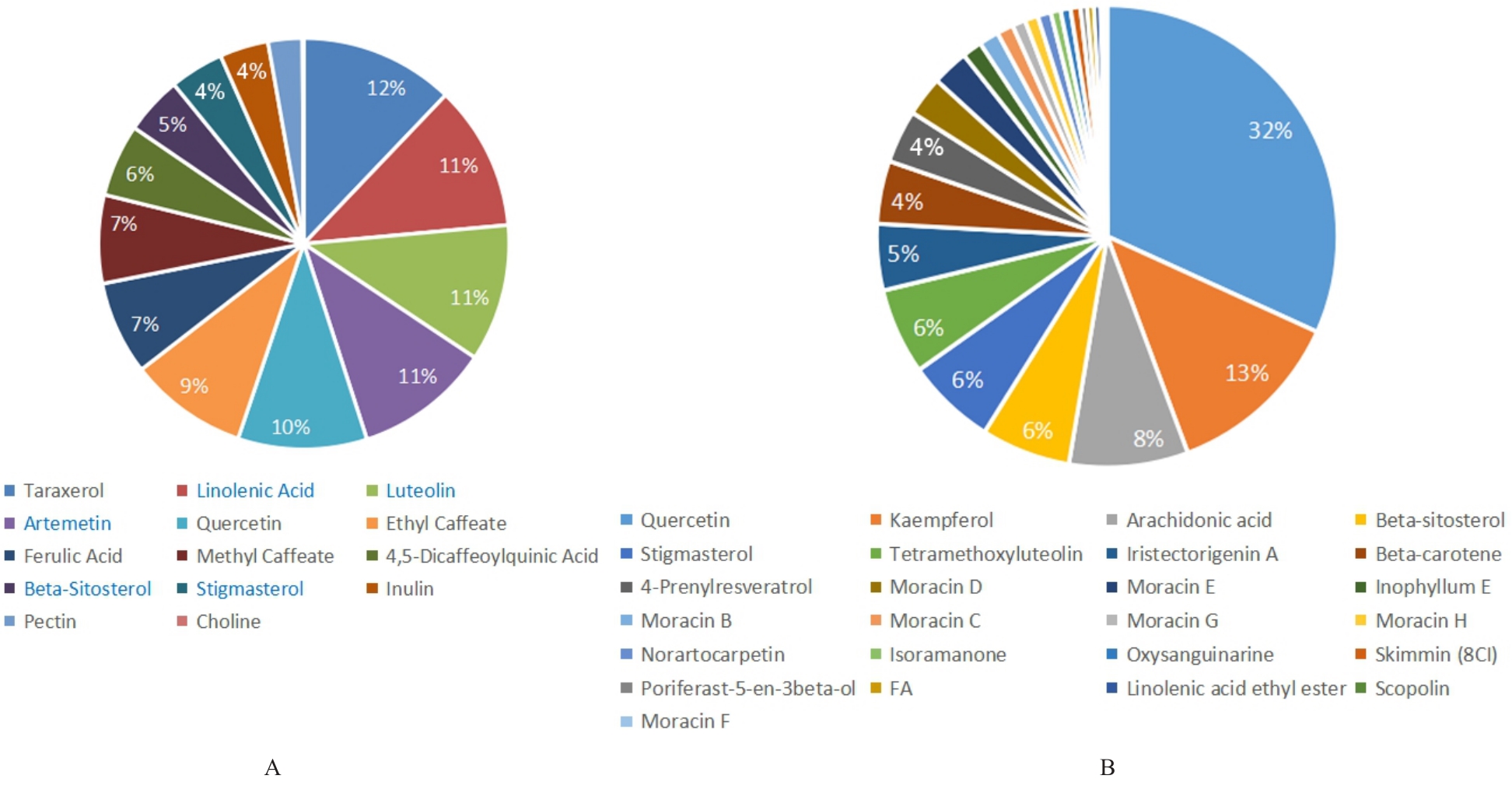
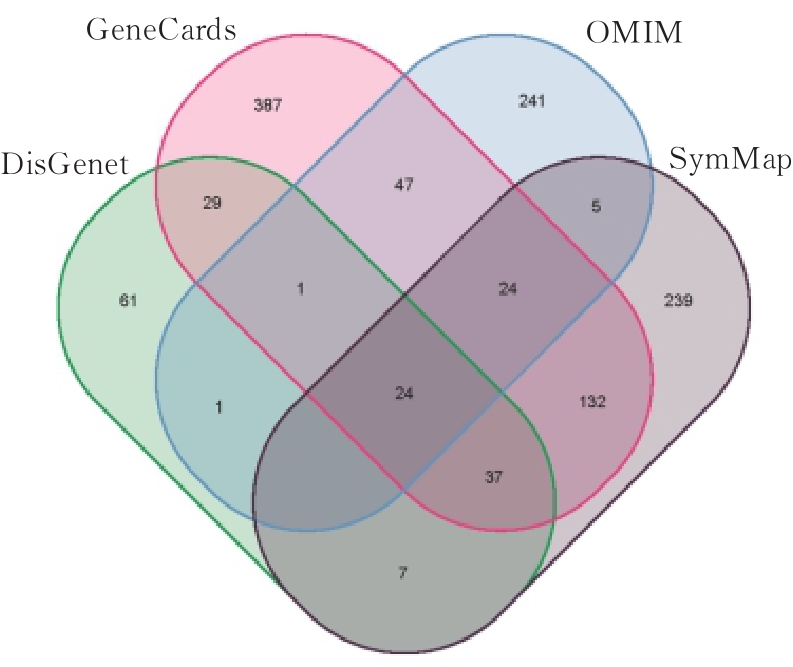
| 1 |
SIEGEL R L, MILLER K D, FUCHS H E,et al.Cancer statistics, 2022[J]. CA: Cancer J Clin,2022, 72 (1): 7-33.
|
| 2 |
梁欣荃, 唐亦舒, 朱 平, 等. 不同类型急性白血病患者血流感染流行病学及预后分析: 一项长达九年多中心947例患者回顾性研究[J]. 临床血液学杂志, 2023, 36(1): 27-32.
|
| 3 |
NAGEL G, WEBER D, FROMM E, et al. Epidemiological, genetic, and clinical characterization by age of newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia based on an academic population-based registry study (AMLSG BiO)[J]. Ann Hematol, 2017, 96(12): 1993-2003.
|
| 4 |
ZENG Y J, WU M, ZHANG H, et al. Effects of qinghuang powder on acute myeloid leukemia based on network pharmacology, molecular docking, and in vitro experiments[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2021, 2021: 6195174.
|
| 5 |
FANG T T, LIU L Q, LIU W J. Network pharmacology-based strategy for predicting therapy targets of Tripterygium wilfordii on acute myeloid leukemia[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2020, 99(50): e23546.
|
| 6 |
霍俊明, 于维贤, 李维奇, 等. 急性白血病临床治疗体会与分析[J]. 中医杂志, 1987, 28(8): 31-33.
|
| 7 |
DEEPA M, SURESHKUMAR T, SATHEESHKUMAR P K, et al. Purified mulberry leaf lectin (MLL) induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human breast cancer and colon cancer cells[J]. Chem Biol Interact, 2012, 200(1): 38-44.
|
| 8 |
杨子辉, 董 朕, 伍蕙岚, 等. 基于网络药理学分析蒲公英抗氧化功能的物质基础与作用机制[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2023, 54(5): 2170-2185.
|
| 9 |
WU Z Y, JI X W, SHAN C, et al. Exploring the pharmacological components and effective mechanism of Mori Folium against periodontitis using network pharmacology and molecular docking[J]. Arch Oral Biol, 2022, 139: 105391.
|
| 10 |
RU J L, LI P, WANG J N, et al. TCMSP: a database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines[J]. J Cheminform, 2014, 6: 13.
|
| 11 |
WU Y, ZHANG F L, YANG K, et al. SymMap: an integrative database of traditional Chinese medicine enhanced by symptom mapping[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2019, 47(D1): D1110-D1117.
|
| 12 |
LIU Z Y, GUO F F, WANG Y, et al. BATMAN-TCM: a bioinformatics analysis tool for molecular mechANism of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 21146.
|
| 13 |
UNIPROT CONSORTIUM. UniProt: a worldwide hub of protein knowledge[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2019, 47(D1): D506-D515.
|
| 14 |
PIÑERO J, RAMÍREZ-ANGUITA J M, SAÜCH-PITARCH J, et al. The DisGeNET knowledge platform for disease genomics: 2019 update[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2020, 48(D1): D845-D855.
|
| 15 |
STELZER G, ROSEN N, PLASCHKES I, et al. The GeneCards suite: from gene data mining to disease genome sequence analyses[J]. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics, 2016, 54. DOI: 10.1002/cpbi.5 .
doi: 10.1002/cpbi.5
|
| 16 |
AMBERGER J S, HAMOSH A. Searching online Mendelian inheritance in man (OMIM): a knowledgebase of human genes and genetic phenotypes[J]. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics, 2017, 58: 1.2.1-1.2.1.2.12.
|
| 17 |
SZKLARCZYK D, GABLE A L, NASTOU K C, et al. The STRING database in 2021: customizable protein-protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2021, 49(D1): D605-D612.
|
| 18 |
GONZÁLEZ-CASTEJÓN M, VISIOLI F, RODRIGUEZ-CASADO A. Diverse biological activities of dandelion[J]. Nutr Rev, 2012, 70(9): 534-547.
|
| 19 |
ZHANG Y L, LIANG Y E, HE C W. Anticancer activities and mechanisms of heat-clearing and detoxicating traditional Chinese herbal medicine[J]. Chin Med, 2017, 12: 20.
|
| 20 |
MA G Q, CHAI X Y, HOU G G, et al. Phytochemistry, bioactivities and future prospects of mulberry leaves: a review[J]. Food Chem, 2022, 372: 131335.
|
| 21 |
刘晓燕, 龙 凤, 赵 玉, 等. 蒲公英中有效成分抗肿瘤作用机制的研究进展[J]. 中草药, 2023, 54(10): 3391-3400.
|
| 22 |
袁鑫怡, 曾淑欣, 杨 润, 等. 基于网络药理学与分子对接的蒲公英抗乳腺癌的机制研究[J]. 天津中医药, 2023, 40(1): 110-116.
|
| 23 |
OVADJE P, CHATTERJEE S, GRIFFIN C, et al. Selective induction of apoptosis through activation of caspase-8 in human leukemia cells (Jurkat) by dandelion root extract[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2011, 133(1): 86-91.
|
| 24 |
YU H, PARDOLL D, JOVE R. STATs in cancer inflammation and immunity: a leading role for STAT3[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2009, 9(11): 798-809.
|
| 25 |
LARRUE C, HEYDT Q, SALAND E, et al. Oncogenic KIT mutations induce STAT3-dependent autophagy to support cell proliferation in acute myeloid leukemia[J]. Oncogenesis, 2019, 8: 39.
|
| 26 |
VENUGOPAL S, BAR-NATAN M, MASCARENHAS J O. JAKs to STATs: a tantalizing therapeutic target in acute myeloid leukemia[J]. Blood Rev, 2020, 40: 100634.
|
| 27 |
ZENG Y J, LIU F, WU M, et al. Curcumin combined with arsenic trioxide in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia: network pharmacology analysis and experimental validation[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2023, 149(1): 219-230.
|
| 28 |
AMJAD E, SOKOUTI B, ASNAASHARI S. A systematic review of anti-cancer roles and mechanisms of kaempferol as a natural compound[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2022, 22(1): 260.
|
| 29 |
XIAO J, ZHANG B, YIN S M, et al. Quercetin induces autophagy-associated death in HL-60 cells through CaMKKβ/AMPK/mTOR signal pathway[J]. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin, 2022, 54(9): 1244-1256.
|
| 30 |
SHAHBAZ M, IMRAN M, ALSAGABY S A, et al. Anticancer, antioxidant, ameliorative and therapeutic properties of kaempferol[J]. Int J Food Prop, 2023, 26(1): 1140-1166.
|
| 31 |
Al-Mosawe E H.The effect of luteolin on lymphocyte cells in leukemia patient[J]. Al-Mustansiriyah J Sci, 2013, 24 (1): 1-8.
|
| 32 |
ZHENG D D, ZHOU Y M, LIU Y, et al. Molecular mechanism investigation on monomer kaempferol of the traditional medicine Dingqing Tablet in promoting apoptosis of acute myeloid leukemia HL-60 cells[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2022, 2022: 8383315.
|
| 33 |
MUS A A, GOH L P W, MARBAWI H, et al. The biosynthesis and medicinal properties of taraxerol[J]. Biomedicines, 2022, 10(4): 807.
|
| 34 |
KHANRA R, DEWANJEE S, DUA T K, et al. Taraxerol, a pentacyclic triterpene from Abroma Augusta leaf, attenuates acute inflammation via inhibition of NF-κB signaling[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother, 2017, 88: 918-923.
|
| 35 |
KHANRA R, BHATTACHARJEE N, DUA T K, et al. Taraxerol, a pentacyclic triterpenoid, from Abroma Augusta leaf attenuates diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetic rats[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother, 2017, 94: 726-741.
|
| 36 |
YAO X Y, LI G L, BAI Q, et al. Taraxerol inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory responses through suppression of TAK1 and Akt activation[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2013, 15(2): 316-324.
|
| 37 |
YAOI X, LU B Y, LÜ C T, et al. Taraxerol induces cell apoptosis through A mitochondria-mediated pathway in HeLa cells[J]. Cell J, 2017, 19(3): 512-519.
|
| 38 |
KO W G, KANG T H, LEE S J, et al. Polymethoxyflavonoids from Vitex rotundifolia inhibit proliferation by inducing apoptosis in human myeloid leukemia cells[J]. Food Chem Toxicol, 2000, 38(10): 861-865.
|
| 39 |
MARTELLI A M, NYÅKERN M, TABELLINI G, et al. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway and its therapeutical implications for human acute myeloid leukemia[J]. Leukemia, 2006, 20(6): 911-928.
|
 )
)