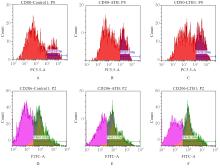
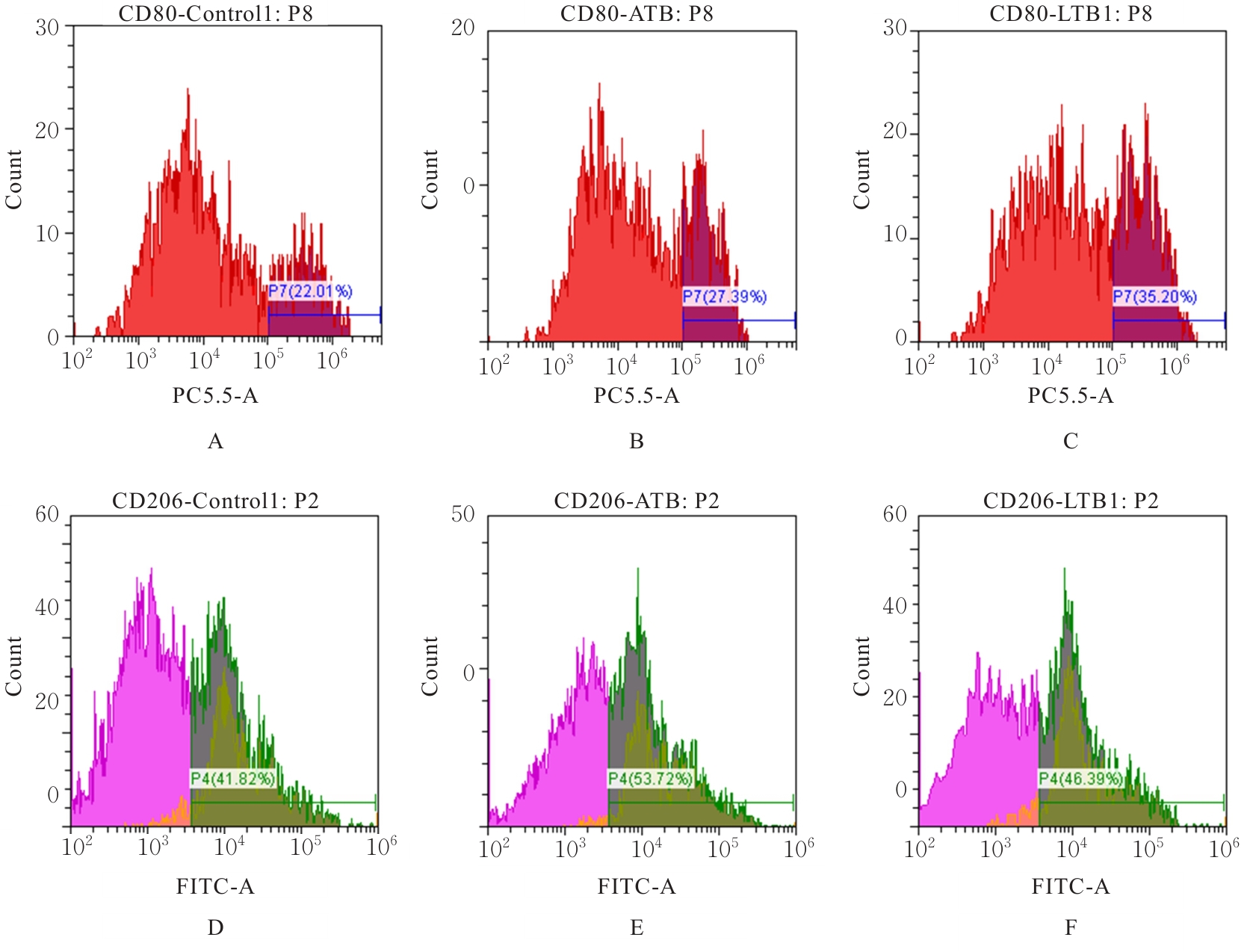
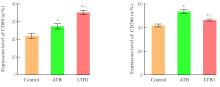
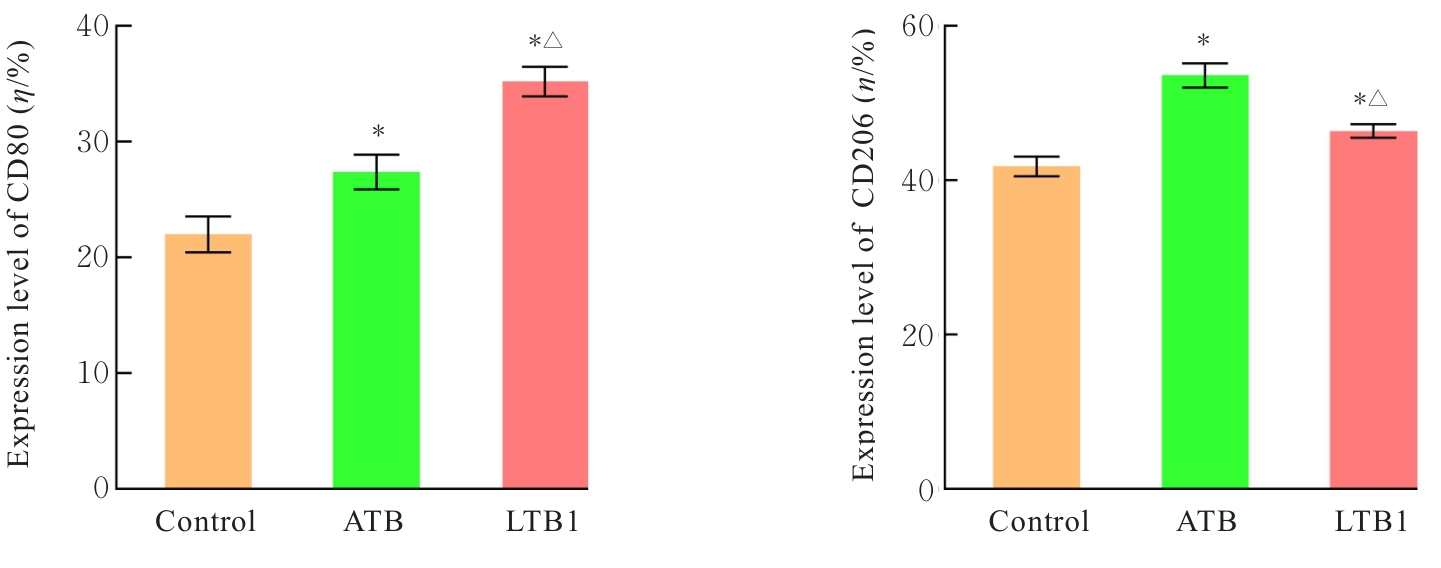
| [1] |
BAGCCHI S. WHO’s global tuberculosis report 2022[J]. Lancet Microbe, 2023, 4(1): e20.
|
| [2] |
SCHRAUFNAGEL D E. “Latent tuberculosis infection” is a term that should go dormant, and the significance of latent tuberculosis should be rethought[J]. Annals ATS, 2016, 13(5): 593-594.
|
| [3] |
GANESAN V, JANAGOND A, VIJAY KUMAR G S, et al. Screening of health-care workers for latent tuberculosis infection in a Tertiary Care Hospital[J]. Int J Mycobacteriol, 2017, 6(3): 253.
|
| [4] |
MAES R. Evaluation of the therapeutic, diagnostic, and prognostic means currently applied to counter the surge of tuberculosis[J]. Biomed Biotechnol Res J, 2019, 3(3): 140.
|
| [5] |
AI J W, RUAN Q L, LIU Q H, et al. Updates on the risk factors for latent tuberculosis reactivation and their managements[J]. Emerg Microbes Infect, 2016, 5(1): 1-8.
|
| [6] |
GETAHUN H, MATTEELLI A, CHAISSON R E, et al. Latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection[J]. N Engl J Med, 2015, 372(22): 2127-2135.
|
| [7] |
朱鹏, 张伟. 肺结核合并诺卡菌病1例报告[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2024, 44(3): 261-264.
|
| [8] |
DHEDA K, DAVIDS M. Latent tuberculosis infection-associated immunodiagnostic test responses as biomarkers of incipient tuberculosis: fruitful or futile?[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2020, 201(8): 895-898.
|
| [9] |
EZEONU C T, IKEAGWULONU R C, ASIEGBU U V, et al. Tuberculin skin tests following Bacille Calmette Guerin vaccination in Africa: a protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Pan Afr Med J, 2022, 41: 12.
|
| [10] |
QIU X, TANG Y, ZOU R, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of interferon-gamma-induced protein 10 for differentiating active tuberculosis from latent tuberculosis: a meta-analysis[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9: 11408.
|
| [11] |
HWANG H, HWANG B Y, BUENO J. Biomarkers in infectious diseases[J]. Dis Markers, 2018, 2018: 8509127.
|
| [12] |
LEE S H. Tuberculosis infection and latent tuberculosis[J]. Tuberc Respir Dis, 2016, 79(4): 201.
|
| [13] |
GÜNER A E, KIZILTAS S, BABALIK A, et al. Outcomes of latent tuberculosis infection treatment in Istanbul[J]. Int J Mycobacteriol, 2022, 11(4): 442-447.
|
| [14] |
SABIR N, HUSSAIN T, ZALI SHAH S, et al. miRNAs in tuberculosis: new avenues for diagnosis and host-directed therapy[J]. Front Microbiol, 2018, 9: 602.
|
| [15] |
冯真, 张博, 邓思齐, 等. 血浆外泌体miR-26a-5p和miR-151a-3p在结核病中的表达及诊断价值[J]. 安徽医科大学学报, 2022, 57(12): 1979-1984.
|
| [16] |
PENG Z L, CHEN L, ZHANG H. Serum proteomic analysis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens for discriminating active tuberculosis from latent infection[J]. J Int Med Res, 2020, 48(3): 0300060520910042.
|
| [17] |
刘守江, 张帆, 魏巍, 等. 结核潜伏感染者全血miR-144-3p、 miR-146a-5p的表达[J]. 临床肺科杂志, 2013, 18(7): 1270-1271.
|
| [18] |
GINHOUX F, GUILLIAMS M. Tissue-resident macrophage ontogeny and homeostasis[J]. Immunity, 2016, 44(3): 439-449.
|
| [19] |
KIM S W, RAMASAMY K, BOUAMAR H, et al. microRNAs miR-125a and miR-125b constitutively activate the NF-κB pathway by targeting the tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 3 (TNFAIP3, A20)[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2012, 109(20): 7865-7870.
|
| [20] |
JAYARAMAN J, JESUDOSS V A S, MENON V P, et al. Anti-inflammatory role of naringenin in rats with ethanol induced liver injury[J]. Toxicol Mech Meth, 2012, 22(7): 568-576.
|
| [21] |
中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 肺结核诊断标准(WS 288-2017)[J]. 新发传染病电子杂志, 2018, 3(1): 59-61.
|
| [22] |
中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 结核病分类(WS196-2017)[J]. 新发传染病电子杂志, 2018, 3(3): 191-192.
|
| [23] |
舒薇, 刘宇红. 世界卫生组织《2023年全球结核病报告》解读[J]. 结核与肺部疾病杂志, 2024, 5(1): 15-19.
|
| [24] |
艾克旦, 商越, 王兆芬, 等. 青海省南部2009-2019年肺结核时空分布特征演变研究[J]. 中国预防医学杂志, 2021, 22(8): 582-586.
|
| [25] |
SELF-FORDHAM J B, NAQVI A R, UTTAMANI J R, et al. microRNA: dynamic regulators of macrophage polarization and plasticity[J]. Front Immunol, 2017, 8: 1062.
|
| [26] |
LIANG S F, MA J C, GONG H L, et al. Immune regulation and emerging roles of noncoding RNAs in Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 987018.
|
| [27] |
ALIJANI E, RIAZI RAD F, KATEBI A, et al. Differential expression of miR-146 and miR-155 in active and latent tuberculosis infection[J]. Ijph, 2023: 1749-1757.
|
| [28] |
久太, 颜然然, 冯喜英, 等. 差异表达的miR-181a-5p、miR-141-3p在青海藏族肺结核诊断中作用[J]. 中华肺部疾病杂志(电子版), 2019, 12(6): 702-707.
|
| [29] |
余海茹, 闫晔鑫, 杨娇, 等. 2004至2021年中国肺结核发病趋势及空间分布特征[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版), 2024, 59(2): 274-279.
|
| [30] |
GRAFF J W, DICKSON A M, CLAY G, et al. Identifying functional microRNAs in macrophages with polarized phenotypes[J]. J Biol Chem, 2012, 287(26): 21816-21825.
|
| [31] |
WANG N, LIANG H W, ZEN K. Molecular mechanisms that influence the macrophage M1–M2 polarization balance[J]. Front Immunol, 2014, 5: 614.
|
| [32] |
LI Q, WANG C, GOU J Z, et al. Deciphering lung granulomas in HIV & TB co-infection: unveiling macrophages aggregation with IL6R/STAT3 activation[J]. Emerg Microbes Infect, 2024, 13: 2366359.
|
| [33] |
IZUMIDA M, JOBE H, COKER E G, et al. HBHA induces IL-10 from CD4+ T cells in patients with active tuberculosis but IFN-γ and IL-17 from individuals with Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection[J]. Front Immunol, 2024, 15: 1422700.
|
 )
)