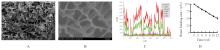
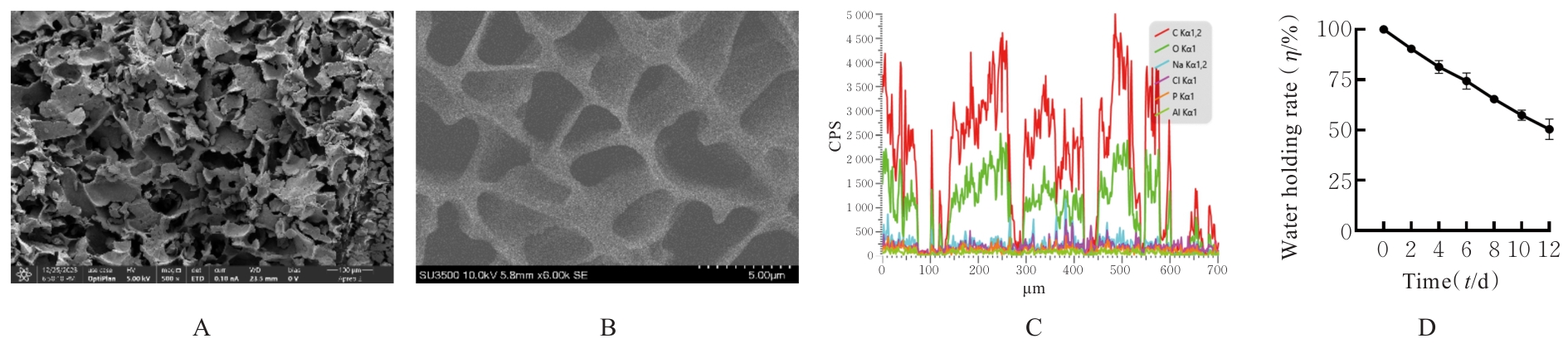
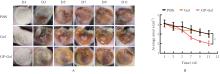
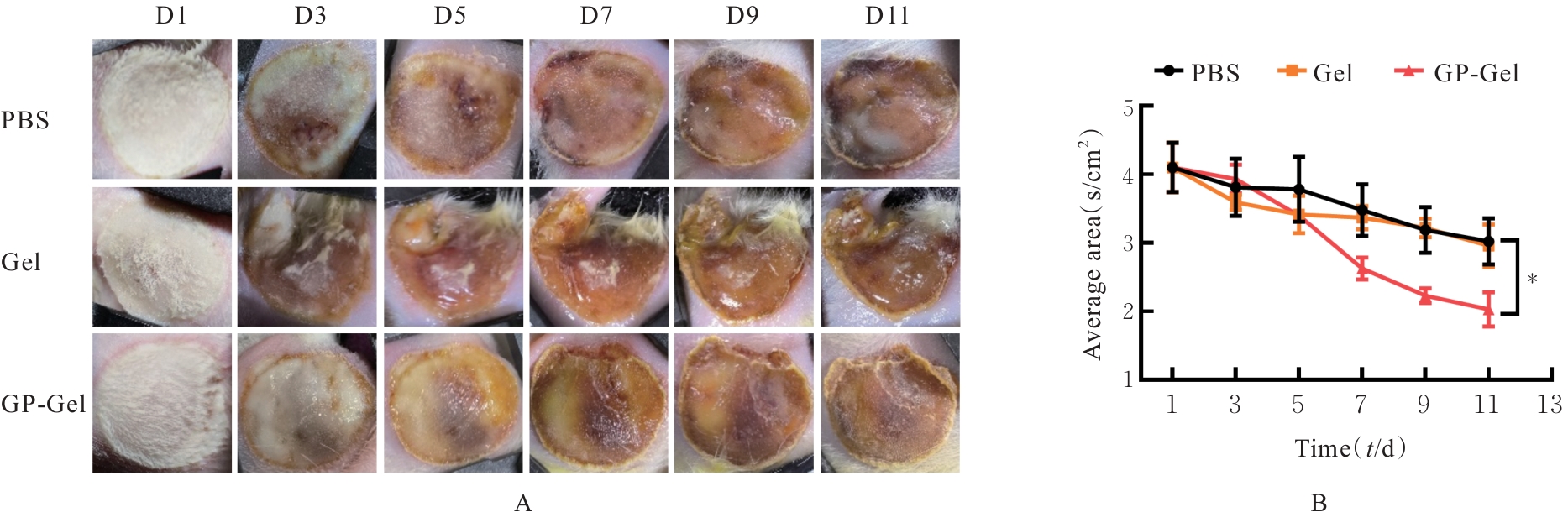
| [1] |
Yue WANG,Ning MA,Jiajun LU,Chengyao WANG,Linyu CHEN,Yuchen REN,Jingwu LI,Hong SUN.
Protective effect of novel composite hydrogels on H₂O₂-induced oxidative stress injury in cardiomyocytes
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 352-359.
|
| [2] |
Xingqi SU,Lingmin ZHAO,Di MA,Jiulin YOU,Ying CHEN,Liangshu FENG,Jing WANG,Jiachun FENG,Chuan WANG.
Analysis on correlation of cerebral infarct area with cytokines and immune status in patients with acute ischemic stroke
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 124-132.
|
| [3] |
Yanyan BAI,Yutong ZHOU,Haijuan SUI,Zhuo LIU.
Improvement effect of asiatic acid on damage of lipopolysaccharide-induced hippocampum neuron in rats through Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 85-95.
|
| [4] |
Haixia CHEN,Hongru LI,Jingyi LIU,Zhifang XU,Shuwen LIU,Yuan YANG,Yang CHEN,Yu LUO,Yinjie CUI.
Research progress in changes of intestinal flora after spinal cord injury and their effects on spinal neuroinflammation
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1751-1756.
|
| [5] |
Wenhui LIU,Miao YU,Ying GUO,Yupeng LIU,Yang XING,Xinyu HONG,Jiale CUI.
Research progress in effect of CXC chemokine receptor 3 on occurrence and development of nervous system diseases
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(5): 1474-1480.
|
| [6] |
Xiaoyu WANG,Bing LI,Guohui LIU.
Research progress in application of inflammatory markers in diagnosis and treatment of coronary heart disease
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1173-1181.
|
| [7] |
Xuejun JIN,Chuyuan LU.
Inhibitory effect of leucovorin on growth and angiogenesis of subcutaneous transplanted tumors in mouse lung cancer cells and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 612-619.
|
| [8] |
Yiyan YU,Zhimin ZHANG,Jiawen CHEN,Xin LIU,Yan LI,Hongyan ZHAO.
Research progress in relationship between macrophage polarization and oral diseases
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 864-871.
|
| [9] |
Shuang YANG,Na XU,Jianxu ZHANG,Chengbiao SUN,Yan WANG,Mingxin DONG,Wensen LIU.
Improvement effect of rubusoside on motor dysfunction and neuroinflammation in mice with spinal cord injury and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 326-335.
|
| [10] |
Hongmei TANG,Yuejiao LI,Xing WANG,Zhibin WANG,Xiefang YUAN,Xiaoyun WANG.
Effect of Jiegeng Yuanshen Tang on airway inflammation and mucus secretion in allergic asthmatic mice and its mechanism
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 10-17.
|
| [11] |
Kongzhao JIANG,Chiyu LI,Yungang LUO,Zhihui LIU.
Preparationof GelMA hydrogel loaded with ZIF-8 and evaluation of drug sustained release and antibacterial effect
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 106-112.
|
| [12] |
Yang YU,Dan TIAN,Donghe NI,Duo ZHANG.
Network pharmacologry and molecular docking analysis based on mechanism of monk fruit in treatment of diabetic nephropathy
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 161-167.
|
| [13] |
Yajie GE,Wen XU,Shimin GUAN,Lina WANG.
Research progress in etiology and pathogenesis of polycystic ovary syndrome
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 288-294.
|
| [14] |
Wenting HUI,Tongtong SONG,Min HUANG,Xia CHEN.
Effect of hydrogel-based delivery of bFGF on function of NIH3T3 cells after oxygen-glucose deprivation
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(6): 1484-1490.
|
| [15] |
Chang GAO,Yan LIU,Haoxiang YANG,Cuicui ZHANG.
Effect of long non-coding RNA MALAT1 on angiogenesis of human brain microvascular endothelial cells induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation hypoxic
[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 832-839.
|
 ),Na LI1(
),Na LI1( )
)