吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (6): 1618-1629.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250617
• 临床研究 • 上一篇
基于肝细胞癌中INPP4B基因表达的TCGA数据库生物信息学分析及其实验验证
文丽梅1,2,郭娅丽2,3,马文梅4,薛涛涛2,3,耿若愚2,3,马冲2,3,张新红2,3,杨建华1,2( )
)
- 1.新疆医科大学第一附属医院药学部,新疆 乌鲁木齐 830011
2.新疆医科大学第一附属医院 新疆药物临床研究重点实验室,新疆 乌鲁木齐 830011
3.新疆医科大学药学院,新疆 乌鲁木齐 830017
4.新疆医科大学第一附属医院病理科,新疆 乌鲁木齐 830011
Bioinformatic analysis of TCGA database based on INPP4B gene expression in hepatocellular carcinoma and its experimental validation
Limei WEN1,2,Yali GUO2,3,Wenmei MA4,Taotao XUE2,3,Ruoyu GENG2,3,Chong MA2,3,Xinhong ZHANG2,3,Jianhua YANG1,2( )
)
- 1.Department of Pharmacy,First Affiliated Hospital,Xinjiang Medical University,Urumqi 830011,China
2.Xinjiang Key Laboratory of Clinical Drug Research,First Affiliated Hospital,Xinjiang Medical University,Urumqi 830011,China
3.School of Pharmacy,Xinjiang Medical University,Urumqi 830017,China
4.Department of Pathology,First Affiliated Hospital,Xinjiang Medical University,Urumqi 830011,China
摘要:
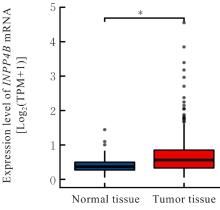
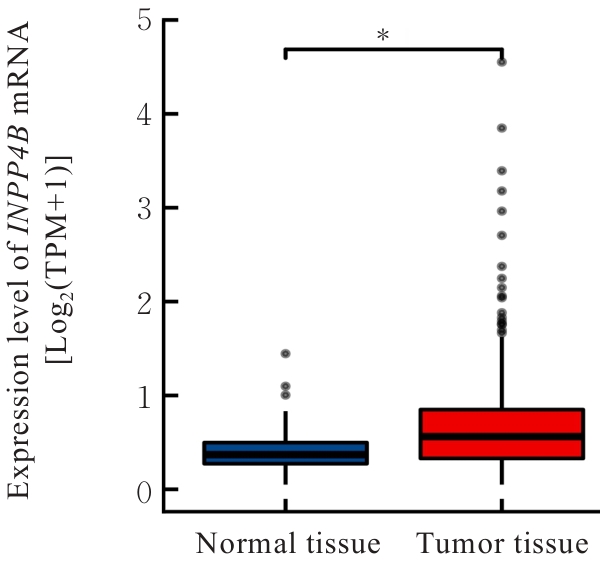
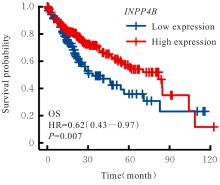
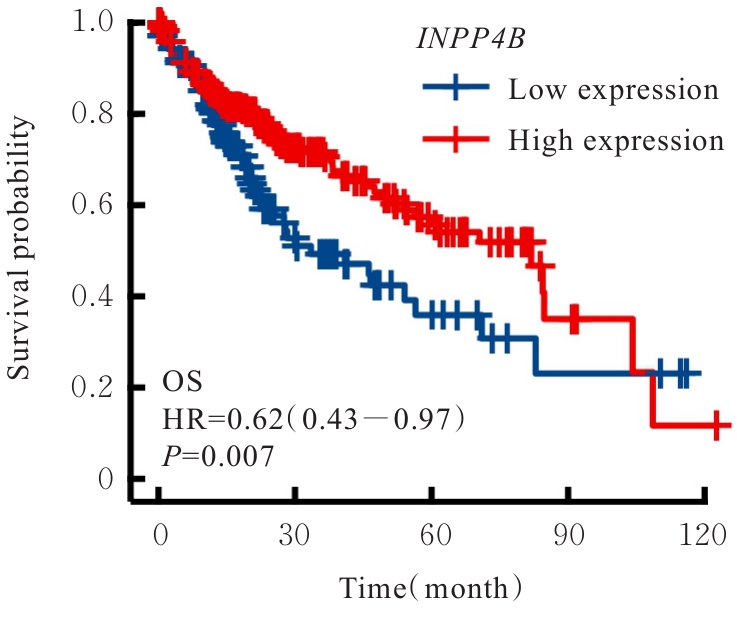
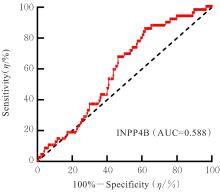
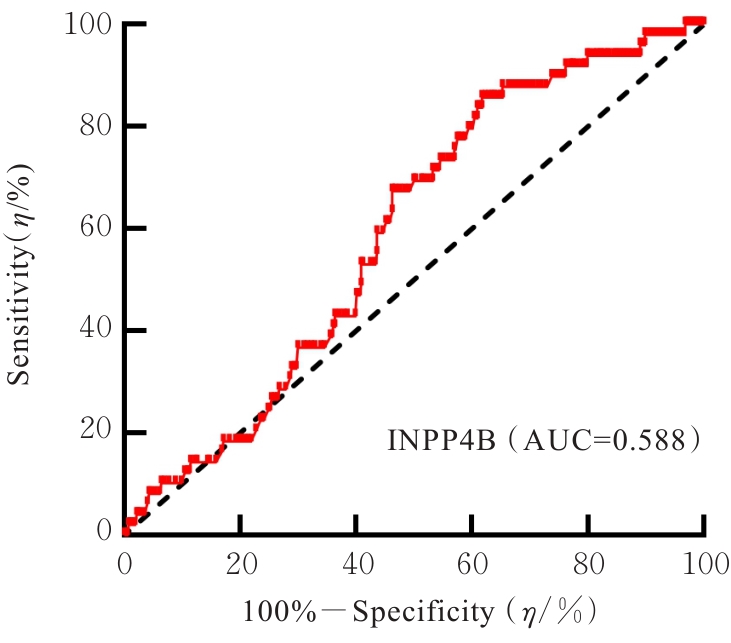
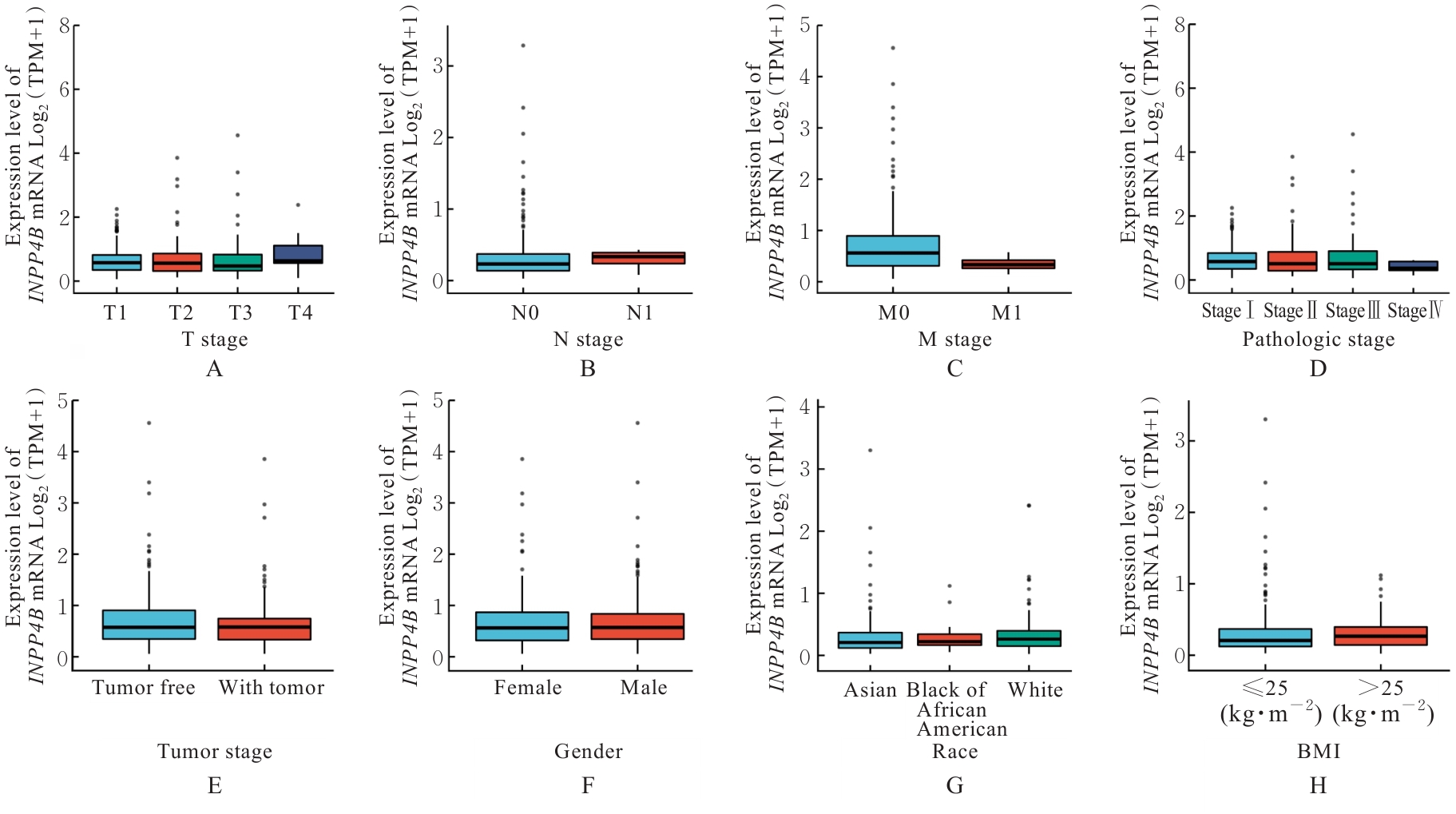
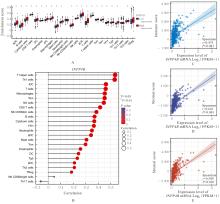
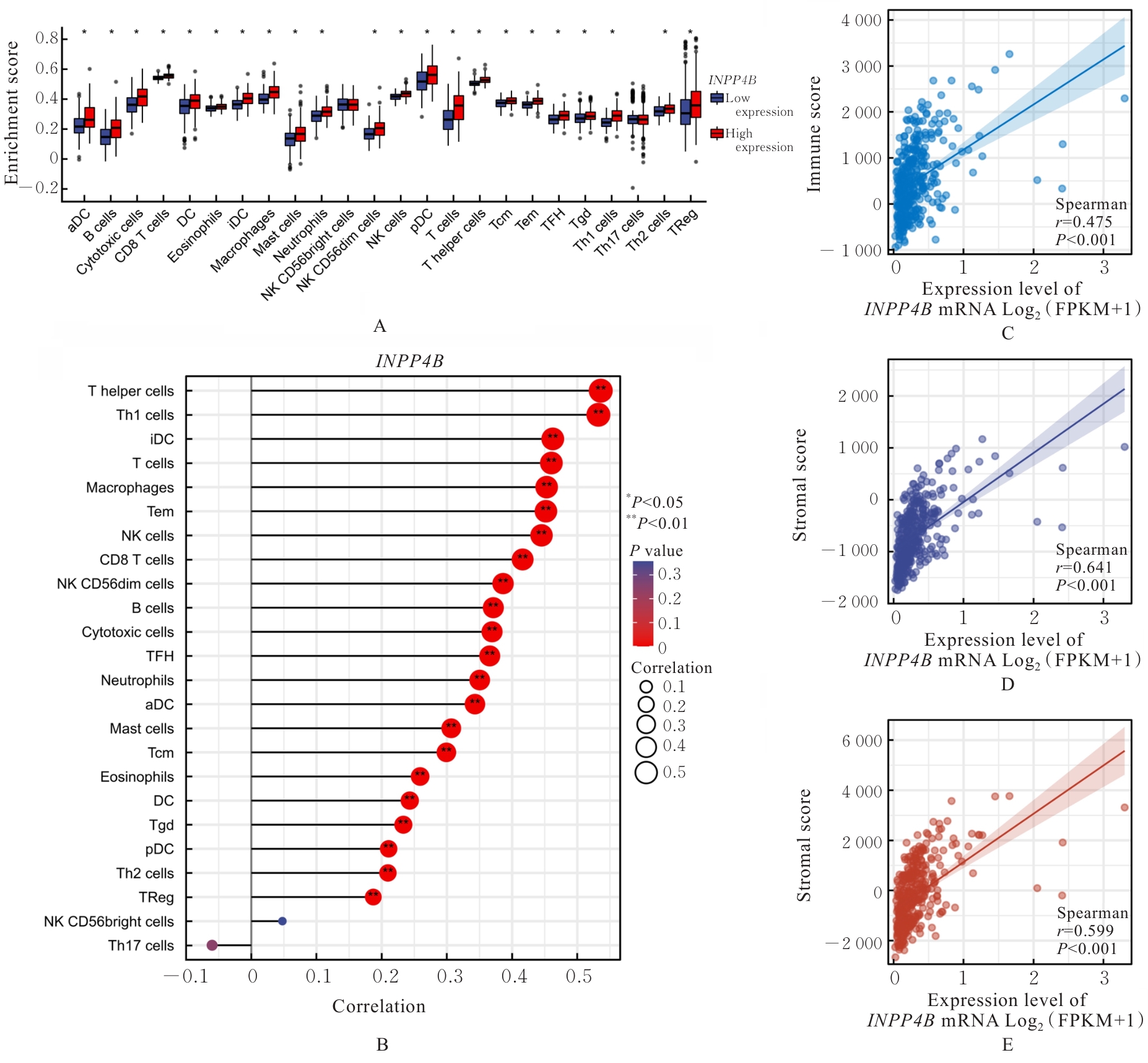
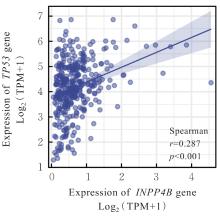
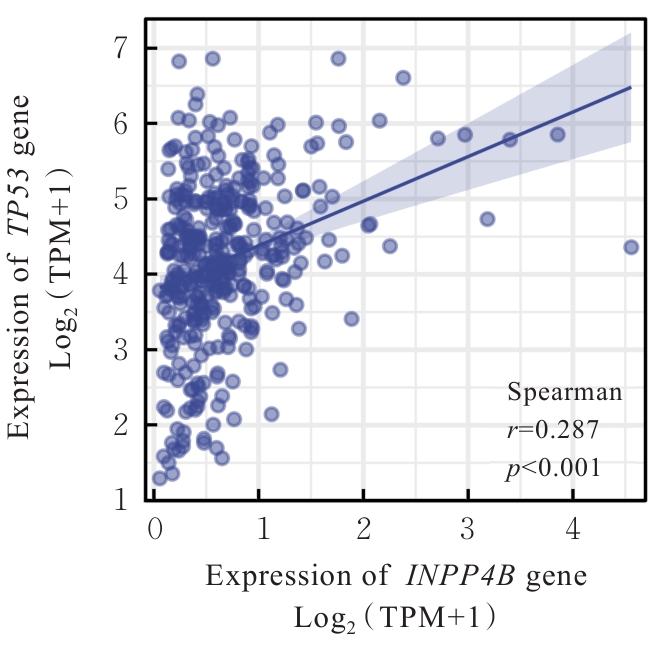
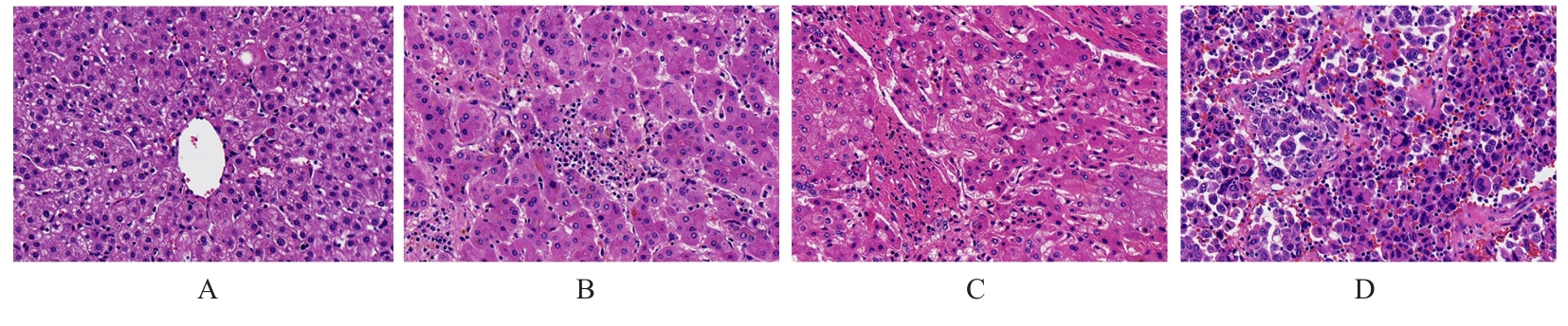
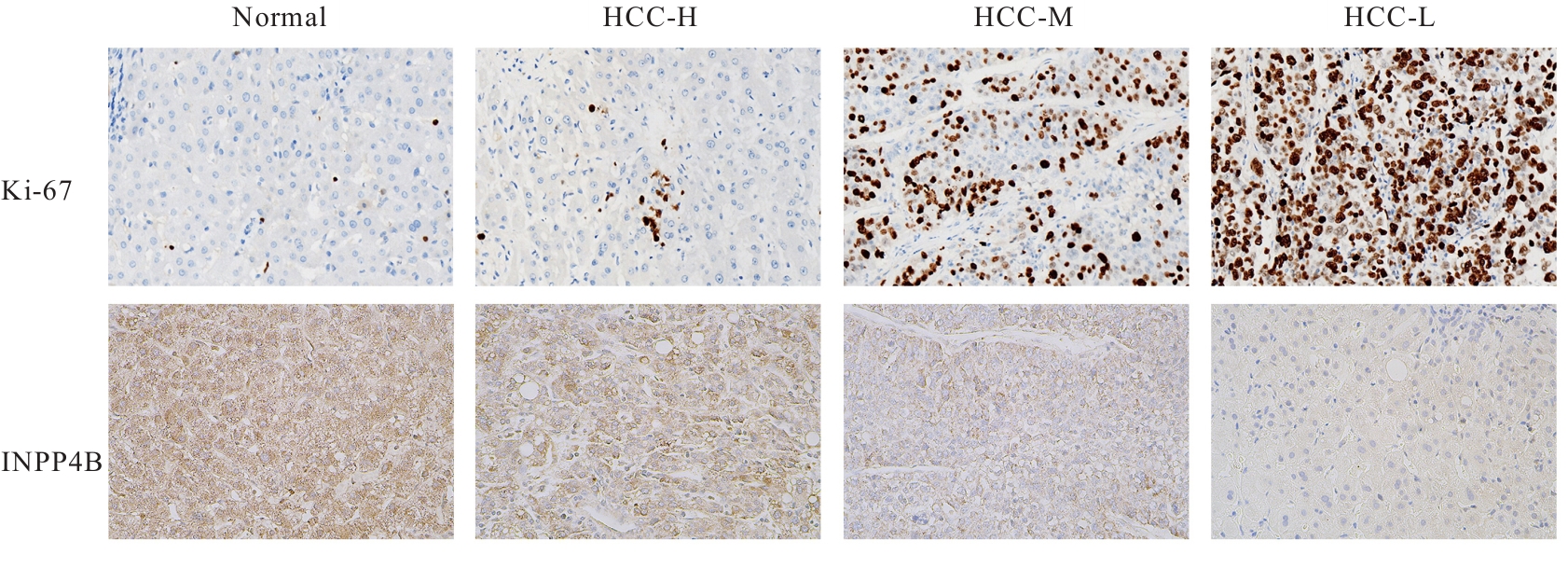
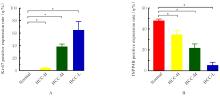
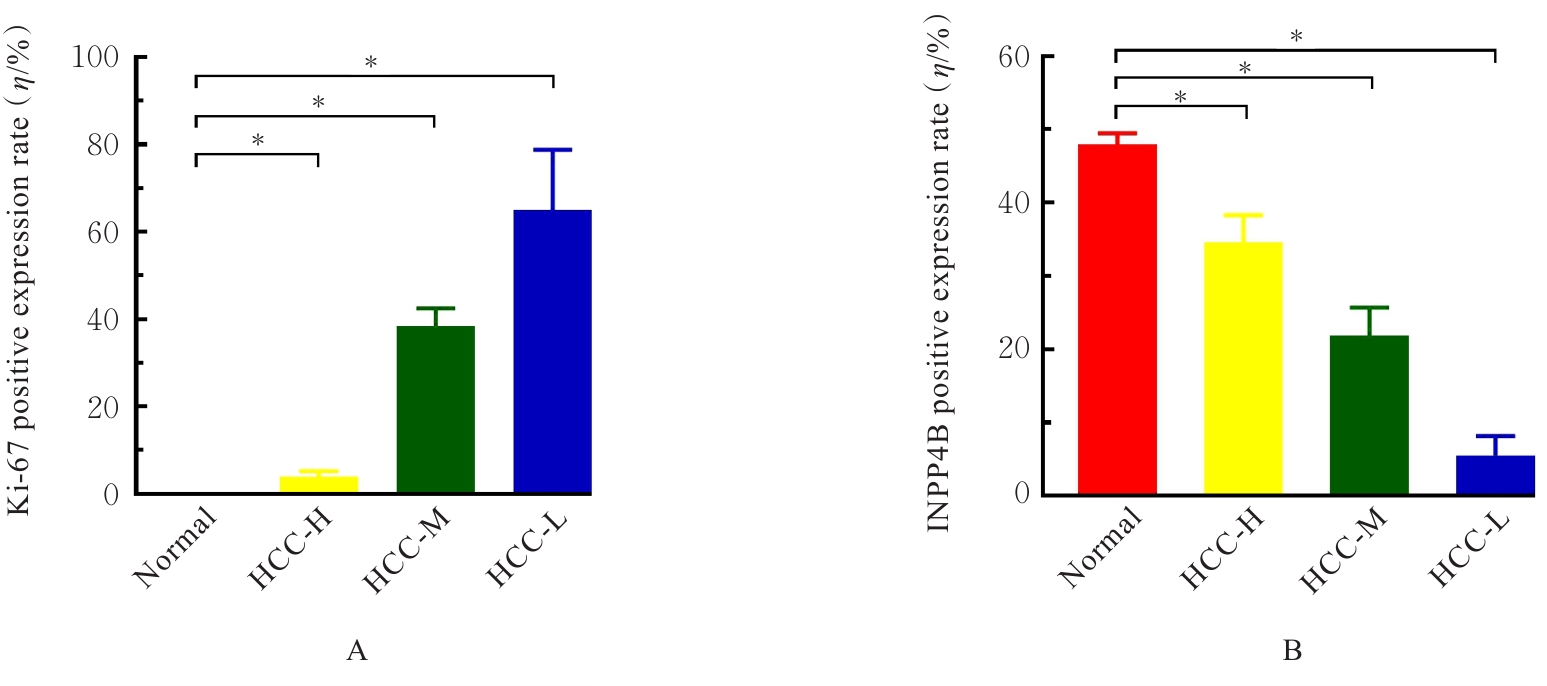
目的 基于癌症基因组图谱(TCGA)数据库和临床样本的实验验证探讨肝细胞癌(HCC)中肌醇多聚磷酸-4-磷酸酶Ⅱ型(INPP4B)基因的表达及临床意义。 方法 基于TCGA数据库中的424例临床样本数据资料(包括HCC组织374例,癌旁组织50例),采用Kaplan-Meier法和Cox回归分析,评估INPP4B基因与HCC患者临床特征及生存预后的关系。分析INPP4B基因与24种免疫细胞数量,肿瘤组织中的基质、肿瘤组织中的免疫细胞浸润和肿瘤纯度,HCC高频突变基因肿瘤蛋白53(TP53)基因表达水平的相关性。收集2022年12月—2023年12月进行手术切除治疗的60例HCC患者临床病理资料及其组织石蜡切片,根据临床诊断分为低分化组(HCC-L组)、中分化组(HCC-M组)和高分化组(HCC-H组),每组20例,选取同时期20例取活检并病理诊断为非肿瘤患者的临床病理资料及其肝组织石蜡切片,作为正常组。HE染色观察各组研究对象HCC组织和正常肝组织病理形态表现,免疫组织化学法检测各组研究对象HCC组织和正常肝组织中Ki-67和INPP4B蛋白表达情况。 结果 与正常组织比较,HCC组织中INPP4B mRNA表达水平明显升高(P<0.01)。与INPP4B低表达组比较,INPP4B高表达组患者的总生存期(OS)均明显延长(P<0.05)。单因素Cox回归分析,肿瘤分期、病理分期、肿瘤状况和残余肿瘤对HCC患者OS存在影响(P<0.05)。单因素回归分析,INPP4B预后风险模型评分危险比(HR)=0.781,95%置信区间(CI):0.552~1.105,P=0.168。INPP4B对HCC患者OS影响的受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线下面积(AUC)值为0.558,表明INPP4B基因预后风险模型在HCC患者生存预后方面具有一定的预测价值。INPP4B mRNA表达水平与TNM分期、Stage分期、患者性别、年龄、种族和体质量指数(BMI)值均无相关关系(P>0.05)。高表达和低表达INPP4B的肿瘤组织中,22种免疫细胞存在统计学差异(P<0.05);INPP4B mRNA表达水平与除辅助性T细胞(Th)17外的23种免疫细胞的数量均呈正相关关系(r>0),其中除自然杀伤细胞(NK)CD56+细胞外,均具有统计学意义(P<0.01);INPP4B与肿瘤组织中的基质(r=0.475)、肿瘤组织中的免疫细胞浸润(r=0.641)和肿瘤纯度(r=0.599)均具有显著的相关性(P<0.01)。INPP4B与TP53存在相关性(r=0.287,P<0.01)。HE染色,正常组研究对象肝组织中可见肝小叶结构清晰、完整,细胞排列整齐,轻微炎性细胞浸润;HCC-L组、HCC-M组和HCC-H组患者HCC组织中可见肝小叶被完全破坏,肝细胞脂肪变性明显,炎性细胞大量浸润,部分细胞出现气球样变、小细胞性增生的病变,且HCC分化程度越低,组织破坏程度越严重;免疫组织化学法,与正常组比较,HCC-L组、HCC-M组和HCC-H组患者HCC组织中Ki-67蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.01),且HCC组患者的分化程度越低,Ki-67阳性率越高。在正常组研究对象肝组织中可观察到细胞中棕褐色颗粒平均分布,INPP4B蛋白呈高表达;与正常组比较,HCC-L组、HCC-M组和HCC-H组患者HCC组织中INPP4B蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.01),且HCC组织分化程度越低,INPP4B阳性率越低。 结论 INPP4B是HCC患者预后的保护因素,INPP4B作为一种新的抑癌基因,可能成为治疗HCC新药筛选的潜在靶标。
中图分类号:
- R735.7