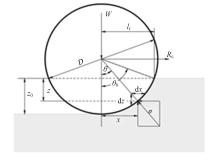
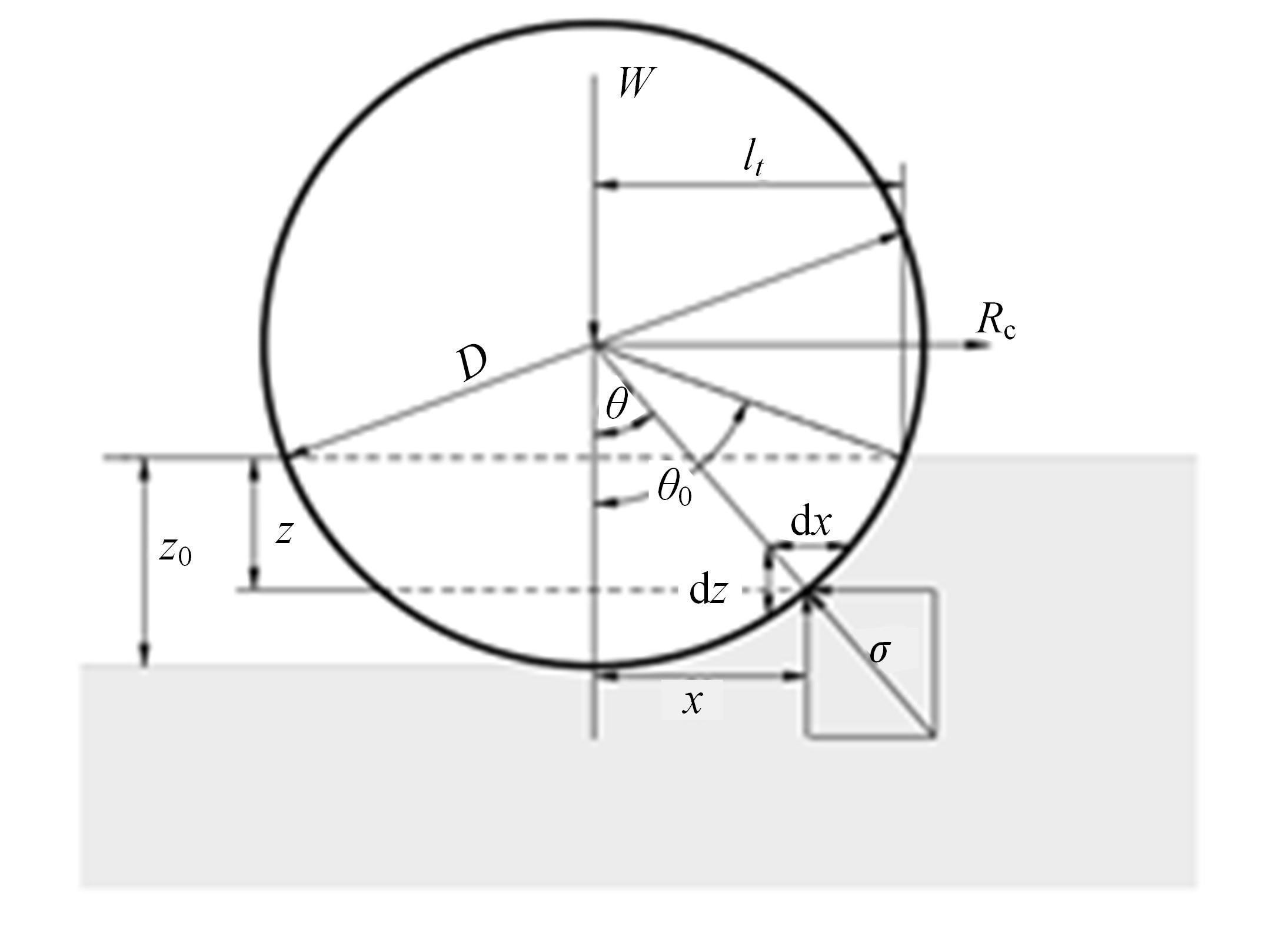
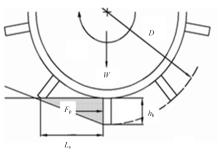
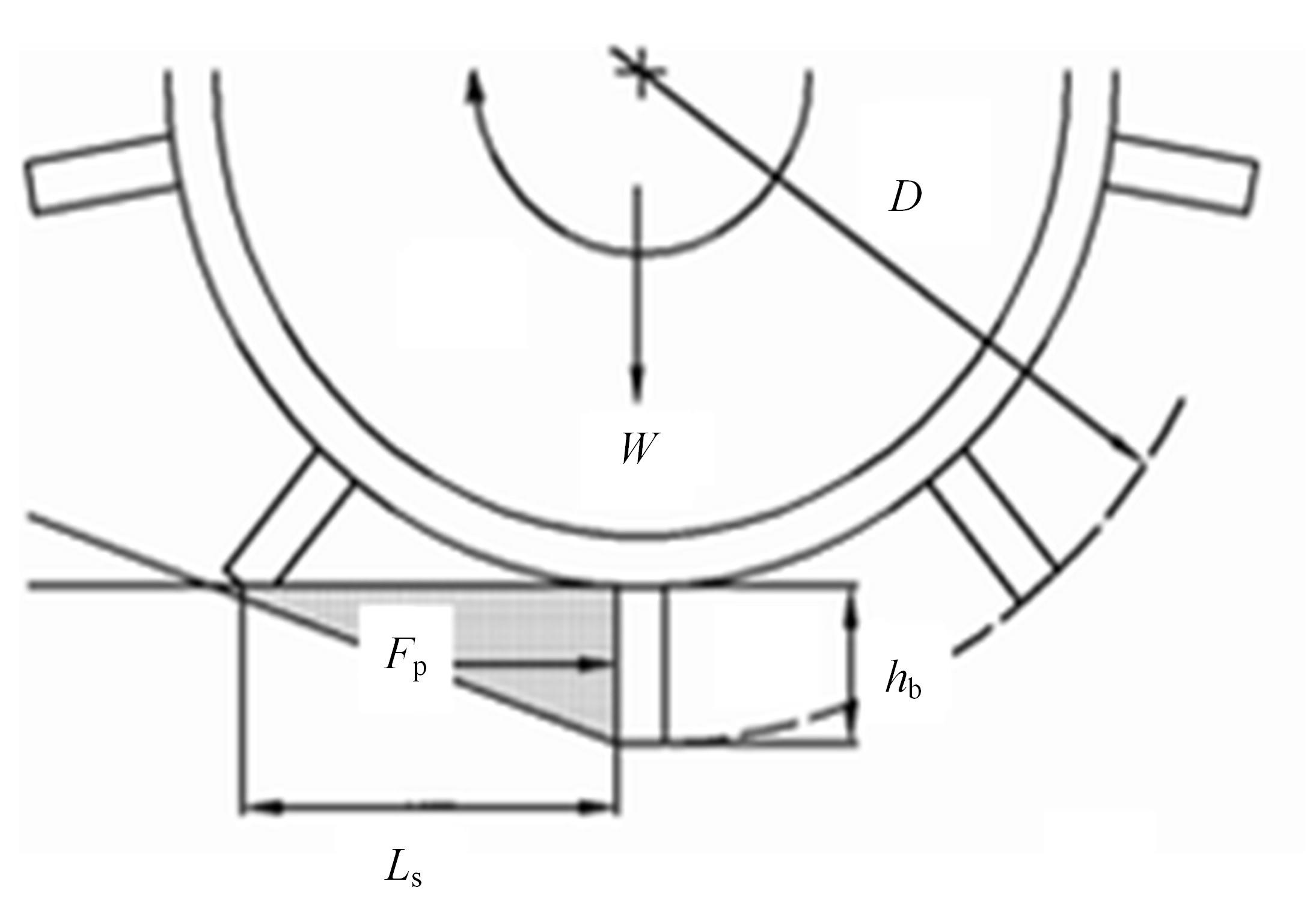
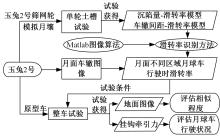
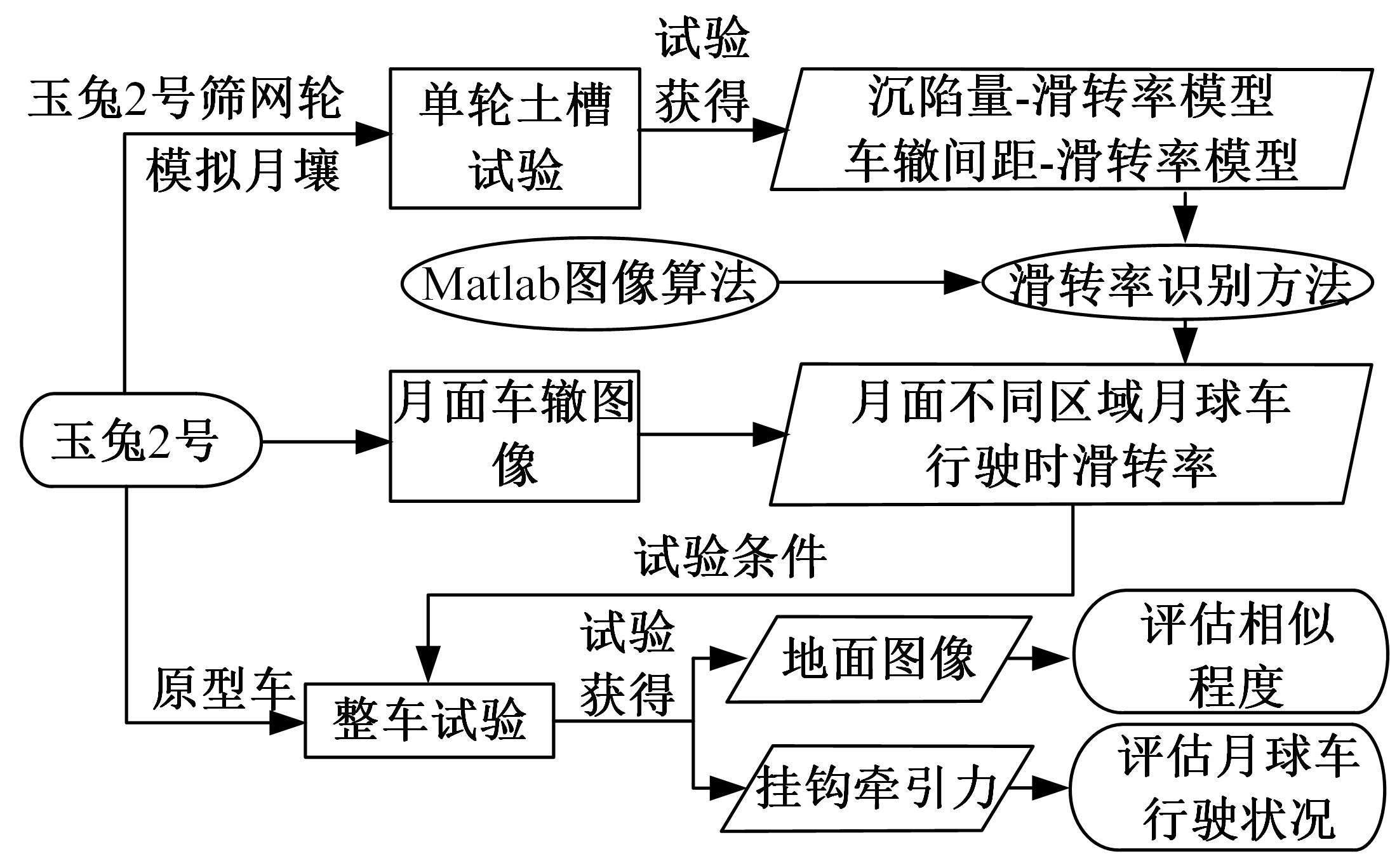
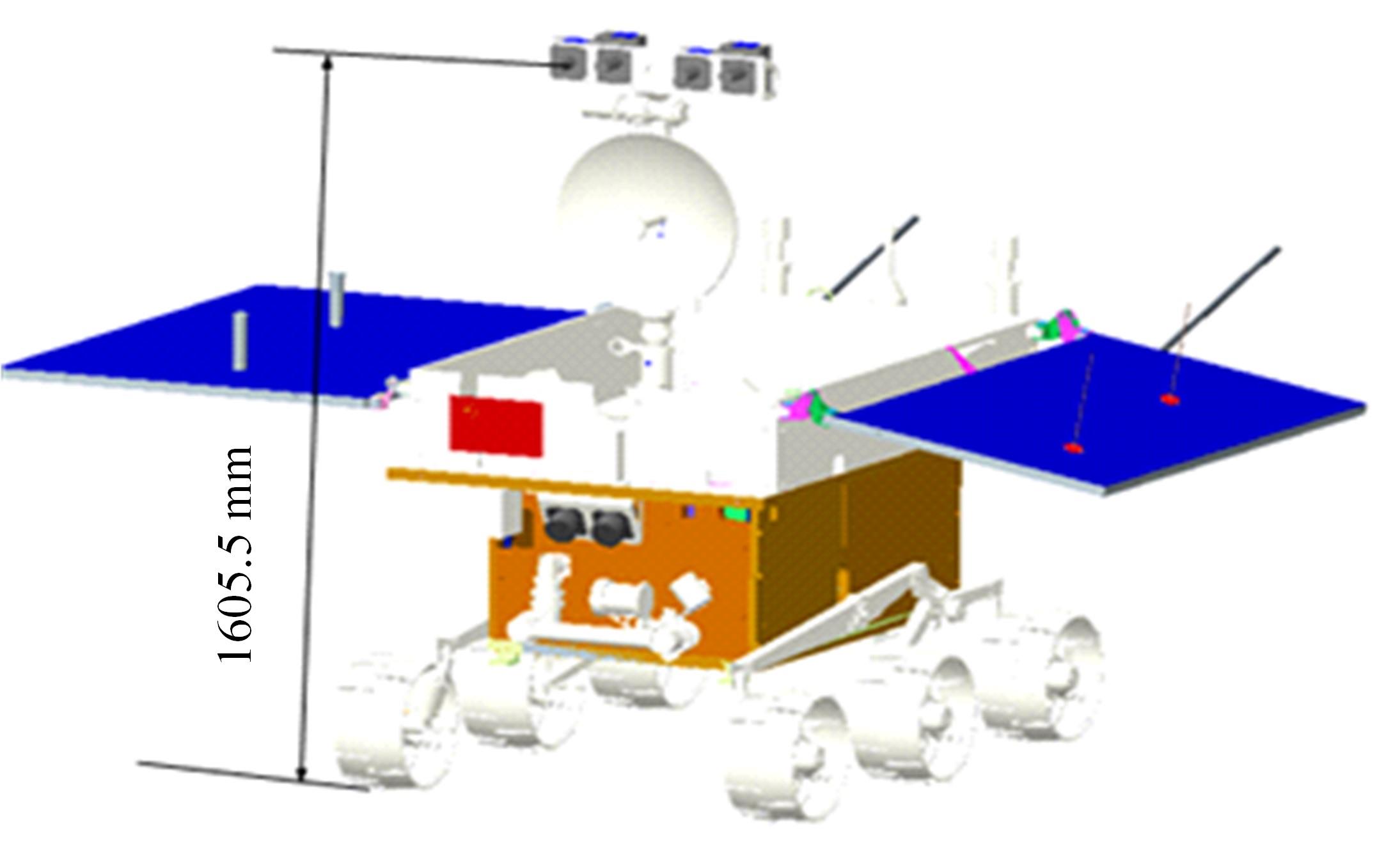
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (9): 2474-2482.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20211193
Previous Articles Next Articles
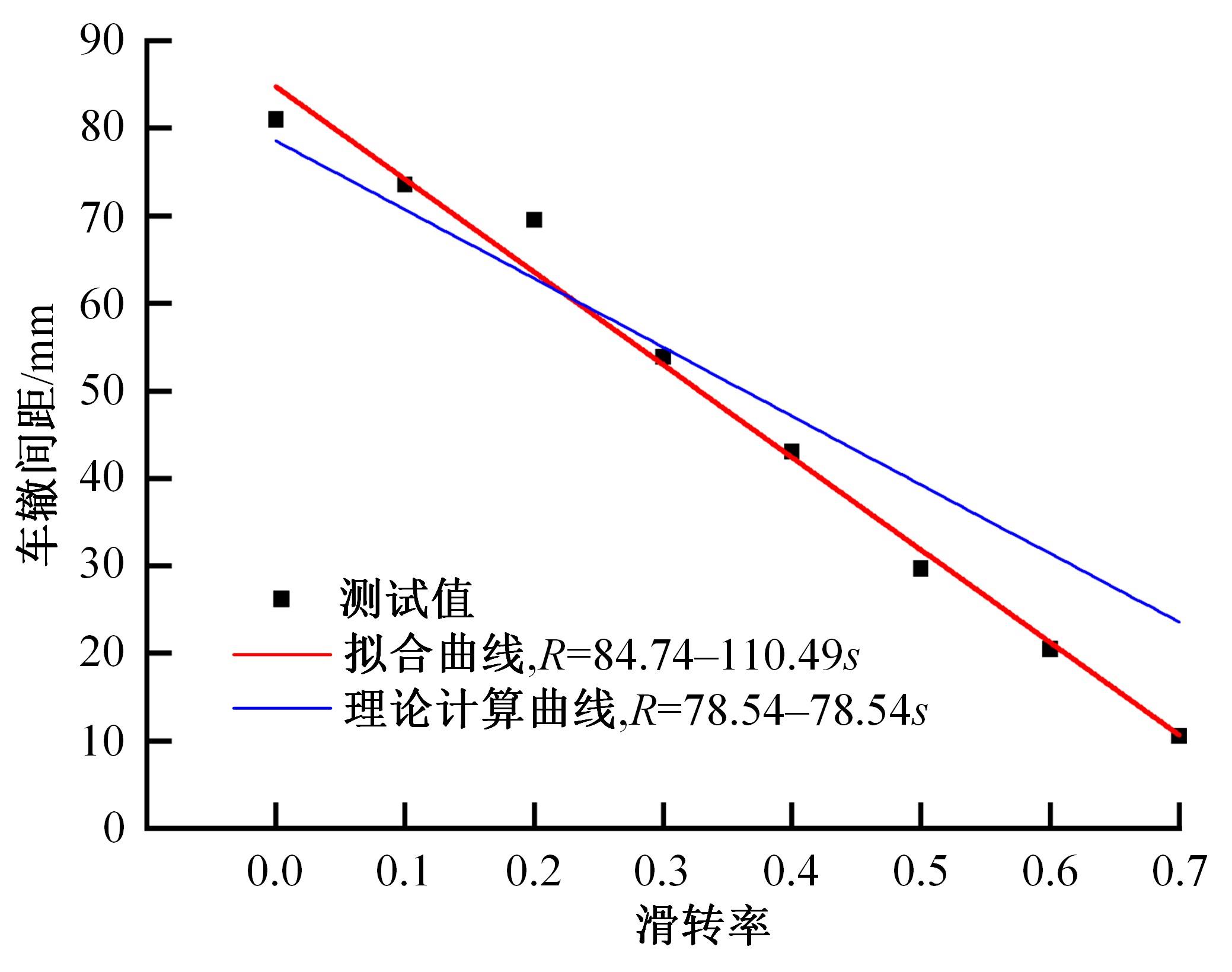
Analysis of drawbar pull to CE⁃4 Lunar rover based on rutting image of wheel
Zhen-yu HU1,2( ),Yan SHEN2,3,Wei-jun WANG1,2,Xiao-tao LUO1,2,Meng ZOU2,3(
),Yan SHEN2,3,Wei-jun WANG1,2,Xiao-tao LUO1,2,Meng ZOU2,3( )
)
- 1.Shanghai Aerospace System Engineering Institute,Shanghai 201109,China
2.Joint Lab for Planetary Terramechanics and Bionics Engineering,Shanghai 201109,China
3.Key Laboratory of Bionics Engineering,Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
CLC Number:
- TU411
| 1 | Cherkasov I I, Shvarev V V. Soviet investigations of the mechanics of lunar soils[J]. Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, 1973, 10(4): 252-256. |
| 2 | Leonovich A K, Gromon V V, Rybakov A V, et al. Studies for lunar ground mechanical properties with the self-propelled lunokhod-l[R]. Moscow: Peredvizhnaya Laboratoriya na Luna-Lunokhod-1, 1971: 120-135. |
| 3 | Leonovich A K, Gromov V V, Rybakov A V, et al. Investigations of the mechanical properties of the lunar soil along the path of Lunokhod-1[R]. Berlin: COSPAR space research Ⅻ, 1972: 53-54. |
| 4 | Zacny K, Wilson J, Craft J, et al. Robotic Lunar Geotechnical Tool[M]. Honolulu: Earth and Space, 2010. |
| 5 | 韩鸿硕, 陈杰. 21世纪国外深空探测发展计划及进展[J]. 航天器工程, 2008, 17(3): 1-22. |
| Han Hong-shuo, Chen Jie. 21st century foreign deep space exploration development plans and their progresses[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2008, 17(3): 1-22. | |
| 6 | 崔平远, 徐瑞, 朱圣英, 等. 深空探测器自主技术发展现状与趋势[J]. 航空学报, 2014, 35(1): 13-28. |
| Cui Ping-yuan, Xu Rui, Zhu Sheng-ying, et al. State of the art and developement trends of on-board autonomy technology for deep space explore[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2014, 35(1): 13-28. | |
| 7 | 解杨敏, 季力, 魏祥泉, 等. 国内外行星表面巡视器自主导航技术研究[J]. 上海航天, 2021, 38(1): 61-71. |
| Xie Yang-min, Ji Li, Wei Xiang-quan, et al. Domestic and overseas research status on autonomous navigation technology of planetary rovers[J]. Aerospace Shanghai, 2021, 38(1): 61-71. | |
| 8 | Team R. Characterization of the martian surface deposits by the Mars pathfinder rover, sojourner[J]. Science, 1997, 278(5344): 1765-1768. |
| 9 | Moore H J, Bickler D B, Crisp J A, et al. Soil-like deposits observed by Sojourner, the pathfinder rover[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Planets, 1999, 104(E4): 8729-8746. |
| 10 | Sullivan R, Anderson R, Biesiadecki J, et al. Cohesions, friction angles, and other physical properties of martian regolith from mars exploration rover wheel trenches and wheel scuffs[J/OL]. [2021-11-02]. |
| 11 | Arvidson R E, Anderson R C, Bartlett P, et al. Localization and physical properties experiments conducted by Spirit at Gusev crater[J]. Science, 2004, 305(5685): 821-824. |
| 12 | Arvidson R E, Bonitz R G, Robinson M L, et al. Results from the mars phoenix lander robotic arm experiment[J/OL]. [2021-11-03]. |
| 13 | Ono M, Fuchs T J, Steffy A, et al. Risk-aware planetary rover operation: autonomous terrain classification and path planning[C]∥2015 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Monoana, USA, 2015: 1-10. |
| 14 | Huang G. Visual-inertial navigation: a concise review[C]∥2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Monertal, Canada, 2019: 9572-9582. |
| 15 | Iagnemma K, Kang S, Brooks C, et al. Multi-sensor terrain estimation for planetary rovers[C]∥Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Artificial Intelligence, Robotics, and Automation in Space, NARA, Japan, 2003: No.12273618. |
| 16 | Reina G, Ojeda L, Milella A, et al. Wheel slippage and sinkage detection for planetary rovers[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2006, 11(2): 185-195. |
| 17 | Cross M, Ellery A, Qadi A. Estimating terrain parameters for a rigid wheeled rover using neural networks[J]. Journal of Terramechanics, 2013, 50(3): 165-174. |
| 18 | 崔平远, 刘冰, 居鹤华. 月壤力学参数在线估计算法研究[J]. 计算机测量与控制, 2008, 16(2): 245-269. |
| Cui Ping-yuan, Liu Bing, Ju He-hua. Research on mechanical parameters online estimation of lunar soil[J]. Computer Measurement&Control, 2008, 16(2): 245-269. | |
| 19 | 李萌, 高峰, 孙鹏, 等. 月壤力学参数反求及试验验证[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2011, 37(9): 1081-1805. |
| Li Meng, Gao Feng, Sun Peng, et al. Mechanical parameters reverse estimation of lunar soil and experimental verification[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2011, 37(9): 1081-1805. | |
| 20 | 薛龙, 邹猛, 李建桥, 等. 基于轮地作用参数和PLSDA方法的月壤力学性能评估[J]. 航空学报, 2015, 36(11): 3751-3758. |
| Xue Long, Zou Meng, Li Jian-qiao, et al. Mechanical performance estimation of lunar soil using wheel-soil interaction parameter and PLSDA[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2015, 36(11): 3751-3758. | |
| 21 | Ding L, Gao H, Deng Z, et al. Slip ratio for lugged wheel of planetary rover in deformable soil: definition and estimation[C]∥2009 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, ST.Louis, USA, 2009: 3343-3348. |
| 22 | 丁亮, 高海波, 邓宗全, 等. 基于应力分布的月球车轮地相互作用地面力学模型[J]. 机械工程学报, 2009, 45(7): 49-55. |
| Ding Liang, Gao Hai-bo, Deng Zong-quan, et al. Terramechanics model for wheel-terrain interaction of lunar rover based on stress distribution[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2009, 45(7): 49-55. | |
| 23 | 李楠, 丁亮, 高海波, 等. 基于视觉检测技术的星球探测车车轮滑转率检测方法[C]∥第三十二届中国控制会议, 西安, 2013: 3673-3679. |
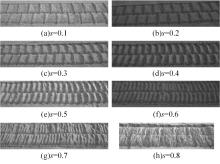
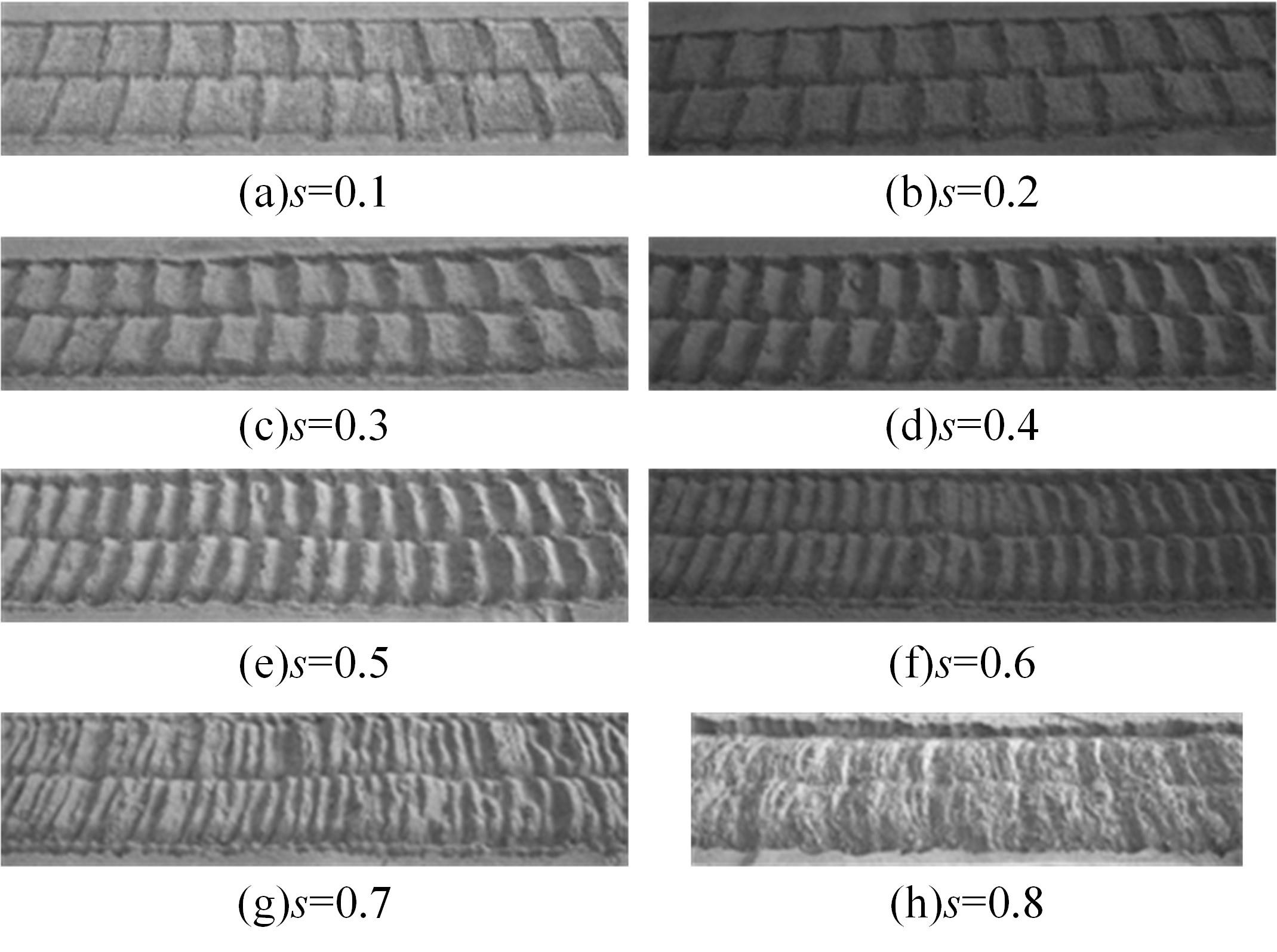
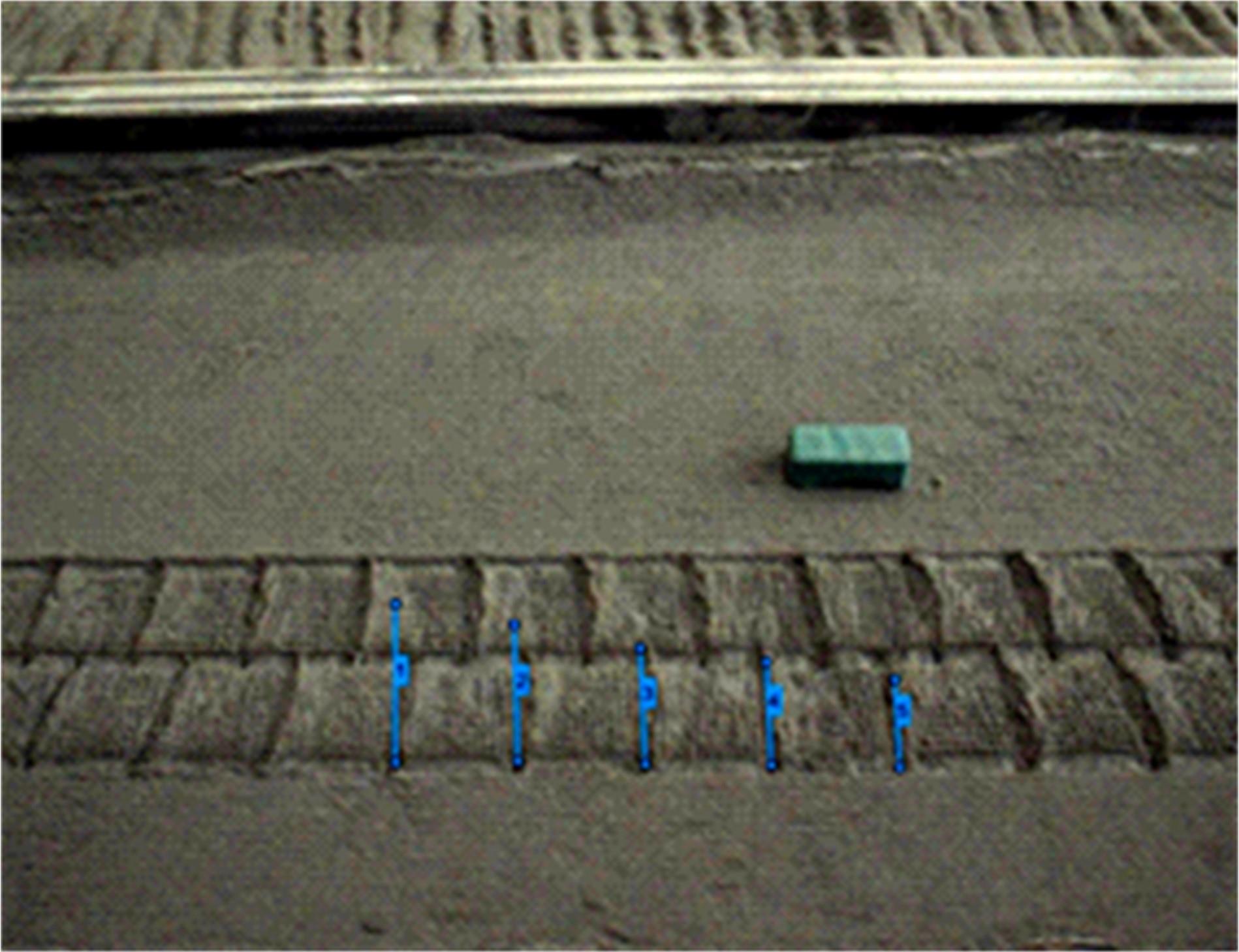
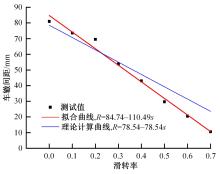
| 24 | 李楠, 高海波, 吕凤天, 等. 车辙图像频域分析及星球车车轮滑转率估计方法[J]. 宇航学报, 2016, 37(11): 1356-1364. |
| LI Nan, Gao Hai-bo, Lv Feng-tian, et al. Wheel trace imprint image frequency domain analysis and rover wheel slip ratio estimation[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2016, 37(11): 1356-1364. | |
| 25 | 黄晗, 许述财, 张金换, 等. 基于轮辙非接触测量的月壤非参数化识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2019, 49(2): 366-374. |
| Huang Han, Xu Shu-cai, Zhang Jin-huan, et al. Non-parametric identification method for lunar regolith based on rut non-contact measurement[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(2): 366-374. | |
| 26 | 黄晗, 李建桥, 陈百超, 等. 基于地面力学的筛网轮牵引通过性研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 2016, 47(): 464-470. |
| Huang Han, Li Jian-qiao, Chen Bai-chao, et al. Traction trafficability of wire mesh wheel based on terramechanics[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(Sup.1): 464-470. | |
| 27 | 陈百超, 邹猛, 党兆龙, 等. CE-3月球车筛网轮月面沉陷行为试验[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(6): 1836-1843. |
| Chen Bai-chao, Zou Meng, Dang Zhao-long, et al. Experiment on preasure-sinkage for mesh wheels of CE-3 lunar rover on lunar regolith[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1836-1843. | |
| 28 | 李建桥, 黄晗, 党兆龙, 等. 轻载荷条件下的筛网轮沉陷[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2015, 45(1):167-173. |
| Li Jian-qiao, Huang Han, Dang Zhao-long, et al. Sinkage of wire mesh wheel under light load[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2015,45(1):167-173. | |
| 29 | 黄晗. 深空探测车辆筛网轮牵引通过性研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学生物与农业工程学院, 2017. |
| Huang Han. Study on traction trafficability for wire mesh wheel of planetary exploration rovers[D]. Changchun: College of Biological and Agricultural Engineering, Jilin University, 2017. | |
| 30 | Bekker M G. Theory of Land Locomotion[M]. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press, 1956. |
| [1] | Ye TIAN,Nan-nan LI,Jun-wei LIU,Sheng-yuan JIANG,Chu WANG,Wei-wei ZHANG. Identification of critical fragments cutting load of simulated lunar soil based on support vector machine [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(7): 2143-2151. |
| [2] | Chen HUA,Run-xin NIU,Biao YU. Methods and applications of ground vehicle mobility evaluation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1229-1244. |
| [3] | Quan-ping XIA,Jiang-ping GAO,Hao-yuan LUO,Qi-gong ZHANG,Zhi-jie LI,Fei YANG. Low⁃temperature performance of composite modified hard asphalt used in high modulus asphalt concrete [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(3): 541-549. |
| [4] | Long XUE,Meng YAO,Li-ben LI,Yin-wu LI,Xiang-jin DENG,Jian-qiao LI,Meng ZOU. Experimental analysis of mechanical properties of surface lunar soil based on lunar indentation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(3): 497-503. |
| [5] | Kang WANG,Meng YAO,Li-ben LI,Jian-qiao LI,Xiang-jin DENG,Meng ZOU,Long XUE. Mechanical performance identification for lunar soil in lunar surface sampling [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 1146-1152. |
| [6] | Guo-ying CHEN,Jun YAO,Peng WANG,Qi-kun XIA. Stability control strategy for rear in⁃wheel motor drive vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 397-405. |
| [7] | Bai-chao CHEN,Meng ZOU,Zhao-long DANG,Han HUANG,Yang JIA,Rui-yang SHI,Jian-qiao LI. Experiment on pressure⁃sinkage for mesh wheels of CE⁃3lunar rover on lunar regolith [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1836-1843. |
| [8] | LI Yi,LIU Li-ping,SUN Li-jun. Prediction model on rutting equivalent temperature for asphalt pavement at different depth [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(6): 1703-1711. |
| [9] | HE Xiang-kun, JI Xue-wu, YANG Kai-ming, WU Jian, LIU Ya-hui. Tire slip control based on integrated-electro-hydraulic braking system [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 364-372. |
| [10] | JIN Li-qiang, SUN Zhi-xiang, ZHENG Ying. Coordinated anti-lock braking control of compound regenerative braking system in electric-wheel vehicle [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1344-1351. |
| [11] | ZHAO De-ming, JIANG Sheng-yuan, TANG De-wei, HOU Xu-yan, DENG Zong-quan. Structure design of lunar subsurface sampling drill [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(4): 1149-1158. |
| [12] | CUI Jin-sheng, HOU Xu-yan, DENG Zong-quan, PAN Wan-jing, JIANG Sheng-yuan. Measurement system and experiment study of the effective thermal conductivity of granular system in a vacuum [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 457-464. |
| [13] | YANG Fei, DENG Zong-quan, TAO Jian-guo, LIU Ji-cheng. Rational wheel number for lunar rover [J]. , 2012, 42(05): 1113-1119. |
| [14] | WANG Guo-fu, GAO Feng, XU Guo-yan. Kinematic analysis and control of omnidirectional hexapod robot with a steering-wheel [J]. , 2012, 42(04): 1008-1014. |
| [15] | WANG Xiao-lan, WANG Rong-ben. Analysis of lunar rover vibration characteristics based on rigid-flexible coupled model [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(02): 279-284. |
|