吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (3): 660-668.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210316
骨髓间充质干细胞来源性外泌体携带miR-196b-5p对结肠癌细胞生物学特性的调控作用
李晓辉1,瞿紫微1( ),卢昕1,孟庆彬1,陈华涛1,任骏1,谭成沛2
),卢昕1,孟庆彬1,陈华涛1,任骏1,谭成沛2
- 1.湖北省武汉第一医院胃肠外科,湖北 武汉 430022
2.湖北省神农架林区中医医院普外科,湖北 神农架 442000
Regulatory effect of exosomes carrying miR-196b-5p derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on biological characteristics of colon cancer cells
Xiaohui LI1,Ziwei QU1( ),Xin LU1,Qingbin MENG1,Huatao CHEN1,Jun REN1,Chengpei TAN2
),Xin LU1,Qingbin MENG1,Huatao CHEN1,Jun REN1,Chengpei TAN2
- 1.Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery,Wuhan First Hospital,Hubei Province,Wuhan 430022,China
2.Department of General Surgery,Shennongjia Forestry Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Hubei Province,Shennongjia 442000,China
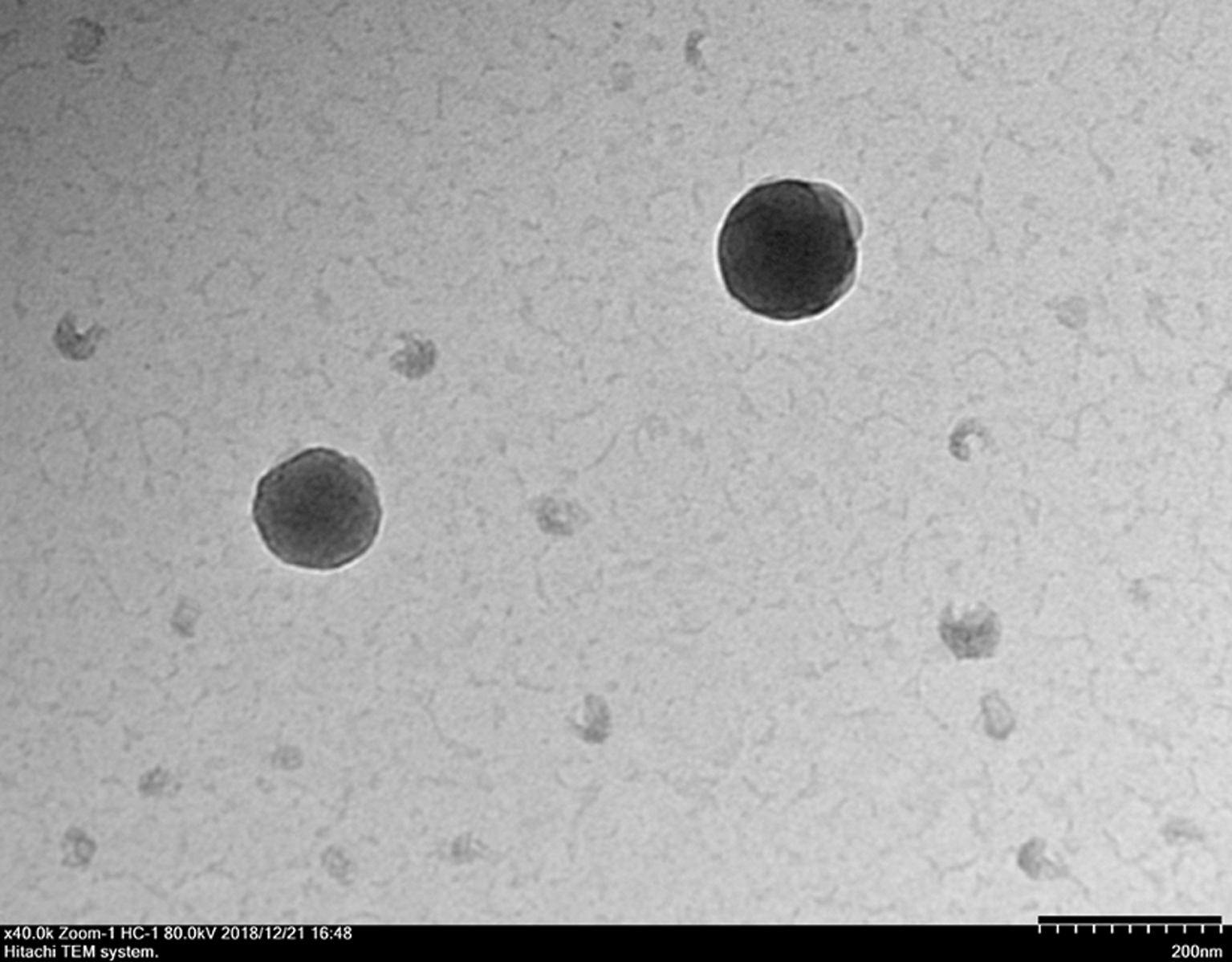
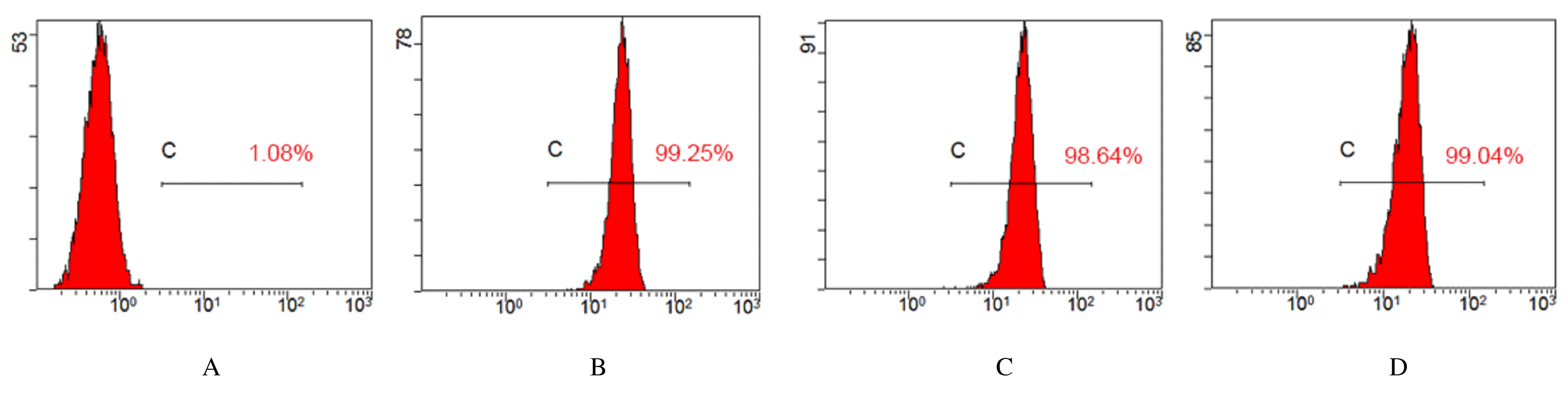
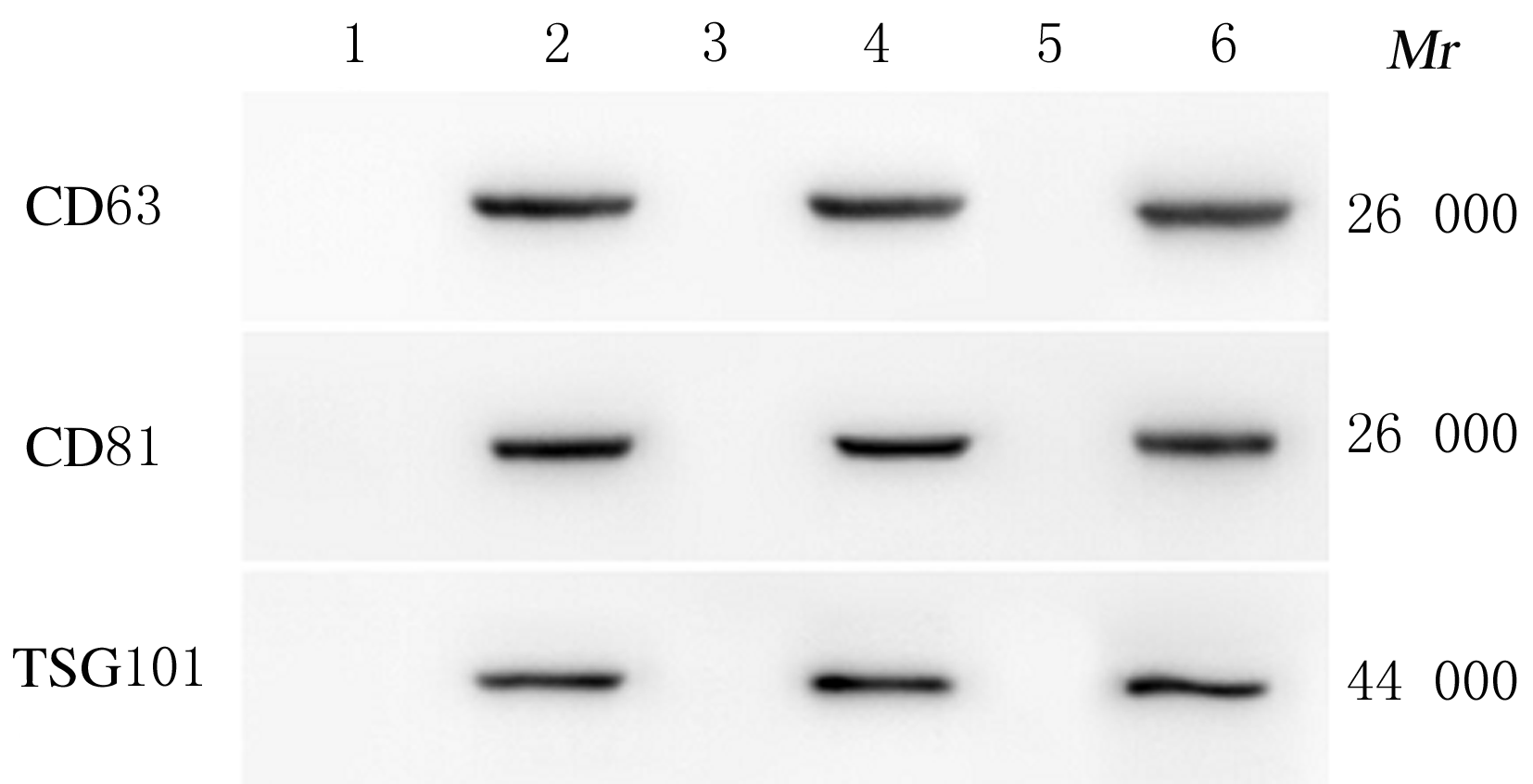
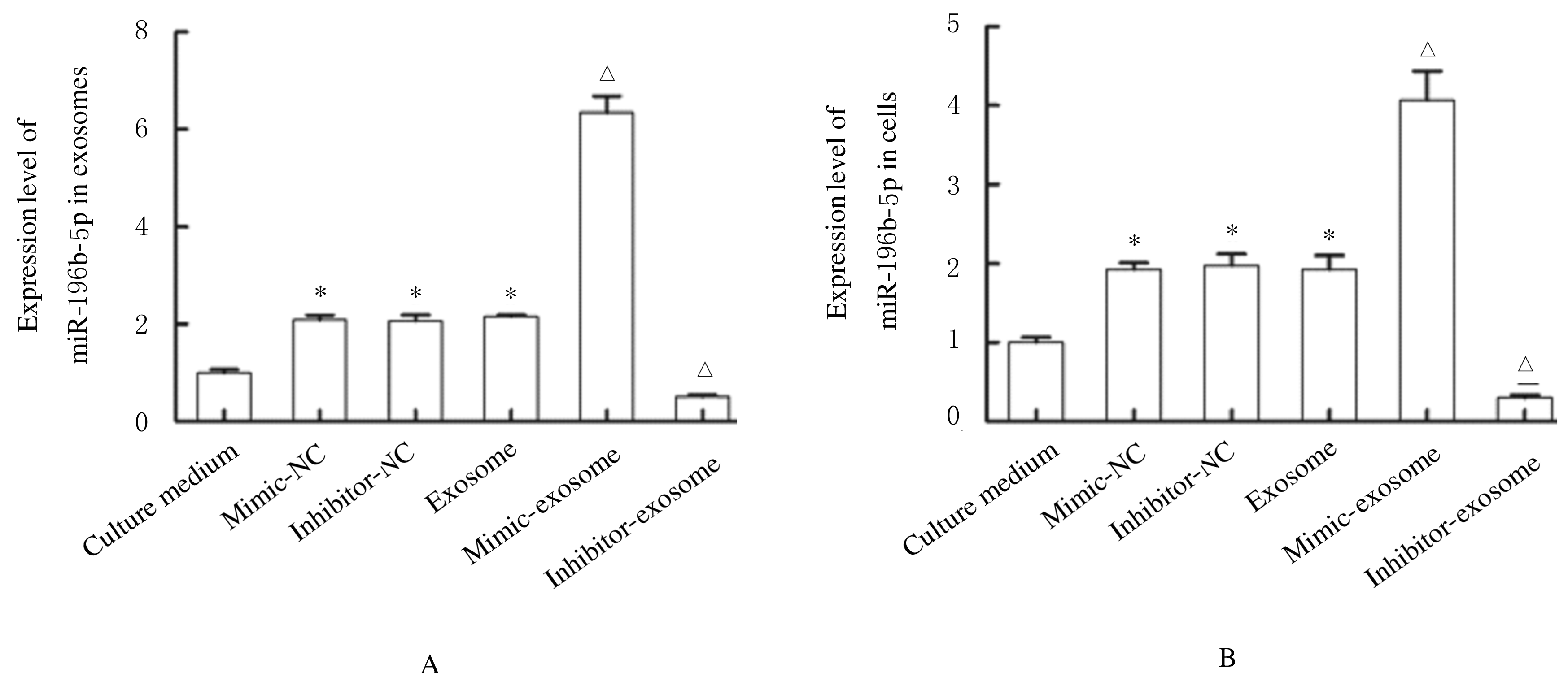
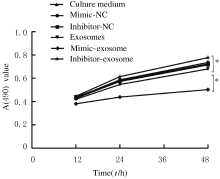
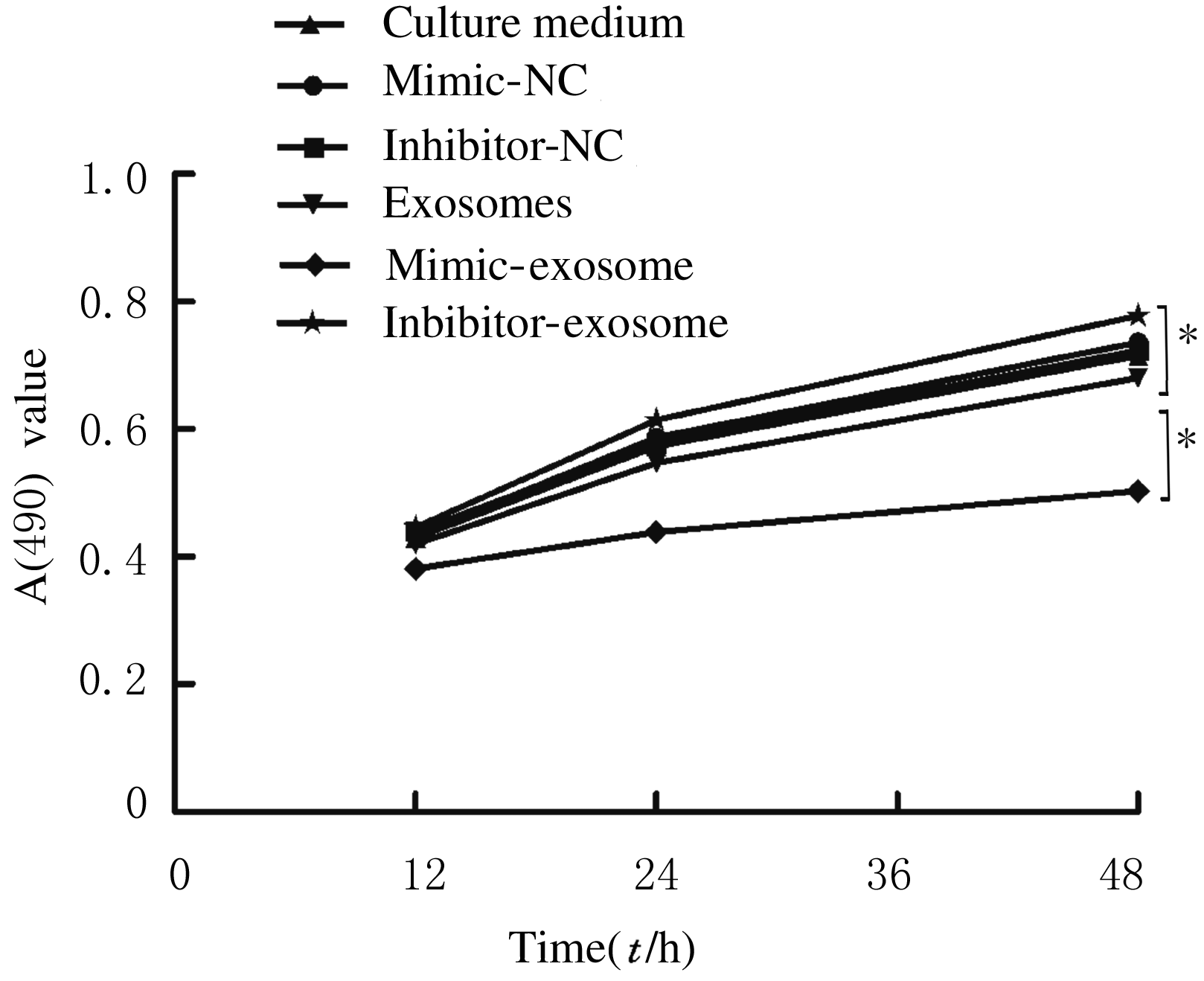
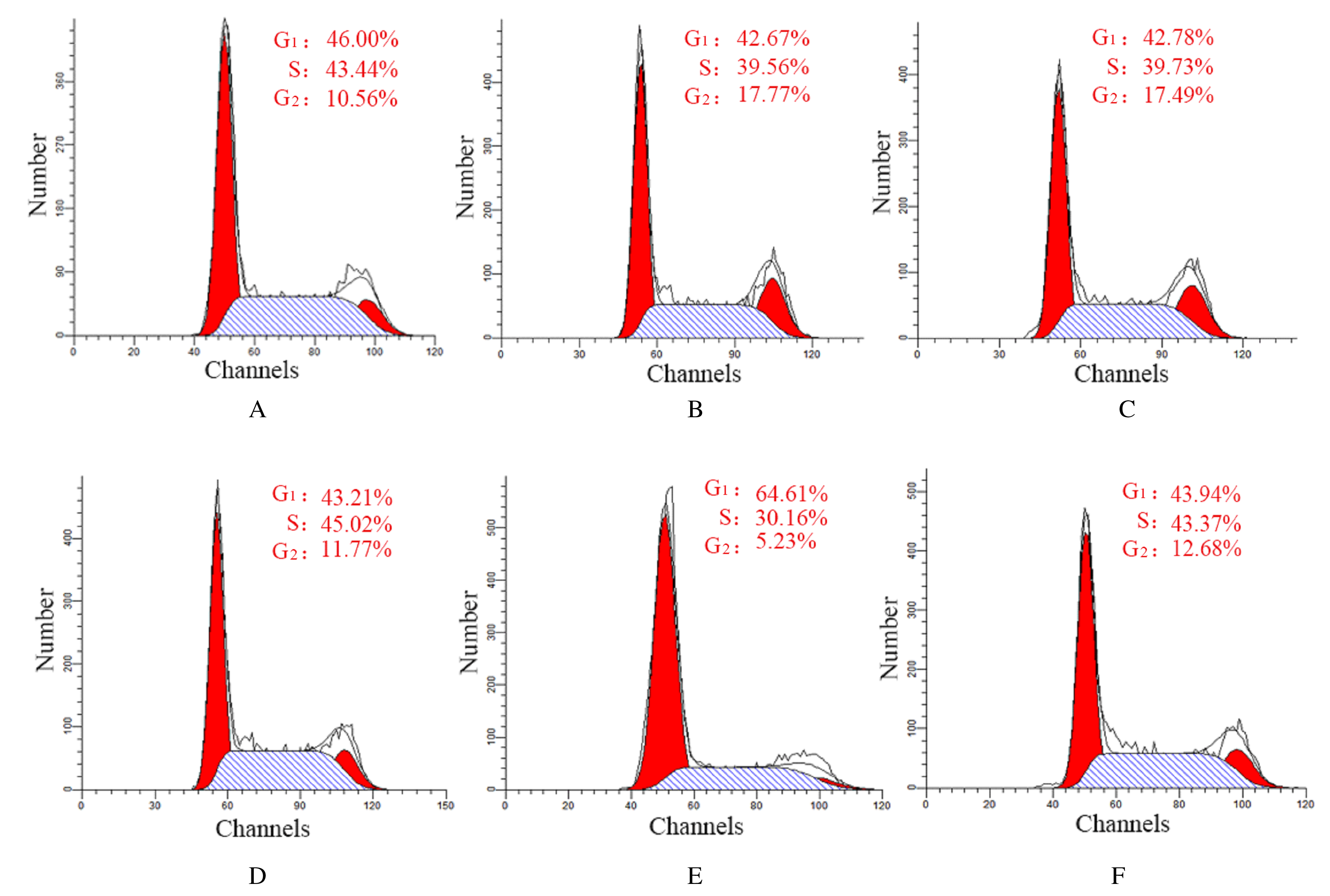
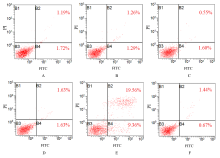
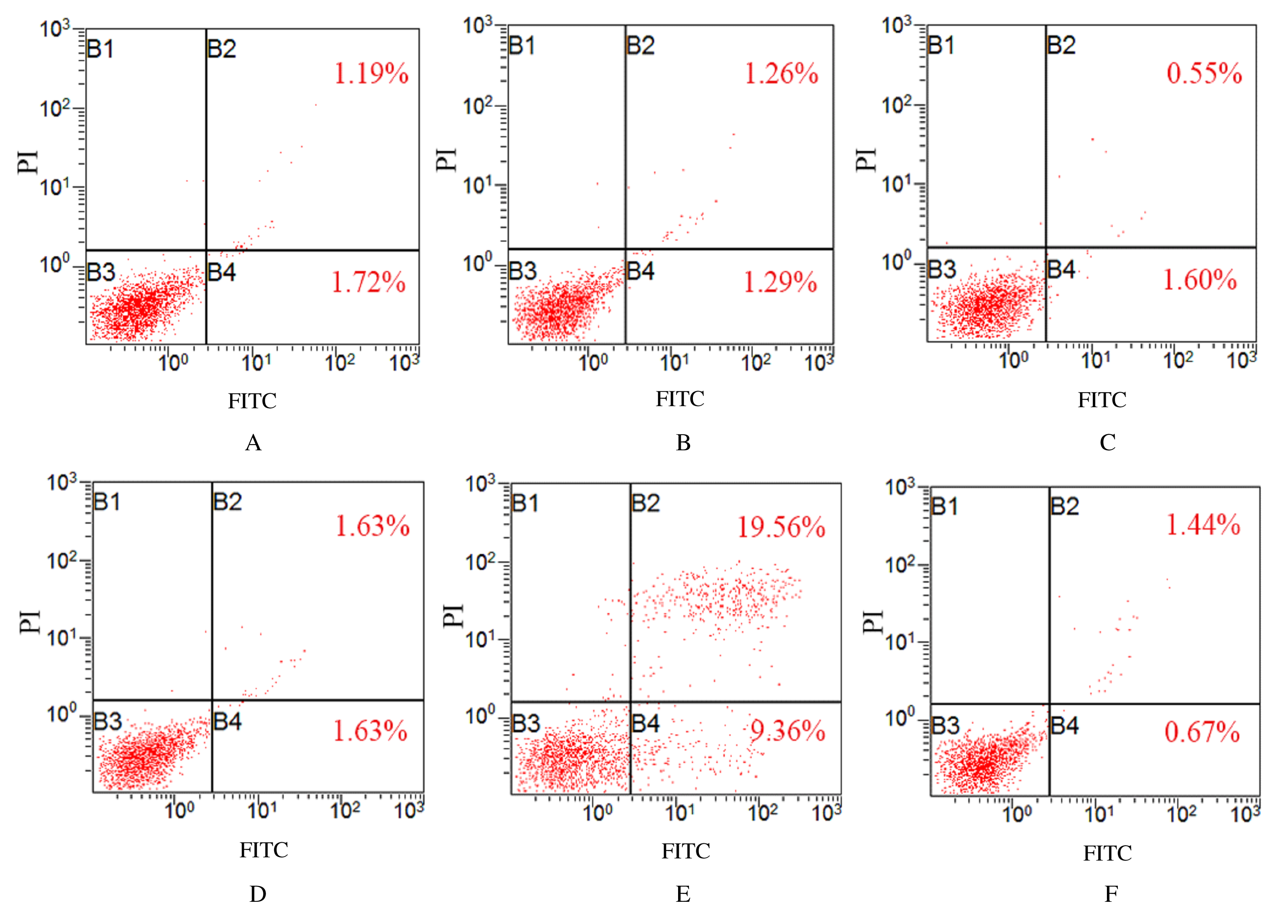
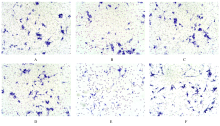
摘要: 探讨骨髓间充质干细胞(MSCs)分泌的携带miR-196b-5p的外泌体对结肠癌细胞生物学特性的影响。 分离培养小鼠骨髓MSCs,采用mimic-196b-5p模拟物(miR-196b-5p miR)和196b-5p抑制物(miR-196b-5p inhibitor)转染MSCs后,收集培养基,分离外泌体。透射电镜下观察外泌体形态表现,采用特定标志物表达鉴定外泌体后采用外泌体干预小鼠结肠癌CT26.WT细胞。将复苏后处于对数生长期的小鼠结肠癌CT26.WT细胞分为培养基组、mimic-NC组、inhibitor-NC组、未转染的外泌体组、mimic-外泌体组和inhibitor-外泌体组。采用MTT法检测各组结肠癌CT26.WT细胞增殖活性,流式细胞术检测各组不同细胞周期结肠癌CT26.WT细胞百分率和细胞凋亡率,Transwell小室实验检测各组结肠癌CT26.WT细胞的迁移和侵袭情况。 与未转染的外泌体组比较,mimic-外泌体组结肠癌细胞增殖活性、迁移细胞数和侵袭细胞数均降低(P<0.05),G1期细胞百分率和细胞凋亡率升高(P<0.05),inhibitor-外泌体组结肠癌细胞增殖活性、迁移细胞数和侵袭细胞数均升高(P<0.05),细胞凋亡率降低(P<0.05)。 MSCs来源携带高水平miR-196b-5p的外泌体可抑制结肠癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭,并诱导细胞凋亡。
中图分类号:
- R735.35