吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (2): 352-359.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250209
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
新型复合水凝胶对H₂O₂诱导心肌细胞氧化应激损伤的保护作用
王岳1,马宁1,卢嘉骏1,王成瑶2,陈琳渝2,任宇晨1,李景武3,孙红1( )
)
- 1.华北理工大学基础医学院 河北省慢性病重点实验室,河北 唐山 063210
2.华北理工大学护理与康复学院 河北省康复工程与再生医学重点实验室,河北 唐山 063000
3.河北省唐山市人民医院 河北省分子肿瘤学重点实验室,河北 唐山 063000
Protective effect of novel composite hydrogels on H₂O₂-induced oxidative stress injury in cardiomyocytes
Yue WANG1,Ning MA1,Jiajun LU1,Chengyao WANG2,Linyu CHEN2,Yuchen REN1,Jingwu LI3,Hong SUN1( )
)
- 1.Key Laboratory of Chronic Diseases,School of Basic Medical Sciences,North China University of Science and Technology,Tangshan 063210,China
2.Key Laboratory of Rehabilitation Engineering and Regenerative Medicine,School of Nursing and Rehabilitation,North China University of Science and Technology,Tangshan 063000,China
3.Key Laboratory of Molecular Oncology,Hebei Provincial People’s Hospital,Tangshan 063000,China
摘要:
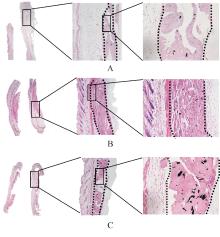
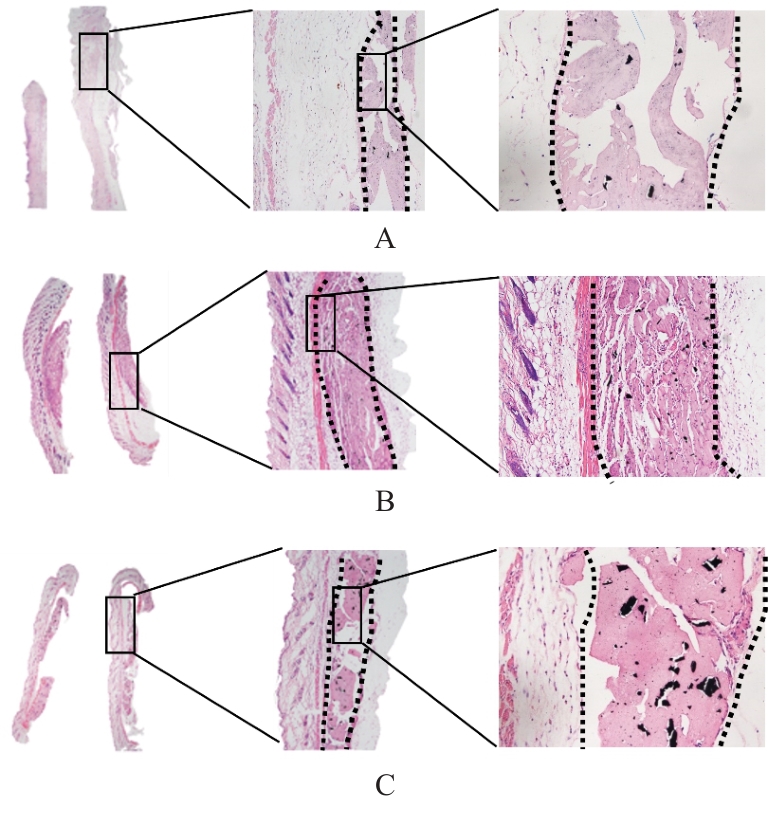
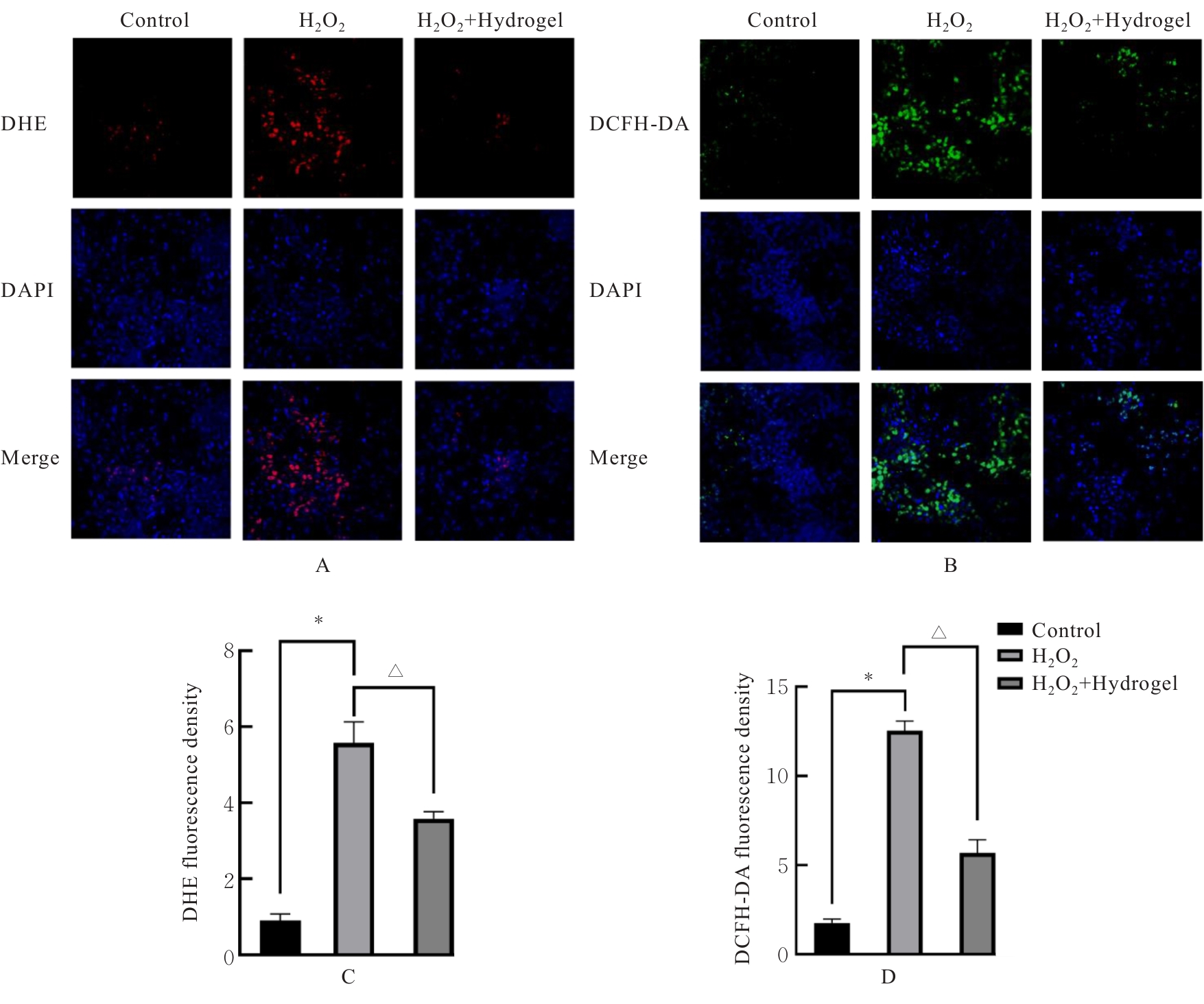
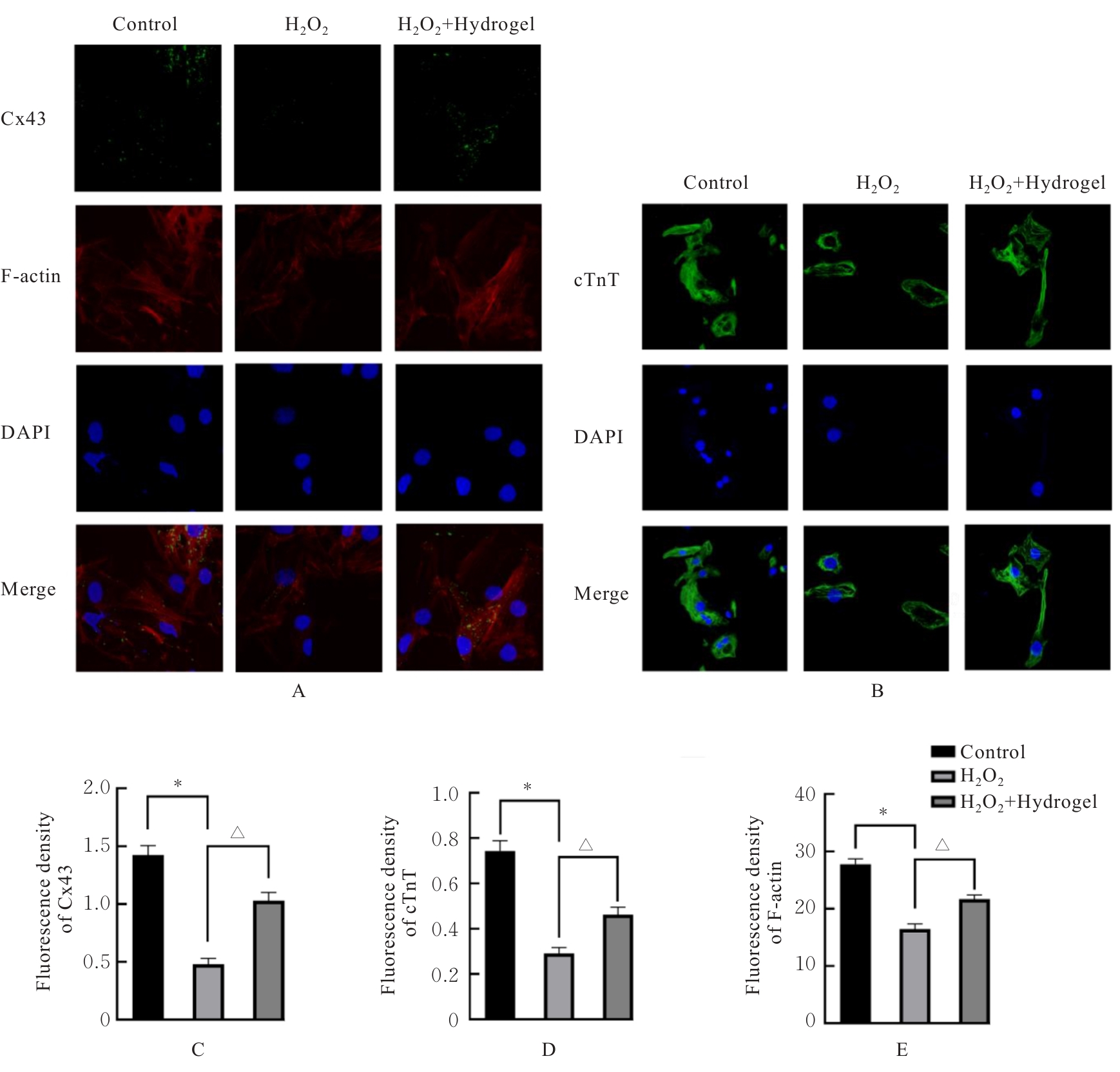
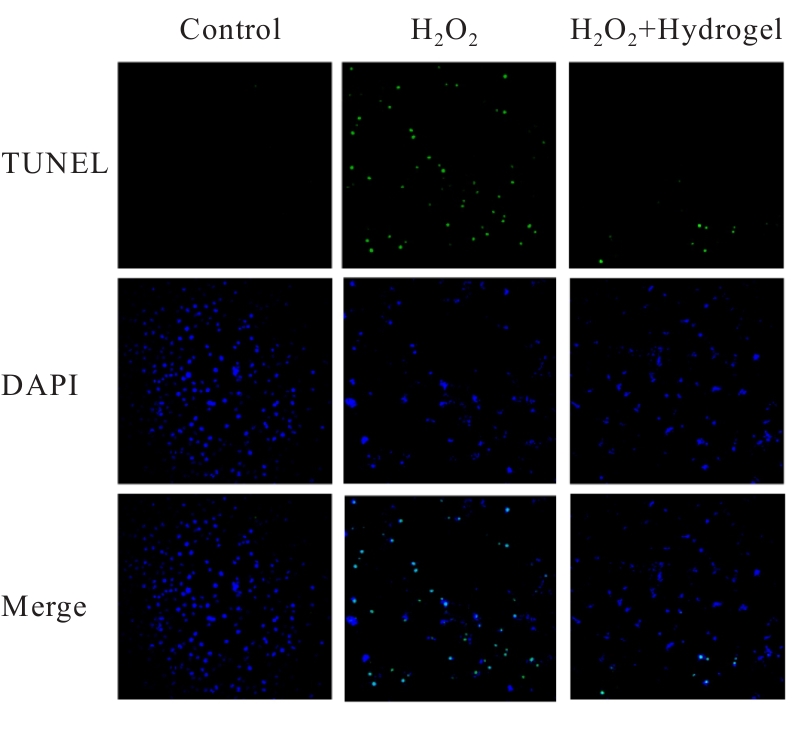
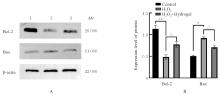
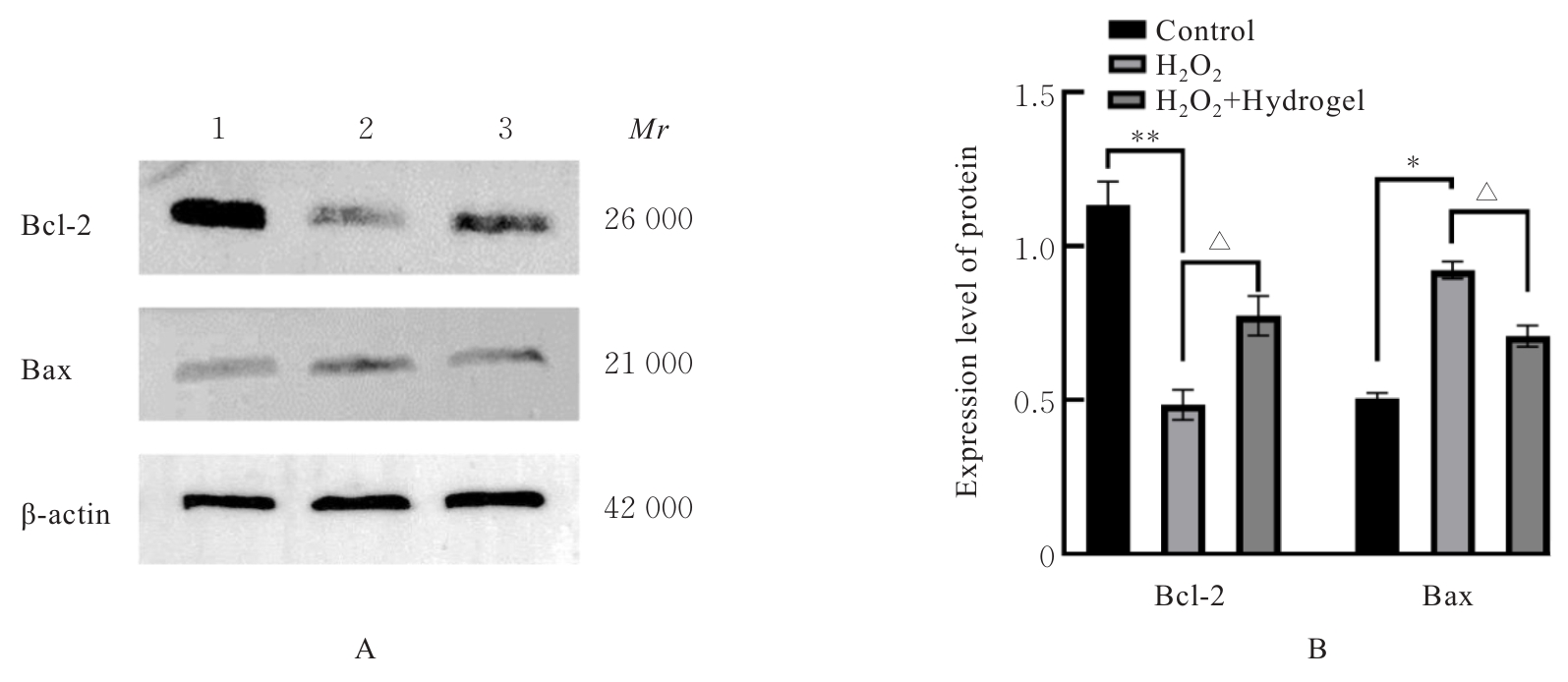
目的 探讨新型复合水凝胶对过氧化氢(H?O?)诱导心肌细胞氧化应激损伤的保护作用,并阐明其可能的作用机制。 方法 小鼠皮下注射水凝胶100 μL,1、14和28 d正常饲养后处死小鼠,取材,HE染色观察水凝胶的组织相容性。提取出生1 d SD大鼠的原代心肌细胞,建立心肌细胞氧化应激损伤模型。原代心肌细胞分为对照组、H?O?组和水凝胶(H?O?+Hydrogel)组。对照组原代心肌细胞正常培养,H?O?组原代心肌细胞采用200 μmol·L-1 H?O?溶液处理24 h;H?O?+Hydrogel组原代心肌细胞采用1 g·L-1的水凝胶与200 μmol·L-1 H?O?共孵育24 h。采用细胞计数试剂盒8(CCK-8)法检测各组心肌细胞活性,双氢乙啶(DHE)和2',7'-二氯荧光素二乙酸酯(DCFH-DA)检测各组心肌细胞中活性氧(ROS)水平,鬼笔环肽荧光染色标记法检测各组心肌细胞中纤维形肌动蛋白(F-actin)表达情况,免疫荧光法检测各组心肌细胞中连接蛋白43(Cx43)和心肌肌钙蛋白T(cTnT)表达情况,TUNEL染色法检测各组心肌细胞凋亡率,Western blotting法检测各组心肌细胞中凋亡相关蛋白B细胞淋巴瘤2(Bcl-2)和Bcl-2相关X蛋白(Bax)的表达水平。 结果 HE染色,水凝胶周围组织炎性细胞浸润较少,皮下埋植的炎症反应较小。与对照组比较,H?O?组心肌细胞活性明显降低(P<0.05),细胞中ROS水平明显升高(P<0.05),细胞中Cx43、cTnT和F-actin蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.001),心肌细胞凋亡率明显升高(P<0.01),心肌细胞中Bcl-2蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.001),Bax蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.01);与H?O?组比较,H?O?+Hydrogel组心肌细胞活性明显升高(P<0.05),细胞中ROS水平明显降低(P<0.01),细胞中cTnT、Cx43和F-actin蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.01),心肌细胞凋亡率明显降低(P<0.001),心肌细胞中Bcl-2蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.01),Bax蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.01)。 结论 水凝胶能够通过清除环境中的ROS促进心肌细胞相关蛋白的表达,抑制心肌细胞凋亡,发挥对氧化应激环境下心肌细胞的保护作用。
中图分类号:
- R542.2