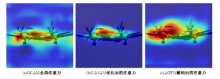
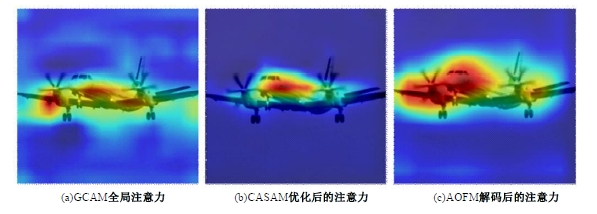
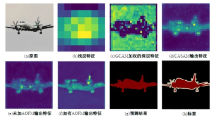
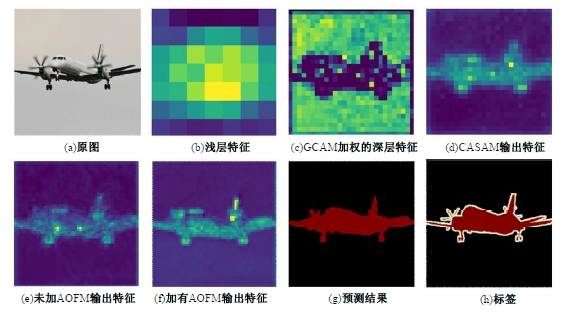
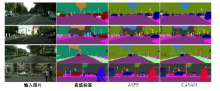
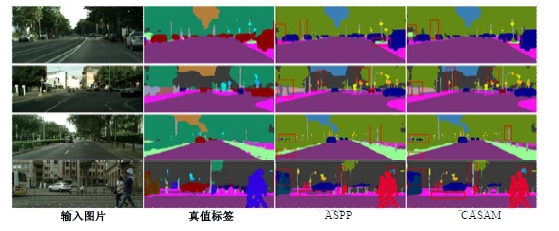
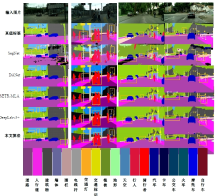
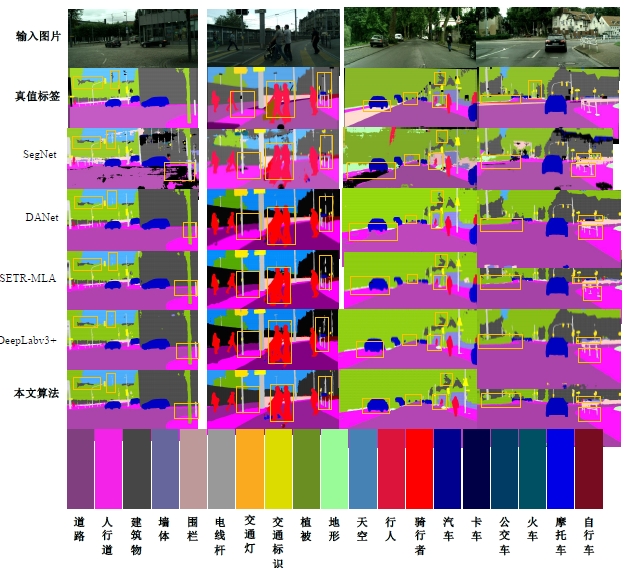
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (4): 1384-1395.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230740
Previous Articles Next Articles
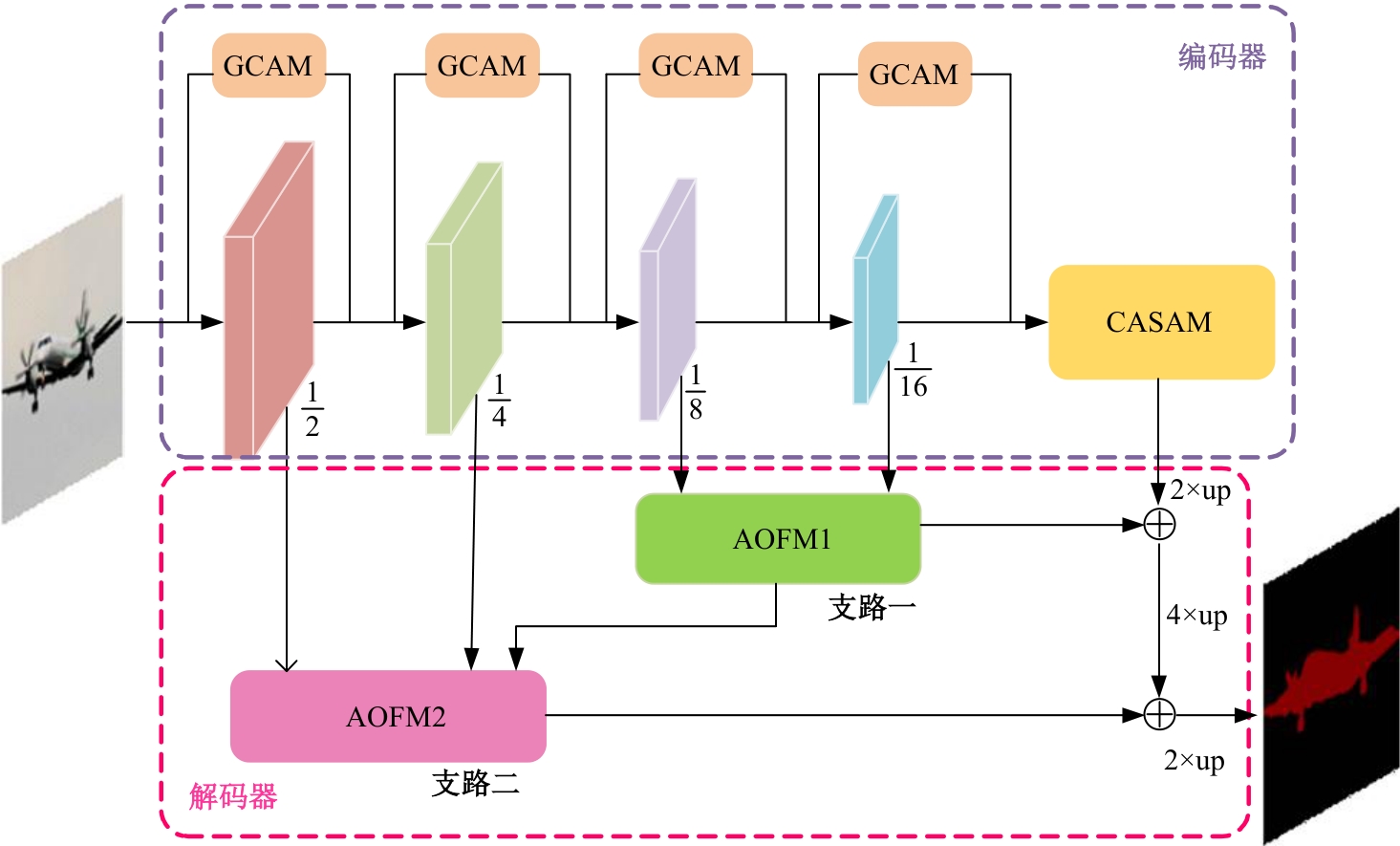
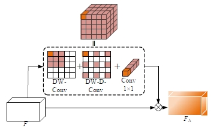
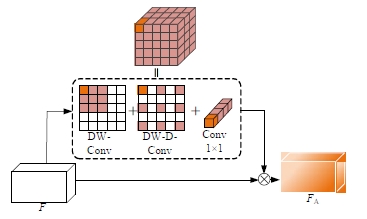
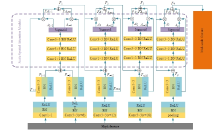
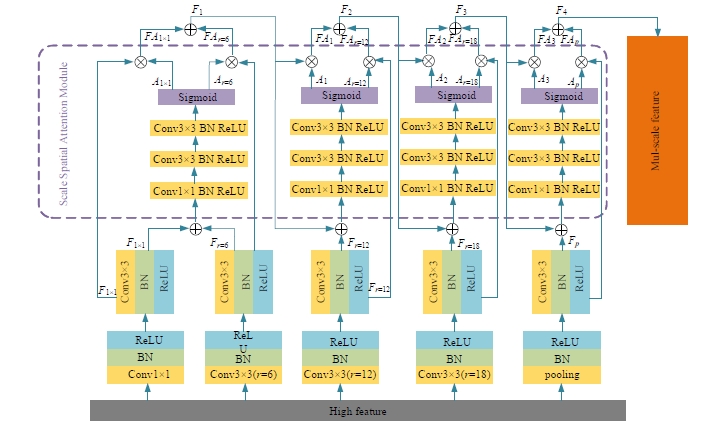
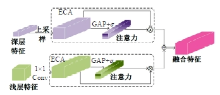
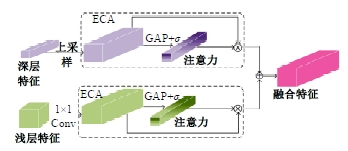
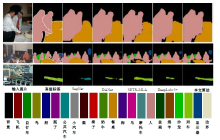
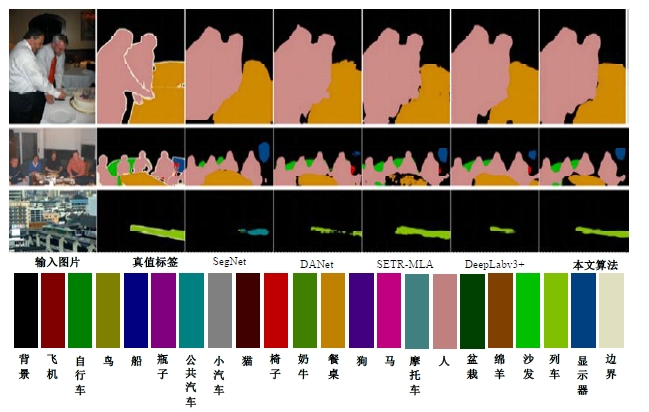
Semantic segmentation network based on attention mechanism and feature fusion
Hua CAI1( ),Yu-yao WANG1,Qiang FU2,Zhi-yong MA3,Wei-gang WANG3,Chen-jie ZHANG1
),Yu-yao WANG1,Qiang FU2,Zhi-yong MA3,Wei-gang WANG3,Chen-jie ZHANG1
- 1.School of Electronic Information Engineer,Changchun University of Science and Technology,Changchun 130022,China
2.School of Opto-Electronic Engineer,Changchun University of Science and Technology,Changchun 130022,China
3.No. 2 Department of Urology,The First Hospital of Jilin University,Changchun 130061,China
CLC Number:
- TP391.4
| [1] | Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]∥Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention-MICCAI: The 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234-241. |
| [2] | Chen J, Lu Y, Yu Q, et al. Transunet: transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation[J/OL]. [2023-07-02].arXiv preprint arXiv: 2102. 04306v1. |
| [3] | Zhao T Y, Xu J D, Chen R, et al. Remote sensing image segmentation based on the fuzzy deep convolutional neural network[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2021, 42(16): 6264-6283. |
| [4] | Yuan X H, Shi J F, Gu L C. A review of deep learning methods for semantic segmentation of remote sensing imagery[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2021, 169: No.114417. |
| [5] | Xu Z Y, Zhang W, Zhang T X, et al. Efficient transformer for remote sensing image segmentation[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(18): No.3585. |
| [6] | Badrinarayanan V, Kendall A, Cipolla R. Segnet: a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(12): 2481-2495. |
| [7] | Yu C, Gao C, Wang J, et al. Bisenet v2: bilateral network with guided aggregation for real-time semantic segmentation[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2021, 129: 3051-3068. |
| [8] | Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA,2015: 3431-3440. |
| [9] | Chen L C, Papandreou G Kokkinos I, et al. Deeplab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 40(4): 834-848. |
| [10] | Chen L C, Papandreou G, Schroff F, et al. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation[J/OL].[2023-07-03]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1706. 05587v3. |
| [11] | Chen L C, Zhu Y, Papandreou G, et al. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation[C]∥Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV),Munich, Germany,2018: 833-851. |
| [12] | Wang J, Sun K, Cheng T, et al. Deep high-resolution representation learning for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 43(10): 3349-3364. |
| [13] | Liu Z, Lin Y, Cao Y, et al. Swin transformer: hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision,Montreal, Canada, 2021: 10012-10022. |
| [14] | Wang W, Xie E, Li X, et al. Pyramid vision transformer: a versatile backbone for dense prediction without convolutions[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision,Montreal, Canada, 2021: 568-578. |
| [15] | Zheng S, Lu J, Zhao H, et al. Rethinking semantic segmentation from a sequence-to-sequence perspective with transformers[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA,2021: 6881-6890. |
| [16] | Xie E, Wang W, Yu Z, et al. SegFormer: simple and efficient design for semantic segmentation with transformers[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2021, 34: 12077-12090. |
| [17] | Dosovitskiy A, Beyer L, Kolesnikov A, et al. An image is worth 16×16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale[J/OL]. [2023-07-04].arXiv preprint arXiv: 2010. 11929v2. |
| [18] | Zhao H, Shi J, Qi X, et al. Pyramid scene parsing network[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 2881-2890. |
| [19] | Hou Q, Zhang L, Cheng M M, et al. Strip pooling: rethinking spatial pooling for scene parsing[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,Seattle, USA, 2020: 4003-4012. |
| [20] | Peng C, Zhang X, Yu G, et al. Large kernel matters-improve semantic segmentation by global convolutional network[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 4353-4361. |
| [21] | Ding X, Zhang X, Han J, et al. Scaling up your kernels to 31×31: revisiting large kernel design in CNNs[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,New Orleans, USA, 2022: 11963-11975. |
| [22] | Guo M H, Lu C Z, Liu Z N, et al. Visual attention network[J/OL]. [2023-07-04].arXiv preprint arXiv:. |
| [23] | Hu J, Shen L, Sun G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7132-7141. |
| [24] | Wang Q, Wu B, Zhu P, et al. ECA-Net: efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,Seattle, USA, 2020: 11534-11542. |
| [25] | Fu J, Liu J, Tian H, et al. Dual attention network for scene segmentation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 3146-3154. |
| [26] | Cordts M, Omran M, Ramos S, et al. The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 3213-3223. |
| [27] | Everingham M, Eslami S M A, Van Gool L, et al. The pascal visual object classes challenge: a retrospective[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 111: 98-136. |
| [28] | 王雪, 李占山, 吕颖达. 基于多尺度感知和语义适配的医学图像分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(3): 640-647. |
| Wang Xue, Li Zhan-shan, Ying-da Lyu. Medical image segmentation algorithm based on multi-scale perception and semantic adaptation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(3): 640-647. |
| [1] | Ya-li XUE,Tong-an YU,Shan CUI,Li-zun ZHOU. Infrared small target detection based on cascaded nested U-Net [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1714-1721. |
| [2] | Guang CHENG,Pei-lin LI. Spatio temporal fusion detection of abnormal traffic in industrial Internet based on MSE improved BiLSTM network algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1406-1411. |
| [3] | He-shan ZHANG,Meng-wei FAN,Xin TAN,Zhan-ji ZHENG,Li-ming KOU,Jin XU. Dense small object vehicle detection in UAV aerial images using improved YOLOX [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1307-1318. |
| [4] | Xue-jun LI,Lin-fei QUAN,Dong-mei LIU,Shu-you YU. Improved Faster⁃RCNN algorithm for traffic sign detection [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 938-946. |
| [5] | De-qiang CHENG,Gui LIU,Qi-qi KOU,Jian-ying ZHANG,He JIANG. Lightweight image super⁃resolution network based on adaptive large kernel attention fusion [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 1015-1027. |
| [6] | Yang LI,Xian-guo LI,Chang-yun MIAO,Sheng XU. Low⁃light image enhancement algorithm based on dual branch channel prior and Retinex [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 1028-1036. |
| [7] | Xiao-ran GUO,Tie-jun WANG,Yue YAN. Entity relationship extraction method based on local attention and local remote supervision [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 307-315. |
| [8] | Lu Li,Jun-qi Song,Ming Zhu,He-qun Tan,Yu-fan Zhou,Chao-qi Sun,Cheng-yu Zhou. Object extraction of yellow catfish based on RGHS image enhancement and improved YOLOv5 network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2638-2645. |
| [9] | Ping YU,Kang ZHAO,Jie CAO. Rolling bearing fault diagnosis based on optimized A-BiLSTM [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2156-2166. |
| [10] | Yun-zuo ZHANG,Yu-xin ZHENG,Cun-yu WU,Tian ZHANG. Accurate lane detection of complex environment based on double feature extraction network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 1894-1902. |
| [11] | Ming-hui SUN,Hao XUE,Yu-bo JIN,Wei-dong QU,Gui-he QIN. Video saliency prediction with collective spatio-temporal attention [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1767-1776. |
| [12] | Yun-long GAO,Ming REN,Chuan WU,Wen GAO. An improved anchor-free model based on attention mechanism for ship detection [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1407-1416. |
| [13] | Xiao-xu LI,Wen-juan AN,Ji-jie WU,Zhen LI,Ke ZHANG,Zhan-yu MA. Channel attention bilinear metric network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 524-532. |
| [14] | Bin ZHAO,Cheng-dong WU,Xue-jiao ZHANG,Ruo-huai SUN,Yang JIANG. Target grasping network technology of robot manipulator based on attention mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(12): 3423-3432. |
| [15] | Lin MAO,Hong-yang SU,Da-wei YANG. Temporal salient attention siamese tracking network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(11): 3327-3337. |
|