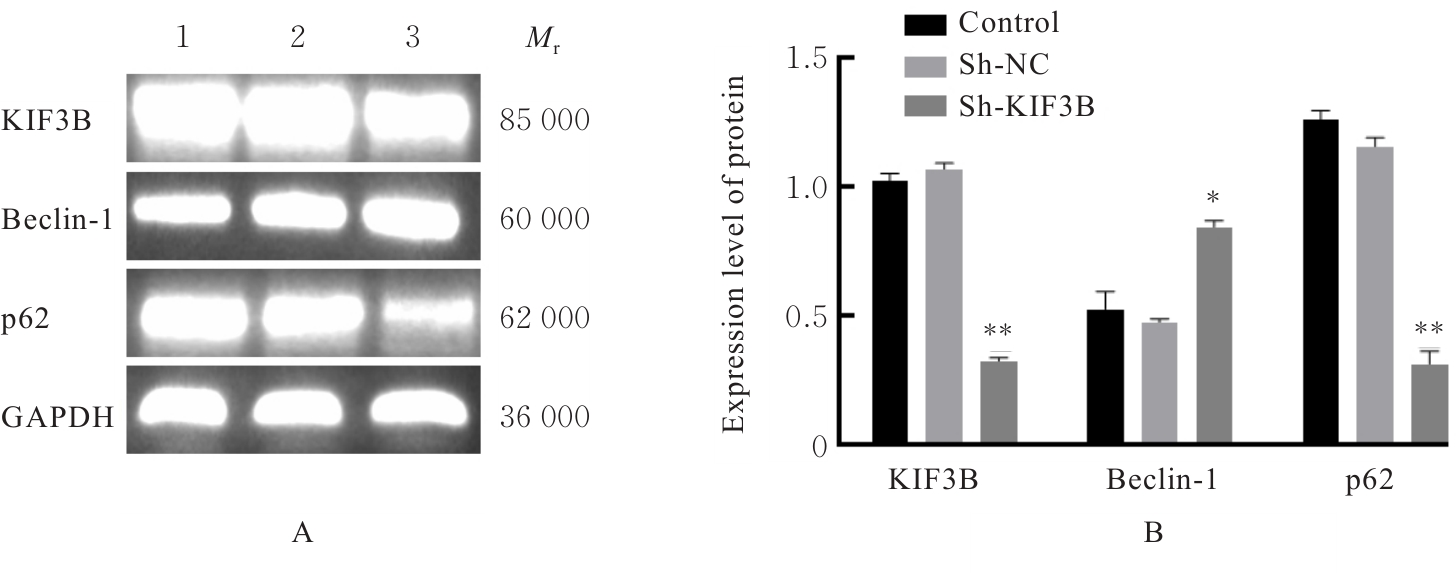
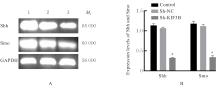
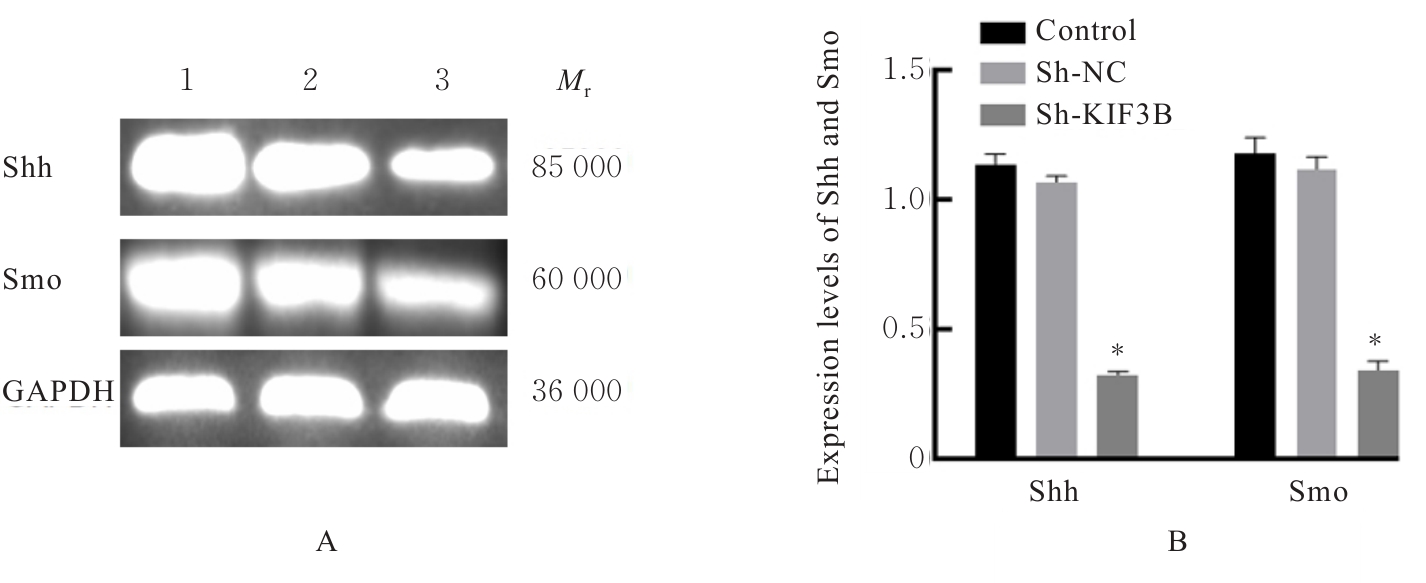
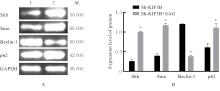
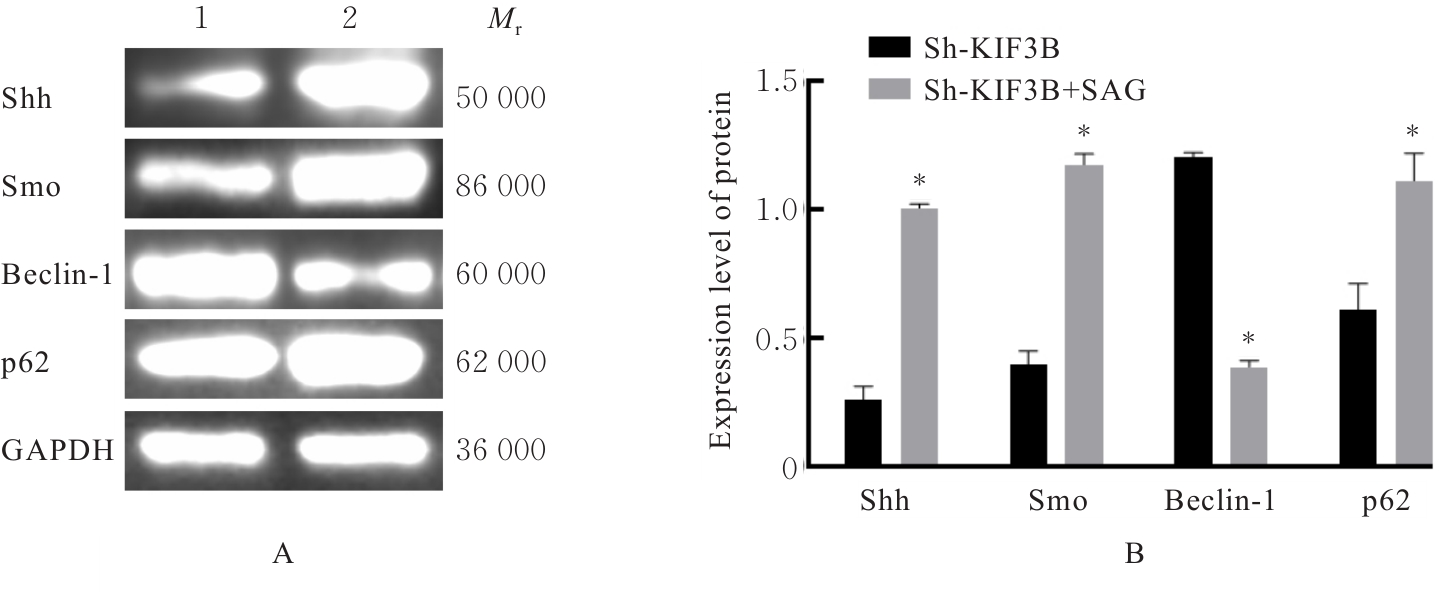
| [1] |
MOSSEY P A, LITTLE J, MUNGER R G, et al. Cleft lip and palate[J]. Lancet, 2009, 374(9703): 1773-1785.
|
| [2] |
XU D P, QU W D, SUN C, et al. A study on environmental factors for nonsyndromic cleft lip and/or palate[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2018, 29(2): 364-367.
|
| [3] |
NASREDDINE G, HAJJ J E L, GHASSIBE-SABBAGH M. Orofacial clefts embryology, classification, epidemiology, and genetics[J]. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res, 2021, 787: 108373.
|
| [4] |
NASRALLAH I, GOLDEN J A. Brain, eye, and face defects as a result of ectopic localization of Sonic hedgehog protein in the developing rostral neural tube[J]. Teratology, 2001, 64(2): 107-113.
|
| [5] |
PRAJAPATI A, MEHAN S, KHAN Z. The role of Smo-Shh/Gli signaling activation in the prevention of neurological and ageing disorders[J]. Biogerontology, 2023, 24(4): 493-531.
|
| [6] |
BEAR K A, SOLOMON B D, ANTONINI S, et al. Pathogenic mutations in GLI2 cause a specific phenotype that is distinct from holoprosencephaly[J]. J Med Genet, 2014, 51(6): 413-418.
|
| [7] |
XIANG Y, LI X L, ZHAN Z Y, et al. A novel nonsense GLI3 variant is associated with polydactyly and syndactyly in a family by blocking the sonic hedgehog signaling pathway[J]. Front Genet, 2020, 11: 542004.
|
| [8] |
HOYOS CADAVID A M, KAMINAGAKURA E, RODRIGUES M F S D, et al. Immunohistochemical evaluation of Sonic Hedgehog signaling pathway proteins (Shh, Ptch1, Ptch2, Smo, Gli1, Gli2, and Gli3) in sporadic and syndromic odontogenic keratocysts[J]. Clin Oral Investig, 2019, 23(1): 153-159.
|
| [9] |
陈珏蓉, 陈菁菁, 刘 觅, 等. 地塞米松和维生素B12干预下小鼠胚胎腭突Shh相关信号因子的研究[J]. 重庆医科大学学报, 2021, 46(12): 1454-1459.
|
| [10] |
MAHARJAN Y, LEE J N, KWAK S, et al. Autophagy alteration prevents primary cilium disassembly in RPE1 cells[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018, 500(2): 242-248.
|
| [11] |
ZHANG S K, LIU Y Y, LIANG Q W. Low-dose dexamethasone affects osteoblast viability by inducing autophagy via intracellular ROS[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2018, 17(3): 4307-4316.
|
| [12] |
LI H J, LI J J, LI Y N, et al. Sonic hedgehog promotes autophagy of vascular smooth muscle cells[J]. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 2012, 303(11): H1319-H1331.
|
| [13] |
YAO Y X, LI T Y, YU T T, et al. Hedgehog signal activates AMPK via Smoothened to promote autophagy and lipid degradation in hepatocytes[J]. Biochem Cell Biol, 2023, 101(4): 284-293.
|
| [14] |
郭佳男. IFT122通过初级纤毛介导的Shh信号通路调控mEPMCs增殖的机制研究[D]. 遵义: 遵义医科大学, 2020.
|
| [15] |
武春艳, 杨 意, 杨 霞, 等. 自噬小体的生物发生和成熟[J]. 中国细胞生物学学报, 2024, 46(1): 118-128.
|
| [16] |
陈珏蓉, 王 新, 陈 尚, 等. 小鼠胚胎腭突上皮细胞初级纤毛生长规律的研究[J]. 医学研究生学报, 2020, 33(9): 914-918.
|
| [17] |
JI Y, GARLAND M A, SUN B, et al. Cellular and developmental basis of orofacial clefts[J]. Birth Defects Res, 2020, 112(19): 1558-1587.
|
| [18] |
BALDARI C T, ROSENBAUM J. Intraflagellar transport: it’s not just for cilia anymore[J]. Curr Opin Cell Biol, 2010, 22(1): 75-80.
|
| [19] |
FUNABASHI T, KATOH Y, OKAZAKI M, et al. Interaction of heterotrimeric kinesin-Ⅱ with IFT-B-connecting tetramer is crucial for ciliogenesis[J]. J Cell Biol, 2018, 217(8): 2867-2876.
|
| [20] |
殷 杰. 小鼠胚胎腭间充质细胞中Smo蛋白在初级纤毛的定位研究[D]. 遵义: 遵义医学院, 2017.
|
| [21] |
LIU A M. Proteostasis in the hedgehog signaling pathway[J]. Semin Cell Dev Biol, 2019, 93: 153-163.
|
| [22] |
CARBALLO G B, HONORATO J R, DE LOPES G P F, et al. A highlight on Sonic hedgehog pathway[J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2018, 16(1): 11.
|
| [23] |
WANG Q, KUROSAKA H, KIKUCHI M, et al. Perturbed development of cranial neural crest cells in association with reduced sonic hedgehog signaling underlies the pathogenesis of retinoic-acid-induced cleft palate[J]. Dis Model Mech, 2019, 12(10): dmm040279.
|
| [24] |
PIETROBONO S, GAGLIARDI S, STECCA B. Non-canonical hedgehog signaling pathway in cancer: activation of GLI transcription factors beyond smoothened[J]. Front Genet, 2019, 10: 556.
|
| [25] |
WANG W C, SHIRAISHI R, KAWAUCHI D. Sonic hedgehog signaling in cerebellar development and cancer[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2022, 10: 864035.
|
| [26] |
SENATORE E, IANNUCCI R, CHIUSO F, et al. Pathophysiology of primary cilia: signaling and proteostasis regulation[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2022, 10: 833086.
|
 )
)