et al. Routing and scheduling of mobile power sources for distribution system resilience enhancement[J]. IEEE Transaction on Smart Grid, 2019, 10(5): 5650-5662. |
| [7] | 杨丽君, 赵宇, 赵优, 等. 考虑交通路网应急电源车调度的有源配电网故障均衡恢复[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45(21): 170-180. |
| Yang Li-jun, Zhao Yu, Zhao You, et al. Balanced fault recovery of active distribution network considering emergency power supply vehicle scheduling in traffic network[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45(21): 170-180. | |
| [8] | Yao S H, Wang P, Zhao T Y. Transportable energy storage for more resilient distribution systems with multiple microgrids[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2019, 10(3): 3331-3341. |
| [9] | Lei S B, Chen C, Li Y P, et al. Resilient disaster recovery logistics of distribution systems: Co-optimize service restoration with repair crew and mobile power source dispatch[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2019, 10(6): 6187-6202. |
| [10] | Ding T, Wang Z K, Jia W H, et al. Multiperiod distribution system restoration with routing repair crews, mobile electric vehicles, and soft-open-point networked microgrids[J]. IEEE Transaction on Smart Grid, 2020, 11(6): 4795-4808. |
| [11] | Imai I. Studies on ice accretion[J]. Researches on Snow and Ice, 1953, 3(1): 35-44. |
| [12] | Lenhard R W. An indirect method for estimating the weight of glaze on wires[J].Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 1955, 36: 1-5. |
| [13] | Makkonen L. Modeling power line icing in freezing precipitation[J]. Atmospheric Research, 1998, 46(1):131-142. |
| [14] | Chen L Z, Shi X H, Peng B, et al. Dynamic simulation of power systems considering transmission lines icing and insulators flashover in extreme weather[J]. IEEE Access, 2022,10: 39656-39664. |
| [15] | Brostrom E, Ahlberg J, Soder L. Modeling of ice storms and their impact applied to a part of the Swedish transmission network[C]∥IEEE Lausanne Power Tech. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE, 2007:1593-1598. |
| [16] | 杨茂, 董昊. 基于数值天气预报风速和蒙特卡洛法的短期风电功率区间预测[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45(5): 79-85. |
| Yang Mao, Dong Hao. Short-term wind power interval prediction based on wind speed of numerical weather prediction and Monte Carlo method[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45(5): 79-85. | |
| [17] | Yuan W, Wang J H, Qiu F. Robust optimization based resilient distribution network planning against natural disasters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2016, 7(6): 2817-2827. |
| [18] | 卫志农, 裴蕾, 陈胜, 等. 高比例新能源交直流混合配电网优化运行与安全分析研究综述[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2021, 41(9): 85-94. |
| Wei Zhi-nong, Pei Lei, Chen Sheng, et al. Review on optimal operation and safety analysis of AC/DC hybrid distribution network with high proportion of renewable energy[J]. Electric Power Automation E-quipment, 2021, 41(9): 85-94. | |
| [19] | Wang Z Y, Chen B K, Wang J H. Robust optimization based optimal DG placement in microgrids[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2014, 5(5): 2173-2182. |
| [20] | 苏凯森, 杨家豪, 郑泽蔚, 等. 计及DG出力相关性的孤岛微电网蒙特卡洛法概率潮流[J]. 电力工程技术, 2018, 37(2): 95-101. |
| Su Kai-sen, Yang Jia-hao, Zheng Ze-wei, et al. Islanded microgrids probabilistic load flow considering correlated DG output based on Monte-Carlo method[J].Electric Power Engineering Technology, 2018, 37(2): 95-101. | |
| [21] | Tan S C, Xu J X, Panda S K. Optimization of distribution network incorporating distributed generators: An integrated approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2013, 28(3): 2421-2432. |
| [22] | 陈泽西, 孙玉树, 张妍, 等. 考虑风光互补的储能优化配置研究[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36():145-153. |
| Chen Ze-xi, Sun Yu-shu, Zhang Yan, et al. Research on energy storage optimal allocation considering complementarity of wind power and PV[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(Sup.1):145-153. | |
| [23] | 杨子龙, 宋振浩, 潘静, 等. 分布式光伏/储能系统多运行模式协调控制策略[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2019, 39(8): 2213-2220. |
| Yang Zi-long, Song Zhen-hao, Pan Jing, et al. Multi-mode coordinated control strategy of distributed PV and energy storage system[J]. Proceeding of the CSEE, 2019, 39(8): 2213-2220. |
| [1] | Hang ZHANG,Yu SUN,Bao-lin MA,Shi-hao NIU,Xing-yue WANG,Neng-chao LYU. Reliability-based design of length for auxiliary lane at dual-lane highway exits [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(8): 2611-2618. |
| [2] | Yan-bo LI,Jing-yuan WANG,Yuan-yuan Chen,Shao-feng CHENG,Hao-nan LYU,Jun-shuo CHEN. RAMS assessment approach of self-consistent energy system in highway service areas [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(7): 2243-2250. |
| [3] | Zhi-you LONG,Zhao-long WAN,Shi DONG,Chao YANG,Xiao-yang LIU. Displacement prediction of highway slope based on variational mode decomposition and extreme gradient boosting [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(7): 2320-2332. |
| [4] | Zhen YANG,Rui-ping ZHENG,Zhe GONG. Highway infrastructure performance and traffic state prediction on road network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 1973-1983. |
| [5] | Xiang-hai MENG,Guo-rui WANG,Ming-yang ZHANG,Bi-jiang TIAN. Traffic accident prediction model of mountain highways based on selection integration [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1298-1306. |
| [6] | Yong-zheng YANG,Zhi-gang DU,Jia-lin MEI. Setting method and effect evaluation of linear guiding system in highway tunnels [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(12): 3885-3897. |
| [7] | Guang-lei QU,Zong-wei YAN,Mu-lian ZHENG,Hong LIU,Yue-ming YUAN. Performance prediction of porous concrete based on neural network and regression analysis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 269-282. |
| [8] | Yong-ming HE,Cong QUAN,Kun WEI,Jia FENG,Ya-nan WAN,Shi-sheng CHEN. Perceptual fusion method of vehicle road cooperation roadside unit in superhighway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 1923-1934. |
| [9] | Xiao-feng JI,Ying-hao XU,Yong-ming PU,Jing-jing HAO,Wen-wen QIN. Risk prediction model of passenger car following behavior under truck movement interruption of two-lane highway in mountainous area [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1323-1331. |
| [10] | Ying-jun JIANG,Hong-jian SU,Ming-jie LI,Yan HE,Ya-wei BAI,Peng-fei WANG,Yu-hao BAO,Min-feng CAI. Durability of AC-16 asphalt mixture under vibration molding design [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(10): 2849-2858. |
| [11] | Yong-ming HE,Shi-sheng CHEN,Jia FENG,Ya-nan WAN. Superhighway virtual track system based on high precision map [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(7): 2016-2028. |
| [12] | Zhen-liang LIU,Cun-bao ZHAO,Yun-peng WU,Mi-na MA,Long-shuang MA. Life⁃cycle seismic resilience assessment of highway bridge networks using data⁃driven method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1695-1701. |
| [13] | Jun-qing ZHU,Xue-ru ZHAO,Tao MA,Xiao-ming HUANG,Hong-zhou ZHU. Monitoring road geological disaster based on satellite remote sensing [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1861-1872. |
| [14] | Xiao-ming HUANG,Run-min ZHAO. Status and prospects of highway transportation infrastructure resilience research [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1529-1549. |
| [15] | Yang ZHANG,Ao-peng WANG,Jing-lin ZHANG,Tao MA,Si-yu CHEN. Dry shrinkage in cement⁃stabilized macadam: a review [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(2): 297-311. |
|
||