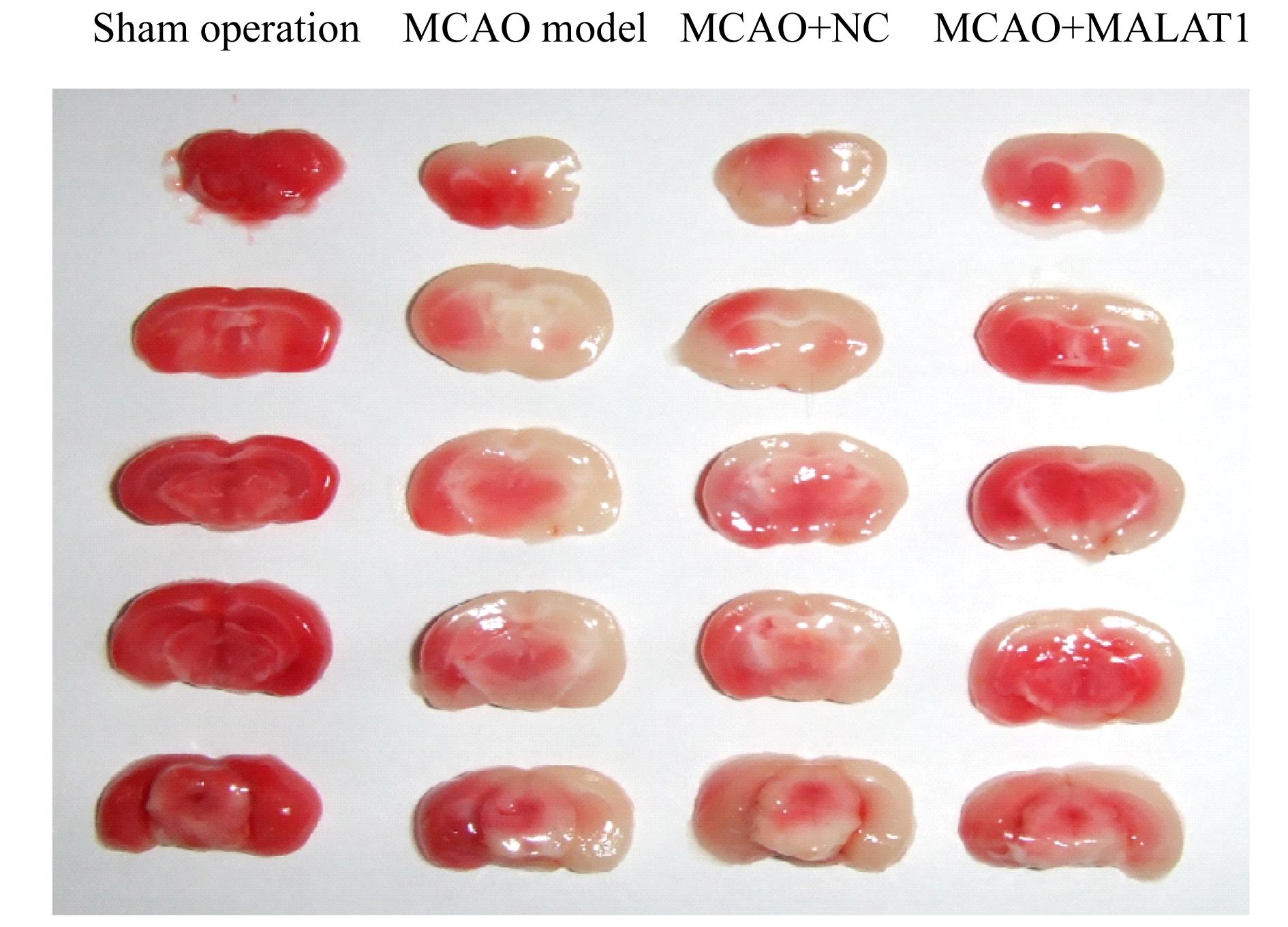
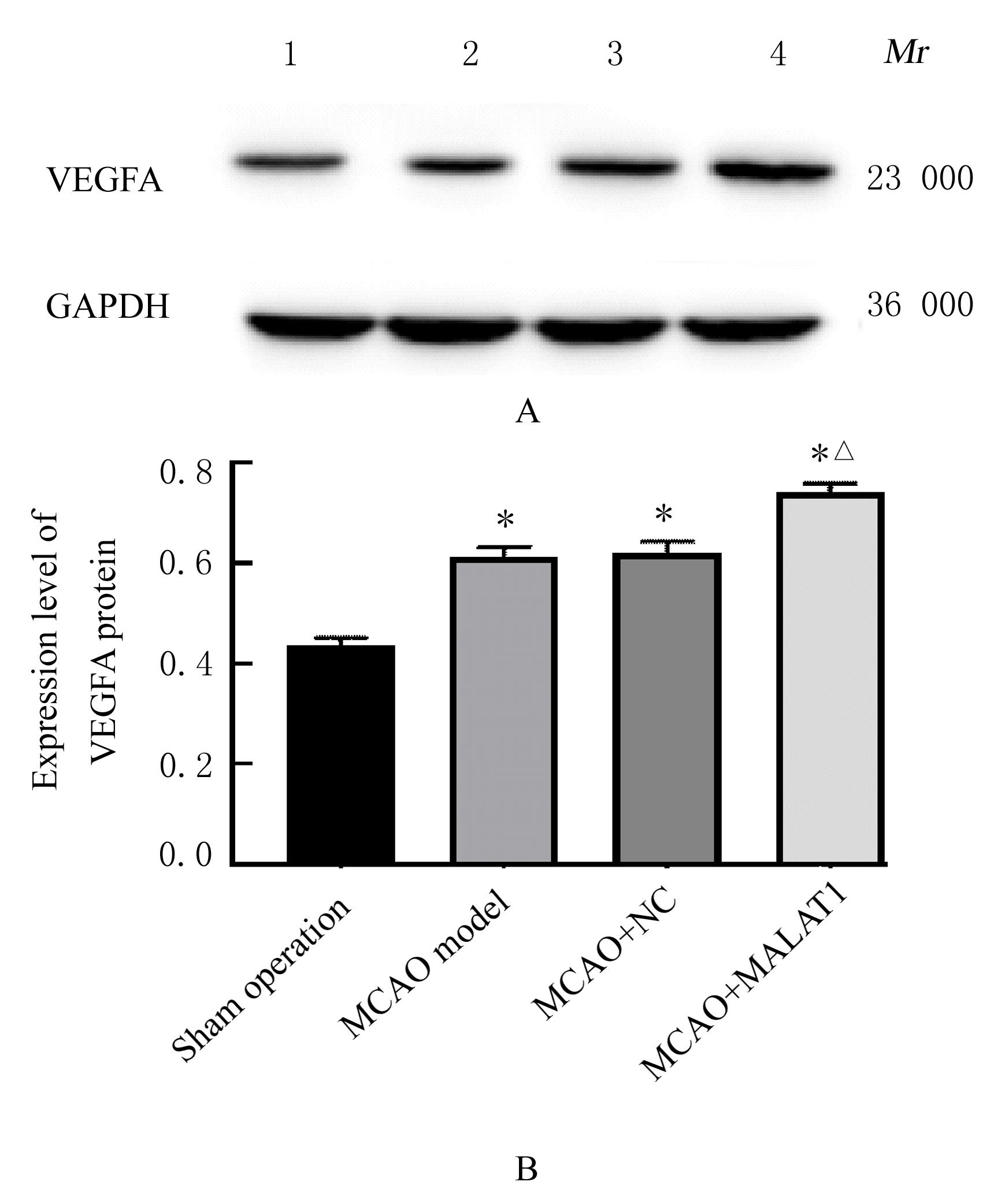
| 1 |
MATHERS C D, LONCAR D. Projections of global mortality and burden of disease from 2002 to 2030[J]. PLoS Med, 2017, 3(11): e442.
|
| 2 |
LIU L P, WANG D, LAWRENCE WONG K S, et al. Stroke and stroke care in China: huge burden, significant workload, and a national priority[J].Stroke,2011,42(12): 3651-3654.
|
| 3 |
GIBSON C L. Cerebral ischemic stroke: is gender important?[J].J Cereb Blood Flow Metab,2013,33(9): 1355-1361.
|
| 4 |
CHEN J, LIU P Y, DONG X H, et al. The role of lncRNAs in ischemic stroke[J]. Neurochem Int, 2021, 147: 105019.
|
| 5 |
VASUDEVA K, DUTTA A, MUNSHI A. Role of lncRNAs in the development of ischemic stroke and their therapeutic potential[J].Mol Neurobiol,2021,58(8):3712-3728.
|
| 6 |
ZHANG X J, TANG X L, LIU K, et al. Long noncoding RNA Malat1 regulates cerebrovascular pathologies in ischemic stroke[J].J Neurosci,2017,37(7): 1797-1806.
|
| 7 |
MICHALIK K M, YOU X T, MANAVSKI Y, et al. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 regulates endothelial cell function and vessel growth[J]. Circ Res, 2014, 114(9): 1389-1397.
|
| 8 |
WANG H W, ZHENG X X, JIN J, et al. LncRNA MALAT1 silencing protects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through miR-145 to regulate AQP4[J]. J Biomed Sci, 2020, 27(1): 40.
|
| 9 |
TAN X D, GUO W J, PENG Z, et al. LncRNA-Malat1 down-regulates miR-211-5p expression to promote neuronal damage from cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2021, 192: 114694.
|
| 10 |
MENG S, WANG B, LI W. LncRNA MALAT1 improves cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury and cognitive dysfunction by regulating miR-142-3p/SIRT1 axis[J]. Int J Neurosci, 2023.DOI:10.1080/00207454. 2021.1972999 .
doi: 10.1080/00207454. 2021.1972999
|
| 11 |
SARKAR S, CHAKRABORTY D, BHOWMIK A, et al. Cerebral ischemic stroke: cellular fate and therapeutic opportunities[J]. Front Biosci, 2019,24(3): 435-450.
|
| 12 |
ZHANG J, YUAN L, ZHANG X, et al. Altered long non-coding RNA transcriptomic profiles in brain microvascular endothelium after cerebral ischemia[J]. Exp Neurol, 2016, 277: 162-170.
|
| 13 |
JI P, DIEDERICHS S, WANG W B,et al.MALAT-1, a novel noncoding RNA, and thymosin beta4 predict metastasis and survival in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Oncogene, 2003, 22(39): 8031-8041.
|
| 14 |
XIAO H B, TANG K, LIU P J, et al. LncRNA MALAT1 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate ZEB2 expression by sponging miR-200s in clear cell kidney carcinoma[J].Oncotarget,2015,6(35):38005-38015.
|
| 15 |
LIU J Y, YAO J, LI X M, et al. Pathogenic role of lncRNA-MALAT1 in endothelial cell dysfunction in diabetes mellitus[J].Cell Death Dis,2014,5(10): e1506.
|
| 16 |
UCHIDA S, DIMMELER S. Long noncoding RNAs in cardiovascular diseases[J]. Circ Res, 2015, 116(4): 737-750.
|
| 17 |
THUM T, FIEDLER J. LncRNA MALAT1 and angiogenesis[J]. Circ Res, 2014, 114(9): 1366-1368.
|
| 18 |
UEDA Y, NAKAGAWA T, KUBOTA T, et al. Glioma cells under hypoxic conditions block the brain microvascular endothelial cell death induced by serum starvation[J]. J Neurochem, 2005, 95(1): 99-110.
|
| 19 |
陈宇恒, 王正龙. 长链非编码RNA在动脉粥样硬化“损伤-应答”中的作用机制研究进展[J].解放军医学杂志,2022,47(6): 614-624.
|
| 20 |
JIA P, CAI H, LIU X B, et al. Long non-coding RNA H19 regulates glioma angiogenesis and the biological behavior of glioma-associated endothelial cells by inhibiting microRNA-29a[J].Cancer Lett,2016,381(2): 359-369.
|
| 21 |
PAGE S, MUNSELL A, AL-AHMAD A J. Cerebral hypoxia/ischemia selectively disrupts tight junctions complexes in stem cell-derived human brain microvascular endothelial cells[J]. Fluids Barriers CNS, 2016, 13(1): 16.
|
| 22 |
HUANG J K, MA L, SONG W H, et al. LncRNA-MALAT1 promotes angiogenesis of thyroid cancer by modulating tumor-associated macrophage FGF2 protein secretion[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2017, 118(12): 4821-4830.
|
| 23 |
LI Y, WU Z Z, YUAN J, et al. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 promotes gastric cancer tumorigenicity and metastasis by regulating vasculogenic mimicry and angiogenesis[J]. Cancer Lett, 2017, 395: 31-44.
|
| 24 |
TEE A E, LIU B, SONG R H, et al. The long noncoding RNA MALAT1 promotes tumor-driven angiogenesis by up-regulating pro-angiogenic gene expression[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(8): 8663-8675.
|
| 25 |
LI Z J, LI J, TANG N. Long noncoding RNA Malat1 is a potent autophagy inducer protecting brain microvascular endothelial cells against oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced injury by sponging miR-26b and upregulating ULK2 expression[J]. Neuroscience, 2017, 354: 1-10.
|
| 26 |
REN L F, WEI C X, LI K, et al. LncRNA MALAT1 up-regulates VEGF-A and ANGPT2 to promote angiogenesis in brain microvascular endothelial cells against oxygen-glucose deprivation via targetting miR-145[J].Biosci Rep,2019,39(3).DOI:10.1042/BSR20180226 .
doi: 10.1042/BSR20180226
|
| 27 |
MEHTA S L, KIM T, VEMUGANTI R. Long noncoding RNA FosDT promotes ischemic brain injury by interacting with REST-associated chromatin-modifying proteins[J]. J Neurosci,2015,35(50): 16443-16449.
|
| 28 |
CHENG H, SUN M, WANG Z L, et al. LncRNA RMST-mediated miR-107 transcription promotes OGD-induced neuronal apoptosis via interacting with hnRNPK[J]. Neurochem Int, 2020, 133: 104644.
|
| 29 |
LECOUTER J, MORITZ D R, LI B, et al. Angiogenesis-independent endothelial protection of liver: role of VEGFR-1[J]. Science, 2003,299(5608): 890-893.
|
| 30 |
MCLAREN J. Vascular endothelial growth factor and endometriotic angiogenesis[J]. Hum Reprod Update, 2000, 6(1): 45-55.
|
| 31 |
MǍRGǍRITESCO O, PIRICI D, MǍRGǍRITESCO C.VEGF expression in human brain tissue after acute ischemic stroke[J].Revue Roumaine De Morphol Embryol, 2011, 52(4): 1283-1292.
|
| 32 |
MA Y H, ZECHARIAH A, QU Y, et al. Effects of vascular endothelial growth factor in ischemic stroke[J]. J Neurosci Res, 2012, 90(10): 1873-1882.
|
 )
)