Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1): 58-70.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240108
• Research in basic medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Network pharmacological analysis on Balanophora involucrataHook.f. in treatment of hyperuricemia and its therapeutic effect on hyperuricemia cell model and hyperuricemia model mouse
Li LIU1,2,Linsheng HUANG3,Yongheng ZHAO1,Wenjie CAO1,2,Yongshuai QIAN1,2,Huifan YU1,2,Fei LI1,2( )
)
- 1.College of Pharmaceutical Sciences,Hubei Medical College,Shiyan 442000,China
2.Key Laboratory of Wudang Local Chinese Medicine Research,Hubei Medical College,Shiyan 442000,China
3.Department of Hepatopancreatobiliary Surgery,Taihe Hospital,Shiyan City,Hubei Province,Shiyan 442000,China
-
Received:2023-02-12Online:2024-01-28Published:2024-01-31 -
Contact:Fei LI E-mail:piaopodexinlifei@163.com
CLC Number:
- R285.5
Cite this article
Li LIU,Linsheng HUANG,Yongheng ZHAO,Wenjie CAO,Yongshuai QIAN,Huifan YU,Fei LI. Network pharmacological analysis on Balanophora involucrataHook.f. in treatment of hyperuricemia and its therapeutic effect on hyperuricemia cell model and hyperuricemia model mouse[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 58-70.
share this article
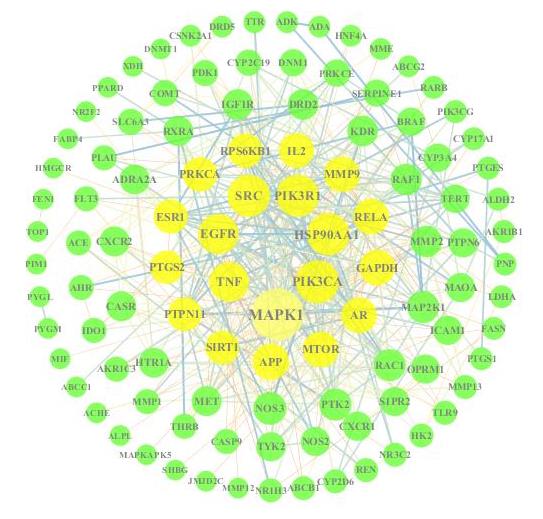
Tab. 1
Active components of Balanophora involucrataHook.f in treatment of hyperuricemia"
| No. | Component | PubChem CID |
|---|---|---|
| SG1 | Coniferin | 5319518 |
| SG2 | Methylconiferin | 5319561 |
| SG3 | Eriodictyol | 440735 |
| SG4 | Methyl brevifolincarboxylate | 5319518 |
| SG5 | Ethyl brevifolincarboxylate | 5487248 |
| SG6 | Gallic acid | 348787247 |
| SG7 | Scaphopetalone | 637239 |
| SG8 | (+)-pinoresinol | 73399 |
| SG9 | (+)-Isolariciresinol | 160521 |
| SG10 | Burselignan | 11631864 |
| SG11 | (-)-Secoisolariciresinol | 6336781 |
| SG12 | Dihydrocubebin | 193042 |
| SG13 | 2,3-Dihydroflavone | 10251 |
SG14 | 3-(3-Methoxy-4-(((2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3, 4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl) tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy)phenyl) acrylaldehyde | - |
| SG15 | Naringenin | 932 |
| SG16 | Homoeriodictyol | 73635 |
| SG17 | Hesperetin | 72281 |
| SG18 | Sakuranetin | 73571 |
| SG19 | Penicillic acid | 1268111 |
| SG20 | Dihydroartemisinic acid | 11020893 |
| SG21 | 2-Methylfuran-3-ylmethanol | 2777165 |
| SG22 | 5-Hydroxymaltol | 70627 |
| SG23 | 5,7-Dihydroxychromone | 5281343 |
| SG24 | 5,7,3′,5′-Tetrahydroxydihydroflavonoid | - |
| SG25 | (+)-9-Acetoxyisolariciresinol | - |
| SG26 | Yunnanensin A | - |
| SG27 | Calycosin-7-O-β-D-glucoside | 5318267 |
| SG28 | β-sitosterol | 222284 |
| SG29 | (E)-1-Caffeoyl-β-D-glucopyranoside | - |
| SG30 | (E)-1-O-p-coumaroyl-β-D-glucopyranoside | - |
| “-”:No data. | ||
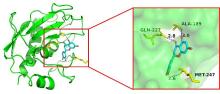
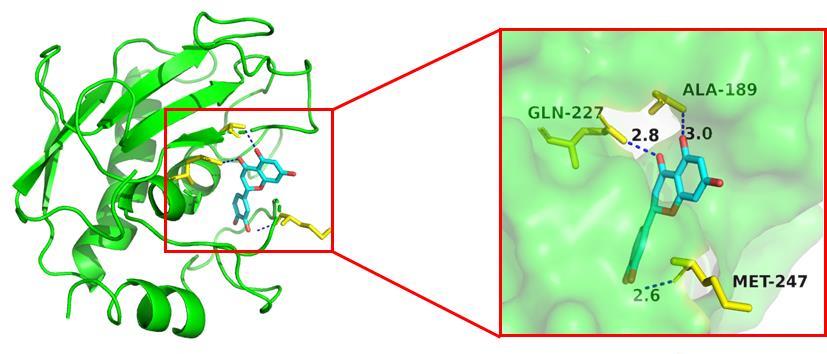
Tab. 2
Molecular docking results"
| Target | PDB ID | Affinity(kcal·mol-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gallic acid | 5-hydroxy maltol | (+)-pinoresinol | 5,7-dihydroxy chromone | Penicillic acid | Eriodictyol | ||
| MAPK1 | 6SLG | -5.8 | -4.9 | -7.3 | -5.9 | -5.2 | -7.3 |
| PIK3CA | 5DXT | -6.2 | -5.8 | -8.3 | -6.5 | -5.2 | -9.2 |
| HSP90AA1 | 4BQG | -5.9 | -5.1 | -8.1 | -7.0 | -5.5 | -9.8 |
| PIK3R1 | 5GJI | -6.7 | -6.3 | -7.3 | -7.0 | -6.1 | -7.9 |
| SRC | 2BDF | -6.1 | -5.3 | -8.0 | -6.6 | -5.1 | -8.5 |
| EGFR | 3W2S | -6.2 | -5.4 | -8.3 | -6.4 | -5.0 | -9.1 |
| TNF | 2ZA5 | -6.6 | -6.2 | -6.9 | -6.5 | -4.3 | -7.0 |
| APP | 3KTM | -6.1 | -5.3 | -7.4 | -6.5 | -5.0 | -8.4 |
| AR | 1E3G | -6.4 | -5.8 | -8.4 | -7.7 | -5.5 | -9.2 |
| GAPDH | 1U8F | -6.7 | -5.8 | -8.9 | -6.7 | -5.2 | -9.4 |
| RELA | 1NFI | -5.7 | -5.5 | -7.6 | -6.1 | -4.8 | -8.8 |
| MMP-9 | 6ESM | -7.1 | -6.3 | -8.2 | -7.8 | -5.8 | -10.8 |
| MTOR | 5WBH | -5.6 | -5.3 | -7.2 | -6.4 | -5.1 | -8.4 |
| IL-2 | 1M48 | -5.4 | -5.1 | -8.2 | -6.3 | -5.0 | -7.4 |
Tab. 5
Levels of serum UA, Cr, BUN and kidney indexes of mice in various groups"
| Group | UA [cB/(μmol·L-1)] | Cr [cB /(μmol·L-1)] | BUN [cB /(mmol·L-1)] | Kidney index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank control | 37.32±1.71 | 34.38±1.06 | 7.46±0.67 | 1.58±0.05 |
| Blank administration | 39.75±1.01 | 32.05±1.33 | 8.37±0.43 | 1.60±0.04 |
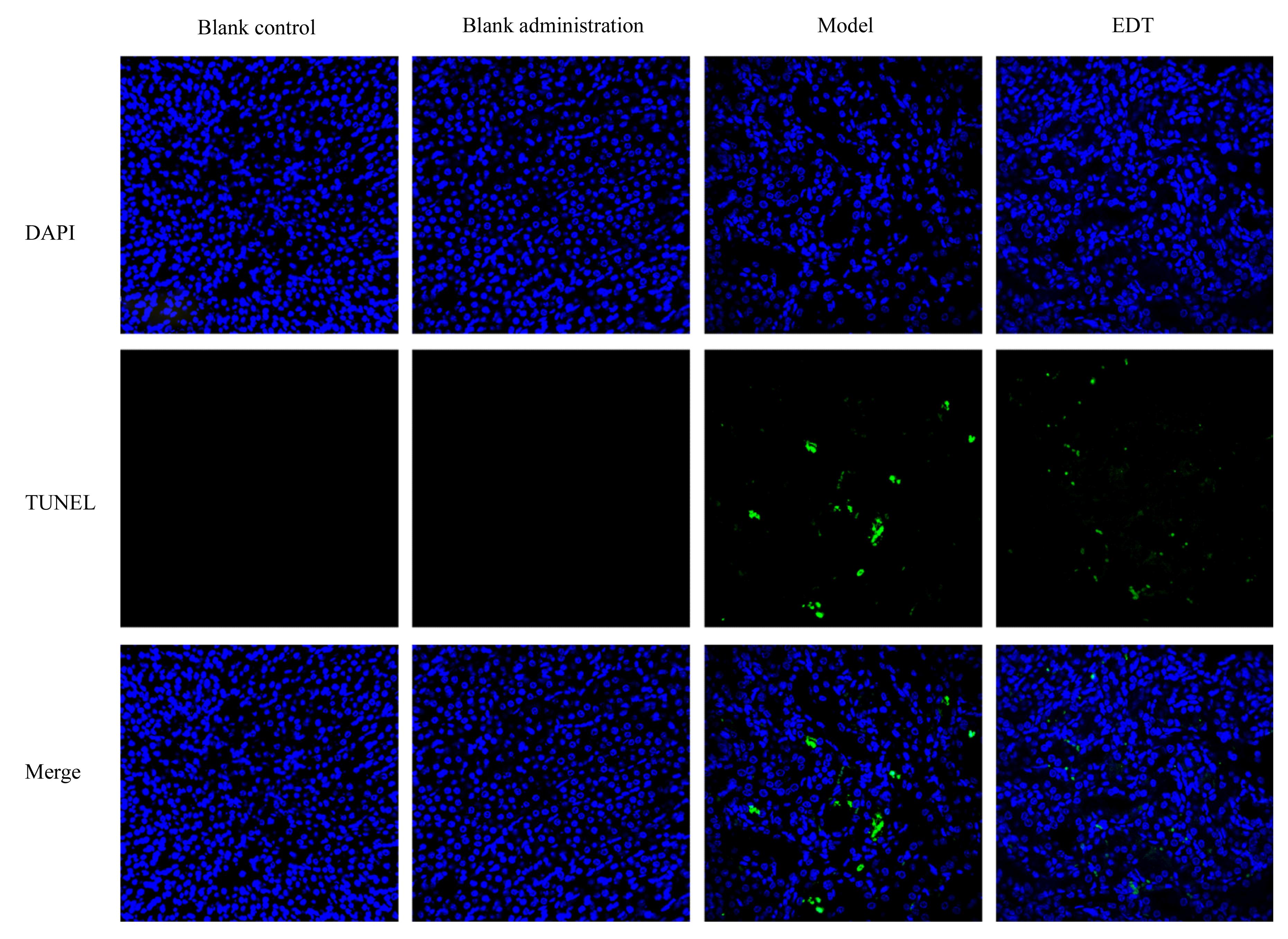
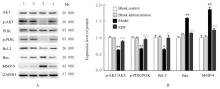
| Model | 831.57±20.82* | 110.14±0.64* | 27.99±0.93* | 2.70±0.04* |
| EDT | 384.31±22.93△△ | 64.99±4.74△△ | 23.32±0.56△△ | 2.42±0.08△ |
| 1 | YOKOSE C, MCCORMICK N, CHOI H K. The role of diet in hyperuricemia and gout[J]. Curr Opin Rheumatol, 2021, 33(2): 135-144. |
| 2 | DALBETH N, MERRIMAN T R, STAMP L K. Gout[J]. Lancet, 2016, 388(10055): 2039-2052. |
| 3 | ROBINSON P C. Gout-An update of aetiology, genetics, co-morbidities and management[J]. Maturitas, 2018, 118: 67-73. |
| 4 | REY A, BATTEUX B, LAVILLE S M, et al. Acute kidney injury associated with febuxostat and allopurinol: a post-marketing study[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2019, 21(1): 229. |
| 5 | 郭钦惠, 方 宏, 陈俊文, 等. 非布司他药物相关不良反应文献分析[J]. 中国医学创新, 2020, 17(22): 104-107. |
| 6 | 袁 华, 李静华, 封宇飞. 114例别嘌醇不良反应文献分析[J]. 中国药物应用与监测, 2016, 13(6): 359-362. |
| 7 | 傅恒涛, 张 苗, 慈小燕, 等. 治疗痛风和高尿酸血症药物的研究进展[J]. 药物评价研究, 2021, 44(8): 1811-1816. |
| 8 | 中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会. 中国植物志·第三十九卷[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1988: 250-268. |
| 9 | 阮汉利, 张勇慧, 皮慧芳, 等. 蛇菰的化学成分研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 2006, 18(1): 74-75. |
| 10 | 阮汉利, 李 娟, 赵晓亚, 等. 筒鞘蛇菰镇痛有效部位的筛选[J]. 医药导报, 2006, 25(5): 383-384. |
| 11 | SUN X, ZHANG L, CAO Y, et al. Anti-neuraminidase activity of chemical constituents of Balanophora involucrata[J]. Biomed Chromatogr, 2020, 34(12): e4949. |
| 12 | 周卫华, 石慧娟, 杨梅松竹, 等. 蛇菰水提物对大鼠酒精性肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2012, 32(20): 4438-4440. |
| 13 | 汤子春, 邹 坤, 汪鋆植, 等. 开口箭与筒鞘蛇菰提取物醒酒作用机制的研究[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2007, 18(12): 2958-2960. |
| 14 | 黄徐英, 宋红萍, 柳 鑫, 等. 筒鞘蛇菰乙酸乙酯萃取物的止血作用[J]. 医药导报, 2019, 38(9): 1160-1162. |
| 15 | 王 慧, 张红歧, 邬昊洋, 等. 筒鞘蛇菰提取物及松柏苷的抗氧化作用研究[J]. 三峡大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 31(3): 99-101. |
| 16 | 何 玲, 高 辉, 李春艳. 筒鞘蛇菰多糖抗疲劳作用研究[J]. 怀化学院学报, 2011, 30(S1): 43-45. |
| 17 | 侯文彬, 周丽丽, 周卫华. 蛇菰水提物对自然衰老小鼠的抗衰老作用研究[J]. 中国民族民间医药, 2012, 21(3): 33. |
| 18 | HO S T, TUNG Y T, HUANG C C, et al. The hypouricemic effect of Balanophora laxiflora extracts and derived phytochemicals in hyperuricemic mice[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2012, 2012: 910152. |
| 19 | WANG Y M, KONG W, WANG L, et al. Multiple-purpose connectivity map analysis reveals the benefits of esculetin to hyperuricemia and renal fibrosis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(20): 7695. |
| 20 | YANAI H, ADACHI H, HAKOSHIMA M, et al. Molecular biological and clinical understanding of the pathophysiology and treatments of hyperuricemia and its association with metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular diseases and chronic kidney disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(17): 9221. |
| 21 | LI Y, SHEN Z Y, ZHU B W, et al. Demographic, regional and temporal trends of hyperuricemia epidemics in mainland China from 2000 to 2019: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Glob Health Action, 2021, 14(1): 1874652. |
| 22 | HOU C L, LIU D, WANG M, et al. Novel xanthine oxidase-based cell model using HK-2 cell for screening antihyperuricemic functional compounds[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2019, 136: 135-145. |
| 23 | 黄佳豪, 李先平, 赵军英, 等. 益生菌缓解高尿酸血症作用机制研究进展 [J/OL]. 食品科学. . |
| 24 | 吴 芃, 王 亮, 李海涛, 等. 高尿酸血症模型的建立及降尿酸药物的研究进展[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2021, 37(7): 1283-1294. |
| 25 | HUBER T B, HARTLEBEN B, KIM J, et al. Nephrin and CD2AP associate with phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase and stimulate AKT-dependent signaling[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2003, 23(14): 4917-4928. |
| 26 | CHEN K Q, LI Y Q, ZHANG X H, et al. The role of the PI3K/AKT signalling pathway in the corneal epithelium: recent updates[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2022, 13(5): 513. |
| 27 | CHEN H J, ZHANG Y, ZOU M M, et al. Bisphenol A aggravates renal apoptosis and necroptosis in selenium-deficient chickens via oxidative stress and PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2022, 237(8): 3292-3304. |
| 28 | YUAN Q, TANG B, ZHANG C. Signaling pathways of chronic kidney diseases, implications for therapeutics[J].Signal Transduct Target Ther,2022,7(1): 182. |
| 29 | EL-MAADAWY W H, HASSAN M, HAFIZ E,et al. Co-treatment with Esculin and erythropoietin protects against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury via P2X7 receptor inhibition and PI3K/Akt activation[J]. Sci Rep, 2022, 12(1): 6239. |
| 30 | HU T T, CHEN F, CHEN D, et al. DNMT3a negatively regulates PTEN to activate the PI3K/AKT pathway to aggravate renal fibrosis[J]. Cell Signal, 2022, 96: 110352. |
| 31 | XIAO Q. Cinnamaldehyde attenuates kidney senescence and injury through PI3K/Akt pathway-mediated autophagy via downregulating miR-155[J]. Ren Fail, 2022, 44(1): 601-614. |
| 32 | 宋璐霞. 温肾益髓生血方对肾性贫血大鼠肾脏的保护作用及对肾组织PI3K/AKT信号通路影响的实验研究[D]. 北京: 北京中医药大学, 2019. |
| 33 | LI Y Y, TIAN Z H, SU S S, et al. Anti-apoptotic effect of HeidihuangWan in renal tubular epithelial cells via PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2023, 302(Pt A): 115882. |
| 34 | 翟志恒, 田 杨, 周玉妮, 等. lncRNA NEAT1激活PI3K/Akt信号通路对Aβ25-35诱导的PC12细胞凋亡的影响及机制[J].解放军医学杂志, 2021,46(12): 1188-1195. |
| 35 | 陈彦名. 加味活血四妙汤干预慢性尿酸性肾病进展的临床及动物实验研究[D]. 北京: 北京中医药大学, 2017. |
| 36 | WOZNIAK J, FLOEGE J, OSTENDORF T, et al. Key metalloproteinase-mediated pathways in the kidney[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2021, 17(8): 513-527. |
| [1] | Yang YU,Dan TIAN,Donghe NI,Duo ZHANG. Network pharmacologry and molecular docking analysis based on mechanism of monk fruit in treatment of diabetic nephropathy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 161-167. |
| [2] | Aiying CHEN,Jinwen JIANG,Hui ZHANG. Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis based on mechanism of Huangqin Tang in treatment of colorectal cancer [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 208-220. |
| [3] | Meng QYU,Yuzhu JIANG,Rui HUANG,Zhenzhuo MA,Jichen XIA,Yuan ZHANG,Zhiheng DONG. Protective effect of ginsenoside Rh2 on kidney injury in rats with diabetic kidney lesions and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1168-1173. |
| [4] | Chunling WANG,Sinuo WU,Xiaoyan YU,Weidong ZHANG. Analysis on network pharmacology and molecular docking technique based on effective chemical components and action targets of epimedium in treatment of hypothalamus-pituitary- adrenal gland/ gonad / thyroid gland axis function damage [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1296-1303. |
| [5] | Sihan LAI,Juntong LIU,Luying TAN,Jinping LIU,Pingya LI. Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis on anti-ischemic stroke mechanism of Panax quinquefolium triolsaponins [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 913-922. |
| [6] | Yumeng LIU,Song LENG, SARENGAOWA,Daijie LIN,Linsheng XIE,Mengrui LI,Xiao XU,Wannan LI. Network pharmacology analysis based on therapeutic effect of Sanghuang on pneumonia and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 923-930. |
| [7] | Yushuang GONG,Yefan FU,Huijing XU,Jian GUO,Lin XIANG,Rui HU,Rui FAN,Jie WANG,Miao LI,Meiyan SUN. Network pharmacology analysis on mechanism of Tonifying Slpeen and Kidney Empirical Prescription in treatment of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 261-271. |
| [8] | Zhouquan LI,Hui LI,Ying TANG,Lijun YANG,Yinghong JIANG,Lipin YIN. Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis on mechanism of Tongluo Tangtai Power in treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 341-350. |
| [9] | Qiaoling YANG,Lu FU,Yu SHI,Yanjue YE,Rifeng LU,Yong LIU,Li YIN. Inhibitory effect of rosiglitazone on ferroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells in mice with acute renal injury induced by lipopolysaccharide and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 351-359. |
| [10] | Minghui WANG,Moyi LIU,Helin WANG,Ying LI,Xiangjun WANG,Hetong HUI,Xinyuan FAN,Tianqi WANG,Limei LIU. Bioinformatics analysis of network pharmacology and molecular docking technology based on mechanism of Physalis Calyx seu Fructus on leukemia [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(1): 74-83. |
| [11] | Shaojie FU,Sensen SU,Yiying CHEN,Zhonggao XU. Analysis on network pharmacology and molecular docking technique based on mechanism of Shenqi Dihuang Decoction in treatment of membranous nephropathy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(6): 1518-1527. |
| [12] | Xin LI,Xu DING,Xiaomeng LIU,Xinchan LIU,Zhou WU,Weixian YU. Effect of silencing information regulator 1 on kidney injury in chronic periodontitis model rats [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(5): 1200-1208. |
| [13] | Yan LI,Yue HOU,Xingwei MU,Bingqing LIU,Hong WAN,Chang LIU,Wei XIA. Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis on mechanism of Schisandrae Chinensis Fructus in occurrence and development of thoracic aortic aneurysm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 414-425. |
| [14] | Xinghua WANG,Hongjuan YANG,Xiuhong HU,Hongrei CUI,Baozhen XU,Danlu LI,Tao WANG,Yuwei GAO. Effects of N-acetyl-L-cysteine on oxidative stress and vascular endothelial function in rats with hyperuricemia and their mechanisms [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(5): 1209-1214. |
| [15] | Liyan ZHU,Yaoming WANG,Zheng QIN,Huanhuan ZHAO,Zengying WANG,Xiuhong YANG. Improvement effect of angiotensin(1-7) on kidney injury induced by limb ischemia-reperfusion in mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(4): 834-841. |
|
||