Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (6): 1455-1461.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210615
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Protective effect of exogenous nerve growth factor on scleral tissue of guinea pigs with form-deprived myopia and its mechanism
Xin ZHANG,Chaojuan JU( ),Xin JIN,Chaohui XIONG,Yan ZHAO
),Xin JIN,Chaohui XIONG,Yan ZHAO
- Department of Ophthalmology,First Hospital,Hebei Medical University,Shijiazhuang 050031,China
-
Received:2020-09-04Online:2021-11-28Published:2021-12-14 -
Contact:Chaojuan JU E-mail:xinzh1978@163.com
CLC Number:
- R788.1
Cite this article
Xin ZHANG,Chaojuan JU,Xin JIN,Chaohui XIONG,Yan ZHAO. Protective effect of exogenous nerve growth factor on scleral tissue of guinea pigs with form-deprived myopia and its mechanism[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(6): 1455-1461.
share this article
Tab. 1
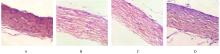
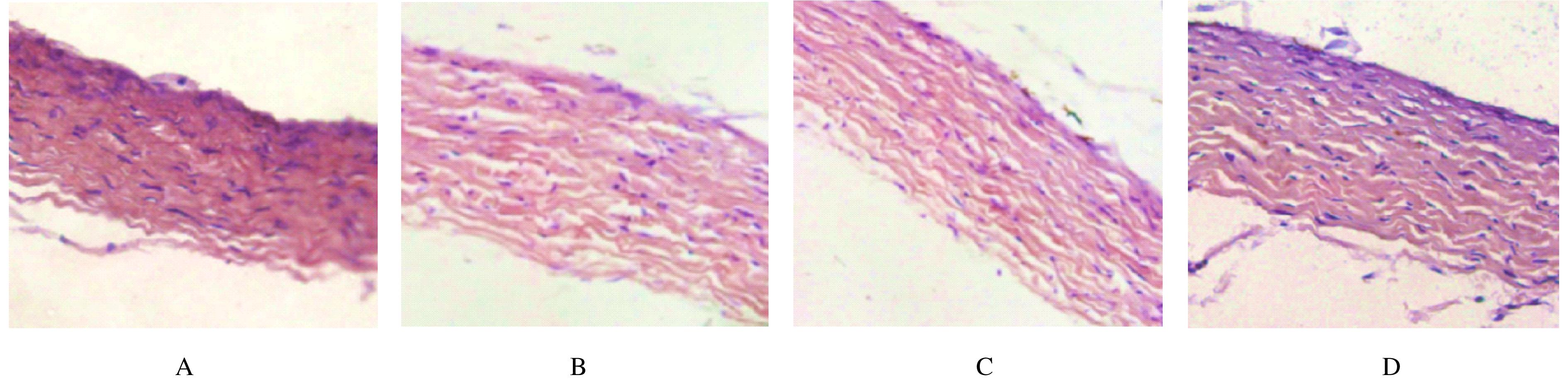
D and axis lengths of eyes of guinea pigs in various groups"
| Group | D | Axis length of eye (l/mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right eye | Left eye | Right eye | Left eye | |
| Control | 3.42±0.28 | 3.36±0.31 | 7.34±0.20 | 7.40±0.23 |
| Model | 0.75±0.16* | 3.40±0.48 | 10.17±0.34* | 7.56±0.28 |
| NGF | ||||
| Low concentration | 1.60±0.50△ | 3.33±0.41 | 8.93±0.37△ | 7.50±0.22 |
| High concentration | 2.21±0.62△# | 3.43±0.44 | 8.06±0.36△# | 7.44±0.30 |
Tab.2
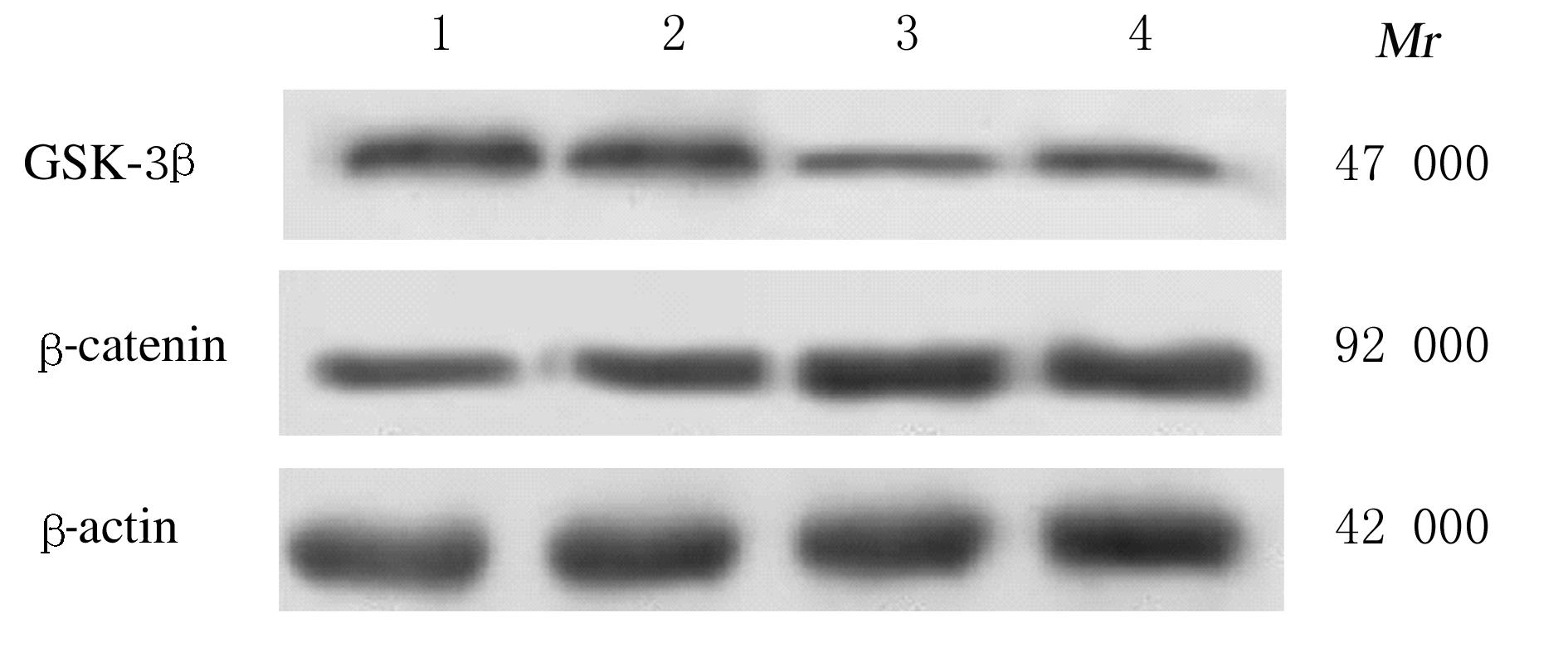
Expression levels of GSK-3β, β-catenin, and VEGF mRNA in scleral tissue of guinea pigs in various groups"
| Group | GSK-3β mRNA | β-catenin mRNA | VEGF mRNA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 0.340±0.021 | 0.162±0.013 | 0.114±0.014 |
| Model | 0.329±0.022 | 0.261±0.019* | 0.293±0.024* |
| NGF | |||
| Low concentration | 0.283±0.023△ | 0.359±0.033△ | 0.342±0.026△ |
| High concentration | 0.215±0.020△# | 0.415±0.029△# | 0.387±0.033△# |
Tab.3
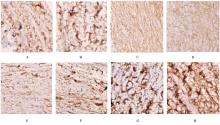
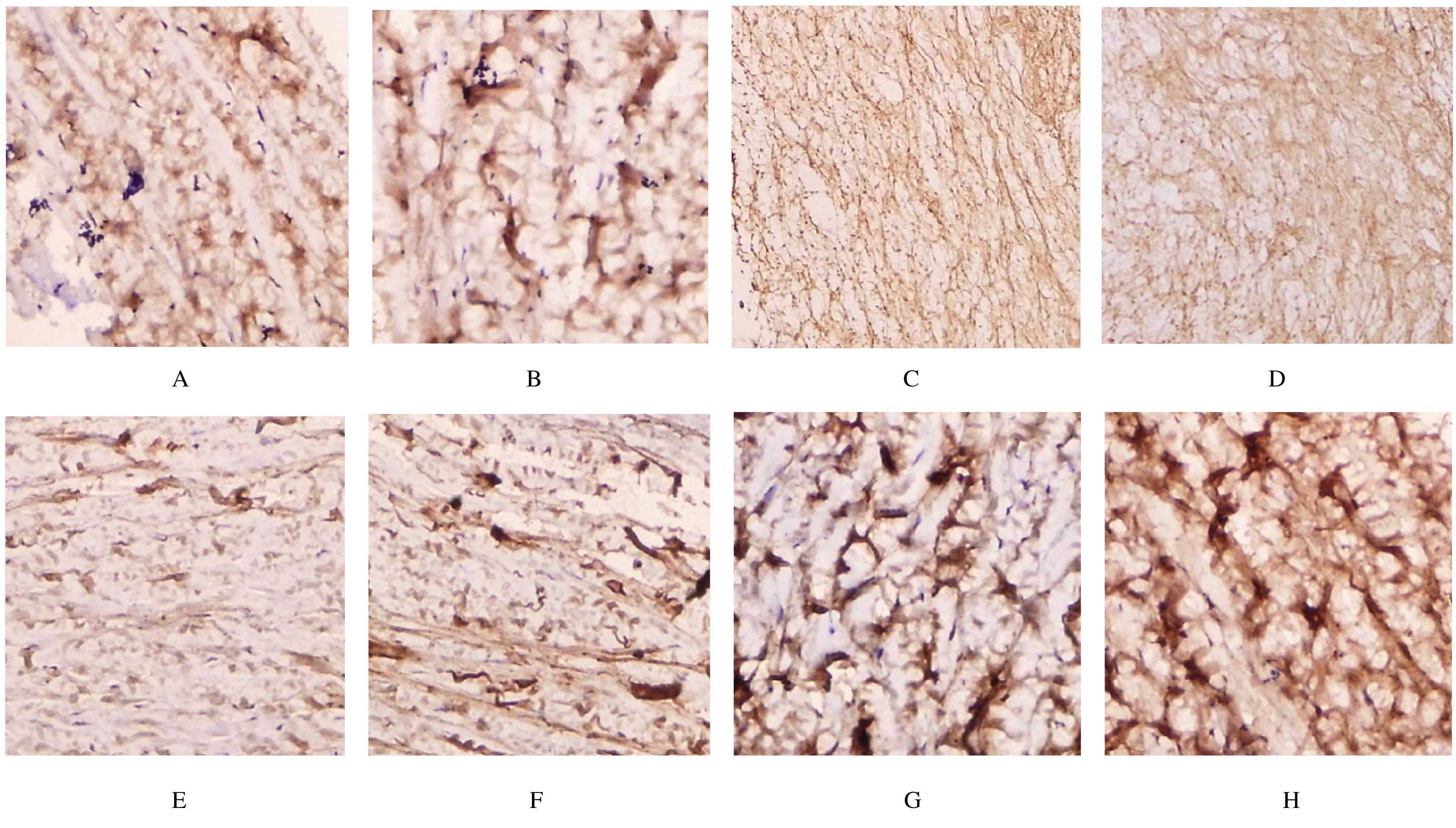
Rates of GSK-3β和β-catenin positive cells in scleral tissue of guinea pigs in various groups"
| Group | Rate of GSK-3β positive cells | Rate of β-catenin positive cells |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 24.32±6.47 | 10.24±5.21 |
| Model | 28.42±7.51 | 32.50±6.05* |
| NGF | ||
| Low concentration | 25.24±5.02 | 37.19±5.43△ |
| High concentration | 24.27±7.87 | 44.22±6.24△# |
| 1 | 周清怡, 赵 斐, 周翔天. 近视巩膜生物力学研究进展[J]. 科技导报, 2018, 36(13): 39-43. |
| 2 | 韦晓丹, 刘 荣, 甘亚平, 等. 高度近视合并青光眼患者视神经纤维层厚度的变化[J]. 国际眼科杂志, 2020, 20(2): 343-345. |
| 3 | MAJIDINIA M, AGHAZADEH J, JAHANBAN-ESFAHLANI R, et al. The roles of Wnt/β-catenin pathway in tissue development and regenerative medicine[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2018, 233(8): 5598-5612. |
| 4 | HU S Y, OUYANG S, LIU H H, et al. The effect of Wnt/β-catenin pathway on the scleral remolding in the mouse during form deprivation[J]. Int Ophthalmol, 2021, 41(9): 3099-3107. |
| 5 | 张 新, 巨朝娟, 张 剑, 等. 形觉剥夺性近视模型大鼠巩膜成纤维细胞中TGF-β1表达及Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的调控作用[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2019, 45(4): 861-866. |
| 6 | 杨 畅, 张宝辉, 刘玉丽, 等. 外源性神经生长因子对APP/PS1转基因小鼠Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的调节[J]. 解剖学杂志, 2015, 38(2): 129-132,152. |
| 7 | 吕晓彤, 宋彦铮, 张丰菊. 近视眼相关Lumican基因突变对人巩膜成纤维细胞中bFGF和TGF-β2的影响[J]. 中华眼科杂志, 2021, 57(4): 277-283. |
| 8 | HSIAO Y, CAO Y, YUE Y, et al. Relationship between axial length and levels of TGF-β in the aqueous humor and plasma of myopic patients[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2021, 2021: 8863637. |
| 9 | ZIDAN H E, REZK N A, FOUDA S M, et al. Association of insulin-like growth factor-1 gene polymorphisms with different types of myopia in Egyptian patients[J]. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers, 2016, 20(6): 291-296. |
| 10 | ZHANG D, DENG Z, TAN J, et al. All-trans retinoic acid stimulates the secretion of TGF-β2 via the phospholipase C but not the adenylyl cyclase signaling pathway in retinal pigment epithelium cells[J]. BMC Ophthalmol, 2019, 19(1): 23. |
| 11 | 姜 波, 史春生, 吴章友, 等. 豚鼠近视模型中屈光度眼轴长度及巩膜Ⅰ型胶原纤维变化的研究[J]. 安徽医学, 2018, 39(3): 256-260. |
| 12 | 肖 博, 王红燕, 楚艳华. 病理性近视的发病机制及治疗的研究进展[J]. 中国城乡企业卫生, 2018, 33(3): 51-54. |
| 13 | VACIK T, STUBBS J L, LEMKE G. A novel mechanism for the transcriptional regulation of Wnt signaling in development[J].Genes Dev,2011,25(17): 1783-1795. |
| 14 | 董新岩, 任 珺, 盛建中. GSK-3β在相关疾病中的作用及致病机制的研究进展[J]. 生理科学进展,2018,49(2): 87-91. |
| 15 | 蔺海旗, 唐 璐, 吴菊花, 等. 运动调节Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的研究进展[J]. 生命的化学, 2020, 40(8): 1358-1364. |
| 16 | 田楠楠, 亢泽峰, 张 庆. 加减驻景方对病理性近视脉络膜新生血管动物模型血管内皮生长因子及色素上皮衍生因子表达的影响[J]. 眼科新进展, 2015, 35(10): 906-908. |
| 17 | SUO N C, LEI C L, ZHANG Y C, et al. Effects of latanoprost on the expression of TGF-β1 and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in the choroid of form-deprivation myopia rats[J]. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-Le-Grand), 2020, 66(6): 71-75. |
| 18 | PENG M, WEI Y, ZHANG Z, et al. Increased levels of DKK1 in vitreous fluid of patients with pathological myopia and the correlation between DKK1 levels and axial length[J]. Curr Eye Res, 2020, 45(1): 104-110. |
| 19 | 李慧勇, 彭余江, 何玺君, 等. 过表达NGF的间充质干细胞对神经元损伤的修复作用研究[J]. 浙江医学, 2018, 40(19): 2126-2129. |
| 20 | 余 娜, 朱克俭, 马思静, 等. 臭牡丹总黄酮通过调控Wnt/β-catenin通路影响A549细胞上皮间质转化研究[J]. 中草药, 2018, 49(3): 663-670. |
| 21 | GAO K, WANG Y S, YUAN Y J, et al. Neuroprotective effect of rapamycin on spinal cord injury via activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway[J]. Neural Regen Res, 2015, 10(6): 951-957. |
| [1] | Chengyuan HE,Hongyu YANG,Yujing TAN,Hang SU,Hongshu LI,Chun LI. Expression of IL-17A in non-small cell lung cancer tissue and its regulation on VEGF expression via NF-κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 1003-1009. |
| [2] | Yuanliang DU,Wang REN,Lin LIU,Shuodan HU,Mingyu LIU,Pengfei DU,Xiumei FU. Effect of Schwann cell-like cells on growth of neurites and expression of nerve growth factor in dorsal root ganglion cells of rats and their mechanisms [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(3): 684-691. |
| [3] | Siyu LI,Min ZHAO,Maoling YANG,Nong XIAO,Wei JIANG. Regulatory effect of retinoic acid on proliferation of hippocampal neural stem cells after hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in rats via GSK-3β [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(5): 1077-1085. |
| [4] | Dongli ZHANG,Ruifang FU,Guixia SUN. Effect of oxymatrine on proliferation and apoptosis of cervical cancer SiHa cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(4): 951-957. |
| [5] | Zhenhui MA,shulian LYU,Yaping TIAN. Effects of Bozhi glycopeptide on proliferation and adhesion function of human keratinocytes and its mechanism in treatment of psoriasis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(4): 965-970. |
| [6] | Yingjun REN, Hui ZHANG, Ying ZHOU. Inhibitory effects of centromere protein U knockdown on self-renewal, cisplatin resistance and Wnt/β-catenin signaling activity in cisplatin resistant ovarian cancer cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(3): 608-614. |
| [7] | Bo WANG,Yan YANG,Rui FEI,Niancai JING,Zhaodong LI,Yi LU,Hongyu XIAO,Yue ZHANG. Inhibitory effect of Shuganhuazheng Formula on growth of triple negative breast cancer of subcutaneous transplantation in mice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 299-306. |
| [8] | Haoxuan TANG,Nanfeng MENG,Meiling DU,Wei WANG,Tao HE. Inhibitory effect of new VEGF monoclonal antibody combined with all-trans retinoic acid on proliferation of breast cancer MCF-7 cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 344-351. |
| [9] | Zishen XIAO,Shuteng DIAO,Lishuang ZHANG,Jie LIU,Lijuan YANG,Xinyu FENG,Zhenjiang WANG,Yanbo LIU. Promotion effect of IL-17A on migration of prostatic cancer cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(6): 1194-1201. |
| [10] | Xiao LI,Zhenhui MA,Yuanyuan WANG,Yaping TIAN. Effects of Astragalus Injection on proliferation and adhesion function of human keratinocytes and its mechanism in treatment of psoriasis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(6): 1202-1207. |
| [11] | Jinghai DU,Xin GUO. Effects of BTg-3 on proliferation, invasion, migration and WNT / β-catenin signaling pathway of thyroid follicular carcinoma cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(6): 1234-1240. |
| [12] | CHEN Yan, PAN Dianzhu, LIU Zhong, MA Yanmei, ZHANG Lan. Inhibitory effect of sileneing Frat2 on NCI-H1688 cells and its Wnt/β catenin signaling pathway mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 751-758. |
| [13] | BU Yi, ZHANG Shuo, QIAN Xudong, WANG Hongmei, DOU Zhijie. Expression of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 in ischemic brain tissue of cerebral infarction model rats and its relationship with angiogenesis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 759-764. |
| [14] | LIU Jing, WANG Jing, GE Jing, FENG Yanping, FANG Guiying, WANG Xu, YANG Yanhong, LI Lin. Effect of HeLa cell exosomes on migration and invasion and its mechanism of Wnt/ β-catenin signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(04): 798-803. |
| [15] | DENG Yuening, ZHOU Daan, MA Xiande, CHEN Dan, SHI Dan, JIANG Yanan. Effects of electro-acupuncture on urodynamics and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in rats with neurogenic bladder after T10 spinal cord transection [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(02): 221-227. |
|