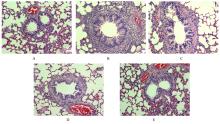
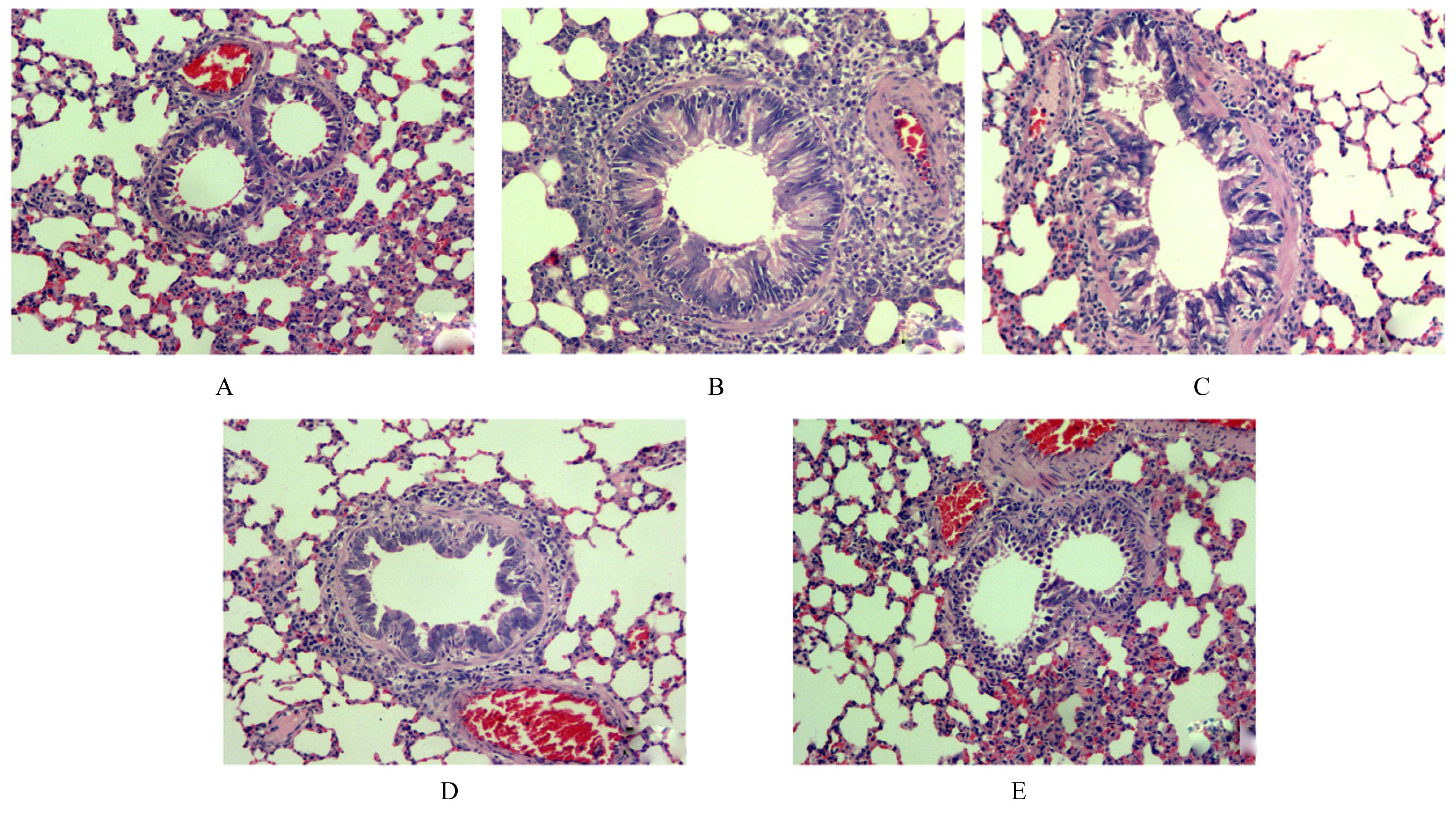
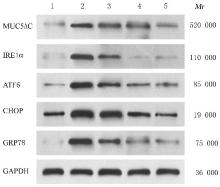
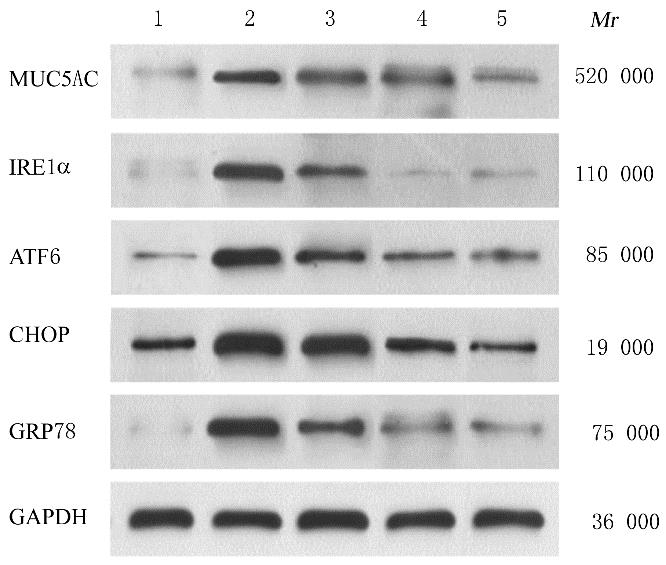
| 1 |
ZHANG C, ZHU W, MENG Q, et al. Halotherapy relieves chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by alleviating NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2022, 10(23): 1279.
|
| 2 |
TANNER L, SINGLE A B. Animal models reflecting chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and related respiratory disorders: translating pre-clinical data into clinical relevance[J]. J Innate Immun, 2020, 12(3): 203-225.
|
| 3 |
LIN V Y, KAZA N, BIRKET S E, et al. Excess mucus viscosity and airway dehydration impact COPD airway clearance[J]. Eur Respir J, 2020, 55(1): 1900419.
|
| 4 |
ZHANG L, LUO B, TING Y, et al. SIRT1 attenuates endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in rat models of COPD[J]. Growth Factors, 2020, 38(2): 94-104.
|
| 5 |
SP N, KANG D Y, LEE J M, et al. Mechanistic insights of anti-immune evasion by nobiletin through regulating miR-197/STAT3/PD-L1 signaling in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(18): 9843.
|
| 6 |
傅慧婷, 平键, 吴冬梅, 等. 泽漆化痰方对慢性阻塞性肺疾病气道黏液高分泌模型大鼠肺组织EGFR信号通路相关蛋白表达的影响[J]. 中医杂志,2021, 62(9): 802-807.
|
| 7 |
HE M, ZHANG G, SHEN F, et al. Effects of Z-VaD-Ala-Asp-Fluoromethyl ketone (Z-VAD-FMK) and Acetyl-Asp-Glu-Val-Asp-Aldehyde (Ac-DEVD-CHO) on inflammation and mucus secretion in mice exposed to cigarette smoke[J]. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis, 2023, 18: 69-78.
|
| 8 |
LIU W, HOU H P, LI C F, et al. Effects of Shiwei Longdanhua formula on LPS induced airway mucus hypersecretion, cough hypersensitivity, oxidative stress and pulmonary inflammation[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2023, 163: 114793.
|
| 9 |
ROJAS D A, PONCE C A, BUSTOS A, et al. Pneumocystis exacerbates inflammation and mucus hypersecretion in a murine, elastase-induced-COPD model[J]. J Fungi (Basel), 2023, 9(4): 452.
|
| 10 |
LEE E H, SHIN M H, GI M, et al. Inhibition of pendrin by a small molecule reduces lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury[J].Theranostics,2020,10(22):9913-9922.
|
| 11 |
HUGHES R, RAPSOMANIKI E, JANSON C, et al. Frequent productive cough: Symptom burden and future exacerbation risk among patients with asthma and/or COPD in the NOVELTY study[J]. Respir Med, 2022, 200: 106921.
|
| 12 |
GAO C, PAN H, MA F, et al. Centipeda minima active components and mechanisms in lung cancer[J]. BMC Complement Med Ther, 2023, 23(1): 89.
|
| 13 |
GHASEMI-TARIE R, KIASALARI Z, FAKOUR M, et al. Nobiletin prevents amyloid β1-40-induced cognitive impairment via inhibition of neuroinflammation and oxidative/nitrosative stress[J]. Metab Brain Dis, 2022, 37(5): 1337-1349.
|
| 14 |
YUAN S, YE Z, LI Y, et al. Hypoglycemic effect of nobiletin via regulation of islet β-cell mitophagy and gut microbiota homeostasis in streptozocin-challenged mice[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2022, 70(19):5805-5818.
|
| 15 |
LU R, XU K, QIN Y, et al. Network pharmacology and experimental validation to reveal effects and mechanisms of icariin combined with nobiletin against chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2022, 2022: 4838650.
|
| 16 |
LI J, MA J, TIAN Y, et al. Effective-component compatibility of Bufei Yishen formula II inhibits mucus hypersecretion of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease rats by regulating EGFR/PI3K/mTOR signaling[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2020, 257: 112796.
|
| 17 |
DUAN Q, ZHOU Y, YANG D. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in airway hyperresponsiveness[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2022, 149:112904.
|
| 18 |
YU Y, YANG A, YU G, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: mechanisms and future perspectives[J]. Biomolecules, 2022, 12(11): 1637.
|
| 19 |
ZAIDI MAL, MARGGRAF V, REPGES E, et al. Relevance of serum levels of the endoplasmic reticulum stress protein GRP78 (glucose-regulated protein 78 kDa) as biomarker in pulmonary diseases[J]. Cell Stress Chaperones, 2023, 28(3): 333-341.
|
| 20 |
WANG J, DING L, WANG K, et al. Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in cadmium-induced hepatocyte apoptosis and the protective effect of quercetin[J]. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf, 2020, 241: 113772.
|
| 21 |
LI Y R, FAN H J, SUN R R, et al. Wuzi Yanzong Pill plays a neuroprotective role in parkinson’s disease mice via regulating unfolded protein response mediated by endoplasmic reticulum stress[J]. Chin J Integr Med, 2023, 29(1): 19-27.
|
| 22 |
MOON J Y, CHO S K. Nobiletin induces protective autophagy accompanied by ER-stress mediated apoptosis in human gastric cancer SNU-16 cells[J]. Molecules, 2016, 21(7): 914.
|
| 23 |
ZHANG B F, JIANG H, CHEN J, et al. Nobiletin ameliorates myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated apoptosis through regulation of the PI3K/AKT signal pathway[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2019, 73: 98-107.
|
 ),周向东1,2,陈小妹3,刘峰1,2,刘畅1,2,钟有清1,2,李亮1,2
),周向东1,2,陈小妹3,刘峰1,2,刘畅1,2,钟有清1,2,李亮1,2
 ),Xiangdong ZHOU1,2,Xiaomei CHEN3,Feng LIU1,2,Chang LIU1,2,Youqing ZHONG1,2,Liang LI1,2
),Xiangdong ZHOU1,2,Xiaomei CHEN3,Feng LIU1,2,Chang LIU1,2,Youqing ZHONG1,2,Liang LI1,2