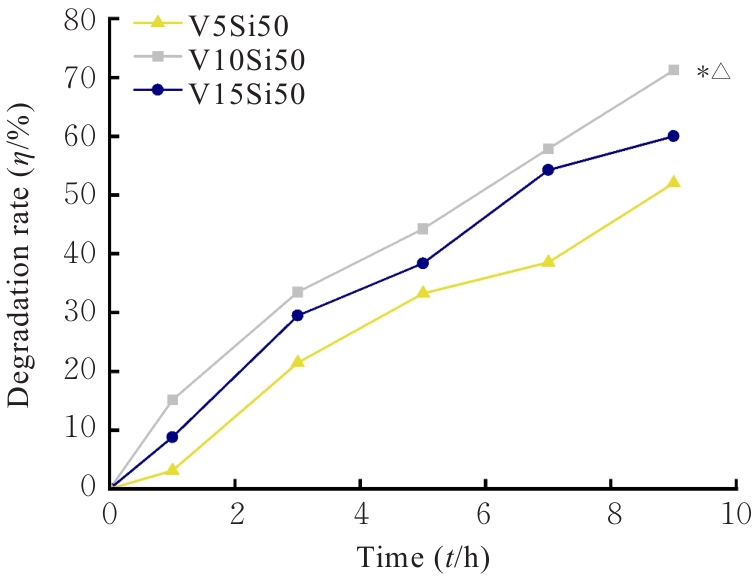
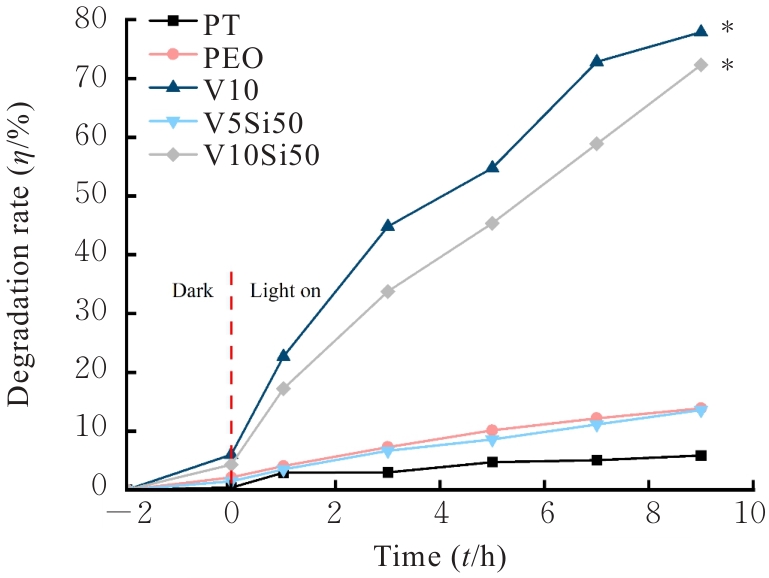
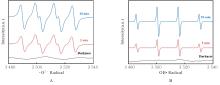
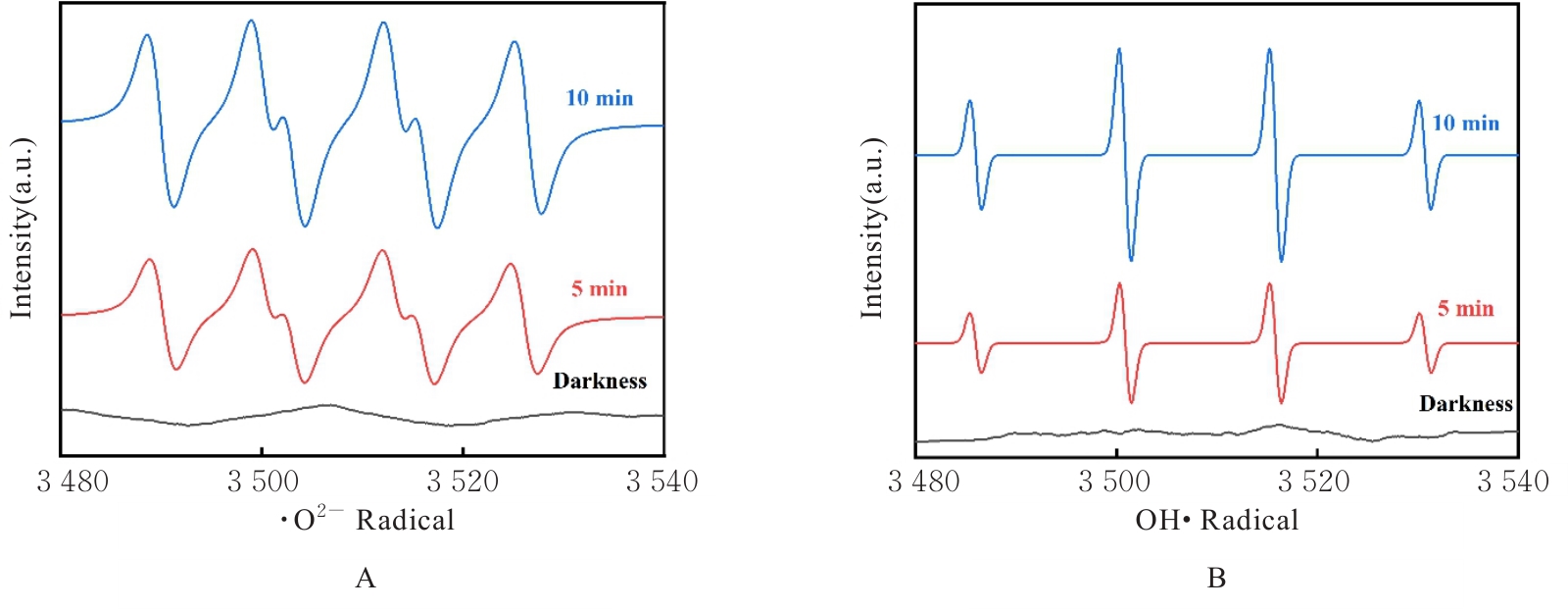
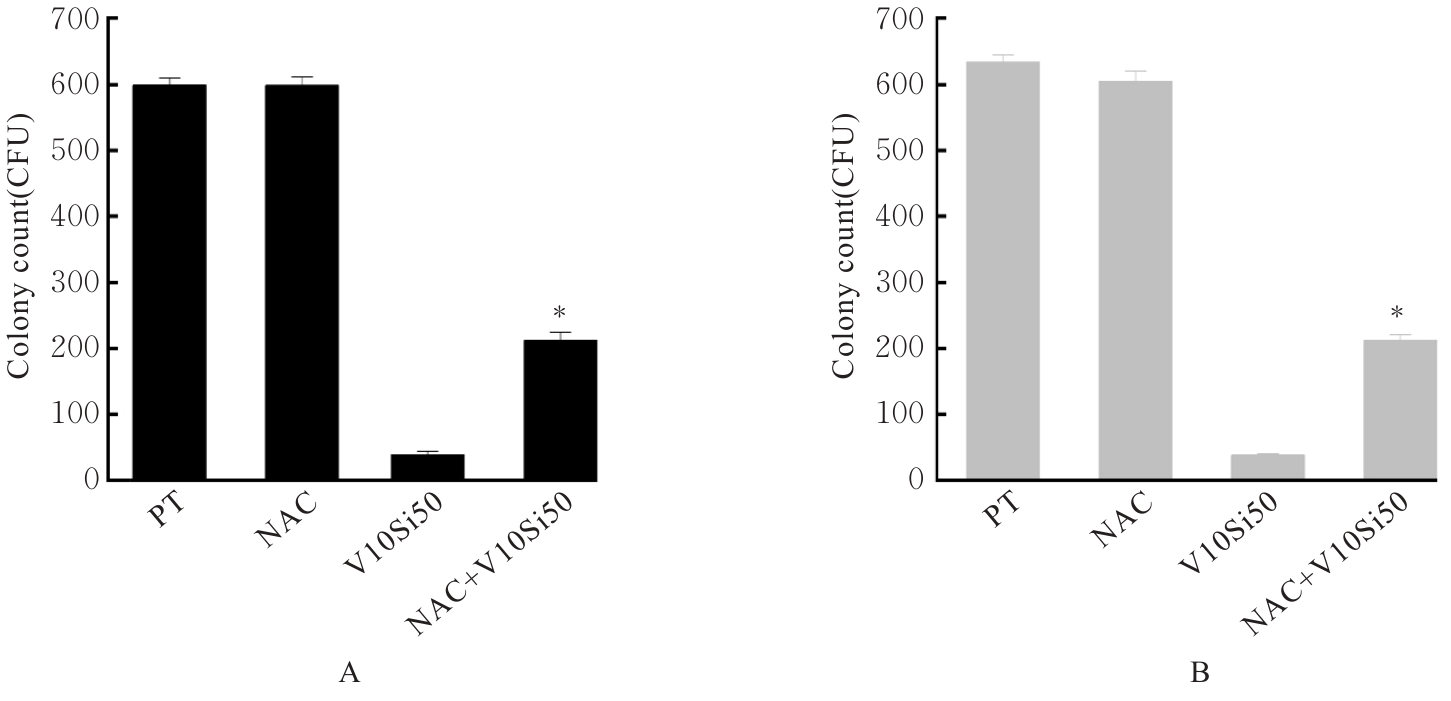
| [1] |
TING M, SUZUKI J B. Peri-implantitis[J]. Dent J, 2024, 12(8): 251.
|
| [2] |
MEYLE J, FISCHER-WASELS L. Non-surgical treatment of peri-implantitis[J]. Br Dent J, 2024, 237(10): 780-785.
|
| [3] |
YIN W W, YANG Y M, BAO R, et al. Necessity of removing implant-supported prostheses when conducting supportive peri-implant therapy: A clinical study[J]. J Prosthet Dent, 2024: S0022-S3913(24)00653-X.
|
| [4] |
IONESCU C, KAMAL F Z, CIOBICA A, et al. Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of oral cancer[J]. Biomedicines, 2024, 12(6): 1150.
|
| [5] |
CHEN T, YANG D, LEI S X, et al. Photodynamic therapy-a promising treatment of oral mucosal infections[J]. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther, 2022, 39: 103010.
|
| [6] |
AZZAWI Z G M, HAMAD T I, KADHIM S A, et al. Osseointegration evaluation of laser-deposited titanium dioxide nanoparticles on commercially pure titanium dental implants[J]. J Mater Sci Mater Med, 2018, 29(7): 96.
|
| [7] |
ZOU X S, VADELL R B, LIU Y W, et al. Photophysical study of electron and hole trapping in TiO2 and TiO2/Au nanoparticles through a selective electron injection[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2022, 126(50): 21467-21475.
|
| [8] |
ŠULIGOJ A, POVIRK N, MAVER K, et al. Transparent vanadium doped titania-silica films: Structural characterization and self-cleaning properties[J]. J Environ Chem Eng, 2024, 12(5): 113904.
|
| [9] |
DEEPA M J, ARUNIMA S R, ELIAS L, et al. Development of antibacterial V/TiO2-based galvanic coatings for combating biocorrosion[J]. ACS Appl Bio Mater, 2021, 4(4): 3332-3349.
|
| [10] |
NGWA H A, AY M, JIN H J, et al. Neurotoxicity of vanadium[A].Neurotoxicity of Metals[M]. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2017: 287-301.
|
| [11] |
MIGUEZ-PACHECO V, HENCH L L, BOCCACCINI A R. Bioactive glasses beyond bone and teeth: Emerging applications in contact with soft tissues[J]. Acta Biomater, 2015, 13: 1-15.
|
| [12] |
ZHANG X E, ZHANG X, ZHOU W C, et al. Modified multilayered porous titanium scaffolds with silicon-doped coating surface-loaded BMP-2 prepared by microarc oxidation for bone defect repair[J]. Surf Coat Technol, 2025, 495: 131570.
|
| [13] |
RASHAD M M, MOSTAFA A G, RAYAN D A. Structural and optical properties of nanocrystalline mayenite Ca12Al14O33 powders synthesized using a novel route[J]. J Mater Sci Mater Electron, 2016, 27(3): 2614-2623.
|
| [14] |
LI L Y, ZHAO H, NI N, et al. Study on the origin of linear deviation with the Beer-Lambert law in absorption spectroscopy by measuring sulfur dioxide[J]. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc, 2022, 275: 121192.
|
| [15] |
LIU W B, ZHANG K, SUN Y, et al. Multidimensional treatment of periprosthetic joint infection using fusion peptide-grafted chitosan coated porous tantalum scaffold[J]. Bioact Mater, 2025, 44: 15-33.
|
| [16] |
MORALES-VALENZUELA A A, SCOUGALL-VILCHIS R J, LARA-CARRILLO E, et al. Enhancement of fluoride release in glass ionomer cements modified with titanium dioxide nanoparticles[J]. Medicine, 2022, 101(44): e31434.
|
| [17] |
ZHANG Y J, ZHANG Y L, KONG T T, et al. Effects of titanium nano-foveolae surfaces on human gingival fibroblasts[J]. J Nanosci Nanotechnol, 2020, 20(2): 673-679.
|
| [18] |
WANG S Y, ZHAO X, HSU Y, et al. Surface modification of titanium implants with Mg-containing coatings to promote osseointegration[J]. Acta Biomater, 2023, 169: 19-44.
|
| [19] |
PAPADIAMANTIS A G, JÄNES J, VOYIATZIS E, et al. Predicting cytotoxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles using isalos analytics platform[J]. Nanomaterials, 2020, 10(10): 2017.
|
| [20] |
HANNIBAL V D, GREB L. Tetra-amido macrocyclic ligand (TAML) at silicon(Ⅳ): a structurally constrained, water-soluble silicon lewis superacid[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2024, 146(37): 25727-25737.
|
| [21] |
RASUL M G, AHMED S, SATTAR M A, et al. Hydrodynamic performance assessment of photocatalytic reactor with baffles and roughness in the flow path:a modelling approach with experimental validation[J]. Heliyon, 2023, 9(9): e19623.
|
| [22] |
XUE Y, WANG Z, KANG J T, et al. The effect of doping donor ions in the dielectric properties of (In0.5 B0.5)0.1Ti0.9O2 (BV, Nb, Ta) ceramics[J]. Ceram Int, 2024, 50(23): 51848-51857.
|
| [23] |
HU H Y, LIN Y, HU Y H. Phase role of white TiO2 precursor in its reduction to black TiO2 [J]. Phys Lett A, 2019, 383(24): 2978-2982.
|
| [24] |
ZAHID SHAFIQ M, SHAHID W, SHAHID S, et al. Enhancing photocatalytic efficiency of type Ⅱ V2O5/TiO2 heterojunctions for malachite green dye using solar simulator irradiation[J]. J Saudi Chem Soc, 2024, 28(3): 101869.
|
| [25] |
MA E H, SUN G L, DUAN F L, et al. Visible-light-responsive Z-scheme heterojunction MoS2 NTs/CuInS2 QDs photoanode for enhanced photoelectrocatalytic degradation of tetracycline[J]. Appl Mater Today, 2022, 28: 101504.
|
| [26] |
CHEN Q F, WANG K Y, GAO G M, et al. Singlet oxygen generation boosted by Ag–Pt nanoalloy combined with disordered surface layer over TiO2 nanosheet for improving the photocatalytic activity[J]. Appl Surf Sci, 2021, 538: 147944.
|
| [27] |
ZOU X R, WEI Y Y, JIANG S, et al. ROS stress and cell membrane disruption are the main antifungal mechanisms of 2-phenylethanol against botrytis cinerea[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2022, 70(45): 14468-14479.
|
| [28] |
KOTHANDAN S, SHEELA A. DNA Interaction and Cytotoxic studies on Mono/Di-Oxo and Peroxo- Vanadium (V) complexes - A Review[J]. Mini Rev Med Chem, 2021, 21(14): 1909-1924.
|
| [29] |
DOBSON N L, KLEEBERGER S R, BURKHOLDER A B, et al. Vanadium pentoxide exposure causes strain-dependent changes in mitochondrial DNA heteroplasmy, copy number, and lesions, but not nuclear DNA lesions[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(19): 14507.
|
| [30] |
LIU X C, HOU Y B, YANG M X, et al. N-acetyl-l-cysteine-derived carbonized polymer dots with ROS scavenging via Keap1-Nrf2 pathway regulate alveolar bone homeostasis in periodontitis[J]. Adv Healthc Mater, 2023, 12(26): e2300890.
|
 ),周政1(
),周政1( )
)
 ),Zheng ZHOU1(
),Zheng ZHOU1( )
)