吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (6): 1254-1259.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20200623
雷诺嗪预处理对缺氧/复氧损伤H9C2心肌细胞自噬的调控及对心肌细胞的保护作用
赵茜1,刘明远2( ),李萌2,栾海艳2,杨玉2,马春艳2,张宝成2,赵锦程2,杨光远1(
),李萌2,栾海艳2,杨玉2,马春艳2,张宝成2,赵锦程2,杨光远1( )
)
- 1.佳木斯大学附属第一医院心内一科,黑龙江 佳木斯 154002
2.佳木斯大学基础医学院药理学教研室,黑龙江 佳木斯 154002
Regulation of ranolazine preconditioning on autophagy of H9C2 cardiomyocytes injured by hypoxia/reoxygenation and its protective effect on cardiomyocytes
Xi ZHAO1,Mingyuan LIU2( ),Meng LI2,Haiyan LUAN2,Yu YANG2,Chunyan MA2,Baocheng ZHANG2,Jincheng ZHAO2,Guangyuan YANG1(
),Meng LI2,Haiyan LUAN2,Yu YANG2,Chunyan MA2,Baocheng ZHANG2,Jincheng ZHAO2,Guangyuan YANG1( )
)
- 1.Department of Cardiology,First Affiliated Hospital,Jiamusi University,Jiamusi 154002,China
2.Department of Pharmacology,School of Basic Medical Sciences,Jiamusi University,Jiamusi 154002,China
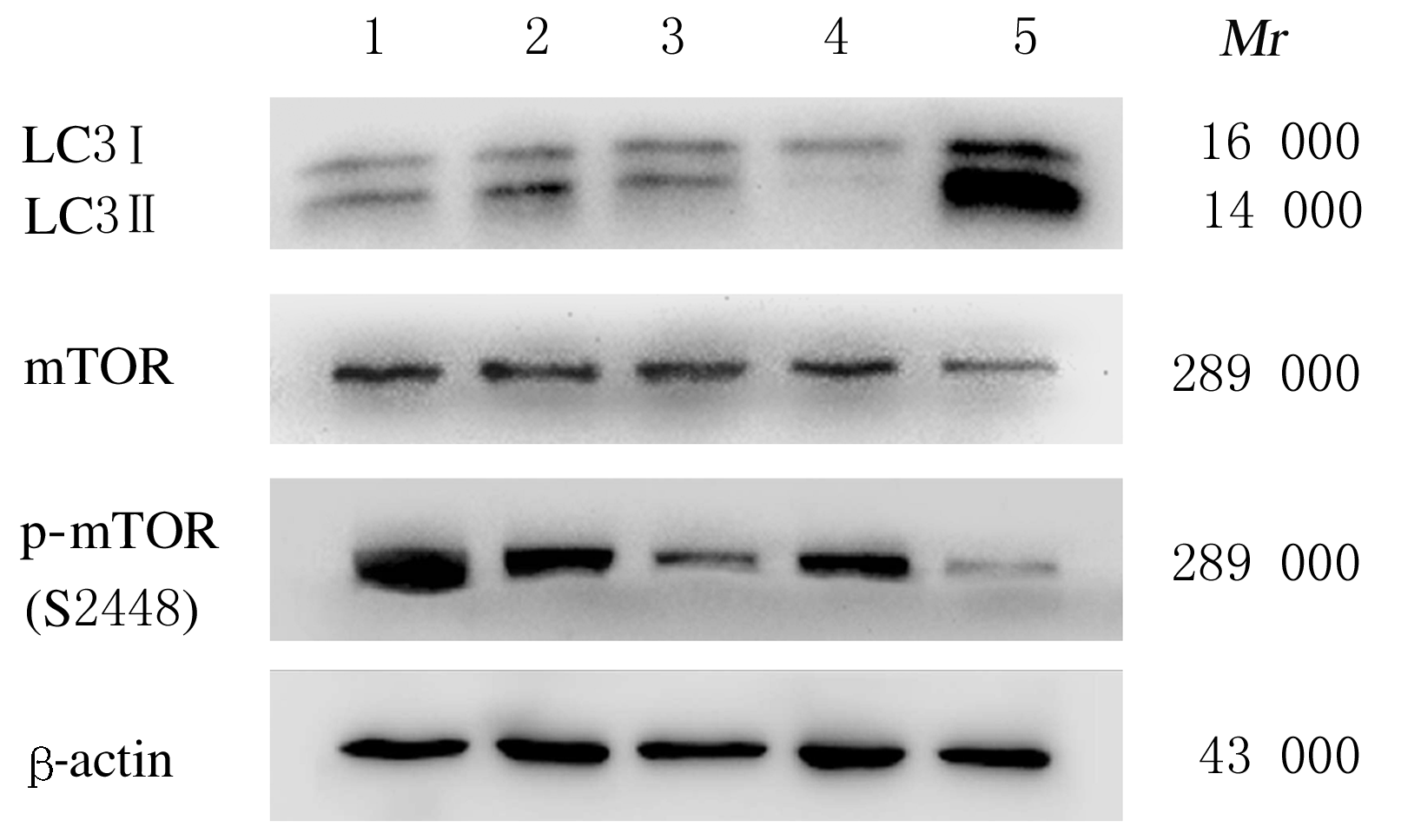
摘要: 探讨雷诺嗪预处理对缺氧/复氧损伤H9C2心肌细胞的保护作用,从自噬调控角度阐明雷诺嗪保护缺血再灌注损伤心肌的作用机制。 将H9C2心肌细胞随机分为正常对照组、缺氧/复氧模型组、雷诺嗪预处理组、雷诺嗪+渥曼青霉素组、雷帕霉素组。正常对照组细胞不做任何处理,其余各组H9C2细胞以相应药物预处理30 min后,行缺氧4 h、复氧3 h处理。采用CCK-8法检测各组H9C2细胞活性,采用乳酸脱氢酶(LDH)试剂盒检测各组H9C2细胞中LDH活性,免疫荧光法检测各组H9C2细胞中微管相关蛋白轻链 3(LC3)阳性表达率,Western blotting法检测各组H9C2细胞中LC3、哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mTOR)和磷酸化mTOR(p- mTOR)蛋白表达水平,计算LC3Ⅱ/LC3Ⅰ和p- mTOR/ mTOR比值。 与缺氧/复氧模型组比较,雷诺嗪预处理组和雷帕霉素组H9C2细胞活性升高(P<0.01),H9C2细胞中LDH活性降低(P<0.01),LC3 阳性表达率升高(P<0.05)。Western blotting法检测,与正常对照组比较,缺氧/复氧模型组H9C2细胞中LC3 Ⅱ/LC3Ⅰ比值升高(P<0.01),p- mTOR/ mTOR比值降低(P<0.01);与缺氧/复氧模型组比较,雷诺嗪预处理组和雷帕霉素组H9C2细胞中LC3 Ⅱ/LC3Ⅰ比值升高(P<0.01),p- mTOR/mTOR比值降低(P<0.01)。 雷诺嗪预处理对缺氧/复氧损伤H9C2心肌细胞具有保护作用,其作用机制可能与雷诺嗪抑制mTOR蛋白磷酸化从而诱导缺氧/复氧H9C2心肌细胞自噬有关联。
中图分类号:
- R329.28