吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (6): 1551-1560.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250611
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
16s rRNA测序技术检测复方地黄颗粒作用下肺炎链球菌诱导肺炎模型大鼠肠道菌群的变化及其意义
- 1.承德医学院中医基础理论教研室,河北 承德 067000
2.承德医学院方剂教研室,河北 承德 067000
3.承德医学院针灸推拿教研室,河北 承德 067000
4.承德医学院中医临床基础教研室,河北 承德 067000
Changes of intestinal flora in rats with Streptococcus pneumoniae-induced pneumonia treated with Compound Dihuang Granules detected by 16s rRNA sequencing technology and its significance
Yuhan ZHANG1,Lingjuan KONG2,Jinying LIU3,Jianen GUO4( )
)
- 1.Department of Basic Theory of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Chengde Medical University,Chengde 067000,China
2.Department of Prescriptions of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Chengde Medical University,Chengde 067000,China
3.Department of Acupuncture,Moxibustion and Tuina,Chengde Medical University,Chengde 067000,China
4.Department of Clinical Foundation of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Chengde Medical University,Chengde 067000,China
摘要:
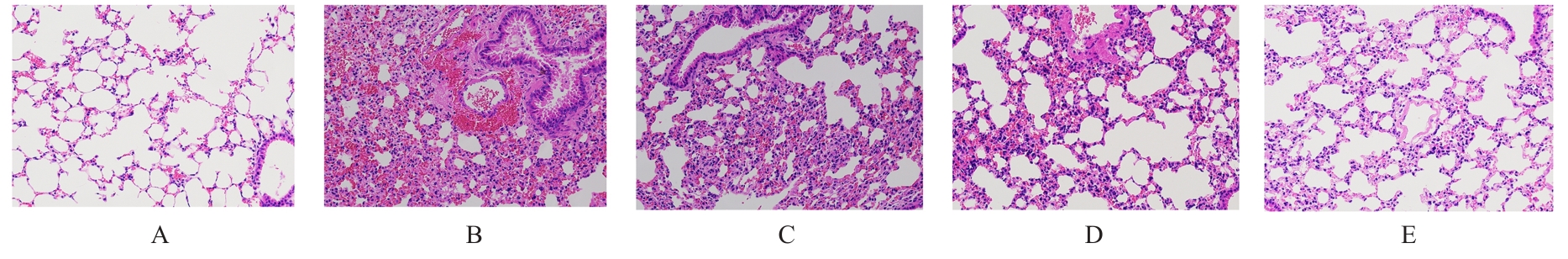
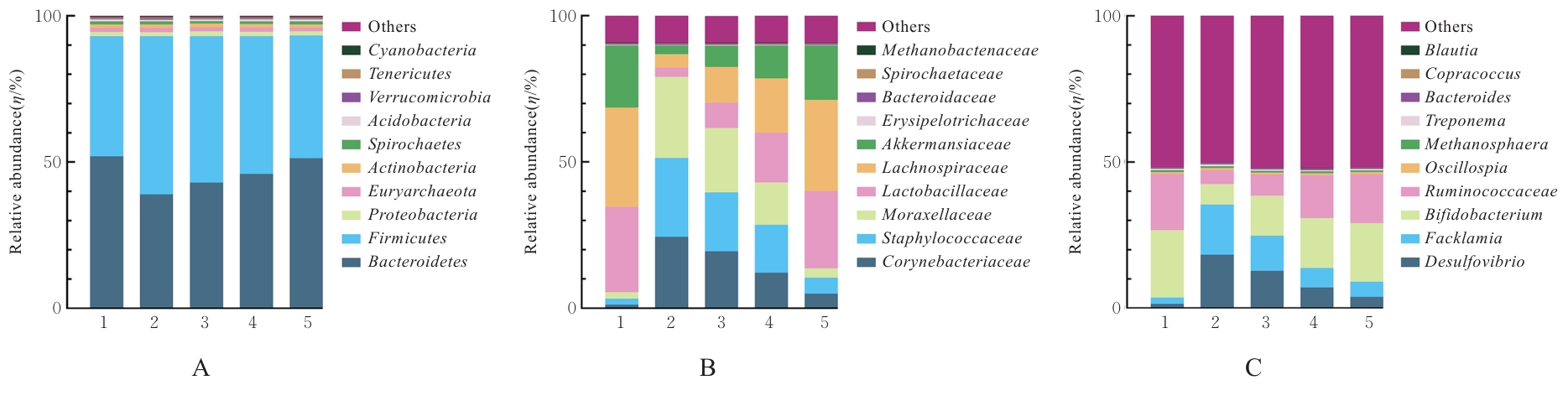
目的 通过16s rRNA测序技术探讨复方地黄颗粒对肺炎链球菌(Spn)诱导肺炎模型大鼠肠道菌群的影响,并阐明其潜在机制。 方法 将30只大鼠随机分为对照组(正常大鼠)、模型组(Spn诱导肺炎大鼠模型)、低剂量复方地黄颗粒组(肺炎大鼠模型灌胃1.75 g·kg-1复方地黄颗粒)、中剂量复方地黄颗粒组(肺炎大鼠模型灌胃3.50 g·kg-1复方地黄颗粒)和高剂量复方地黄颗粒组(肺炎大鼠模型灌胃7.00 g·kg-1复方地黄颗粒),每组6只。测定大鼠肺组织湿/干重(W/D)比值并分析血气指标,HE染色观察各组大鼠肺组织病理形态表现并评估肺组织损伤程度,试剂盒检测各组大鼠肺泡灌洗液(BALF)中细菌负荷水平和白细胞介素(IL)-6、IL-8及IL-10水平,进行16s rRNA肠道菌群测序分析。 结果 与对照组比较,模型组大鼠动脉血二氧化碳分压(PaCO2)明显升高(P<0.05),动脉血氧分压(PaO2)和血氧饱和度(SaO2)明显降低(P<0.05);与模型组比较,低、中和高剂量复方地黄颗粒组大鼠PaCO2明显降低(P<0.05),PaO2和SaO2明显升高(P<0.05),并呈剂量依赖性。HE染色,对照组大鼠肺组织未见明显损伤;模型组大鼠肺组织细胞排列紊乱,大量炎性细胞浸润,肺泡壁毛细血管明显扩张;与模型组比较,低、中和高剂量复方地黄颗粒组大鼠肺组织形态损伤均有所改善。与对照组比较,模型组大鼠肺组织W/D比值和病理评分明显升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,低、中和高剂量复方地黄颗粒组大鼠肺组织W/D比值和病理评分明显降低(P<0.05),并呈剂量依赖性。与对照组比较,模型组大鼠BALF中细菌负荷水平明显升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,低、中和高剂量复方地黄颗粒组大鼠BALF中细菌负荷水平明显降低(P<0.05),并呈剂量依赖性。与对照组比较,模型组大鼠BALF中IL-6和IL-8水平明显升高(P<0.05),IL-10水平明显降低(P<0.05);与模型组比较,低、中和高剂量复方地黄颗粒组大鼠BALF中IL-6和IL-8水平明显降低(P<0.05),IL-10水平明显升高(P<0.05),并呈剂量依赖性。与对照组比较,模型组大鼠菌群丰度指标(Chao1)、菌群多样性和均匀性指标(Shannon)、菌群优势度指标(Simpson)及实际检测物种数指标(Observed_species)均明显降低(P<0.05);与模型组比较,低、中和高剂量复方地黄颗粒组大鼠Chao1、Shannon、Simpson和Observed_species均明显升高(P<0.05),并呈剂量依赖性。与对照组比较,模型组大鼠拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes)相对丰度降低,厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)相对丰度升高,Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes比值明显升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,低、中和高剂量复方地黄颗粒组大鼠Bacteroidetes相对丰度升高,Firmicutes相对丰度降低,Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes比值明显降低(P<0.05),并呈剂量依赖性。在科水平上,与对照组比较,模型组大鼠棒状杆菌科(Corynebacteriaceae)、葡萄球菌科(Staphylococcaceae)和莫拉氏菌科(Moraxellaceae)相对丰度明显升高,而乳酸杆菌科(Lactobacillaceae)、毛螺菌科(Lachnospiraceae)和嗜黏蛋白阿克曼菌科(Akkermansiaceae)相对丰度明显降低;与模型组比较,低、中和高剂量复方地黄颗粒组大鼠Corynebacteriaceae、Staphylococcaceae和Moraxellaceae相对丰度明显降低,Lactobacillaceae、Lachnospiraceae和Akkermansiaceae相对丰度明显升高。在属水平上,与对照组比较,模型组大鼠脱硫弧菌属(Desulfovibrio)和费克蓝姆氏菌属(Facklamia)相对丰度明显升高,双歧杆菌(Bifidobacterium)和瘤胃球菌属(Ruminococcaceae)相对丰度明显降低;与模型组比较,低、中和高剂量复方地黄颗粒组大鼠Desulfovibrio和Facklamia相对丰度明显降低,Bifidobacterium和Ruminococcaceae相对丰度明显升高。 结论 复方地黄颗粒可以改善Spn诱导的肺炎大鼠的炎症和肺损伤,这可能与肠道菌群丰度和多样性的增加有关。
中图分类号:
- R378.12