| 1 |
刘朝晖, 周海燕. miR-192-5p在支气管哮喘气道炎症中的作用[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志, 2021, 37(16): 4.
|
| 2 |
PIJNENBURG M W, FLEMING L.Advances in understanding and reducing the burden of severe asthma in children[J]. Lancet Respir Med, 2020,8(10): 1032-1044.
|
| 3 |
CHUNG K F, WENZEL S E, BROZEK J L, et al. International ERS/ATS guidelines on definition, evaluation and treatment of Severe Asthma [J]. Eur Respir J, 2014,43(1): 343-373.
|
| 4 |
吕秀云, 杨 婷, 徐 磊, 等. SA患者血清MIP-1α和IL-13水平动态变化及其预后评估价值[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2019, 45(6): 1401-1407.
|
| 5 |
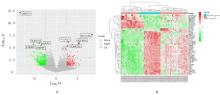
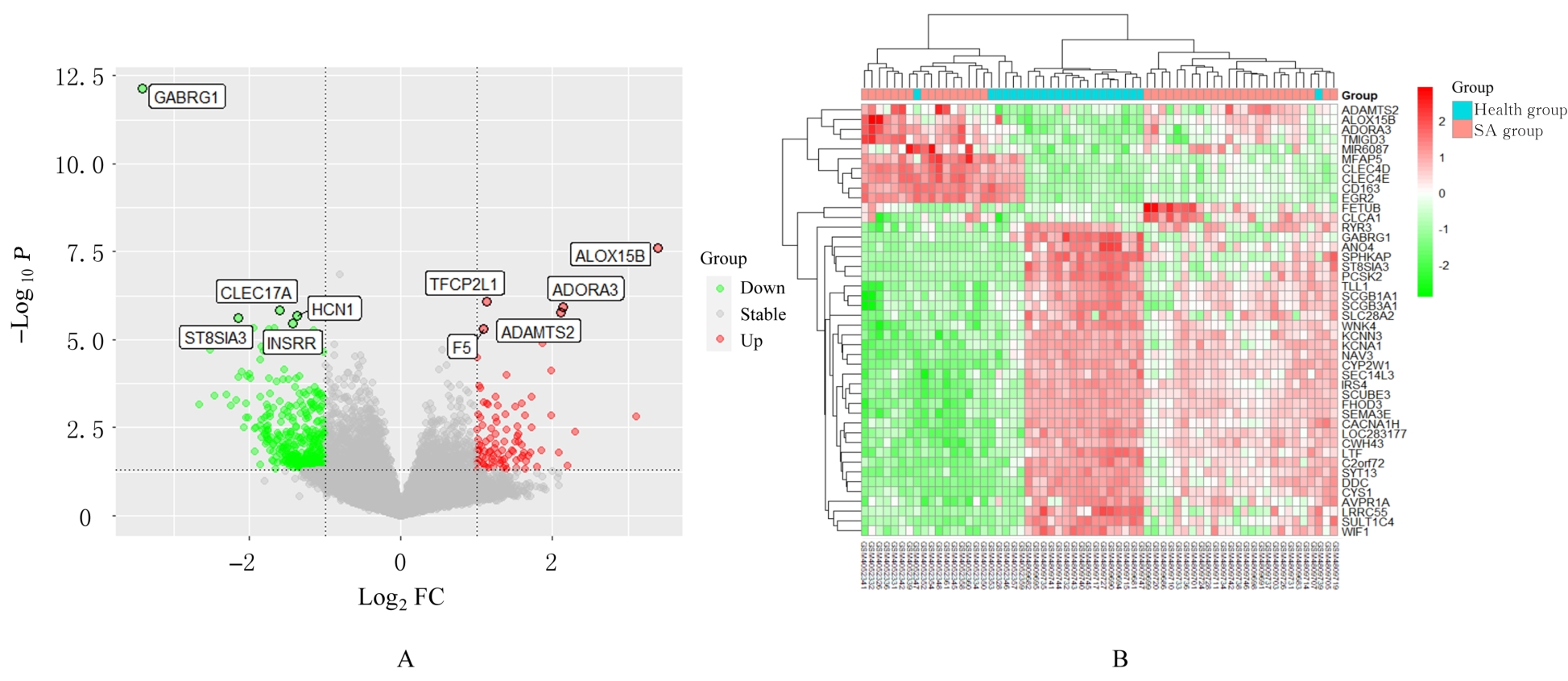
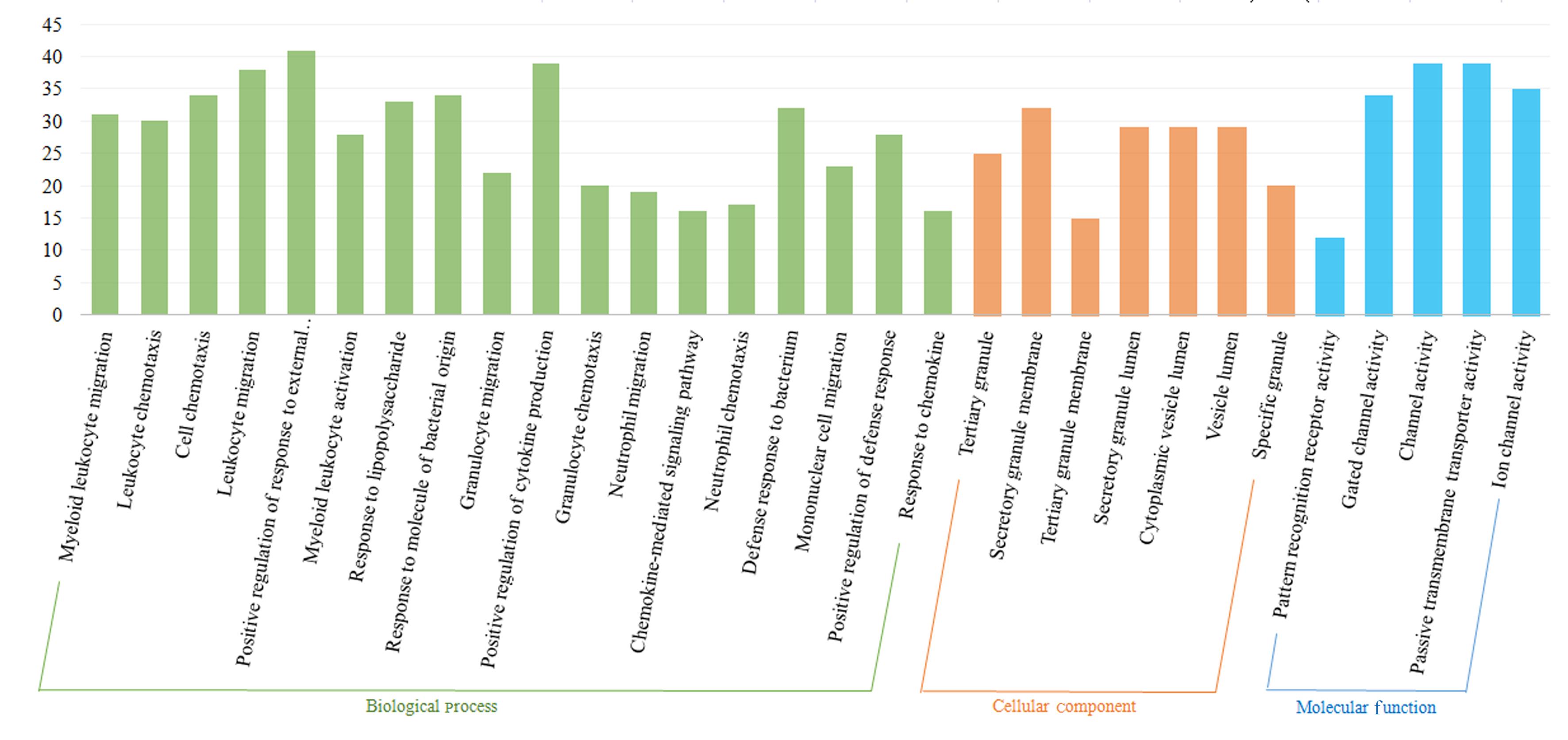
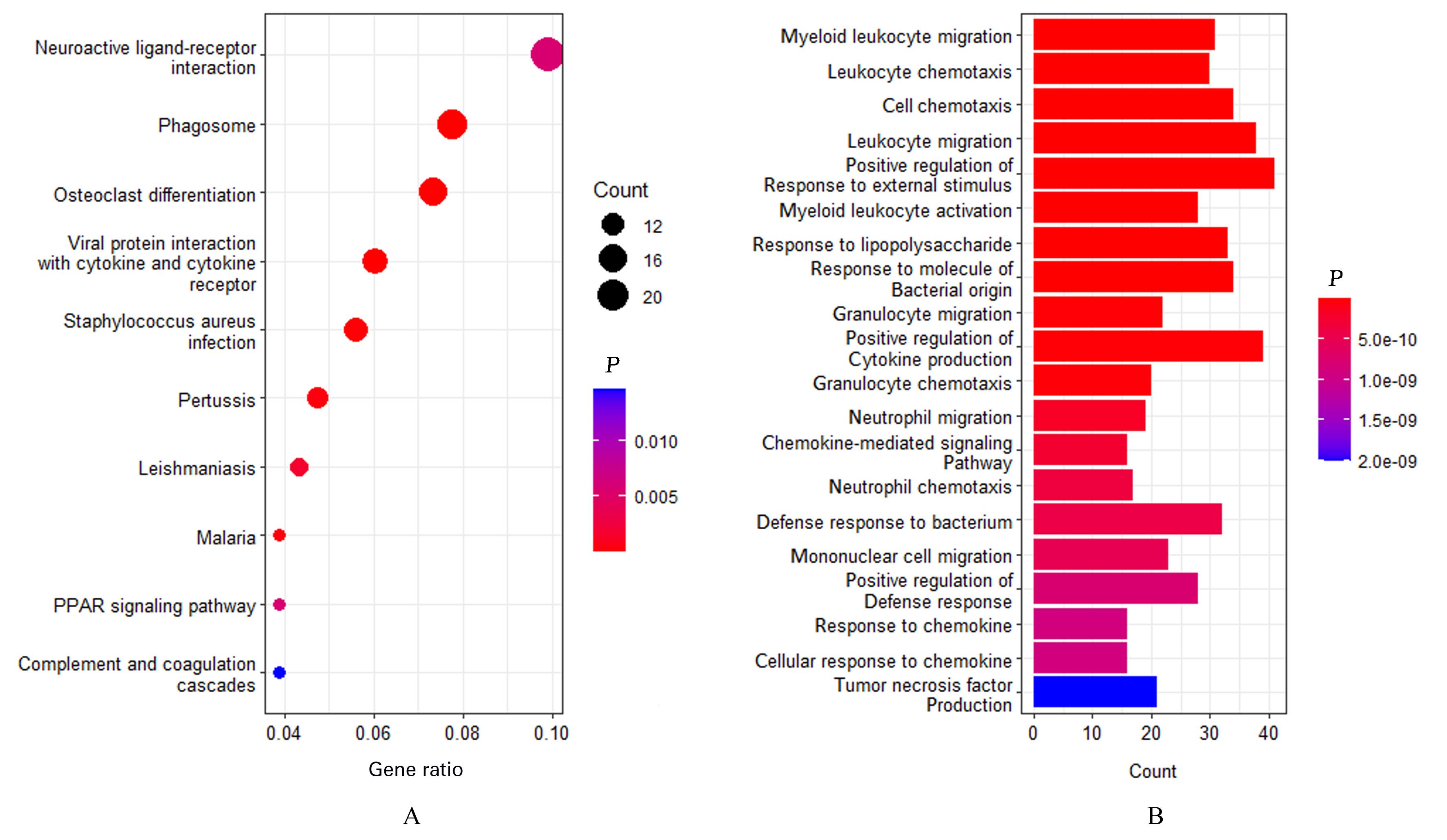
高雅宁, 李 健, 陈 亮, 等. SA患者支气管内膜差异表达基因的生物信息学[J]. 中华临床免疫和变态反应杂志, 2023, 17(1): 27-33.
|
| 6 |
赖 芳, 翁燕娜, 张 燕 等. 国医大师晁恩祥教授防治重症支气管哮喘经验总结[J]. 中国中医急症, 2015, 24(10): 1767-1768.
|
| 7 |
马欢欢. 集束化护理在蒙药八味沉香散治疗重症支气管哮喘中的应用分析[J].中国民族医药杂志,2021,27(5): 67-68.
|
| 8 |
秦欣欣, 吴华阳, 王建云 等. 基于“肾阳虚、肺络热”探析SA的诊治思路[J]. 北京中医药,2022, 41(2): 157-159.
|
| 9 |
ZHANG W, CHEN Y, JIANG H,et al.Integrated strategy for accurately screening biomarkers based on metabolomics coupled with network pharmacology[J]. Talanta, 2020, 211:120710.
|
| 10 |
骆宾妃, 董佳威, 刘红宁, 等. 基于“病-药-量”探讨《中华医典》含竹沥中药方剂相应规律的数据挖掘[J]. 中草药, 2023, 54(8): 2536-2545.
|
| 11 |
MEDREK S K, PARULEKAR A D, HANANIA N A. Predictive Biomarkers for Asthma Therapy[J]. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep,2017 17(10):69.
|
| 12 |
NTONTSI P, PAPATHANASSIOU E, LOUKIDES S,et al. Targeted anti-IL-13 therapies in asthma: current data and future perspectives[J]. Expert Opin Investig Drugs,2018,27(2):179-186.
|
| 13 |
TAUPENOT L, HARPER K L, O’CONNOR D T. The Chromogranin Secretogranin Family[J]. N Engl J Med, 2003, 348(12):1134-1149.
|
| 14 |
SHOOSHTARIZADEH P, ZHANG D, CHICH J F, et al. The antimicrobial peptides derived from chromogranin/secretogranin family, new actors of innate immunity[J]. Regul Pept, 2010, 165(1):102-110.
|
| 15 |
谢 明, 陈晓迎, 刘景仑, 等. 入院时血清嗜铬粒蛋白A浓度和ICU患者病情严重程度的相关性研究[J]. 第三军医大学学报, 2013, 35(2): 157-160.
|
| 16 |
陈晓迎,张丹,姜丽萍,等.CHGA-415T/C和-462G/A基因多态性与重症患者预后的相关性研究[J].重庆医科大学学报,2014,39(12):1744-1748.
|
| 17 |
RØSJØ H, NYGÅRD S, KAUKONEN K M,et al. Prognostic value of chromogranin A in severe sepsis: data from the FINNSEPSIS study[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2012,38(5):820-829.
|
| 18 |
BALKARLI A, SENGÜL C, TEPELI E,et al. Synaptosomal-associated protein 25 (Snap-25) gene polymorphism frequency in fibromyalgia syndrome and relationship with clinical symptoms[J]. BMC Musculoskelet Disord,2014,15:191.
|
| 19 |
ZHAO Y, CHEN S, YOSHIOKA C,et al. Architecture of fully occupied GluA2 AMPA receptor-tarp complex elucidated by cryo-em[J]. Nature,2016,536(7614):108-111.
|
| 20 |
HARRISON V, CONNELL L, HAYESMOORE J, et al. Compound heterozygous deletion of NRXN1 causing severe developmental delay with early onset epilepsy in two sisters.[J]. Am J Med Genet A, 2011, 155(11):2826-2831.
|
| 21 |
WEI Y, LIU J, ZHANG H,et al. Ligustrazine attenuates inflammation and the associated chemokines and receptors in ovalbumine-induced mouse asthma model[J]. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol,2016,46:55-61.
|
| 22 |
CHEN X Q, YANG J, HU SP, et al. Increased expression of CD86 and reduced production of IL-12 and IL-10 by monocyte-derived dendritic cells from allergic asthmatics and their effects on Th1- and Th2-type cytokine balance[J]. Respiration, 2006,73(1):34-40.
|
| 23 |
ZHI Y, GAO P, XIN X,et al. Clinical significance of sCD163 and its possible role in asthma (Review)[J]. Mol Med Rep,2017,15(5):2931-2939.
|
| 24 |
NIELSEN M J, MADSEN M, MØLLER H J, et al. The macrophage scavenger receptor CD163[J]. J Leukoc Biol, 2006,79(4):837-845.
|
| 25 |
AKILA P, PRASHANT V, SUMA MN, et al. CD163 and its expanding functional repertoire[J]. Clin Chim Acta,2012,413(7/8):669-674.
|
| 26 |
MATSUBARA E, KOMOHARA Y, SHINCHI Y,et al.CD163-positive cancer cells are a predictor of a worse clinical course in lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Pathol Int,2021,71(10):666-673.
|
| 27 |
MITCHELL PD, O’BYRNE PM. Epithelial-Derived Cytokines in Asthma[J]. Chest, 2017,151(6):1338-1344.
|
| 28 |
WERDER R B, ZHANG V, LYNCH J P,et al. Chronic IL-33 expression predisposes to virus-induced asthma exacerbations by increasing type 2 inflammation and dampening antiviral immunity[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2018, 141(5):1607-1619.
|
| 29 |
HAMID Q. Inflammatory cells, cytokine and chemokine expression in asthma immunocytochemistry and in situ hybridization[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol,2003,111(4):902-903.
|
| 30 |
CHAPMAN R W, PHILLIPS J E, HIPKIN R W,et al. CXCR2 antagonists for the treatment of pulmonary disease[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2009, 121(1):55-68.
|
| 31 |
姚庆美, 陈 玥, 黎友伦, 等. SA气道上皮细胞损伤机制及潜在生物治疗靶点[J]. 中国呼吸与危重监护杂志, 2022, 21(12): 899-903.
|
| 32 |
BLAISS M S. Pharmacoeconomics of asthma[J]. Allerg Clin Immunol, 2003, 15(6): 240-245.
|
| 33 |
崔 勇, 李世明, 金 燕, 等. 人参皂苷Rh2通过VEGF/MMP-9信号通路抑制哮喘小鼠气道重塑的实验研究[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2017, 35(8): 1932-1935.
|
| 34 |
王鹏丽. 三拗汤加全蝎、僵蚕干预咳嗽变异性哮喘网络调控特点及配伍效应机制研究[D].南京:南京中医药大学, 2020.
|
| 35 |
伍 爽, 李 微, 黎 达, 等. 黄芪皂苷Ⅱ对哮喘幼年大鼠IL-21/STAT3通路及气道炎症反应的影响[J]. 中国比较医学杂志, 2021, 31(12): 53-59.
|
| 36 |
商玉立, 郭彩霞, 石红梅, 等. 黄芪多糖对哮喘小鼠气道炎症启动因子TSLP和DCs表达的影响[J].中国抗生素杂志, 2021, 46(7): 711-716.
|
| 37 |
金 律, 陈 颖, 赵 艳 等. 玉屏风散合人参五味子汤治疗肺脾气虚证咳嗽变异性哮喘患者的疗效及作用机制[J]. 世界中西医结合杂志, 2023, 18(6): 1227-1232.
|
| 38 |
李 华. 人参五味子汤联合布地奈德混悬液治疗小儿哮喘的效果观察[J]. 临床合理用药杂志, 2021, 14(20): 129-130.
|
| 39 |
周 立, 陈琦琦, 李 慧. 人参五味子汤对支气管哮喘患儿外周血白细胞介素-8、白细胞介素-17、瘦素水平和肺功能的影响[J]. 儿科药学杂志, 2021, 27(2): 9-11.
|
 ),Li HAN1,Hua BIAN1,Liye PANG1
),Li HAN1,Hua BIAN1,Liye PANG1