吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (5): 1250-1258.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240508
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
美沙拉嗪对RAW264.7细胞中促炎因子和过氧化物的抑制作用及其对牙周炎模型大鼠的治疗作用
王浩宇1,王宇琪1,王冰倩1,聂瑾涵1,闫嘉晴2( ),胡敏1(
),胡敏1( )
)
- 1.吉林大学口腔医院正畸科,吉林 长春 130021
2.吉林大学口腔医院牙周科,吉林 长春 130021
Inhibitory effect of mesalazine on pro-inflammatory factors and peroxides in RAW264.7 cells and its therapeutic effect on periodontitis model rats
Haoyu WANG1,Yuqi WANG1,Bingqian WANG1,Jinhan NIE1,Jiaqing YAN2( ),Min HU1(
),Min HU1( )
)
- 1.Department of Orthodontics, Stomatology Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China
2.Department of Periodontology, Stomatology Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China
摘要:
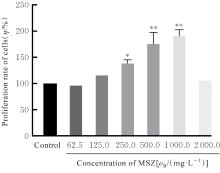
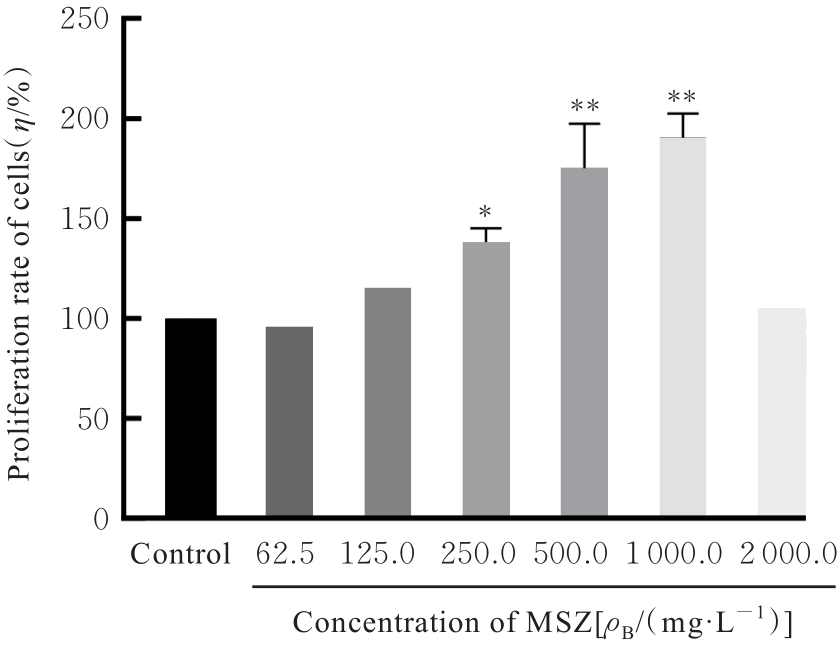
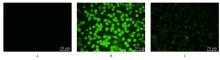
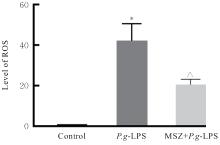
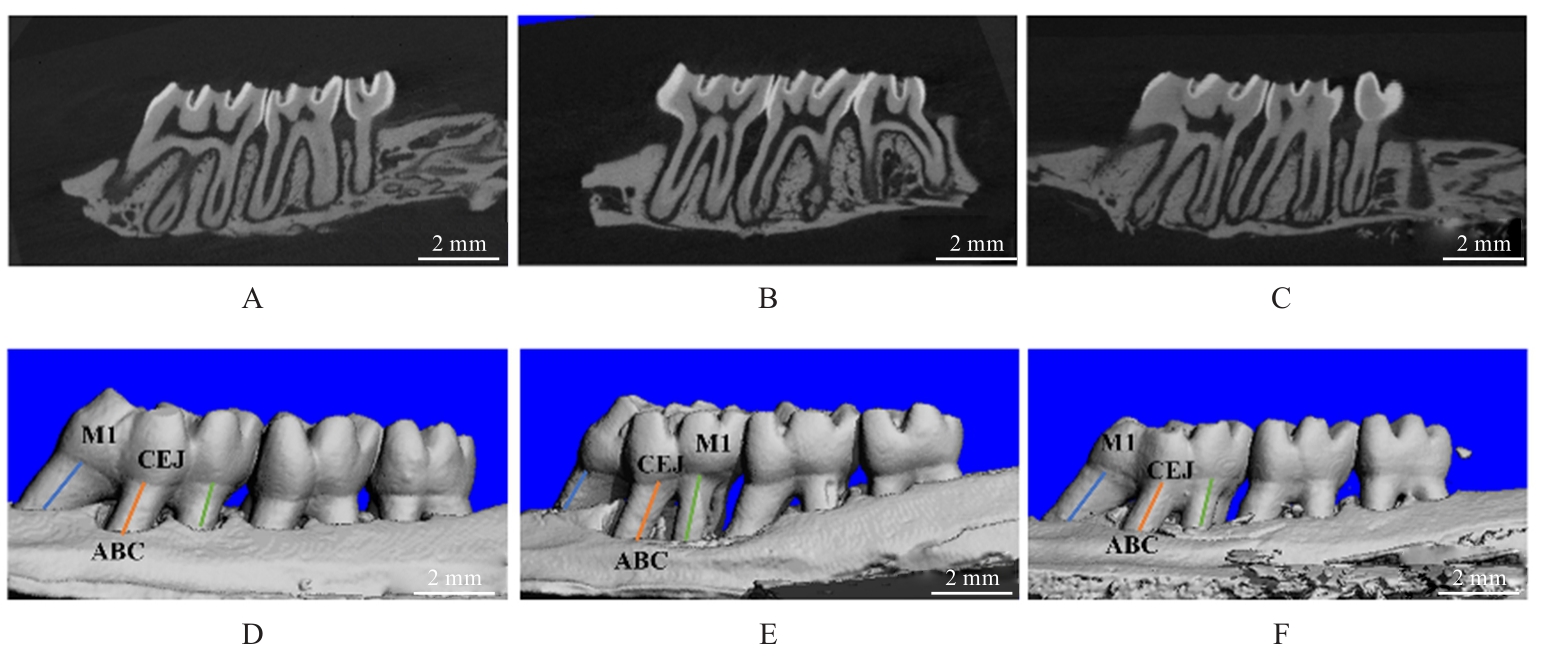
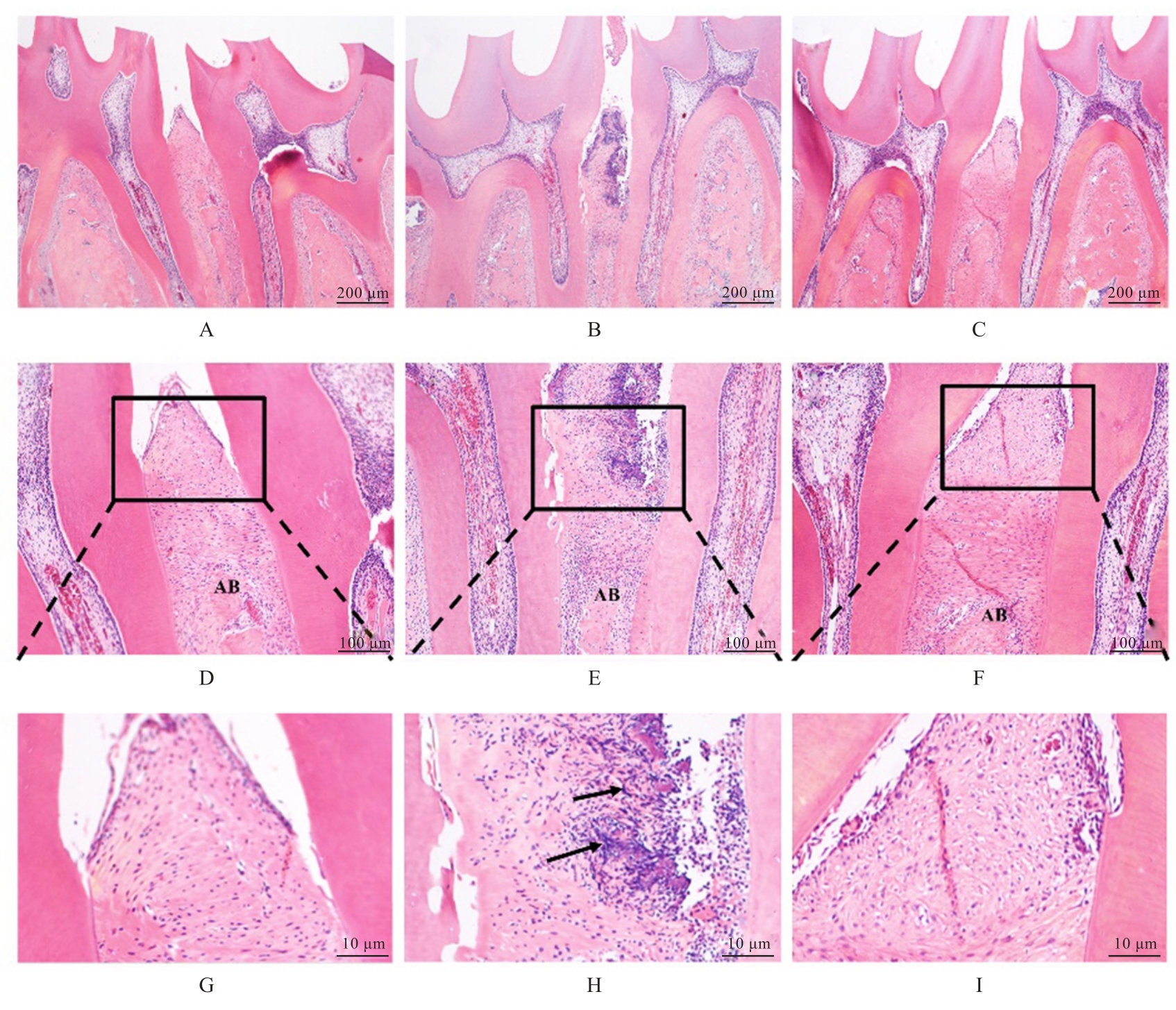
目的 探讨美沙拉嗪(MSZ)在RAW264.7细胞模型中的抗炎和抗氧化作用,阐明其对大鼠牙周炎的治疗效果。 方法 采用CCK-8法检测不同浓度(0、62.5、125.0、250.0、500.0、1 000.0和2 000.0 mg·L-1)MSZ刺激的RAW264.7细胞增殖率,确定MSZ处理细胞的最佳浓度。采用牙龈卟啉单胞菌脂多糖(P.g-LPS)和MSZ处理RAW264.7细胞,并将细胞分为对照组、P.g-LPS组和MSZ+P.g-LPS组。采用DCFH-DA荧光探针法检测各组细胞中活性氧(ROS)水平,采用酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)法检测各组细胞中丙二醛(MDA)和还原型谷胱甘肽(GSH)水平及超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性,采用实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法检测各组细胞中炎症因子白细胞介素1β(IL-1β)和白细胞介素8(IL-8)mRNA表达水平。采用结扎法结合P.g菌液注射建立牙周炎大鼠模型,18只大鼠随机分为对照组(不作处理)、模型组(构建牙周炎模型)和给药组(构建牙周炎模型并给予MSZ),每组6只。采用微型CT评估各组大鼠牙槽骨破坏情况,采用HE染色观察各组大鼠牙周组织病理形态表现。 结果 与对照组比较,500.0 mg·L-1 MSZ组细胞增殖率明显升高(P<0.01),因此后续选用500.0 mg·L-1 MSZ处理细胞。与对照组比较,P.g-LPS组细胞中ROS和MDA水平明显升高(P<0.01),GSH水平和SOD活性明显降低(P<0.01),IL-1β和IL-8 mRNA表达水平明显升高(P<0.01);与P.g-LPS组比较,MSZ+P.g-LPS组细胞中ROS和MDA水平明显降低(P<0.01),GSH水平和SOD活性明显升高(P<0.01),IL-1β和IL-8 mRNA表达水平明显降低(P<0.01)。微型CT检测,与对照组比较,模型组大鼠釉牙骨质界到牙槽嵴顶的距离(CEJ-ABC)明显升高(P<0.01),骨体积分数(BV/TV)明显降低(P<0.05);与模型组比较,给药组大鼠CEJ-ABC明显降低(P<0.01),BV/TV明显升高(P<0.05)。HE染色,与模型组比较,给药组大鼠牙周组织炎症细胞浸润减轻,上皮附着恢复。 结论 MSZ能有效抑制P.g-LPS诱导的RAW264.7细胞中促炎因子和过氧化物的产生,提高细胞抗炎和抗氧化能力,在牙周炎大鼠模型中抑制牙槽骨吸收,缓解牙周组织炎症。
中图分类号:
- R781.4