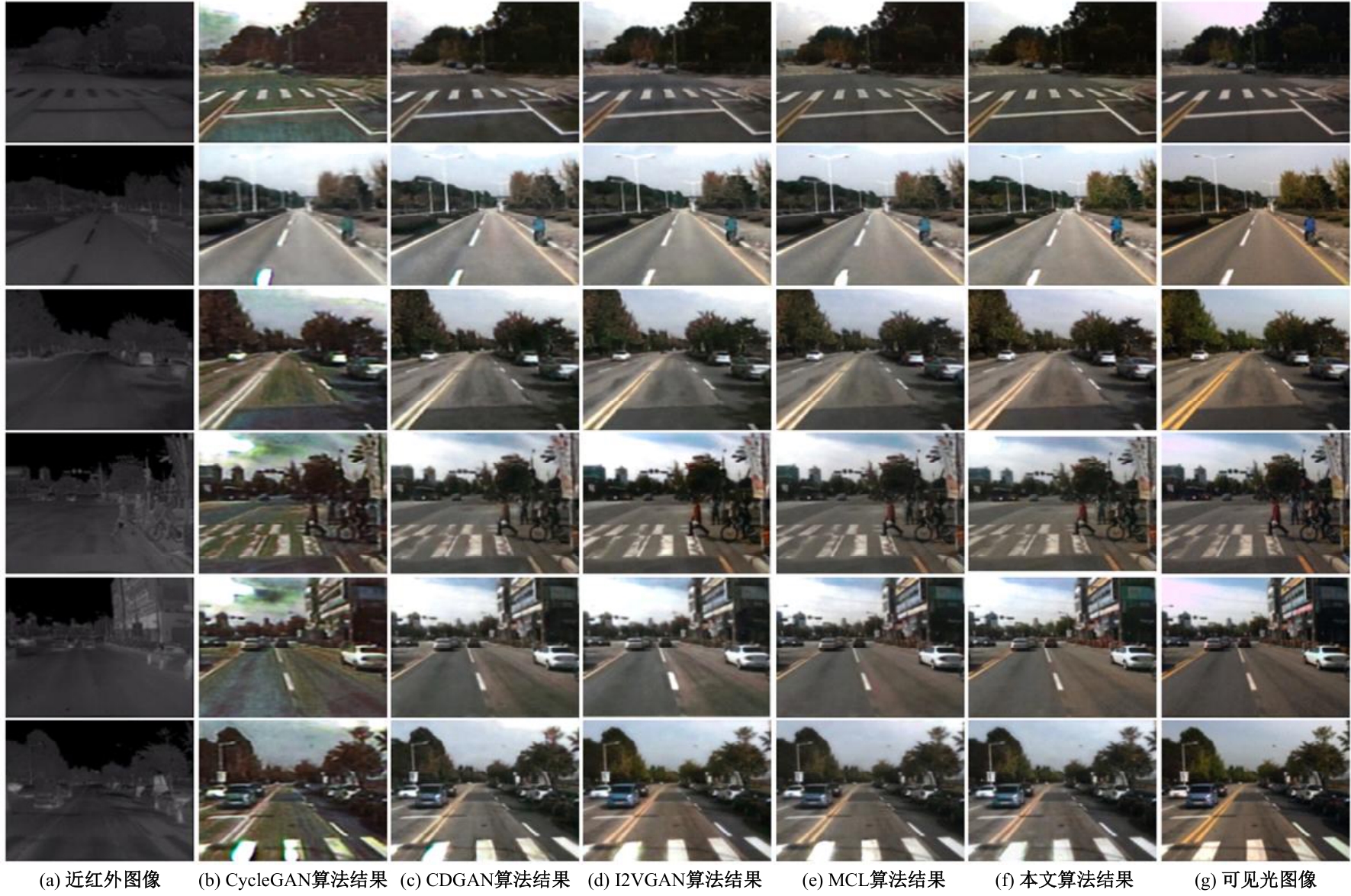
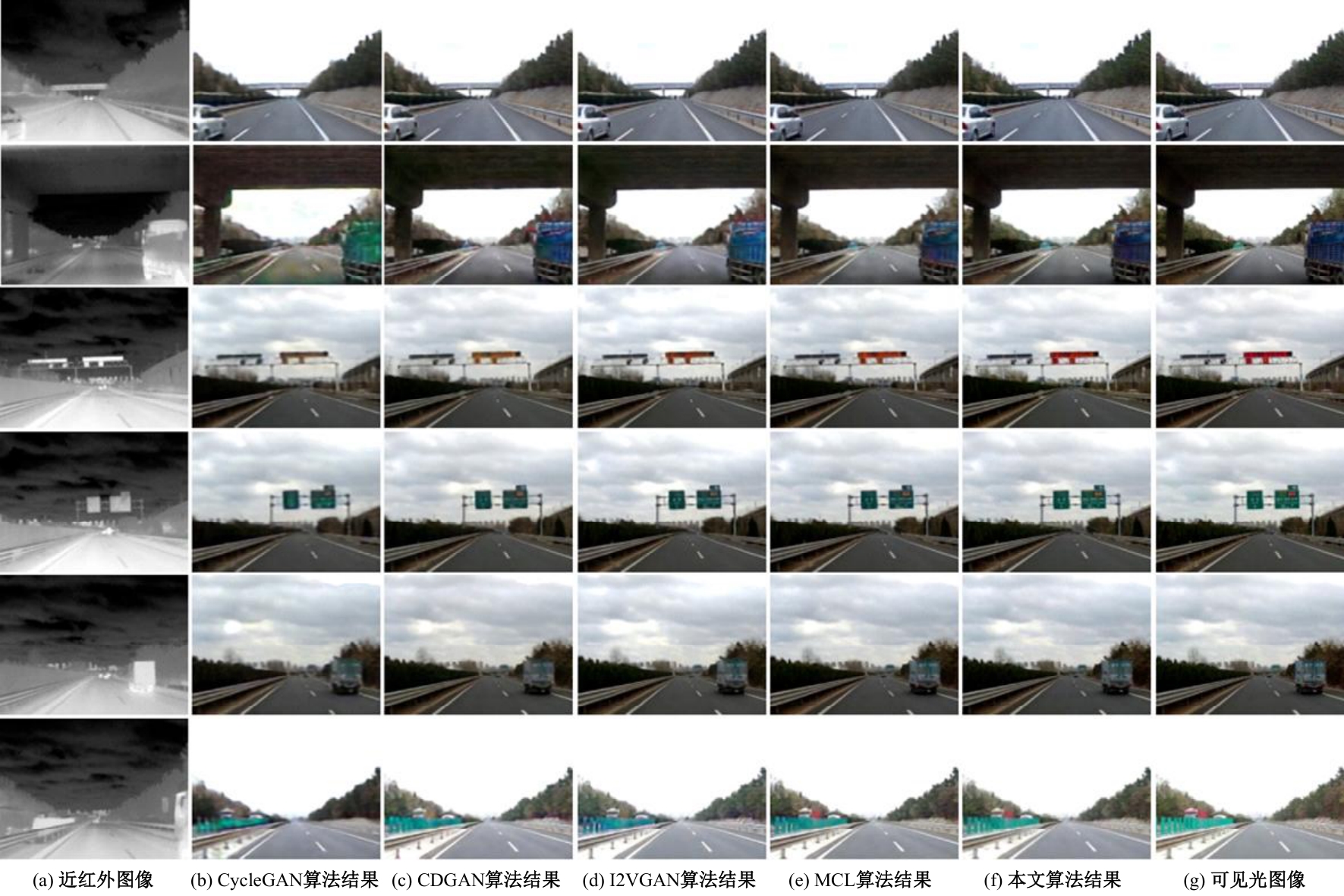
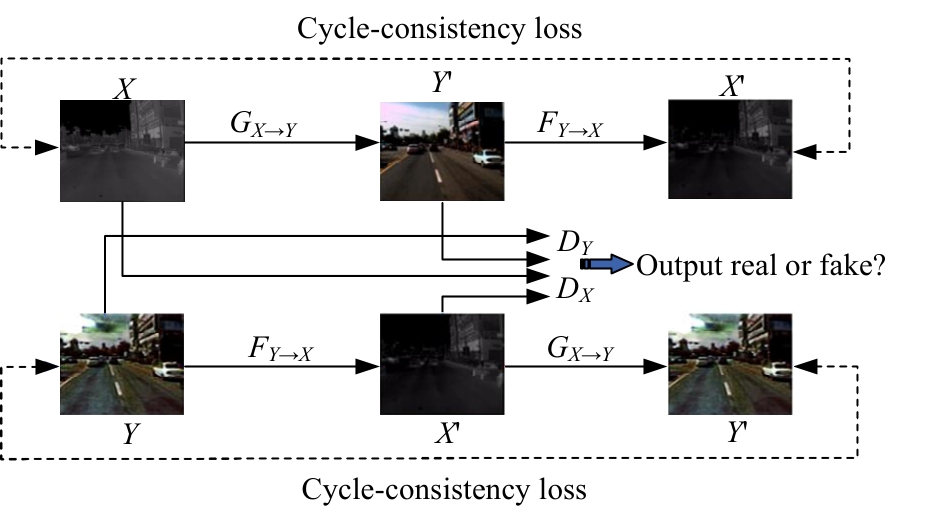
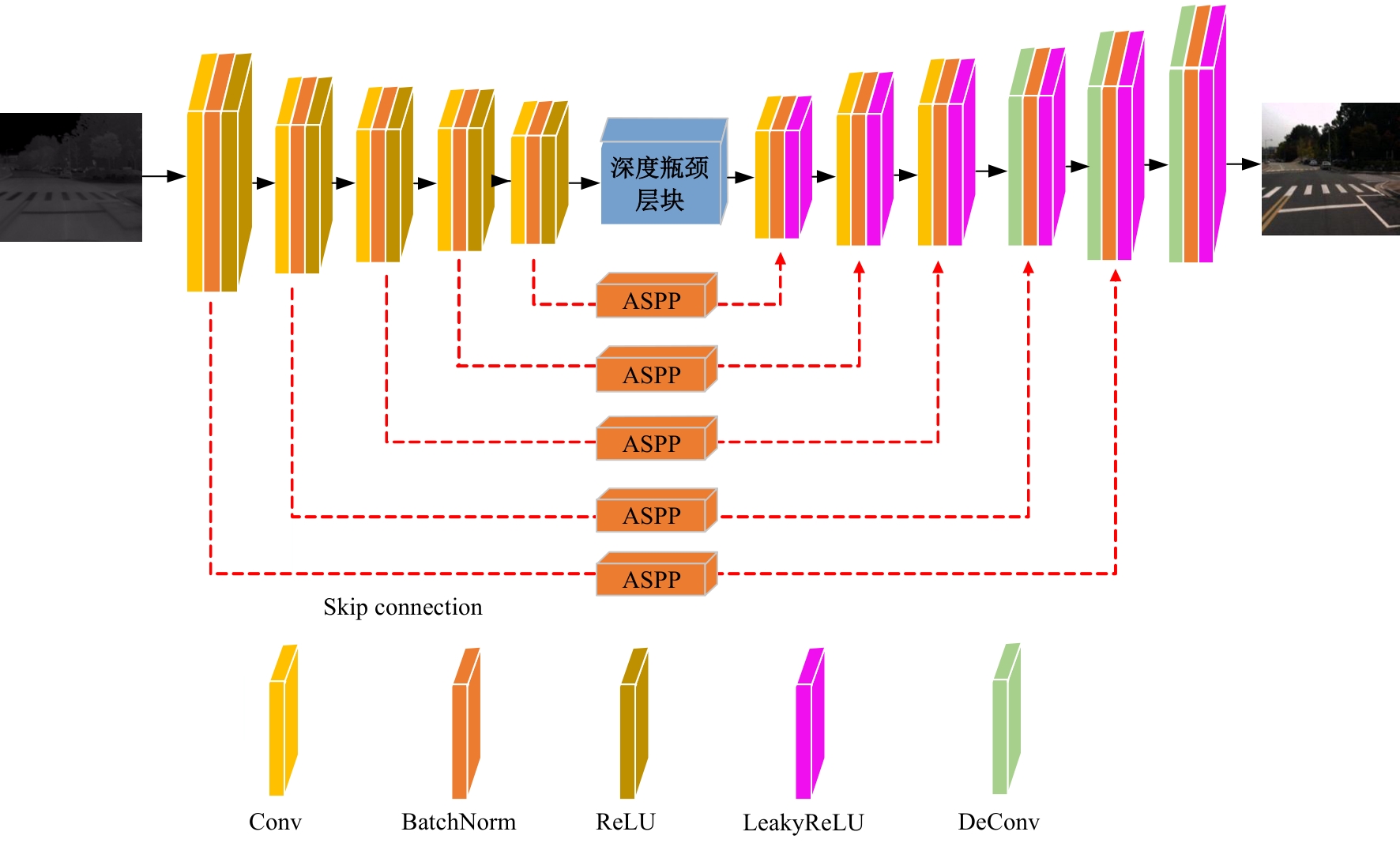
| [1] |
Reinhard E, Adhikhmin M, Gooch B, et al. Color transfer between images[J]. IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, 2001, 21(5): 34-41.
|
| [2] |
Welsh T, Ashikhmin M, Mueller K. Transferring color to greyscale images[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2002, 21(3): 277-280.
|
| [3] |
Levin A, Lischinski D, Weiss Y. Colorization using optimization[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2004, 23(3): 689-694.
|
| [4] |
Goodfellow I J, Pouget A J, Mirza M, et al.Generative adversarial nets[C]∥Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montréal, Canada, 2014:2672-2680.
|
| [5] |
Isola P, Zhu J, Zhou T, et al. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on ComputerVision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1125-1134.
|
| [6] |
Park T, Liu M Y, Wang T C, et al. Semantic imagesynthesis with spatially-adaptive normalization[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 2337-2346.
|
| [7] |
Wang T C, Liu M Y, Zhu J Y, et al. High-resolutionimage synthesis and semantic manipulation withconditional gans[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 8798-8807.
|
| [8] |
Huang X, Liu M Y, Belongie S, et al. Multimodal unsupervised image-to-image translation[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munichi, Germany, 2018:172-189.
|
| [9] |
Lee H Y, Tseng H Y, Huang J B, et al. Diverse image-to-image translation via disentangled representations[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munichi, Germany, 2019:35-51.
|
| [10] |
Yi Z, Zhang H, Tan P, et al. Dualgan: unsupervised dual learning for image-to-image translation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2849-2857.
|
| [11] |
Suárez P L, Sappa A D, Vintimilla B X. Infrared image colorization based on a triplet dcgan architecture[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 212-217.
|
| [12] |
王晓宇.基于颜色迁移的图像彩色化算法研究[D]. 长春: 长春理工大学电子信息工程学院, 2020.
|
|
Wang Xiao-yu. Research on image colorization algorithm based on color migration[D]. Changchun: School of Electronic and Information Engineering, Changchun University of Science and Technology, 2020.
|
| [13] |
Li S, Han B F, Yu Z J, et al. I2VGAN:unpaired Infrared to-visible video translation[C]∥Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, New York,USA, 2021:3061-3069.
|
| [14] |
高美玲, 段锦, 莫苏新, 等. 基于空洞循环卷积的近红外图像彩色化方法[J]. 光学技术, 2022, 48(6):742-748.
|
|
Gao Mei-ling, Duan Jin, Mo Su-xin, et al. Near infrared image colorization method based on dilated-cycle convolution[J]. Optical Technique, 2022, 48(6): 742-748.
|
| [15] |
Chen J, Chen J, Chao H, et al. Image blind denoising with generative adversarial network based noise modeling[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018:3155-3164.
|
| [16] |
陈雪云, 许韬, 黄小巧. 基于条件生成对抗网络的医学细胞图像生成检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(4): 1414-1419.
|
|
Chen Xue-yun, Xu Tao, Huang Xiao-qiao. Detection method of medical cell image generation basedon conditional generative adversarial network[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(4): 1414-1419.
|
| [17] |
王小玉, 胡鑫豪, 韩昌林. 基于生成对抗网络的人脸铅笔画算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(1): 285-292.
|
|
Wang Xiao-yu, Hu Xin-hao, Han Chang-lin. Face pencil drawing algorithms based on generative adversarial network[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering nd Technology Edition), 2021, 51(1): 285-292.
|
| [18] |
Monday H N, Li J, Nneji G U, et al. A wavelet convolutional capsule network with modified super resolution generative adversarial network for fault diagnosis and classification[J]. Complex & Intelligent Systems, 2022, 8: 4831-4847.
|
| [19] |
彭晏飞, 张平甲, 高艺, 等. 融合注意力的生成式对抗网络单图像超分辨率重建[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2021, 58(20): 182-191.
|
|
Peng Yan-fei, Zhang Ping-jia, Gao Yi, et al. Attention fusion generative adversarial network for single-image super-resolution reconstruction[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2021, 58(20): 182-191.
|
| [20] |
Liang C C, George P, Iasonas K, et al. DeepLab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(4): 834-848.
|
| [21] |
Woo S, Park J, Lee J Y, et al. CBAM: convolutional block attention module[C]∥Proceedings of the 15thEurope an Conference on Computer Visdom, Munich, Germany, 2018: 3-19.
|
| [22] |
Li C, Wan D M. Precomputed real-time texture synthesis with markovian generative adversarial networks[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision of IEEE, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016:702-716.
|
| [23] |
Wang S, Park J, Kim N, et al. Multispectral pedestrian detection: benchmark dataset and baseline[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 1037-1045.
|
| [24] |
Park T, Liu M Y, Wang T C, et al. Semantic image synthesis with spatially-adaptive normalization[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019:2337-2346.
|
| [25] |
Zhu J Y, Park T, Isola P, et al. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial network[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2223-2232.
|
| [26] |
Kancharagunta B K, Ram S D. CDGAN: cyclic discriminative generative adversarial networks forimage-to-image transformation[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2022, 82:103382.
|
| [27] |
Gou Y. Multi-feature contrastive learning for unpaired image-to-image translation[J]. Intelligent Systems, 2023, 9: 4111-4122.
|