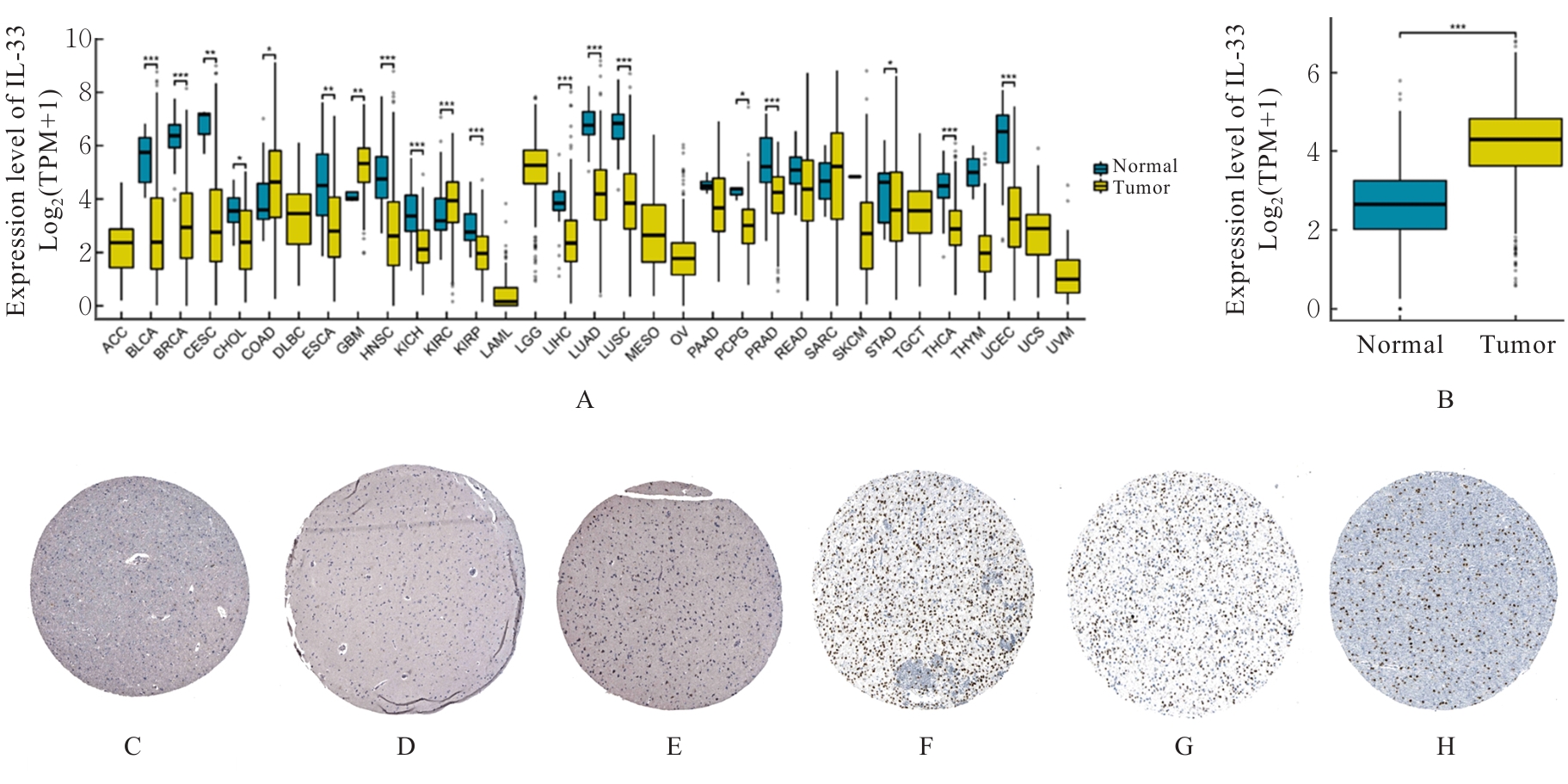
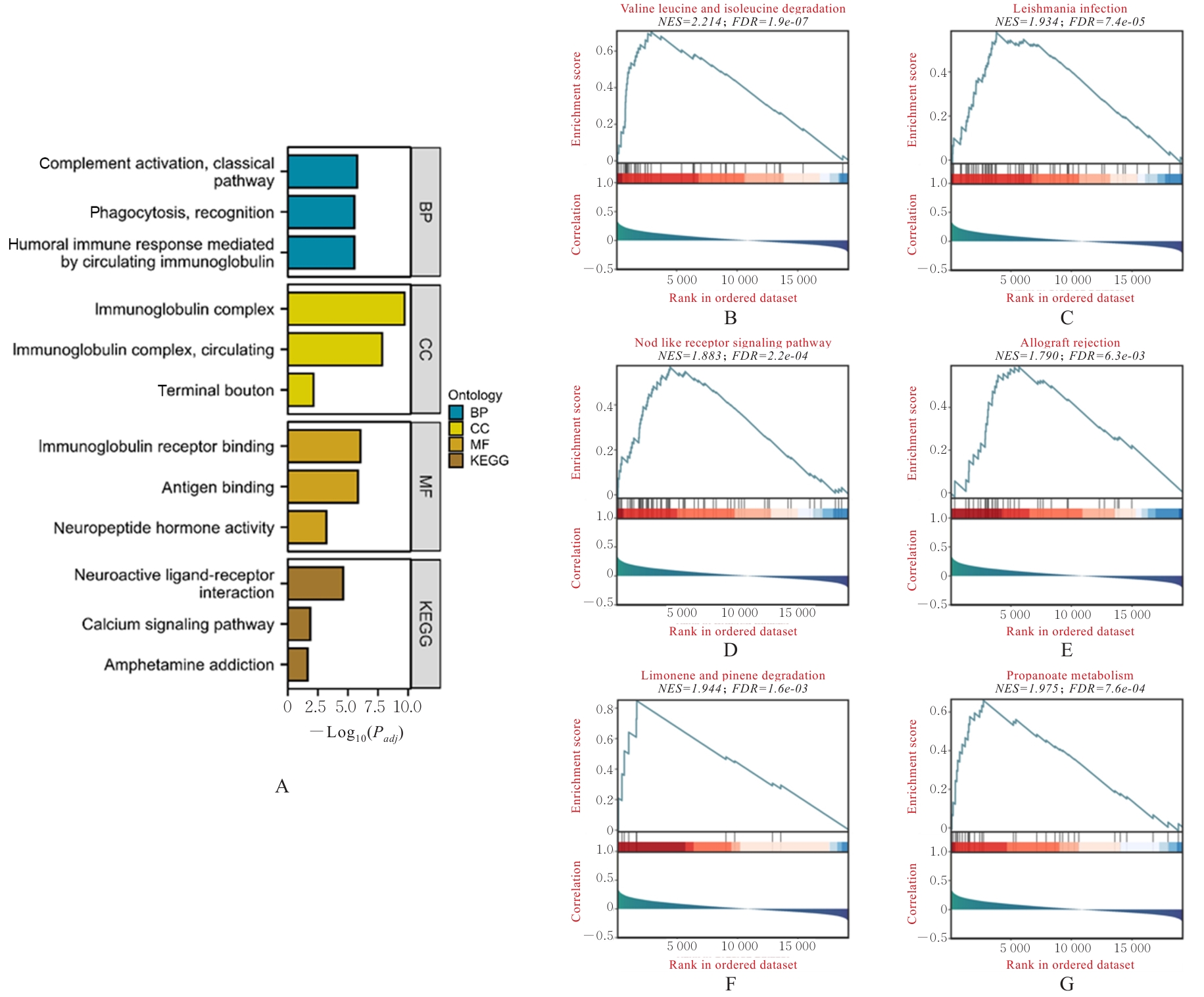
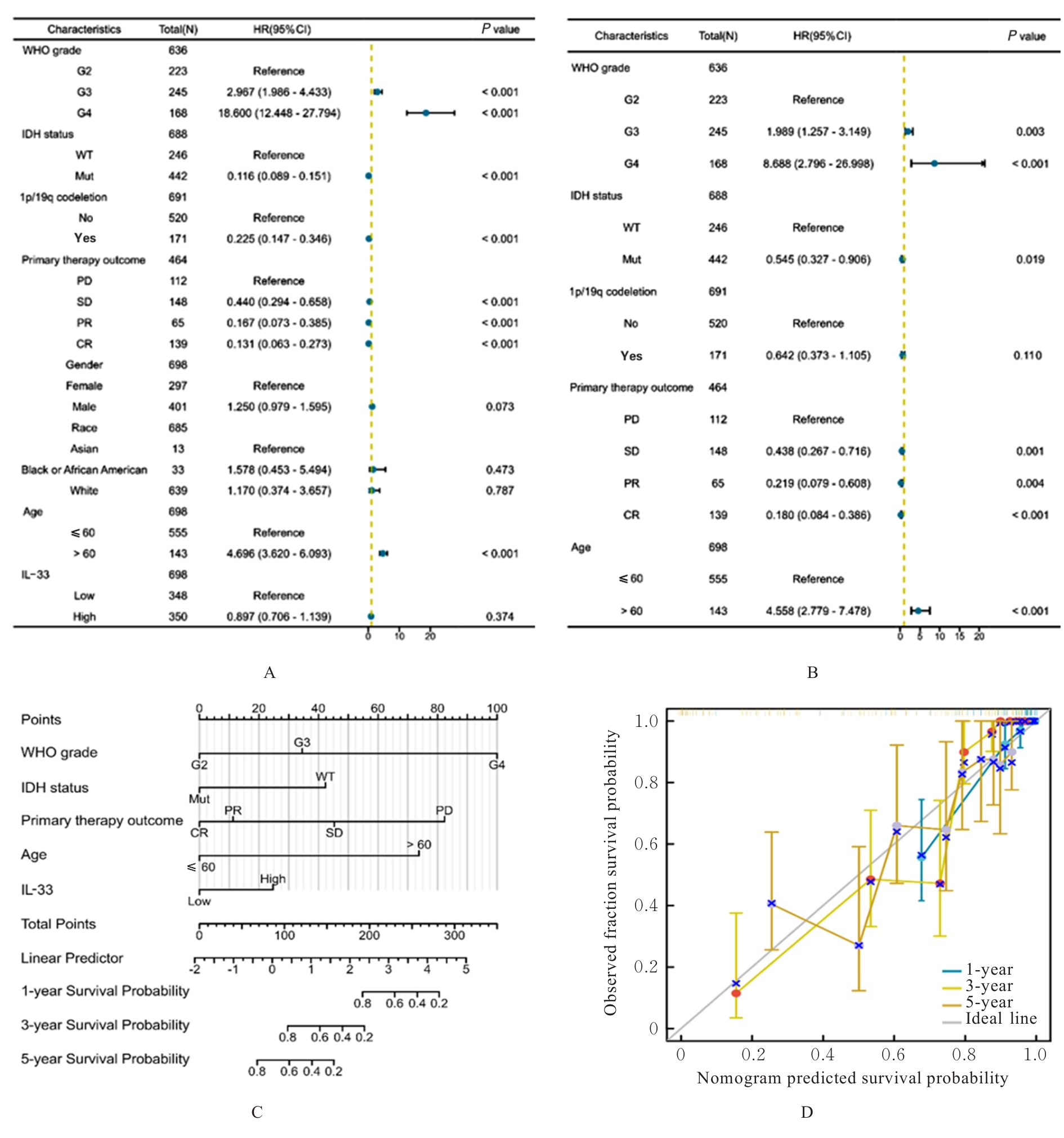
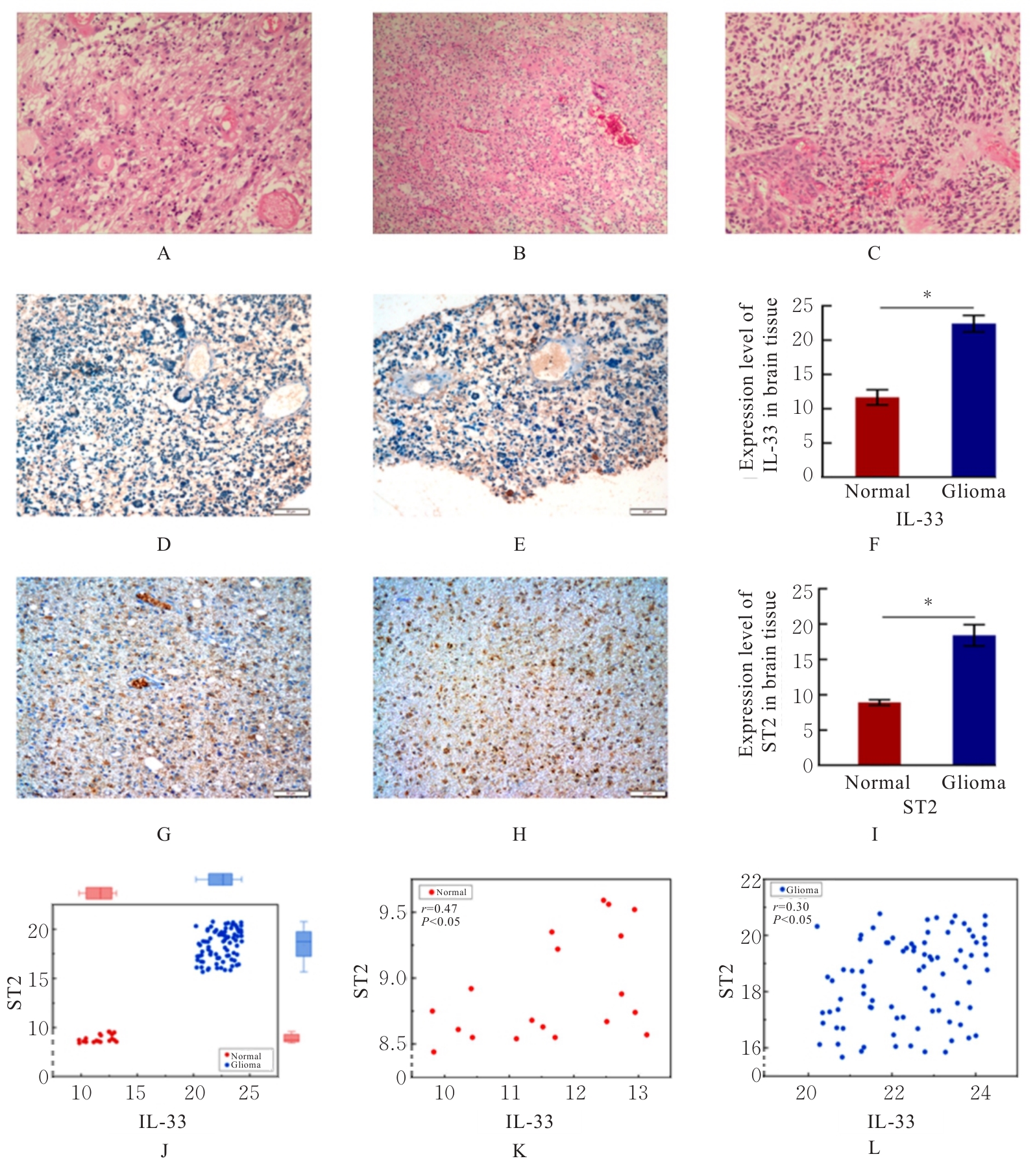
| [1] |
OSTROM Q T, PATIL N, CIOFFI G, et al. CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2013-2017[J]. Neuro Oncol, 2020, 22(12 ): iv1-iv96.
|
| [2] |
OSTROM Q T, CIOFFI G, WAITE K, et al. CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2014-2018[J]. Neuro Oncol, 2021, 23(12 ): iii1-iii105
|
| [3] |
LOUIS D N, PERRY A, WESSELING P, et al. The 2021 WHO classification of tumors of the central nervous system: a summary[J]. Neuro Oncol, 2021, 23(8): 1231-1251.
|
| [4] |
SCHAFF L R, MELLINGHOFF I K. Glioblastoma and other primary brain malignancies in adults: a review[J]. JAMA, 2023, 329(7): 574-587.
|
| [5] |
聂 宏, 仲斌演, 沈 健, 等. 酪氨酸激酶抑制剂联合免疫检查点抑制剂在中晚期肝细胞癌二线治疗中的效果及安全性分析[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2024, 40(8): 1620-1626.
|
| [6] |
RECK M, REMON J, HELLMANN M D. First-line immunotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2022, 40(6): 586-597.
|
| [7] |
YASINJAN F, XING Y, GENG H Y, et al. Immunotherapy: a promising approach for glioma treatment[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1255611.
|
| [8] |
TODO T, ITO H, INO Y, et al. Intratumoral oncolytic herpes virus G47∆ for residual or recurrent glioblastoma: a phase 2 trial[J]. Nat Med, 2022, 28(8): 1630-1639.
|
| [9] |
高 云, 葛俊苗, 王 烜, 等. WDR82在神经胶质瘤发生发展中的作用及其机制[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2024, 49(7): 832-840.
|
| [10] |
CANNAVÒ S P, BERTINO L, DI SALVO E, et al. Possible roles of IL-33 in the innate-adaptive immune crosstalk of psoriasis pathogenesis[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2019, 2019: 7158014.
|
| [11] |
BROG R A, FERRY S L, SCHIEBOUT C T, et al. Superkine IL-2 and IL-33 armored CAR T cells reshape the tumor microenvironment and reduce growth of multiple solid tumors[J]. Cancer Immunol Res, 2022, 10(8): 962-977.
|
| [12] |
ROBBINS S M, SENGER D L. To promote or inhibit glioma progression, that is the question for IL-33[J]. Cell Stress, 2020, 5(1): 19-22.
|
| [13] |
DE BOECK A, AHN B Y, D’MELLO C, et al. Glioma-derived IL-33 orchestrates an inflammatory brain tumor microenvironment that accelerates glioma progression[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 4997.
|
| [14] |
VIVIAN J, RAO A A, NOTHAFT F A, et al. Toil enables reproducible, open source, big biomedical data analyses[J]. Nat Biotechnol, 2017, 35(4): 314-316.
|
| [15] |
LOVE M I, HUBER W, ANDERS S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2[J]. Genome Biol, 2014, 15(12): 550.
|
| [16] |
YU G C, WANG L G, HAN Y Y, et al. clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters[J]. OMICS, 2012, 16(5): 284-287.
|
| [17] |
HÄNZELMANN S, CASTELO R, GUINNEY J. GSVA gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2013, 14: 7.
|
| [18] |
BINDEA G, MLECNIK B, TOSOLINI M, et al. Spatiotemporal dynamics of intratumoral immune cells reveal the immune landscape in human cancer[J]. Immunity, 2013, 39(4): 782-795.
|
| [19] |
LIU J F, LICHTENBERG T, HOADLEY K A, et al. An integrated TCGA pan-cancer clinical data resource to drive high-quality survival outcome analytics[J]. Cell, 2018, 173(2): 400-416.e11.
|
| [20] |
MILLER K D, OSTROM Q T, KRUCHKO C, et al. Brain and other central nervous system tumor statistics, 2021[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(5): 381-406.
|
| [21] |
SIM J, PARK J, MOON J S, et al. Dysregulation of inflammasome activation in glioma[J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2023, 21(1): 239.
|
| [22] |
孙玉学, 刘自强, 吴 豪, 等. 小檗碱对人胶质瘤T98G细胞迁移和侵袭的抑制作用及其机制[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2024, 50(1): 50-57.
|
| [23] |
何涛, 李振江, 丁炳谦. 川芎嗪对胶质瘤干细胞裸鼠皮下移植瘤生长、TGF-β信号通路和上皮-间质转化的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2023, 49(6): 1437-1444.
|
| [24] |
YAN Y J, BAI S W, HAN H X, et al. Knockdown of trem2 promotes proinflammatory microglia and inhibits glioma progression via the JAK2/STAT3 and NF-κB pathways[J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2024, 22(1): 272.
|
| [25] |
TANIGUCHI S, ELHANCE A, VAN DUZER A, et al. Tumor-initiating cells establish an IL-33-TGF-β niche signaling loop to promote cancer progression[J]. Science, 2020, 369(6501): eaay1813.
|
| [26] |
SSHANI O, VOROBYOV T, MONTERAN L, et al. Fibroblast-derived IL33 facilitates breast cancer metastasis by modifying the immune microenvironment and driving type 2 immunity[J]. Cancer Res, 2020, 80(23): 5317-5329.
|
| [27] |
DIXIT A, SARVER A, ZETTERVALL J, et al. Targeting TNF-α-producing macrophages activates antitumor immunity in pancreatic cancer via IL-33 signaling[J]. JCI Insight, 2022, 7(22): e153242.
|
| [28] |
白成霞, 赵 腾, 肖梓屾, 等. IL-33及其受体ST2在前列腺癌组织中的表达及意义[J]. 北华大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 24(2): 179-184.
|
| [29] |
LIU X Q, HANSEN D M, TIMKO N J, et al. Association between interleukin-33 and ovarian cancer[J]. Oncol Rep, 2019, 41(2): 1045-1050.
|
| [30] |
ZHU Z, WANG J, TAN J, et al. Calcyphosine promotes the proliferation of glioma cells and serves as a potential therapeutic target[J]. J Pathol, 2021, 255(4): 374-386.
|
| [31] |
MANGOGNA A, BELMONTE B, AGOSTINIS C, et al. Prognostic implications of the complement protein C1q in gliomas[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 2366.
|
| [32] |
WEI X Q, PAN S S, WANG Z R, et al. LAIR1 drives glioma progression by nuclear focal adhesion kinase dependent expressions of cyclin D1 and immunosuppressive chemokines/cytokines[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2023, 14(10): 684.
|
| [33] |
PANDEY J P, KAUR N, COSTA S, et al. Immunoglobulin genes implicated in glioma risk[J]. Oncoimmunology, 2014, 3: e28609.
|
| [34] |
PEI Z, LEE K C, KHAN A, et al. Pathway analysis of glutamate-mediated, calcium-related signaling in glioma progression[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2020, 176: 113814.
|
| [35] |
SAXENA S, JHA S. Role of NOD- like receptors in glioma angiogenesis: insights into future therapeutic interventions[J]. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, 2017, 34: 15-26.
|
| [36] |
CHARLES N, OZAWA T, SQUATRITO M, et al. Perivascular nitric oxide activates Notch signaling and promotes stem-like character in PDGF-induced glioma cells[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2010, 6(2): 141-152.
|
| [37] |
ZHOU J, LI L H, JIA M Q, et al. Dendritic cell vaccines improve the glioma microenvironment: Influence, challenges, and future directions[J]. Cancer Med, 2023, 12(6): 7207-7221.
|
| [38] |
ZHAO B H, KILIAN M, BUNSE T, et al. Tumor-reactive T helper cells in the context of vaccination against glioma[J]. Cancer Cell, 2023, 41(11): 1829-1834.
|
| [39] |
LOGINOVA N, ANISKIN D, TIMASHEV P, et al. GBM immunotherapy: macrophage impacts[J]. Immunol Invest, 2024, 53(5): 730-751.
|
| [40] |
ERICES J I, BIZAMA C, NIECHI I, et al. Glioblastoma microenvironment and invasiveness: new insights and therapeutic targets[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(8): 7047.
|
| [41] |
CURRAN C S, BERTICS P J. Eosinophils in glioblastoma biology[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2012, 9(1): 11.
|
| [42] |
HAN S E, LIU Y, CAI S J, et al. IDH mutation in glioma: molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets[J]. Br J Cancer, 2020, 122(11): 1580-1589.
|
 )
)