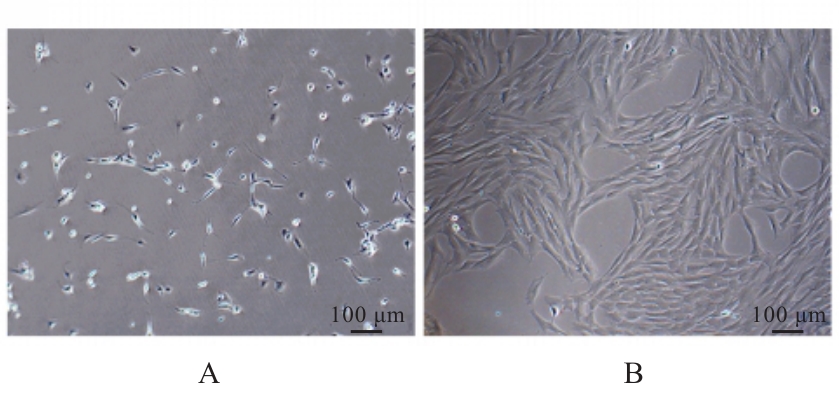
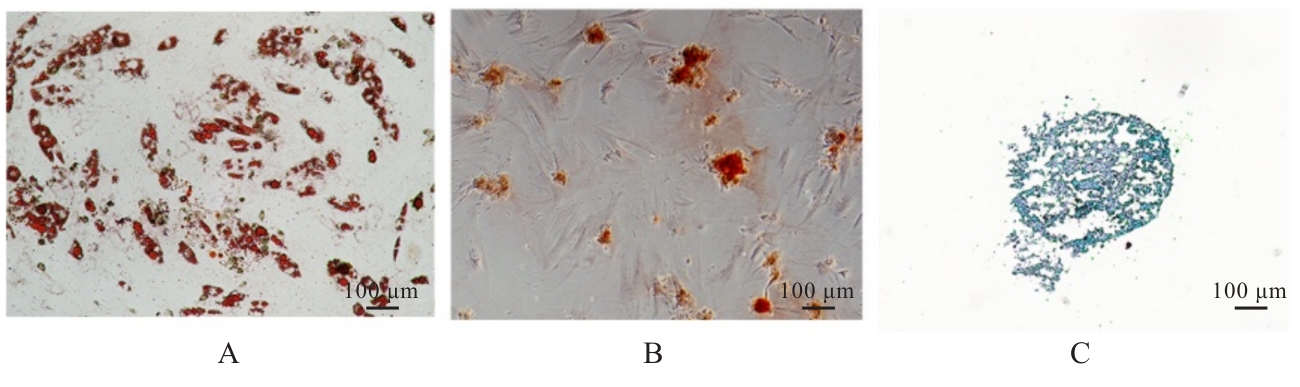
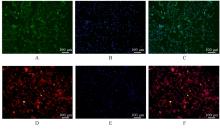
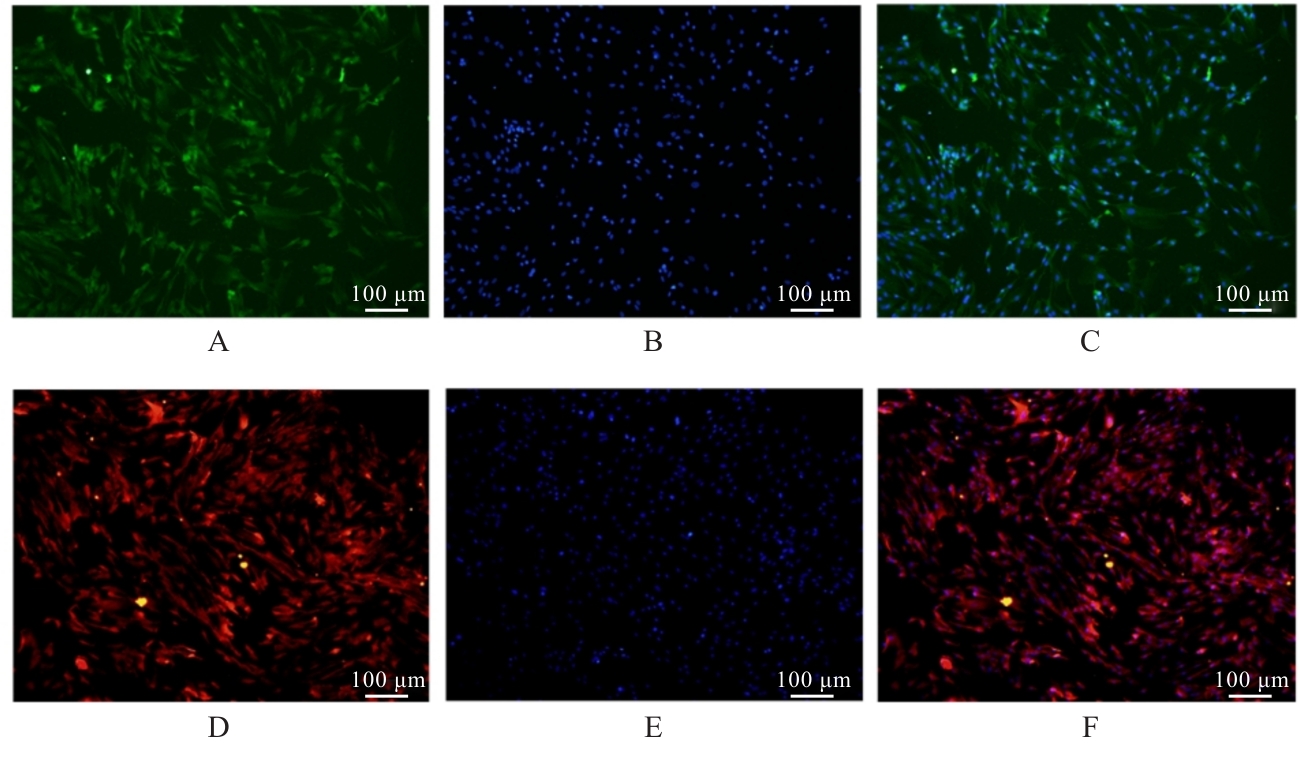
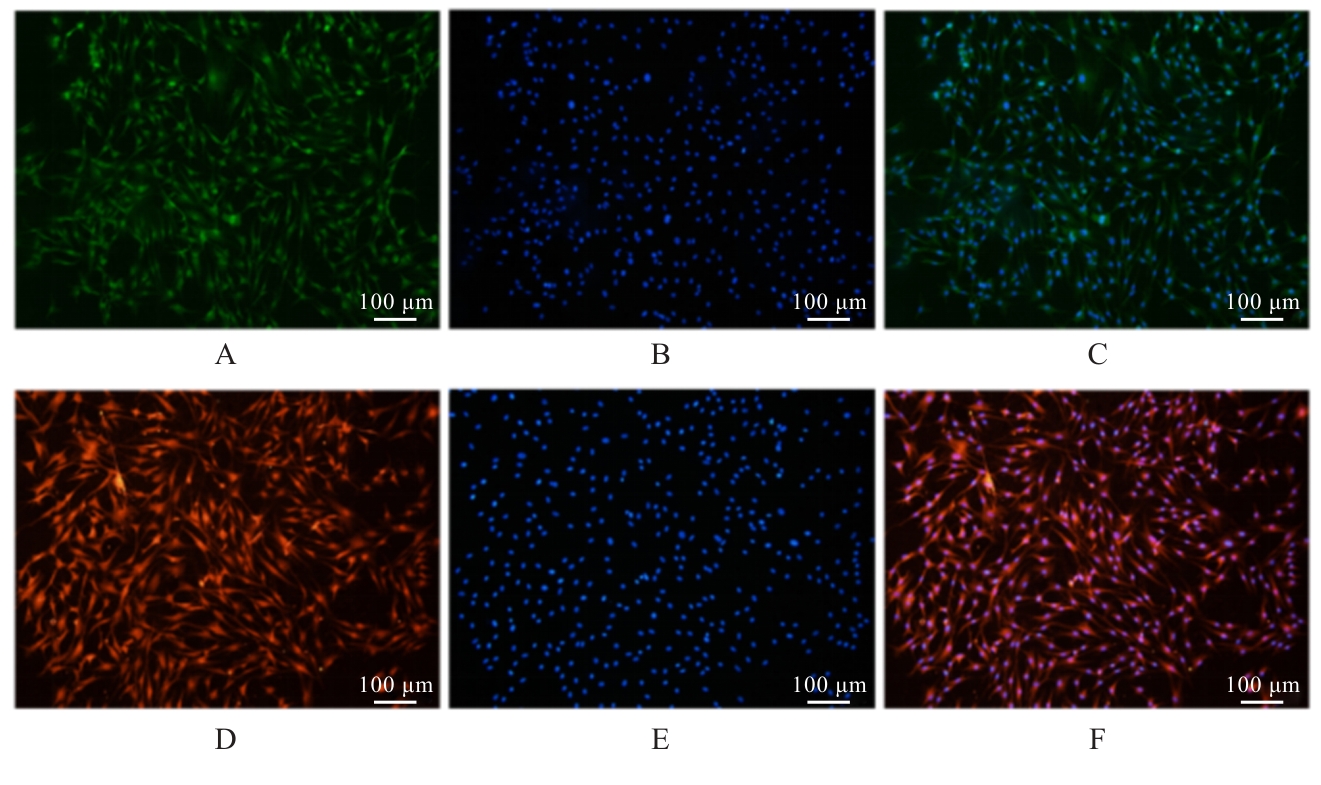
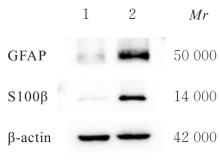
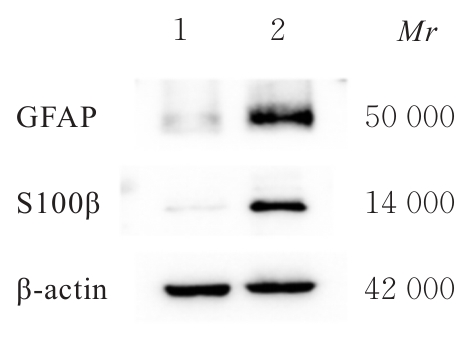
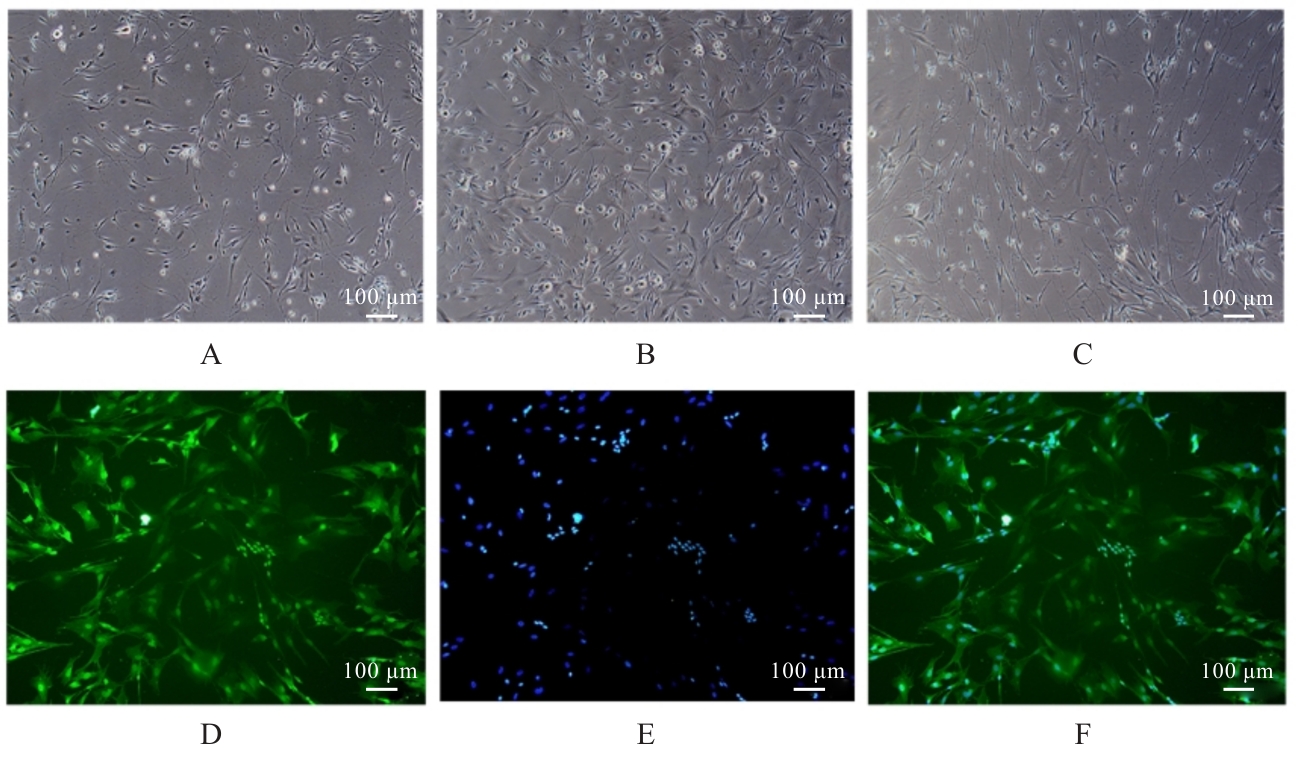
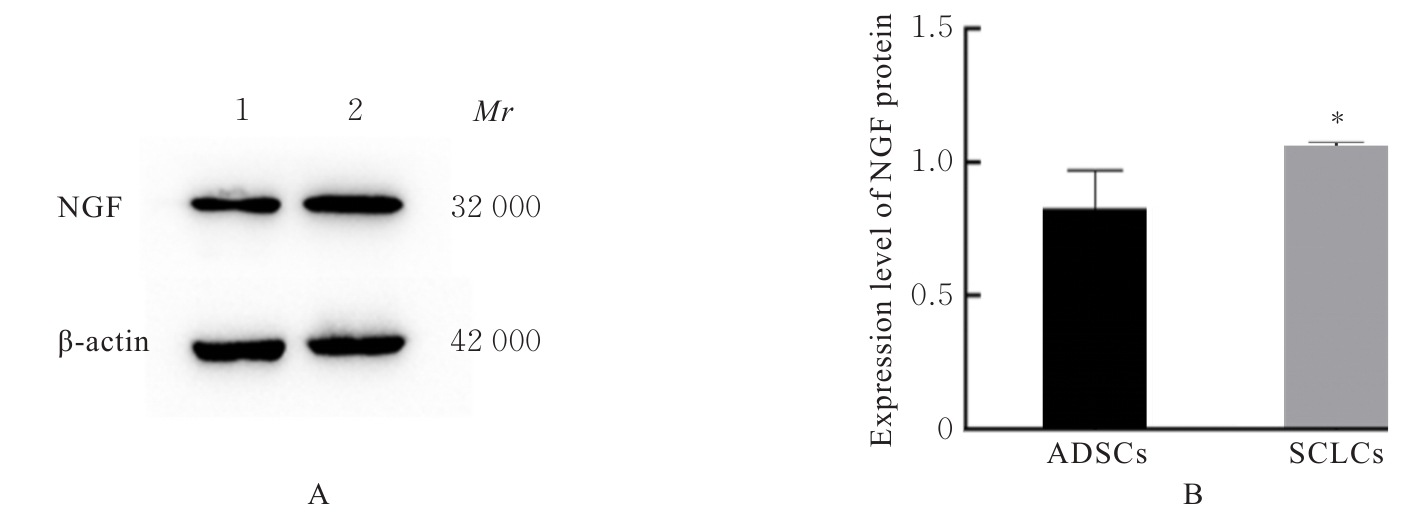
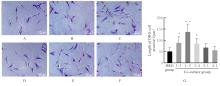
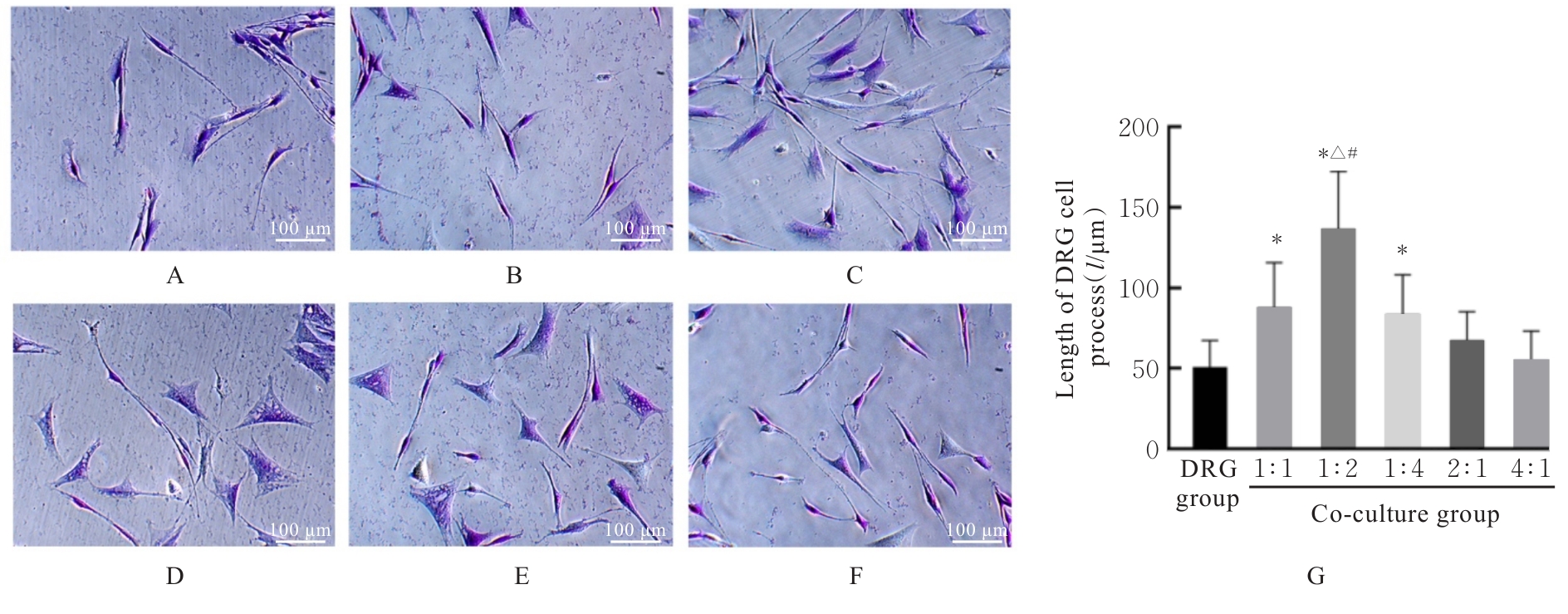
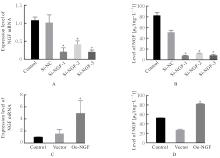
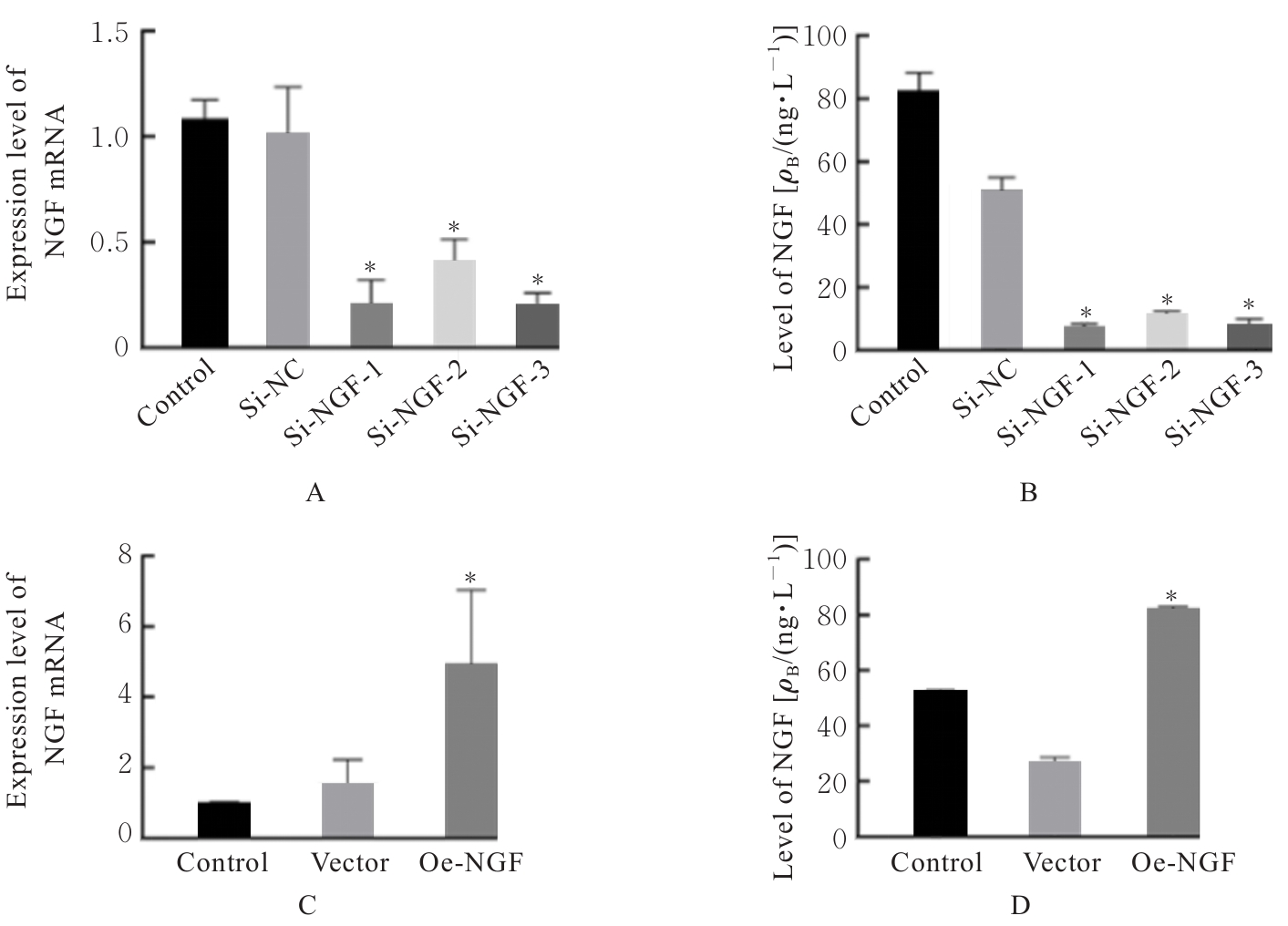
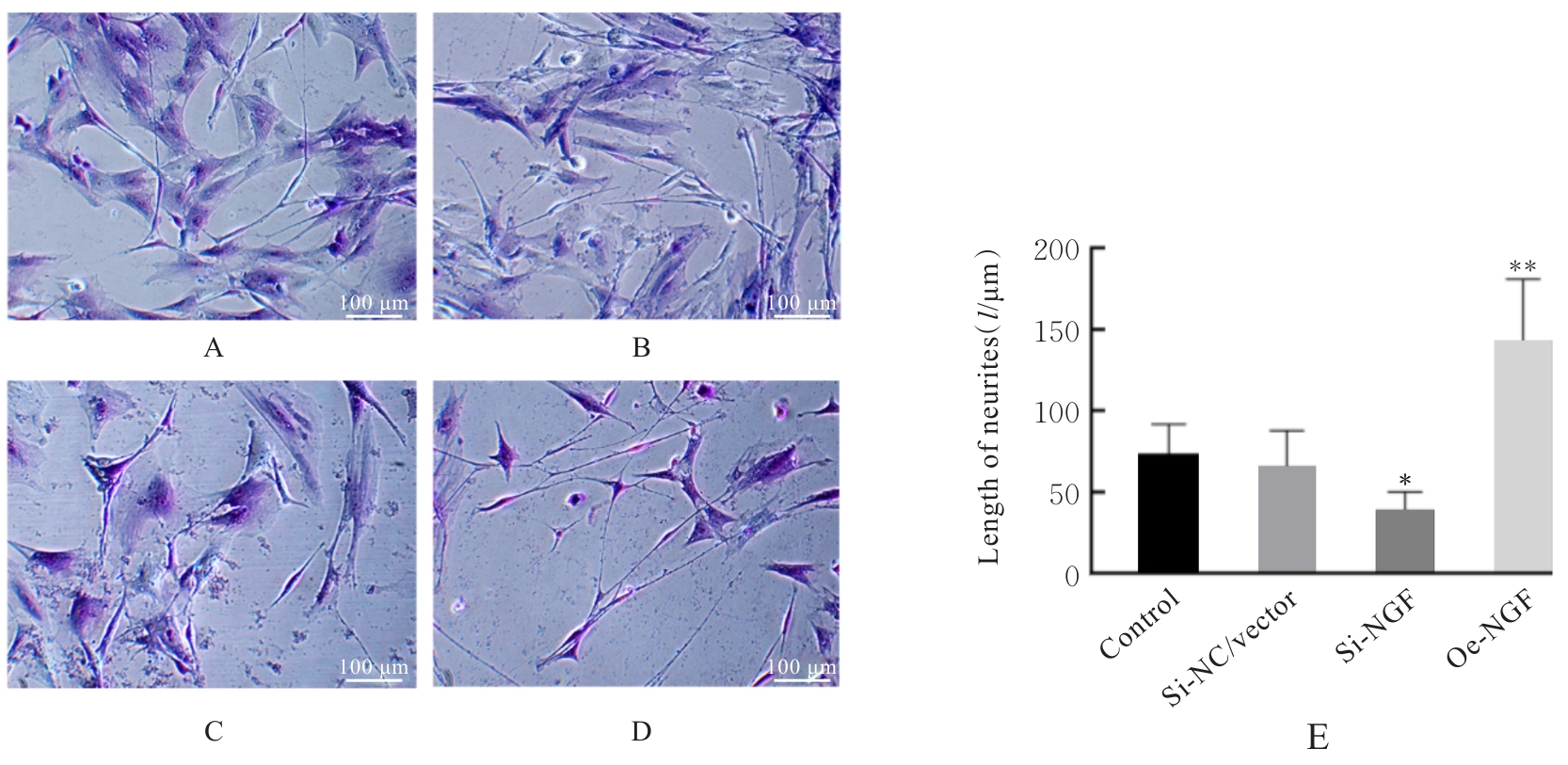
| [1] |
MODRAK M, HASSAN TALUKDER M A, GURGENASHVILI K, et al. Peripheral nerve injury and myelination: potential therapeutic strategies[J]. J Neurosci Res, 2020, 98(5): 780-795.
|
| [2] |
DONG S X, FENG S J, CHEN Y Z, et al. Nerve suture combined with ADSCs injection under real-time and dynamic NIR-II fluorescence imaging in peripheral nerve regeneration in vivo [J]. Front Chem, 2021, 9: 676928.
|
| [3] |
ZHANG S W, HUANG M L, ZHI J C, et al. Research hotspots and trends of peripheral nerve injuries based on web of science from 2017 to 2021: a bibliometric analysis[J]. Front Neurol, 2022, 13: 872261.
|
| [4] |
TUSNIM J, KUTUZOV P, GRASMAN J M. In vitro models for peripheral nerve regeneration[J]. Adv Healthc Mater, 2024, 13(30): e2401605.
|
| [5] |
ZOU X F, ZHANG B Z, QIAN W W, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of peripheral nerve injury[J]. World J Stem Cells, 2024, 16(8): 799-810.
|
| [6] |
MANKAVI F, IBRAHIM R, WANG H J. Advances in biomimetic nerve guidance conduits for peripheral nerve regeneration[J]. Nanomaterials (Basel), 2023, 13(18): 2528.
|
| [7] |
SUN Q N, MOHD ISMAIL Z I, PATAR M N AAB, et al. The limelight of adipose-derived stem cells in the landscape of neural tissue engineering for peripheral nerve injury[J]. Tissue Cell, 2024, 91: 102556.
|
| [8] |
KONOFAOS P, PVER HALEN J. Nerve repair by means of tubulization: past, present, future[J]. J Reconstr Microsurg, 2013, 29(3): 149-164.
|
| [9] |
OLIVEIRA J T, YANICK C, WEIN N, et al. Neuron-Schwann cell interactions in peripheral nervous system homeostasis, disease, and preclinical treatment[J]. Front Cell Neurosci, 2023, 17: 1248922.
|
| [10] |
NAM Y H, PARK S, YUM Y, et al. Preclinical efficacy of peripheral nerve regeneration by schwann cell-like cells differentiated from human tonsil-derived mesenchymal stem cells in C22 mice[J]. Biomedicines, 2023, 11(12): 3334.
|
| [11] |
ELBERG G, LIRAZ-ZALTSMAN S, REICHERT F, et al. Deletion of SIRPα (signal regulatory protein-α) promotes phagocytic clearance of myelin debris in Wallerian degeneration, axon regeneration, and recovery from nerve injury[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2019, 16(1): 277.
|
| [12] |
GOMEZ-SANCHEZ J A, CARTY L, IRUARRIZAGA-LEJARRETA M, et al. Schwann cell autophagy, myelinophagy, initiates myelin clearance from injured nerves[J]. J Cell Biol, 2015, 210(1): 153-168.
|
| [13] |
杨溢铎, 国海东, 邵水金, 等. 雪旺细胞促进周围神经再生机制的研究进展[J]. 基础医学与临床, 2022, 42(1): 145-148.
|
| [14] |
孙莹莹, 刘玉梅, 刘永昌, 等. 褪黑激素体外对脂肪间充质干细胞增殖及向施万样细胞分化的影响[J]. 中国细胞生物学学报, 2022, 44(7): 1330-1338.
|
| [15] |
CAI W X, LIU Y, ZHANG T, et al. GDNF facilitates the differentiation of ADSCs to Schwann cells and enhances nerve regeneration through GDNF/MTA1/Hes1 axis[J]. Arch Biochem Biophys, 2024, 753: 109893.
|
| [16] |
KHALED M M, IBRAHIUM A M, ABDELGALIL A I, et al. Regenerative strategies in treatment of peripheral nerve injuries in different animal models[J]. Tissue Eng Regen Med, 2023, 20(6): 839-877.
|
| [17] |
FU X M, TONG Z X, LI Q, et al. Induction of adipose-derived stem cells into Schwann-like cells and observation of Schwann-like cell proliferation[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2016, 14(2): 1187-1193.
|
| [18] |
杜元良, 任 旺, 刘 琳, 等. 施万细胞样细胞对大鼠背根神经节细胞突起生长和神经生长因子表达的影响及其机制[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2022, 48(3): 684-691.
|
| [19] |
NOCERA G, JACOB C. Mechanisms of Schwann cell plasticity involved in peripheral nerve repair after injury[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2020, 77(20): 3977-3989.
|
| [20] |
袁 博, 谢佳忆, 江思瑜, 等. 脂肪干细胞源性外泌体对体外巨噬细胞迁移能力的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2024, 50(3): 718-727.
|
| [21] |
MENG F Q, LI C C, XU W J, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells enhance acellular nerve allografts to promote peripheral nerve regeneration by facilitating angiogenesis[J]. Neural Regen Res, 2024.
|
| [22] |
陈思凡, 李宏玲, 王海兰, 等. 脂肪干细胞移植治疗1-溴丙烷所致大鼠周围神经损伤[J]. 中国职业医学, 2022, 49(4): 374-379.
|
| [23] |
CASTELNOVO L F, THOMAS P. Membrane progesterone receptor α (mPRα/PAQR7) promotes migration, proliferation and BDNF release in human Schwann cell-like differentiated adipose stem cells[J]. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 2021, 531: 111298.
|
| [24] |
CHING R C, WIBERG M, KINGHAM P J. Schwann cell-like differentiated adipose stem cells promote neurite outgrowth via secreted exosomes and RNA transfer[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2018, 9(1): 266.
|
| [25] |
YUAN Q, SUN L, YU H H, et al. Human microvascular endothelial cell promotes the development of dorsal root ganglion neurons via BDNF pathway in a co-culture system[J]. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem, 2017, 81(7): 1335-1342.
|
| [26] |
管延军, 许文静, 张 健, 等. 细胞外基质修饰的电纺纤维对施万细胞及神经生长的影响[J]. 解放军医学院学报, 2022, 43(3): 328-333.
|
| [27] |
张 娜, 左晓霜, 王文慧. miR-205-5p通过抑制UHRF1表达促进大鼠周围神经再生的研究进展[J]. 创伤外科杂志, 2022, 24(5): 377-385.
|
| [28] |
LEISENGANG S, HEILEN L B, KLYMIUK M C, et al. Neuroinflammation in primary cultures of the rat spinal dorsal horn is attenuated in the presence of adipose tissue-derived medicinal signalling cells (AdMSCs) in a co-cultivation model[J]. Mol Neurobiol, 2022, 59(1): 475-494.
|
| [29] |
ZHOU N, XU Z, LI X, et al. Schwann cell-derived exosomes induce the differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells into schwann cells[J]. Front Mol Biosci, 2022, 8: 835135.
|
| [30] |
HSU M N, LIAO H T, TRUONG V A, et al. CRISPR-based activation of endogenous neurotrophic genes in adipose stem cell sheets to stimulate peripheral nerve regeneration[J]. Theranostics, 2019, 9(21): 6099-6111.
|
| [31] |
WAN T, ZHANG F S, QIN M Y, et al. Growth factors: Bioactive macromolecular drugs for peripheral nerve injury treatment - Molecular mechanisms and delivery platforms[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2024, 170: 116024.
|
| [32] |
陈颖秀, 郭映琪, 张惠媚, 等. 原花青素对大鼠背根神经节神经元突起生长的影响[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2024, 40(10): 1357-1363.
|
| [33] |
刘 震, 袁 庆, 乔 阳. 葛根素对乙醇诱导的原代皮层神经元细胞保护作用[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2024, 40(8): 1599-1600.
|
| [34] |
周泽宇, 马蕴涵, 李佳瑞, 等. 脱细胞异体神经移植物联合电针对坐骨神经损伤大鼠脊神经节的保护作用及机制[J]. 解剖学报, 2024, 55(2): 143-149.
|
| [35] |
SANG Q L, SUN D J, CHEN Z H, et al. NGF and PI3K/Akt signaling participate in the ventral motor neuronal protection of curcumin in sciatic nerve injury rat models[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018, 103: 1146-1153.
|
| [36] |
燕 燕, 崔传举, 王玉香, 等. 神经生长因子过表达治疗帕金森病模型大鼠的效果及其分子机制[J]. 河南医学高等专科学校学报, 2022, 34(1): 1-5.
|
| [37] |
郑良良, 张 弛. 神经生长因子过表达的人脐带血间充质干细胞来源外泌体修复大鼠坐骨神经慢性压迫损伤的效果及作用机制研究[J]. 中医正骨, 2021, 33(9): 3-14.
|
 )
)