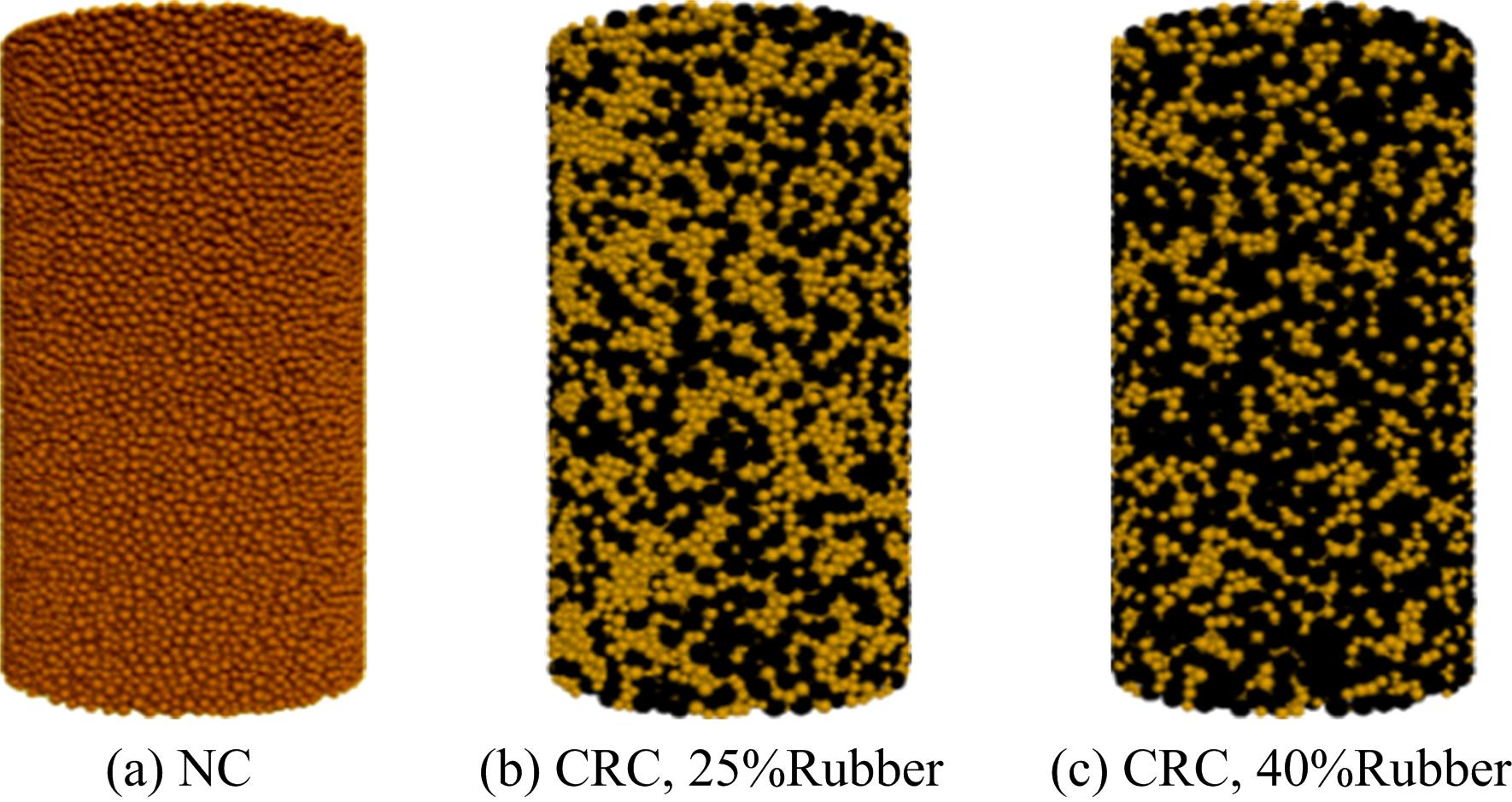
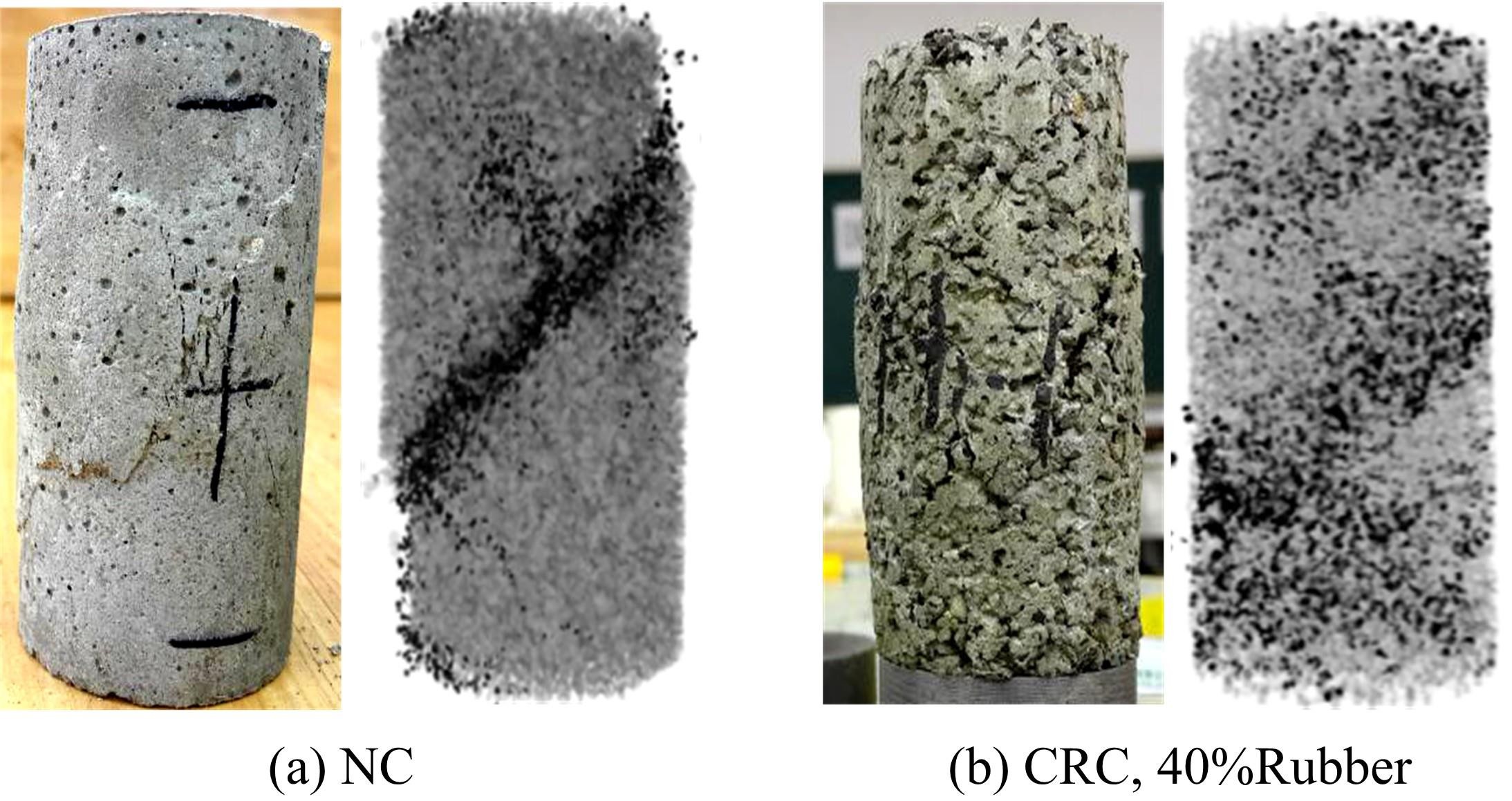
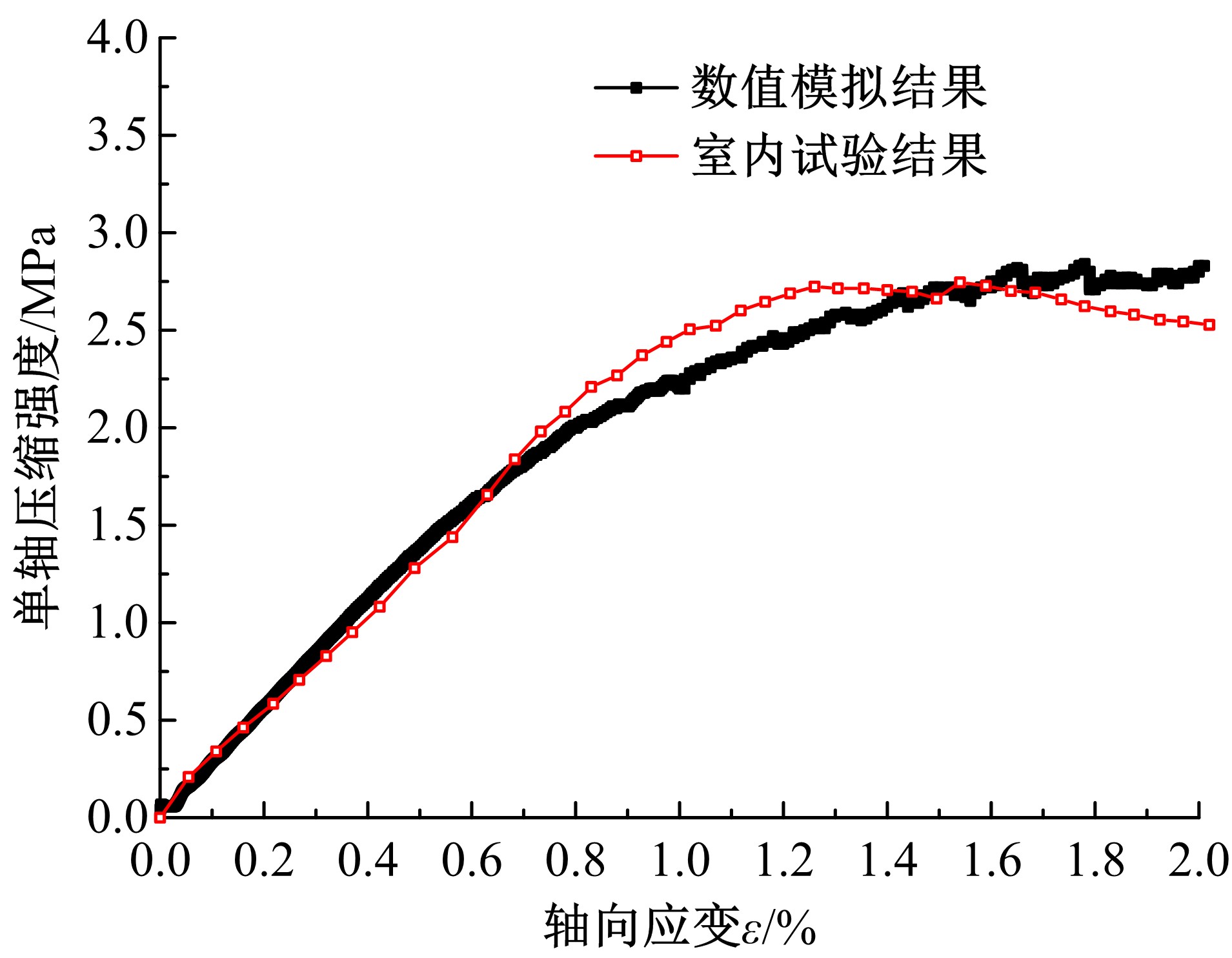
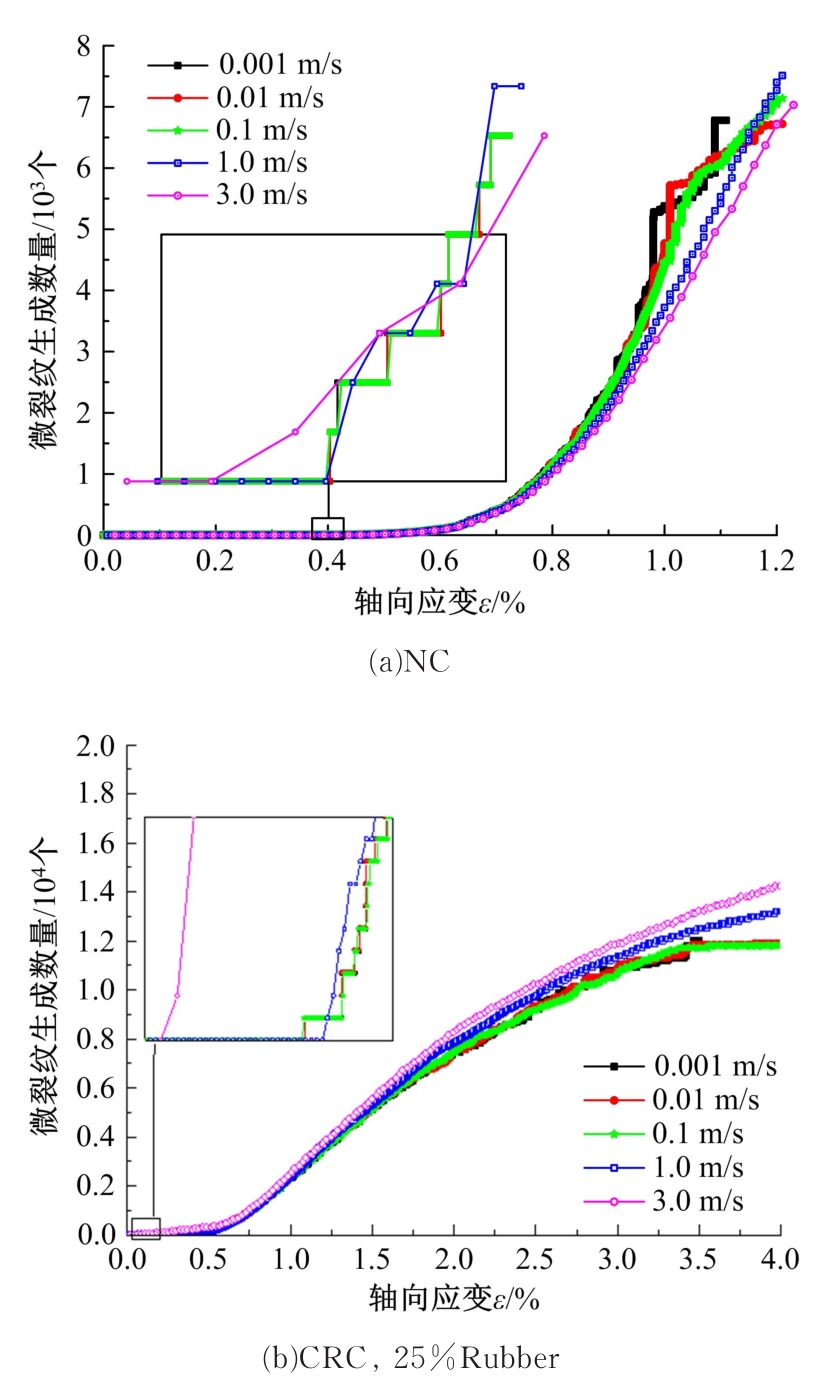
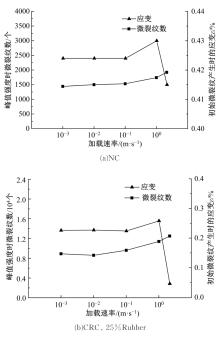
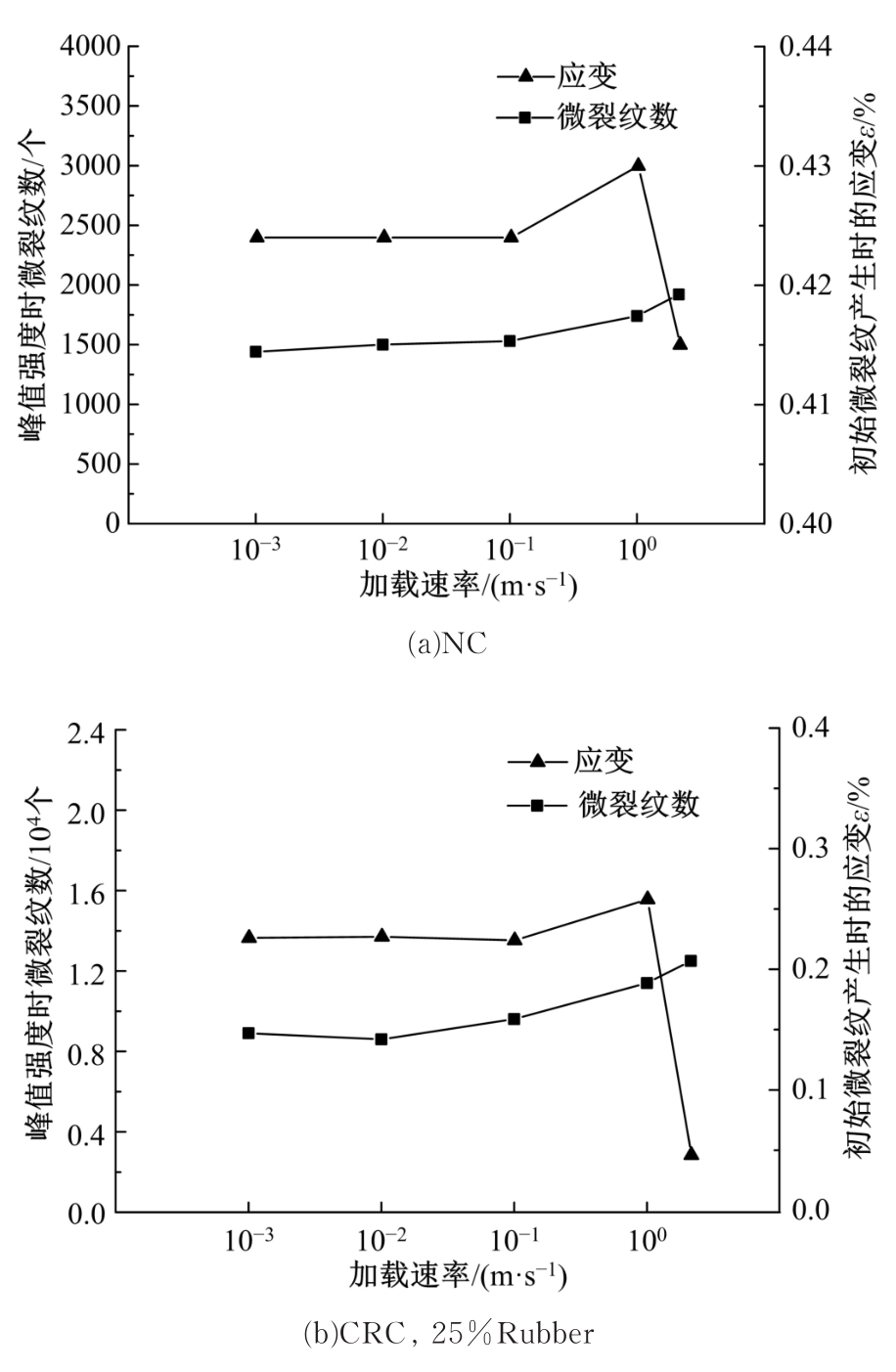
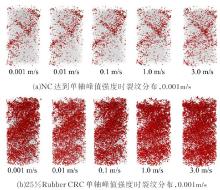
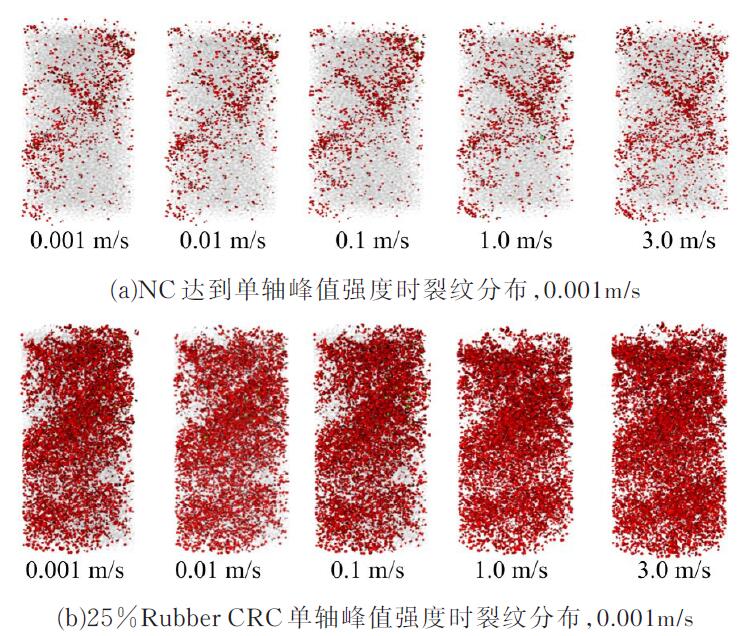
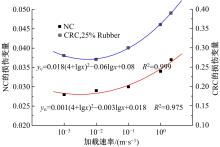
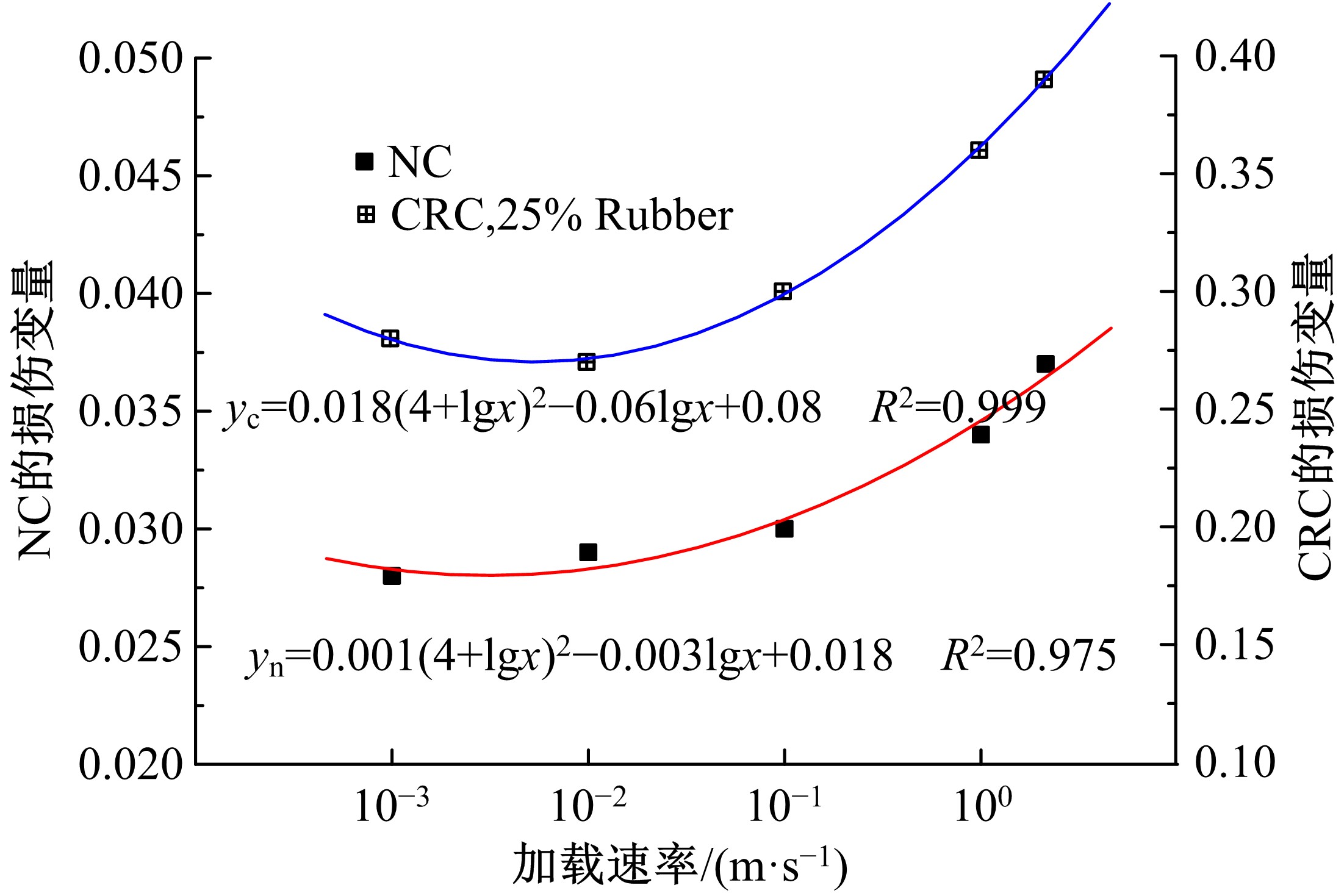
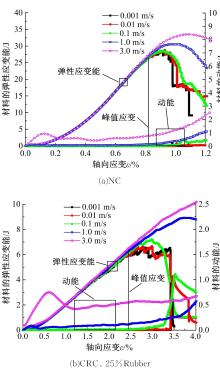
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2019, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (6): 1900-1910.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20180729
Previous Articles Next Articles
Loading rate effect of meso⁃damage characteristics of crumb rubber concrete
Sheng-tong DI1,2,3( ),Chao JIA2(
),Chao JIA2( ),Wei-guo QIAO3,4,Kang LI1,2,Kai TONG1,2
),Wei-guo QIAO3,4,Kang LI1,2,Kai TONG1,2
- 1. School of Civil Engineering, Shandong University, Jinan 250061, China
2. Institute of Marine Science and Technology, Shandong University, Qingdao 266237, China
3. Key Laboratory of Disaster Prevention and Reduction of Civil Engineering, Qingdao 266590, China
4. School of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266590, China
CLC Number:
- TU528
|
| [1] | Yong PENG,Hua GAO,Lei WAN,Gui-ying LIU. Numerical simulation of influence factors of splitting strength of asphalt mixtures [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1521-1530. |
| [2] | Yun-long ZHANG,Liu-guang ZHOU,Jing WANG,Chun-li WU,Xiang LYU. Effects of freeze-thaw cycles on mechanical properties of silty sand and subgrade slope stability [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1531-1538. |
| [3] | Yi-lun LIU,Qing WANG,Chi LIU,Song-bai LI,Jun HE,Xian-qiong ZHAO. Effect of creep and artificial aging on fatigue crack growth performance of 2524 aluminum alloy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1636-1643. |
| [4] | Tian⁃lai YU,Hai⁃sheng LI,Wei HUANG,Si⁃jia WANG. Shear strengthening of reinforced concrete beam with prestressed steel wire ropes [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1134-1143. |
| [5] | Xiao⁃zhen LI,Jun⁃zhe LIU,Yan⁃hua DAI,Zhi⁃min HE,Ming⁃fang BA,Yu⁃shun LI. Effect of carbonation on nitrite ion distribution in cement paste [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1162-1168. |
| [6] | Xiao⁃ming HUANG,Qing⁃qing CAO,Xiu⁃yu LIU,Jia⁃ying CHEN,Xing⁃lin ZHOU. Simulation of vehicle braking performance on rainy daysbased on pavement surface fractal friction theory [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 757-765. |
| [7] | Jing WANG,Xiang LYU,Xiao⁃long QU,Chun⁃ling ZHONG,Yun⁃long ZHANG. Analysis of relationship between subgrade soil shear strength and chemical and minerals component [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 766-772. |
| [8] | LI Yi,LIU Li-ping,SUN Li-jun. Prediction model on rutting equivalent temperature for asphalt pavement at different depth [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(6): 1703-1711. |
| [9] | ZANG Guo-shuai, SUN Li-jun. Method based on inertial point for setting depth to rigid layer [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1037-1044. |
| [10] | NIAN Teng-fei, LI Ping, LIN Mei. Micro-morphology and gray entropy analysis of asphalt characteristics functional groups and rheological parameters under freeze-thaw cycles [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1045-1054. |
| [11] | GONG Ya-feng, SHEN Yang-fan, TAN Guo-jin, HAN Chun-peng, HE Yu-long. Unconfined compressive strength of fiber soil with different porosity [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 712-719. |
| [12] | CHENG Yong-chun, BI Hai-peng, MA Gui-rong, GONG Ya-feng, TIAN Zhen-hong, LYU Ze-hua, XU Zhi-shu. Pavement performance of nano materials-basalt fiber compound modified asphalt binder [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 460-465. |
| [13] | JI Wen-yu, LI Wang-wang, GUO Min-long, WANG Jue. Experimentation and calculation methods of prestressed RPC-NC composite beam deflection [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 129-136. |
| [14] | ZHANG Yang-peng, WEI Hai-bin, JIA Jiang-kun, CHEN Zhao. Numerical evaluation on application of roadbed with composite cold resistance layer inseasonal frozen area [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 121-126. |
| [15] | MA Ye, NI Ying-sheng, XU Dong, DIAO Bo. External prestressed strengthening based on analysis of spatial grid model [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 137-147. |
|