吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (3): 602-611.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240303
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
C57BL/6小鼠大脑皮层区与基底神经节隆起区神经元突触发育过程比较
赵艳1,2,卢广泉2,杜金乐2,潘雨绮2,董子意2,康鑫2,高弋婷2,高方2,杨加周1( )
)
- 1.延安大学医学院组织学与胚胎学教研室,陕西 延安 716099
2.空军军医大学基础医学院神经 生物学教研室,陕西 西安 710032
Comparison of development process of neuronal synapse between cerebral cortex and basal ganglia eminence regions in C57BL/6 mice
Yan ZHAO1,2,Guangquan LU2,Jinle DU2,Yuqi PAN2,Ziyi DONG2,Xin KANG2,Yiting GAO2,Fang GAO2,Jiazhou YANG1( )
)
- 1.Department of Histology and Embryology,School of Medical Sciences,Yan’an University,Yan’an 716099,China
2.Department of Neurobiology,School of Basic Medical Sciences,Air Force Medical University,Xi’an 710032,China
摘要:
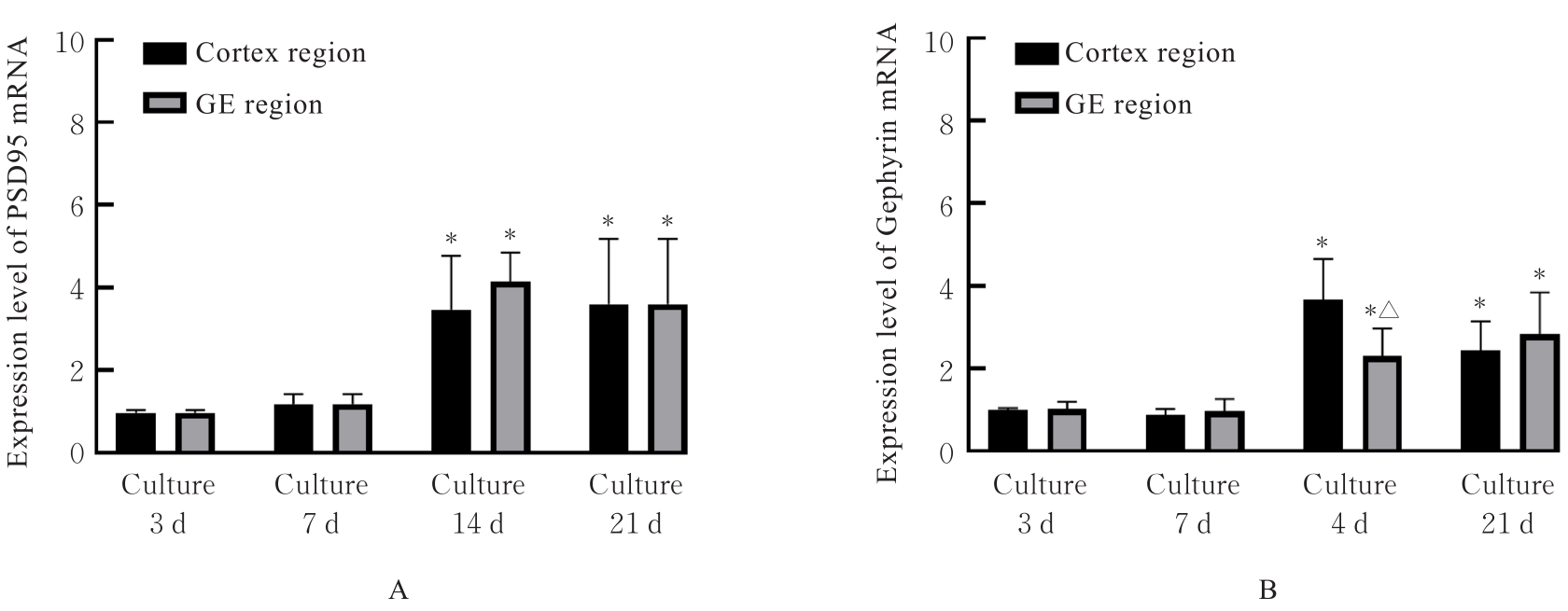
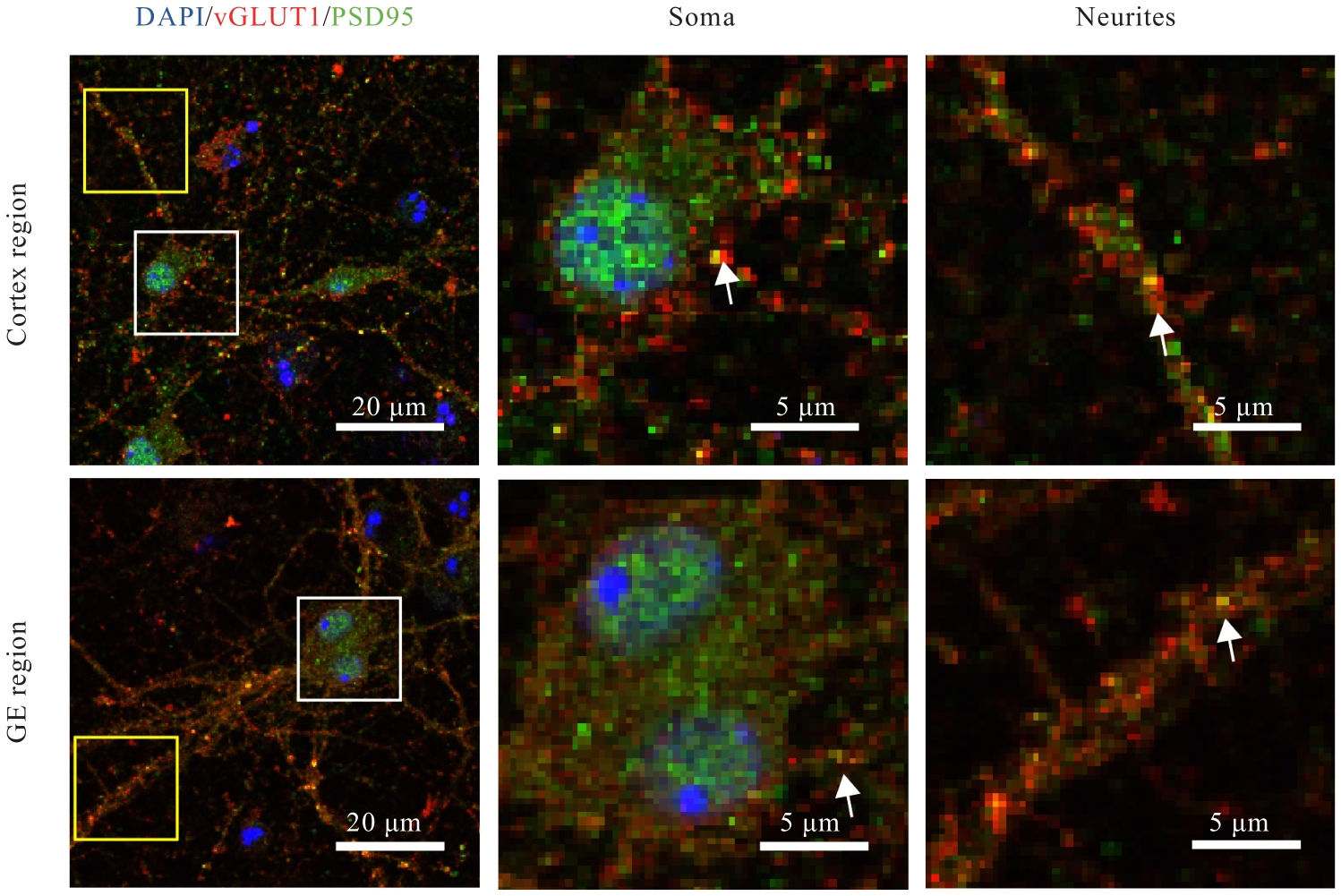
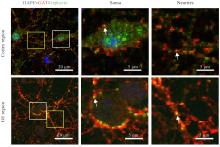
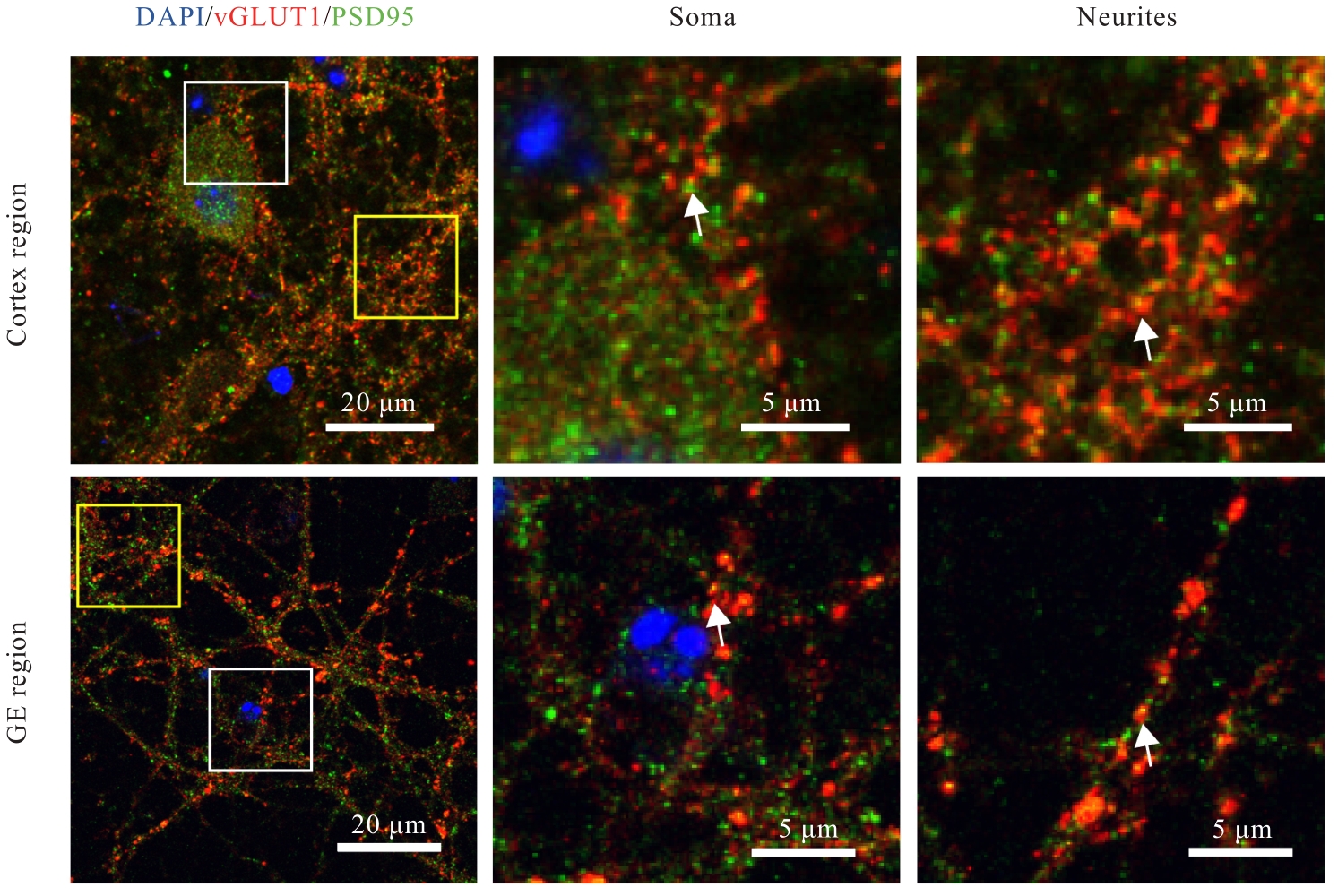
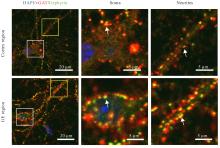
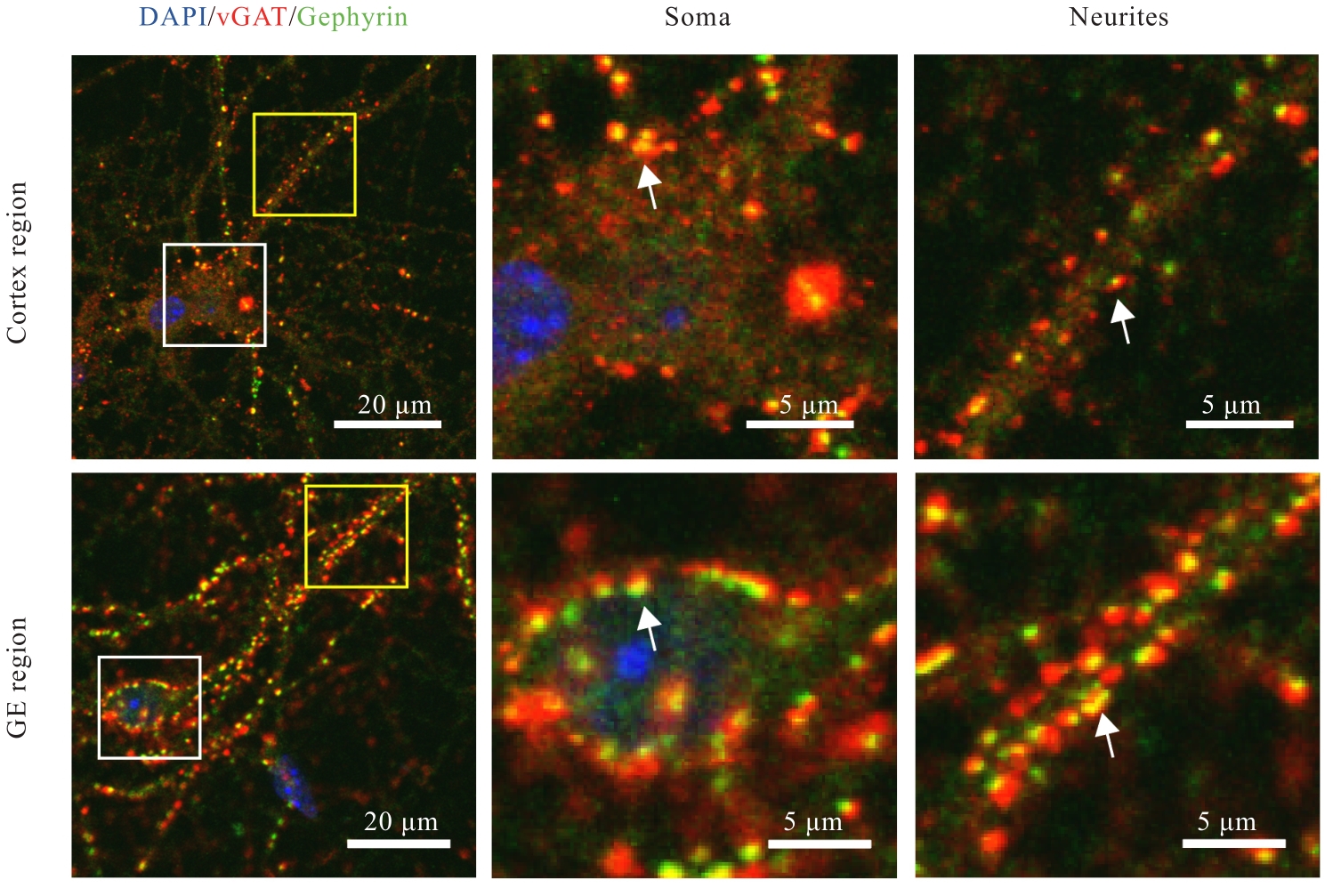
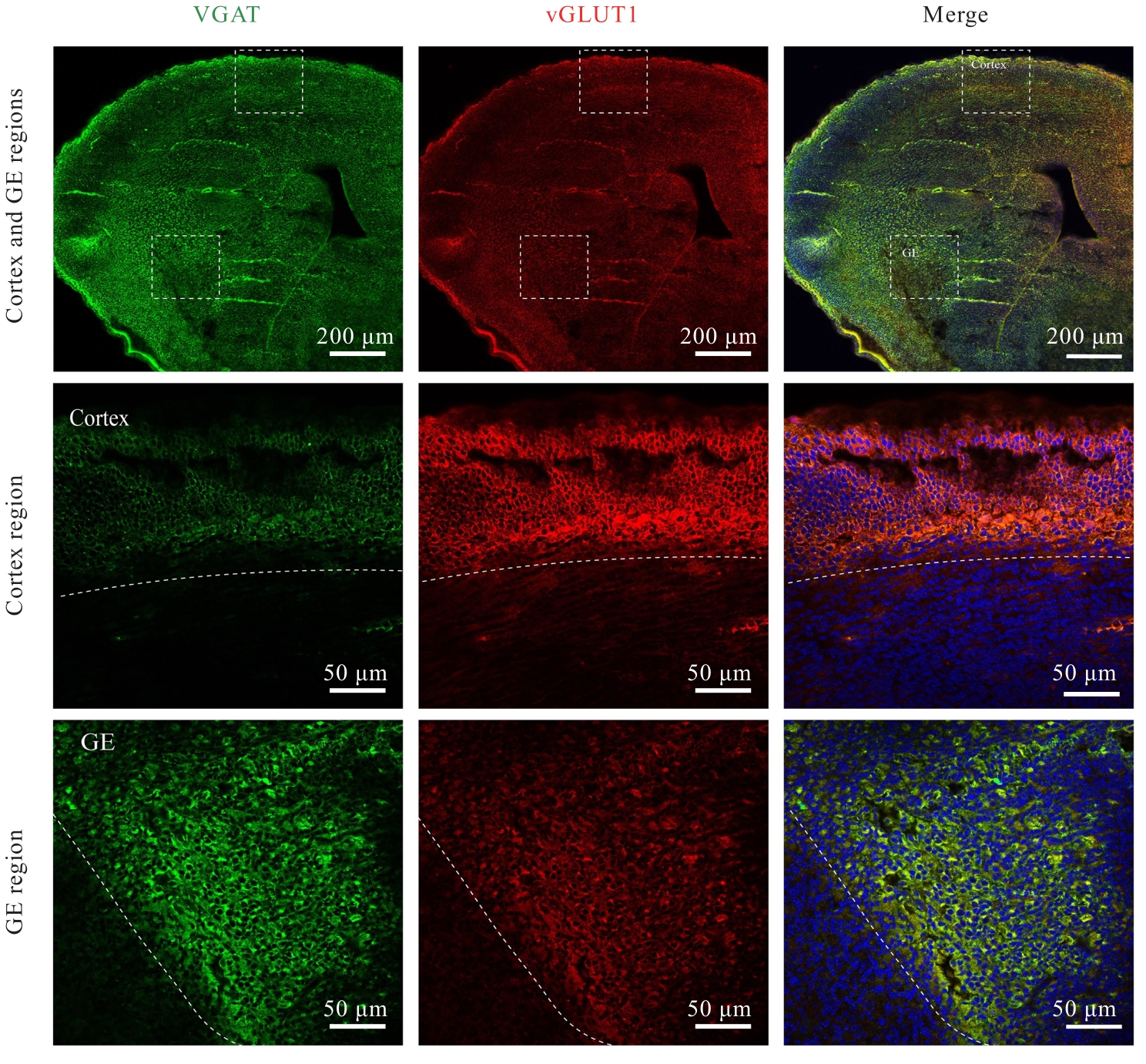
目的 观察小鼠皮层区和基底神经节隆起(GE)区神经元突触发育过程,阐明兴奋性突触和抑制性突触在不同脑区的体内外发育差异。 方法 C57BL/6雌鼠于妊娠第13.5~15.5天断颈处死后,经无菌操作取胚胎小鼠,显微镜下逐步分离获取胚胎小鼠脑组织皮层区和GE区。体外原代培养胚胎小鼠神经元,于培养3、7、14和21 d分别收集细胞样品,并将其作为培养3、7、14和21 d组。采用实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法检测各组小鼠皮层区和GE区原代培养神经元中突触后表达蛋白突触后密度蛋白95(PSD95)及桥尾蛋白(Gephyrin)mRNA表达水平。免疫荧光法检测各组小鼠皮层区和GE区原代培养神经元中囊泡谷氨酸转运蛋白1(vGLUT1)、PSD95、囊泡γ-氨基丁酸(GABA)转运蛋白(vGAT)及Gephyrin蛋白表达水平。免疫荧光法检测胚胎小鼠脑组织皮层区和GE区神经元中vGLUT1及vGAT蛋白表达水平。 结果 与培养3 d组比较,培养14和21 d组小鼠皮层区和GE区原代培养神经元中PSD95及Gephyrin mRNA表达水平明显升高(P<0.01);与皮层区比较,培养14 d组小鼠GE区原代培养神经元中Gephyrin mRNA表达水平明显降低(P<0.01)。显微镜下观察,培养14 d组小鼠皮层区和GE区原代培养神经元中兴奋性突触及抑制性突触均初步发育,相关蛋白呈阳性表达;其中兴奋性突触相关蛋白阳性表达在皮层区神经元中更为明显,且突触前分子vGLUT1和突触后分子PSD95在皮层区神经元的胞体及突起部位均呈现共定位的特征;抑制性突触前分子vGAT蛋白和突触后分子Gephyrin蛋白在GE区神经元胞体及突起中也呈现共定位的特征,且突触前分子较相应的突触后分子蛋白阳性表达更明显。与皮层区比较,培养14 d组小鼠GE区原代培养神经元中vGLUT1和PSD95蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.01),vGAT和Gephyrin蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.01)。培养21 d组小鼠皮层区和GE区原代培养神经元突触相关蛋白阳性表达增加,兴奋性突触和抑制性突触进一步成熟并完善。皮层区和GE区原代培养神经元的胞体及突起部位均形成了丰富的突触前后对应的表达模式,突触结构逐步发育良好,且突触前分子较相应的突触后分子蛋白阳性表达更明显。与皮层区比较,培养21 d组小鼠GE区原代培养神经元中vGLUT1和PSD95蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.01),vGAT和Gephyrin蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.01)。与皮层区比较,胚胎小鼠脑组织GE区神经元中vGLUT1蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.01),vGAT蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.05)。 结论 皮层区和GE区神经元的突触发育具有明显的差异性,皮层区兴奋性突触发育较早,GE区抑制性突触发育较早。突触的脑区特异性发育提示不同细胞类型的神经疾病可能具有不同的发育来源。
中图分类号:
- R394