Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1): 161-167.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240120
• Research in clinical medicine • Previous Articles
Network pharmacologry and molecular docking analysis based on mechanism of monk fruit in treatment of diabetic nephropathy
Yang YU,Dan TIAN,Donghe NI,Duo ZHANG( )
)
- Medical Imaging Center,Affiliated Hospital,Beihua University,Jilin 132011,China
-
Received:2023-01-31Online:2024-01-28Published:2024-01-31 -
Contact:Duo ZHANG E-mail:beihuazhangduo@126.com
CLC Number:
- R285.5
Cite this article
Yang YU,Dan TIAN,Donghe NI,Duo ZHANG. Network pharmacologry and molecular docking analysis based on mechanism of monk fruit in treatment of diabetic nephropathy[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 161-167.
share this article
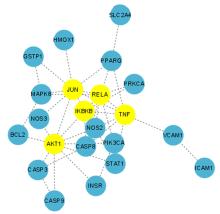
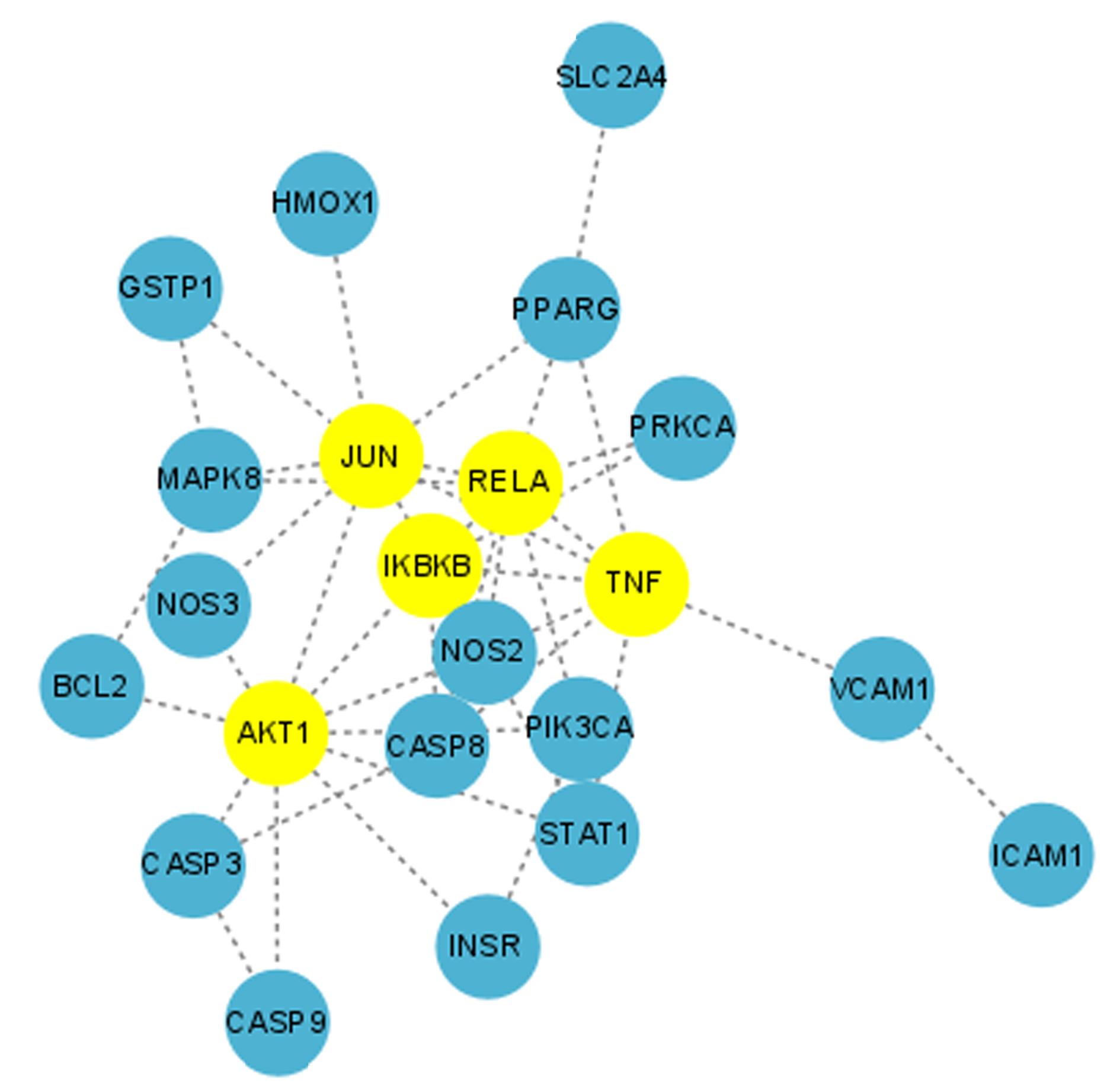
Tab.2
PPI network targets and topological parameters"
| Name | Degree | Closeness | Radiality | Stress | Clustering coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
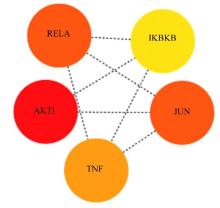
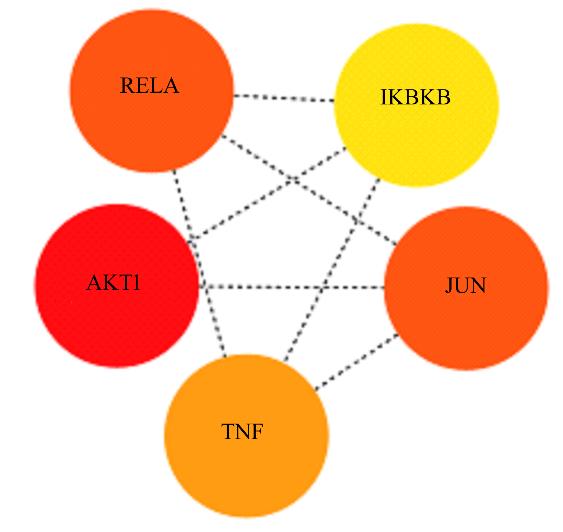
| AKT1 | 10 | 14.916 67 | 4.571 43 | 242 | 0.111 11 |
| RELA | 9 | 14.666 67 | 4.619 05 | 150 | 0.277 78 |
| JUN | 9 | 14.833 33 | 4.666 67 | 210 | 0.250 00 |
| TNF | 8 | 14.000 00 | 4.523 81 | 206 | 0.321 43 |
| IKBKB | 5 | 12.333 33 | 4.333 33 | 62 | 0.400 00 |
| NOS2 | 5 | 12.666 67 | 4.428 57 | 42 | 0.600 00 |
| PPARG | 4 | 11.666 67 | 4.238 10 | 60 | 0.500 00 |
| CASP8 | 4 | 11.333 33 | 4.142 86 | 32 | 0.500 00 |
| MAPK8 | 4 | 11.250 00 | 4.095 24 | 42 | 0.333 33 |
| STAT1 | 3 | 11.000 00 | 4.142 86 | 24 | 0.666 67 |
| CASP3 | 3 | 10.500 00 | 3.952 38 | 18 | 0.333 33 |
| PIK3CA | 3 | 11.083 33 | 4.142 86 | 22 | 0.333 33 |
| PRKCA | 2 | 9.583 33 | 3.809 52 | 0 | 1.000 00 |
| VCAM1 | 2 | 9.250 00 | 3.666 67 | 76 | 0.000 00 |
| GSTP1 | 2 | 9.583 33 | 3.809 52 | 0 | 1.000 00 |
| BCL2 | 2 | 9.866 67 | 3.809 52 | 10 | 0.000 00 |
| CASP9 | 2 | 9.533 33 | 3.714 29 | 0 | 1.000 00 |
| INSR | 2 | 9.533 33 | 3.714 29 | 0 | 1.000 00 |
| NOS3 | 2 | 10.583 33 | 4.095 24 | 0 | 1.000 00 |
| SLC2A4 | 1 | 7.750 00 | 3.285 71 | 0 | 0 |
| ICAM1 | 1 | 6.683 33 | 2.714 29 | 0 | 0 |
| HMOX1 | 1 | 8.916 67 | 3.714 29 | 0 | 0 |
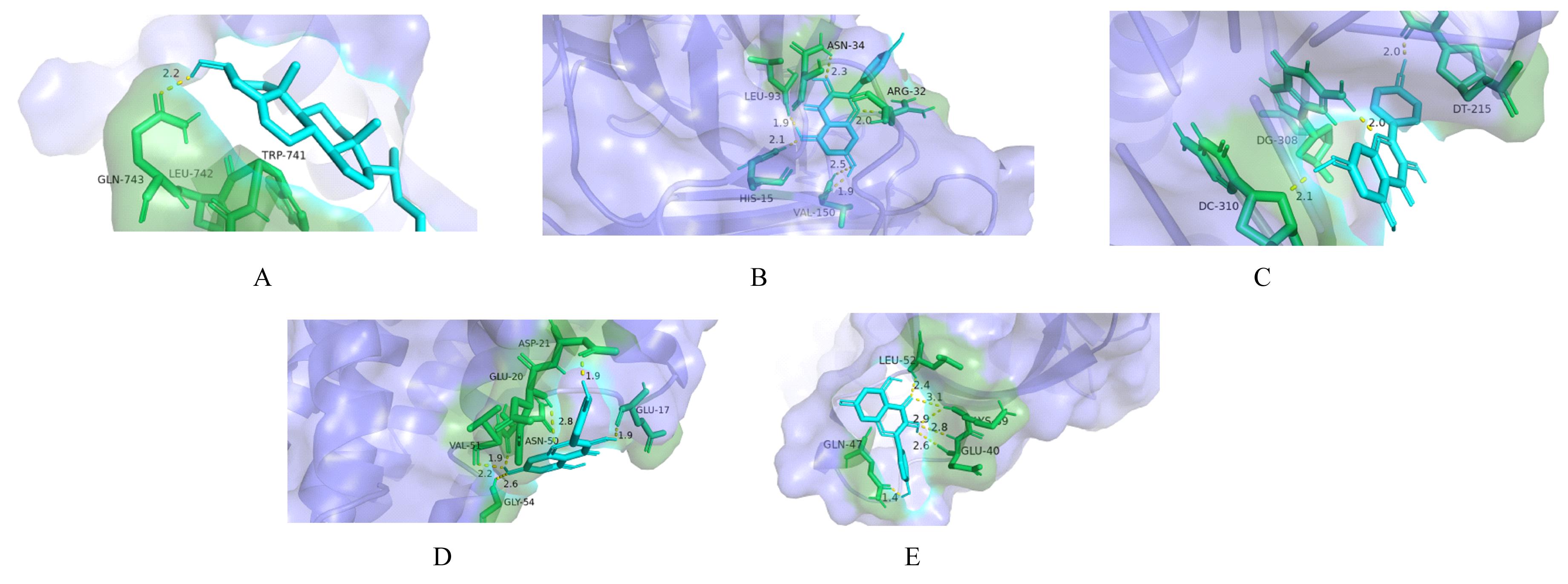
Tab. 3
Binding energy and binding sites between molecular docking of main active ingredients of monk fruit and key targets"
| Protein | Ligand | Affinity(kJ·mol-1) | Binding site |
|---|---|---|---|
| AKT1 | Kaempferol | -6.54 | LEU-52,GLU-40, GLN-47,LYS-59 |
RELA | Kaempferol | -7.18 | ASP-21,GLU-17, GLU-20,VAL-51, ASN-50,GLY-54 |
| JUN | Kaempferol | -5.07 | DT-215,DG-308, DC-310 |
TNF | Kaempferol | -7.32 | ASN-34,LEU-93, ARG-32,HIS-15, VAL-150 |
| IKBKB | Beta-sitosterol | -6.03 | GLN-743,LEU-742, TRP-741 |
| 1 | 莫梓沂, 刘 畅, 薛世圆, 等. 糖尿病肾病发病机制及治疗的研究进展[J]. 局解手术学杂志, 2021, 30(12): 1093-1098. |
| 2 | 陈雪芹, 汪裕伟. 糖尿病肾病治疗进展[J]. 湘南学院学报(医学版), 2022, 24(2): 73-78. |
| 3 | CHO N H, SHAW J E, KARURANGA S, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2018, 138: 271-281. |
| 4 | UMANATH K, LEWIS J B. Update on diabetic nephropathy: core curriculum 2018[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2018, 71(6): 884-895. |
| 5 | 中华医学会糖尿病学分会. 中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2020年版)(上)[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2021,41(8): 668-695. |
| 6 | 徐天华, 姚 丽. 糖尿病肾病诊断及治疗新进展[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2022, 42(12): 1002-1006. |
| 7 | WANG L, WANG Z Y, YANG Z H, et al. Study of the active components and molecular mechanism of Tripterygium wilfordii in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy[J]. Front Mol Biosci, 2021, 8: 664416. |
| 8 | 欧珏平. 罗汉果甜苷提取物对人体代谢的影响研究[J]. 现代食品, 2023, 29(9): 219-221. |
| 9 | 余 华. 系统药理学关键预测技术开发及在中医药研究中的应用[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2013. |
| 10 | 谈建成, 曾思恩. 罗汉果药用功能研究与进展[J]. 中国继续医学教育, 2019, 11(13): 147-149. |
| 11 | 袁 甜, 崔琳琳, 王 莹, 等. 中药网络药理学最新进展[J]. 中医药学报, 2021, 49(1): 101-106. |
| 12 | LI J S, ZHAO Z Z, MIAO X D, et al. Mechanism of Olibanum-Myrrha in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking[J]. China J Chin Mater Med, 2021, 46(10): 2371-2379. |
| 13 | WANG H H, CHEN W L, CUI Y Y, et al. Anhydroicaritin suppresses tumor progression via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Aging, 2023, 15(15): 7831-7843. |
| 14 | PAN J J, YANG H K, ZHU L H, et al. Qingfei Jiedu Decoction inhibits PD-L1 expression in lung adenocarcinoma based on network pharmacology analysis, molecular docking and experimental verification[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 897966. |
| 15 | GUO M F, DAI Y J, GAO J R, et al. Uncovering the mechanism of astragalus membranaceus in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy based on network pharmacology[J]. J Diabetes Res, 2020, 2020: 5947304. |
| 16 | QIANG P P, HAO J, YANG F, et al. Esaxerenone inhibits the macrophage-to-myofibroblast transition through mineralocorticoid receptor/TGF-β1 pathway in mice induced with aldosterone[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 948658. |
| 17 | 徐天华, 姚 丽. 糖尿病肾病诊断及治疗新进展[J].中国实用内科杂志,2022,42(12):1002-1006. |
| 18 | JIANG X S, XIANG X Y, CHEN X M, et al. Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase attenuates renal tubular mitochondrial dysfunction and ER stress by restoring autophagic flux in diabetic nephropathy[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11(5): 385. |
| 19 | 崔丹丹. 罗汉果多糖提取分离、结构解析及对糖尿病肾病小鼠保护作用研究[D]. 西安: 陕西科技大学, 2021. |
| 20 | 李 涛, 邓放明, 覃 思, 等. Nrf2-ARE介导的黄酮类化合物抗氧化应激的研究进展[J]. 食品与机械, 2016, 32(6): 201-207. |
| 21 | LUO Q, ZHOU L, ZHOU N T, et al. Cost-effectiveness of insulin degludec/insulin aspart versus biphasic insulin aspart in Chinese population with type 2 diabetes[J]. Front Public Health, 2022, 10: 1016937. |
| 22 | 孙晓润, 陈苹苹, 林 悦, 等. 天然黄酮类化合物抗肿瘤作用靶点研究进展[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2017, 23(6): 218-228. |
| 23 | 吕 杰. 基于肾络癥瘕理论探讨炎症与糖尿病肾病的相关性[D]. 北京: 北京中医药大学, 2014. |
| 24 | LI Y, HAO H, YU H Z, et al. Ginsenoside Rg2 ameliorates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating TAK1 to inhibit necroptosis[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2022, 9: 824657. |
| 25 | NAKAMURA T, FUKUI M, EBIHARA I, et al. mRNA expression of growth factors in glomeruli from diabetic rats[J]. Diabetes, 1993, 42(3): 450-456. |
| 26 | BAUD L, PEREZ J, FRIEDLANDER G, et al. Tumor necrosis factor stimulates prostaglandin production and cyclic AMP levels in rat cultured mesangial cells[J]. FEBS Lett, 1988, 239(1): 50-54. |
| 27 | LASTER S M, WOOD J G, GOODING L R. Tumor necrosis factor can induce both apoptic and necrotic forms of cell lysis[J]. J Immunol, 1988, 141(8): 2629-2634. |
| 28 | NAVARRO J F, MILENA F J, MORA C, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene expression in diabetic nephropathy: relationship with urinary albumin excretion and effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition[J]. Kidney Int Suppl, 2005(99): S98-S102. |
| 29 | 韩雨红, 董逸舒, 李雪蒙, 等. CXCL1通过促进蛋白激酶B磷酸化导致bEND.3小鼠脑微血管内皮细胞骨架收缩和通透性增加[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2023, 39(2): 117-123. |
| [1] | Jiaxin WANG,Zhenqi WANG,Xuan ZHANG. Expressions of CDKAL1 gene and its splice isomers in peripheral blood lymphocytes of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and their clinical significances [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1290-1295. |
| [2] | Chunling WANG,Sinuo WU,Xiaoyan YU,Weidong ZHANG. Analysis on network pharmacology and molecular docking technique based on effective chemical components and action targets of epimedium in treatment of hypothalamus-pituitary- adrenal gland/ gonad / thyroid gland axis function damage [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1296-1303. |
| [3] | Sihan LAI,Juntong LIU,Luying TAN,Jinping LIU,Pingya LI. Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis on anti-ischemic stroke mechanism of Panax quinquefolium triolsaponins [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 913-922. |
| [4] | Yumeng LIU,Song LENG, SARENGAOWA,Daijie LIN,Linsheng XIE,Mengrui LI,Xiao XU,Wannan LI. Network pharmacology analysis based on therapeutic effect of Sanghuang on pneumonia and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 923-930. |
| [5] | Yushuang GONG,Yefan FU,Huijing XU,Jian GUO,Lin XIANG,Rui HU,Rui FAN,Jie WANG,Miao LI,Meiyan SUN. Network pharmacology analysis on mechanism of Tonifying Slpeen and Kidney Empirical Prescription in treatment of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 261-271. |
| [6] | Zhouquan LI,Hui LI,Ying TANG,Lijun YANG,Yinghong JIANG,Lipin YIN. Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis on mechanism of Tongluo Tangtai Power in treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 341-350. |
| [7] | Minghui WANG,Moyi LIU,Helin WANG,Ying LI,Xiangjun WANG,Hetong HUI,Xinyuan FAN,Tianqi WANG,Limei LIU. Bioinformatics analysis of network pharmacology and molecular docking technology based on mechanism of Physalis Calyx seu Fructus on leukemia [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(1): 74-83. |
| [8] | Donghui LIU,Mingxi ZHANG,Wenliang FU,Xiumei FU,Chengjun SONG,Zhihong CHEN. Effects of sericin on injury of podocytes induced by high glucose and JNK signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(6): 1403-1410. |
| [9] | Shaojie FU,Sensen SU,Yiying CHEN,Zhonggao XU. Analysis on network pharmacology and molecular docking technique based on mechanism of Shenqi Dihuang Decoction in treatment of membranous nephropathy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(6): 1518-1527. |
| [10] | Bingxue QI,Yangwei WANG,Yixian ZHANG,Jingbo ZHAO,Yan MA,Yadong SUN. Ameliorative effect of liraglutide on renal function and podocyte injury of rats with diabetic nephropathy and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 331-339. |
| [11] | Yan LI,Yue HOU,Xingwei MU,Bingqing LIU,Hong WAN,Chang LIU,Wei XIA. Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis on mechanism of Schisandrae Chinensis Fructus in occurrence and development of thoracic aortic aneurysm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 414-425. |
| [12] | Yu ZHU,Jingjing WANG,Fang WU. Expression of miR-150-5p in kidney tissue of diabetic nephropathy model mice and its effect on MPC5 mouse podocyte injury and mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(1): 44-51. |
| [13] | Bingxue QI,Yan MA,Yixian ZHANG,Yadong SUN,Lining MIAO. Effect of liraglutide on expressions of mRNA and protein of related proteins after podocyte injury induced by high glucose and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 275-283. |
| [14] | WANG Lan, ZHU Guoshuang, SUN Long, WANG Xiaoqin. Improvement effect of Shenyuan Granule on vascular calcification in db/db diabetic nephropathy mice and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(03): 431-438. |
| [15] | ZHANG Shuxia, HUO Wenbo, SU Ying, LI Zhen, TIAN Jing, WANG Caixia, SUN Chengbo, ZOU Yinggang, YU Xiaoyan. Effect of herba artemisiae capillaris extracts on PTEN protein expression in kidney tissue of diabetic rats and its protective effect on kidney [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(04): 779-783. |
|
||