吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 68-75.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250109
Yes相关蛋白对人宫颈癌SiHa细胞生物学行为的影响
赵芳1,2,李珍玲1,朴丽花3,韩龙哲1,崔银姬1,权春姬1,4( ),金雪梅1(
),金雪梅1( )
)
- 1.延边大学附属医院病理科,吉林 延吉133000
2.山东省菏泽市立医院病理科,山东 菏泽 274000
3.延边大学医学院组织学与胚胎学教研室,吉林 延吉133000
4.海南省妇女儿童医学中心病理科,海南 海口 570100
Effect of Yes-associated proteins on biological behaviors of human cervical cancer SiHa cells
Fang ZHAO1,2,Zhenling LI1,Lihua PIAO3,Longzhe HAN1,Yinji CUI1,Chunji QUAN1,4( ),Xuemei JIN1(
),Xuemei JIN1( )
)
- 1.Department of Pathology,Affiliated Hospital,Yanbian University,Yanji 133000,China
2.Department of Pathology,Municipal Hospital,Heze City,Shandong Province,Heze 274000,China
3.Department of Histology and Embryology,College of Medical Sciences,Yanbian University,Yanji 133002,China
4.Department of Pathology,Hainan Provincial Women and Children’s Medical Center,Haikou 570100,China
摘要:
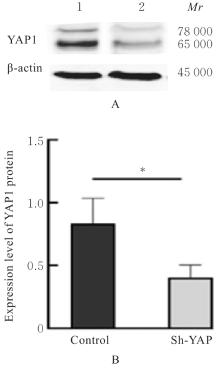
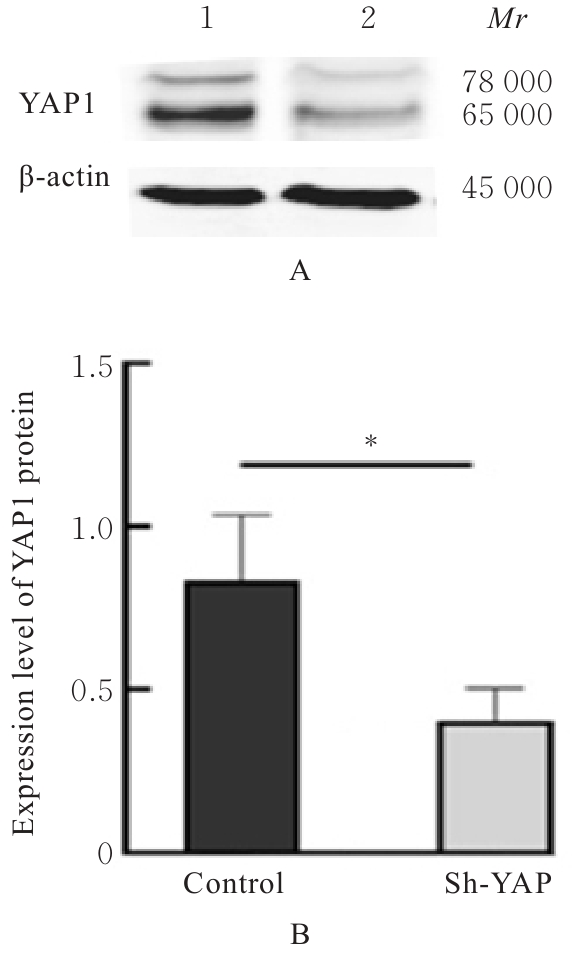
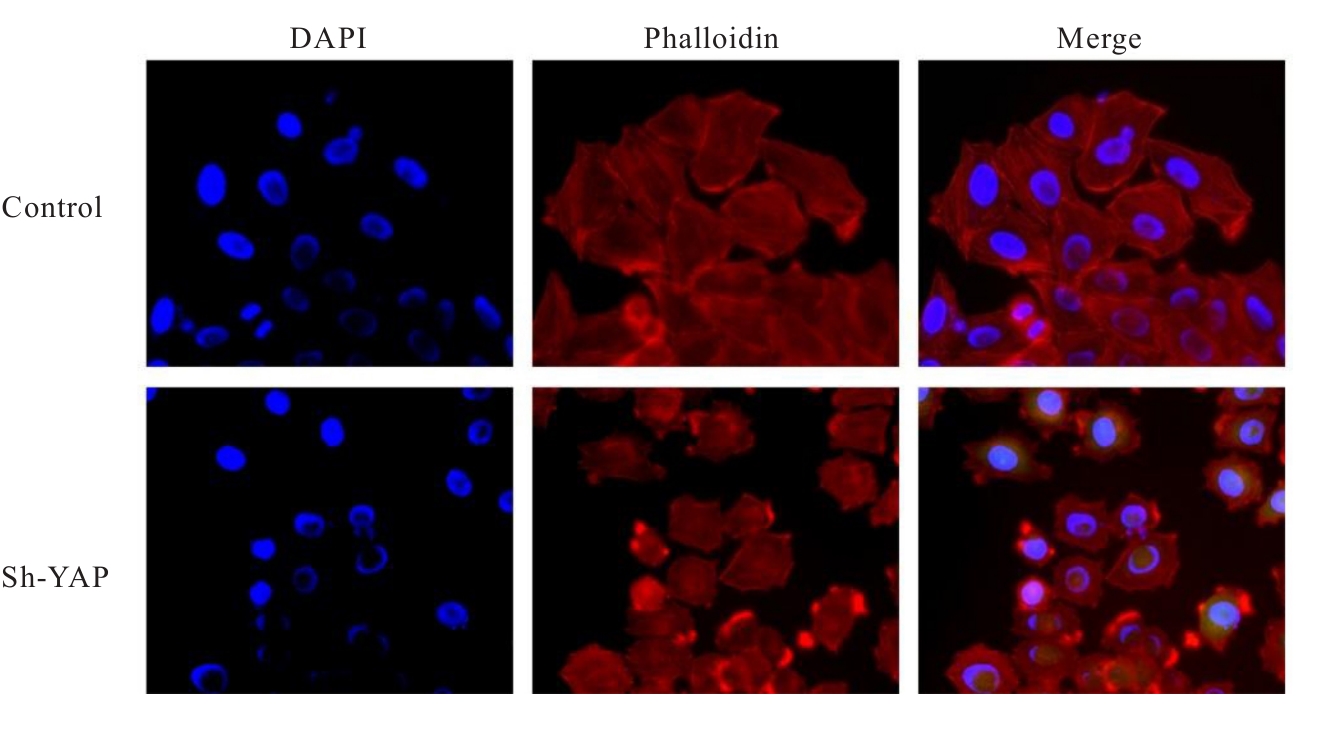
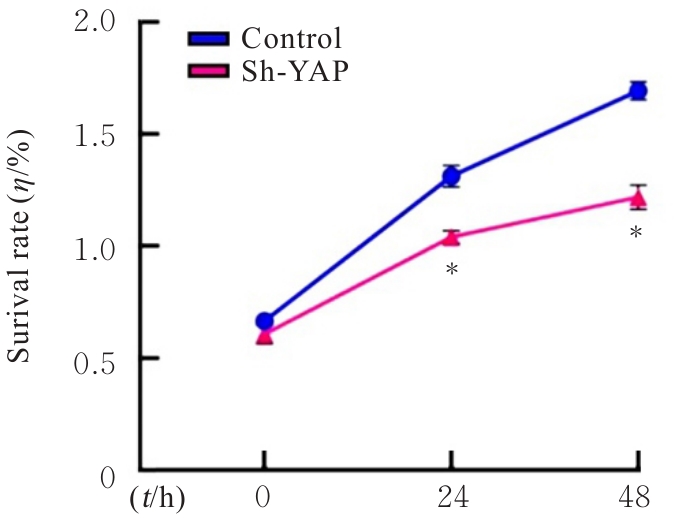
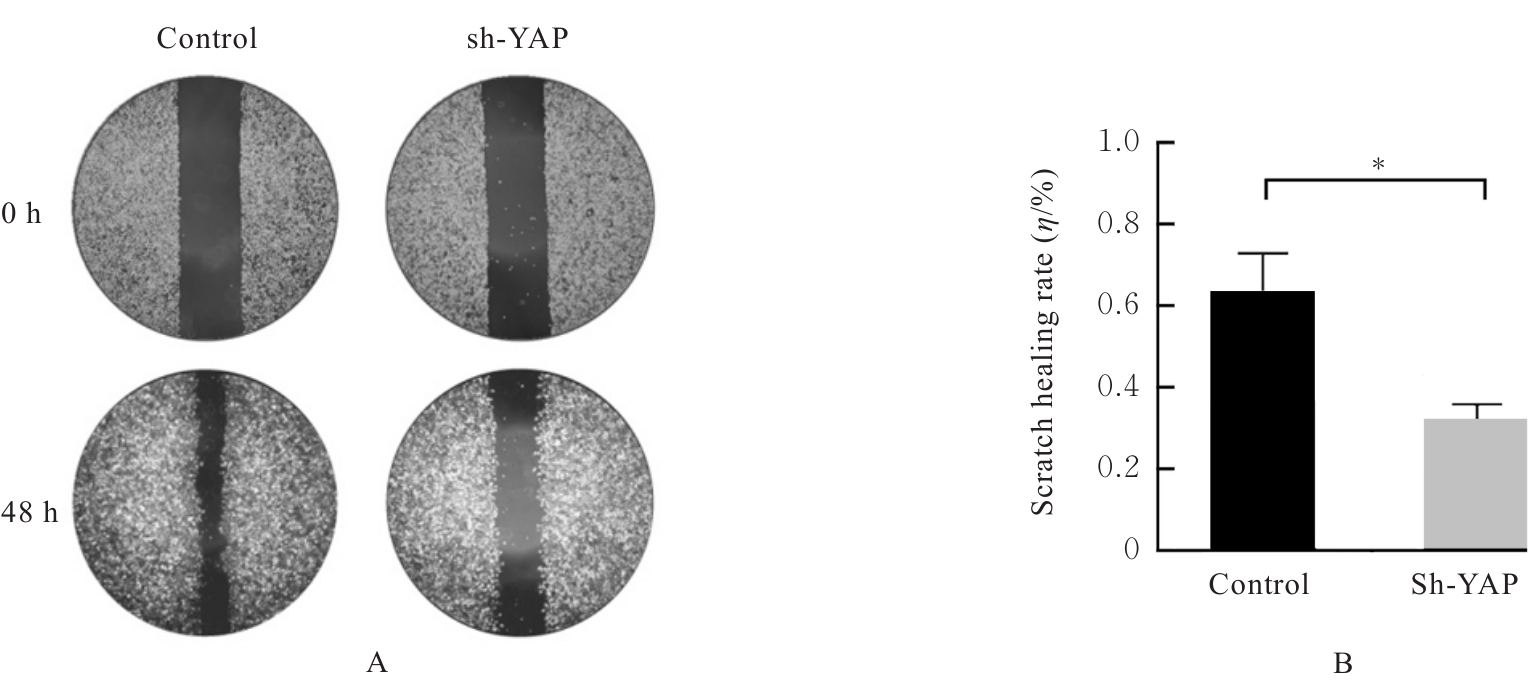
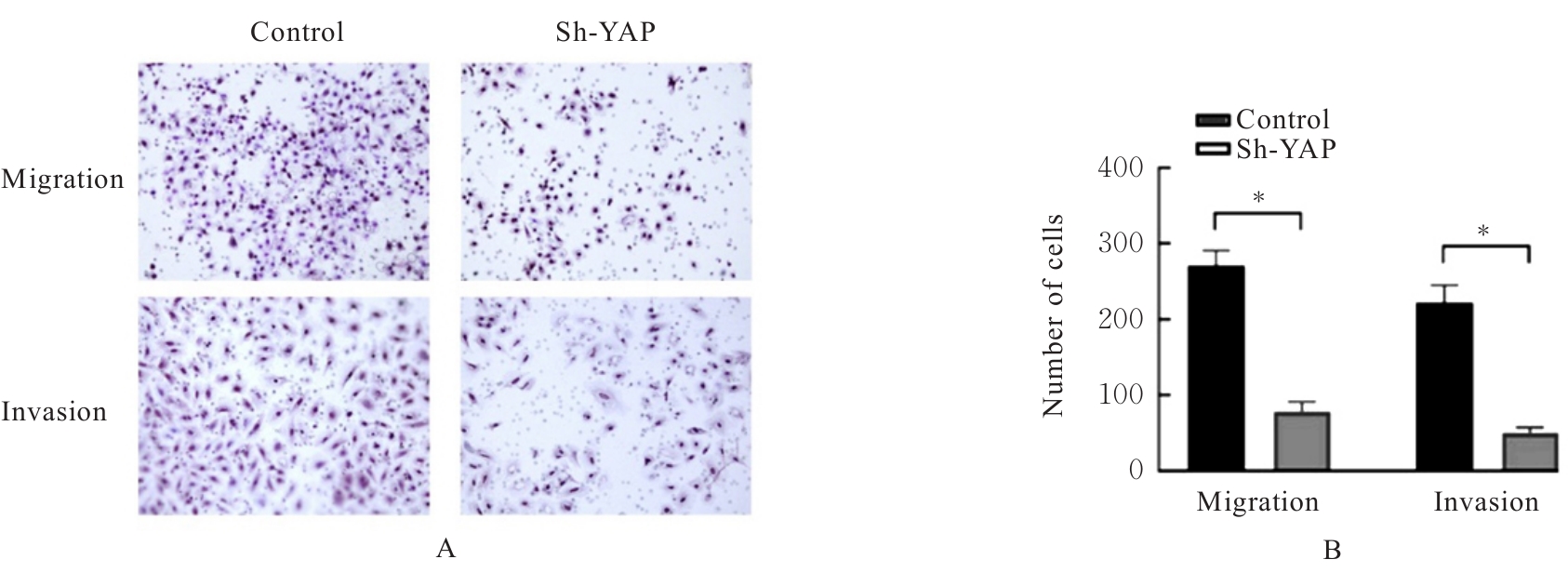
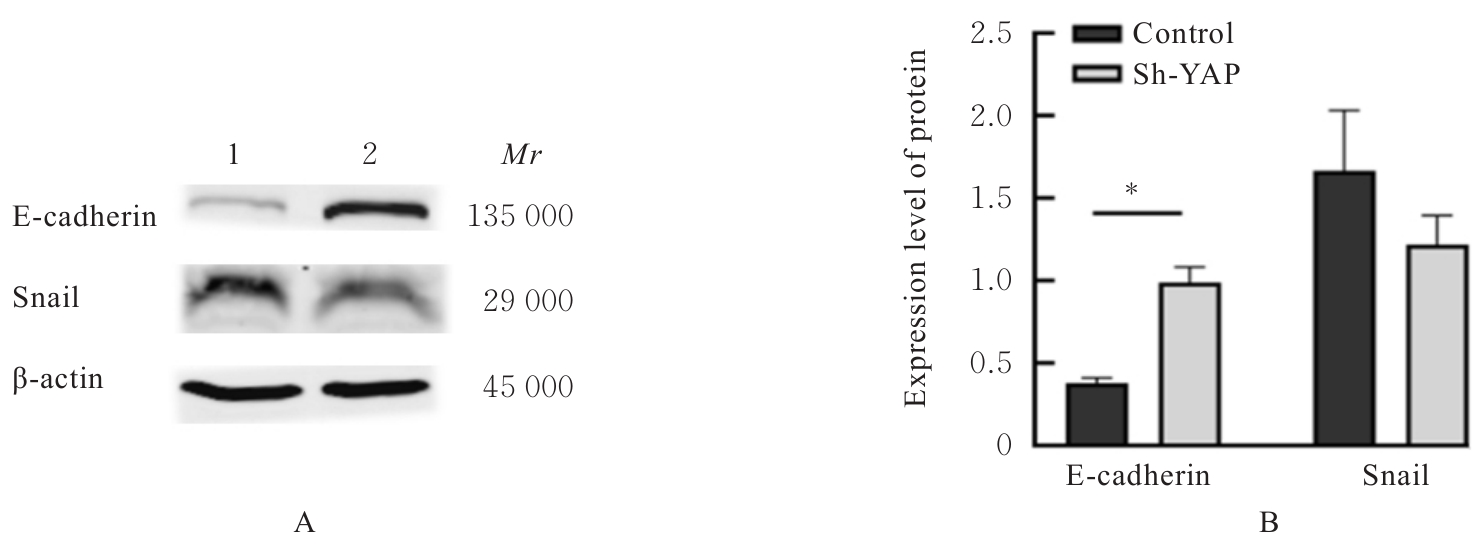
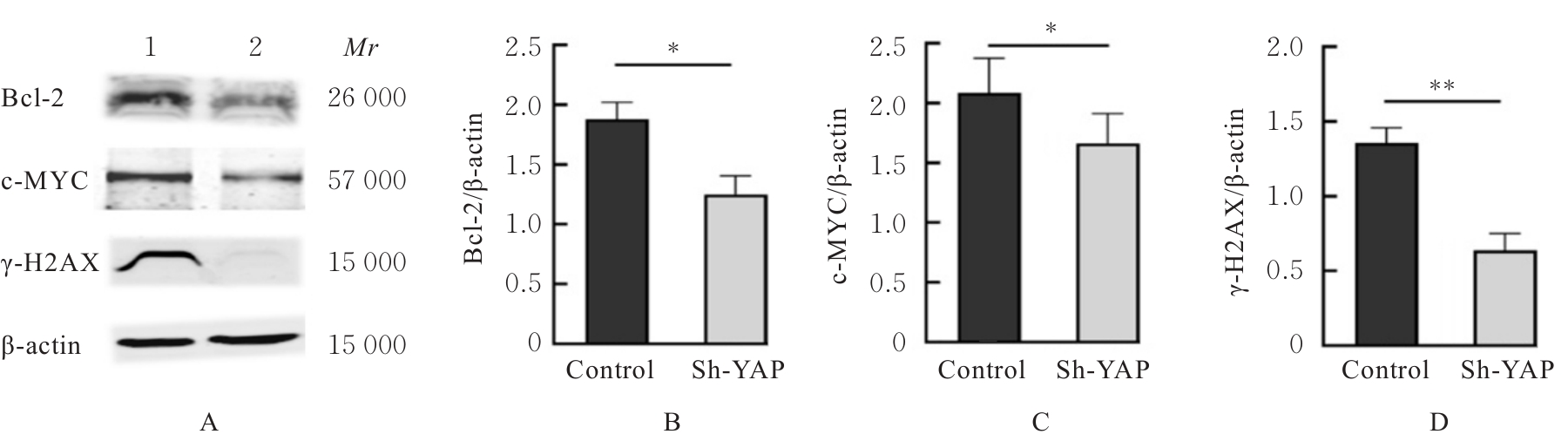
目的 探讨Yes相关蛋白(YAP)沉默对人宫颈癌(CC)SiHa细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭能力的影响。 方法 对人CC细胞株SiHa细胞进行体外培养,慢病毒YAPshRNA转染到SiHa细胞,建立稳定转染的YAP-shRNA实验组(sh-YAP组)和空载质粒对照组(对照组),采用Western blotting法检测YAP沉默效果;免疫荧光法检测2组细胞中肌动蛋白(F-actin)微丝数量及形态变化;CCK-8法、Transwell小室实验和细胞划痕实验检测2组细胞存活率、迁移及侵袭细胞数以及细胞划痕愈合率;Western blotting法检测2组细胞中上皮-间质转化(EMT)相关标记物[E钙黏蛋白(E-cadherin)和锌指转录因子(Snail)]、DNA损伤修复相关蛋白γ(γ-H2AX)和凋亡相关蛋白[c-MYC和B细胞淋巴瘤2 (Bcl-2)]蛋白表达水平。 结果 慢病毒YAPshRNA转染SiHa细胞后,SiHa细胞中YAP蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05)。免疫荧光实验,YAP沉默后SiHa细胞中F-actin微丝稀疏且排列规则,细胞数量减少、细胞呈现蜷缩的状态。CCK-8法,与对照组比较,sh-YAP组培养24和48 h后SiHa细胞存活率明显降低(P<0.01);Transwell小室实验和细胞划痕实验,与对照组比较,sh-YAP组的SiHa细胞迁移和侵袭细胞数明显减少(P<0.01),细胞划痕愈合率明显降低(P<0.05);Western blotting法,与对照组比较,sh-YAP组细胞中E-cadherin蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.05),c-MYC、Bcl-2和γ-H2AX蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05或P<0.01)。 结论 YAP基因沉默导致人CC SiHa细胞F-actin的解聚,并调控细胞凋亡和DNA损伤修复,可能会逆转EMT进程,从而抑制肿瘤细胞增殖和迁移。
中图分类号:
- R737.32