吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (1): 136-145.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220214
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
拥堵空间排队的静态交通流分配迭代加权算法
- 1.北京交通大学 综合交通运输大数据应用技术交通运输行业重点实验室,北京 100044
2.河南工业大学 土木建筑学院,郑州 450007
Iterative weighted algorithms of static congestion traffic assignment considering spatial queuing
Hao YUE1( ),Qi-yue ZHANG1,Zi-yu YANG1,Meng-jie REN1,Xu ZHANG2
),Qi-yue ZHANG1,Zi-yu YANG1,Meng-jie REN1,Xu ZHANG2
- 1.Key Laboratory of Transport Industry of Big Data Application Technologies for Comprehensive Transport,Ministry of Transport,Beijing Jiaotong University,Beijing 100044,China
2.College of Civil Engineering and Architecture,Henan University of Technology,Zhengzhou 450007,China
摘要:
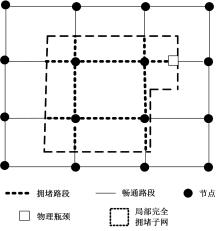
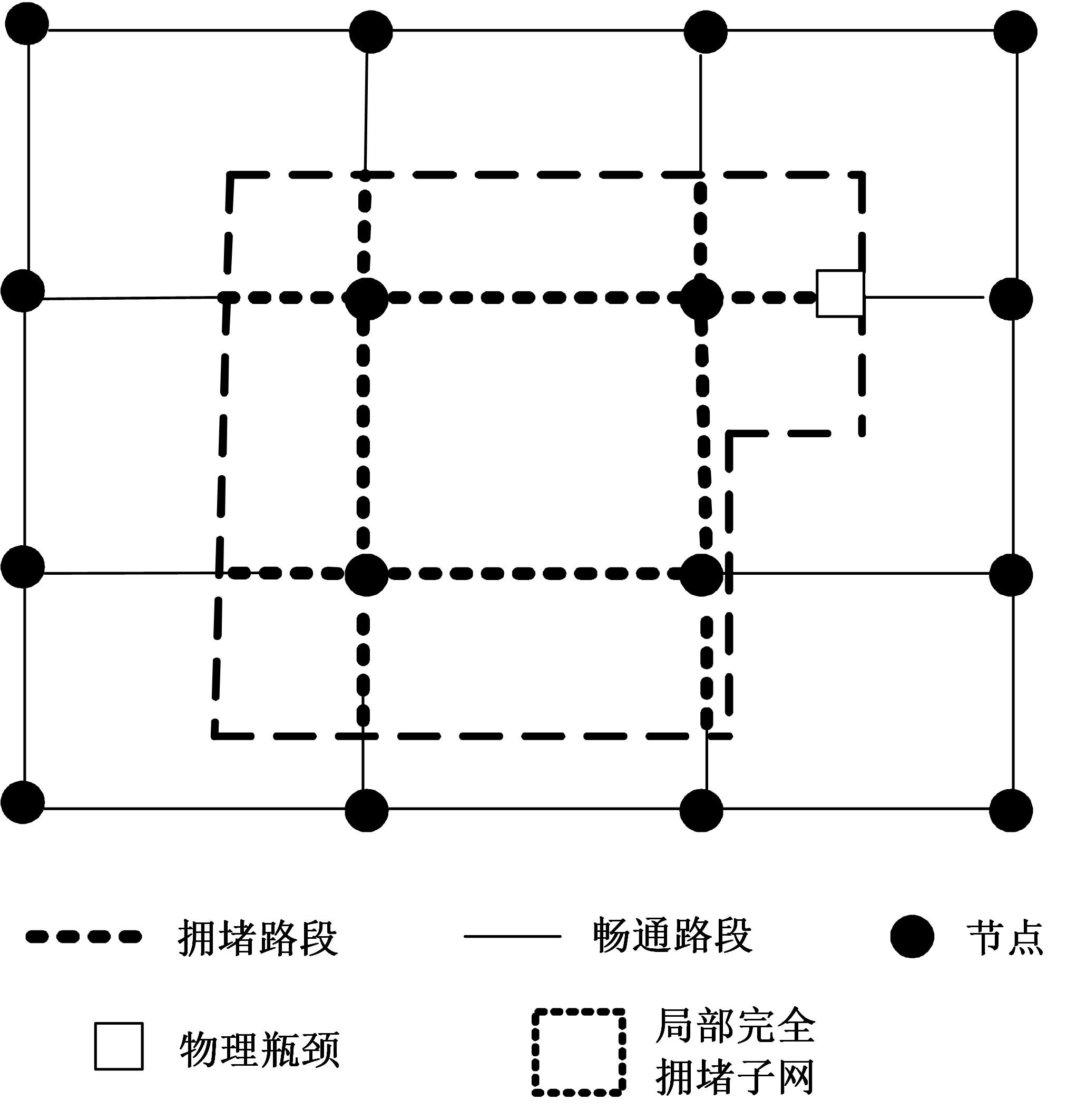
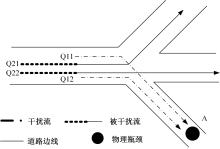
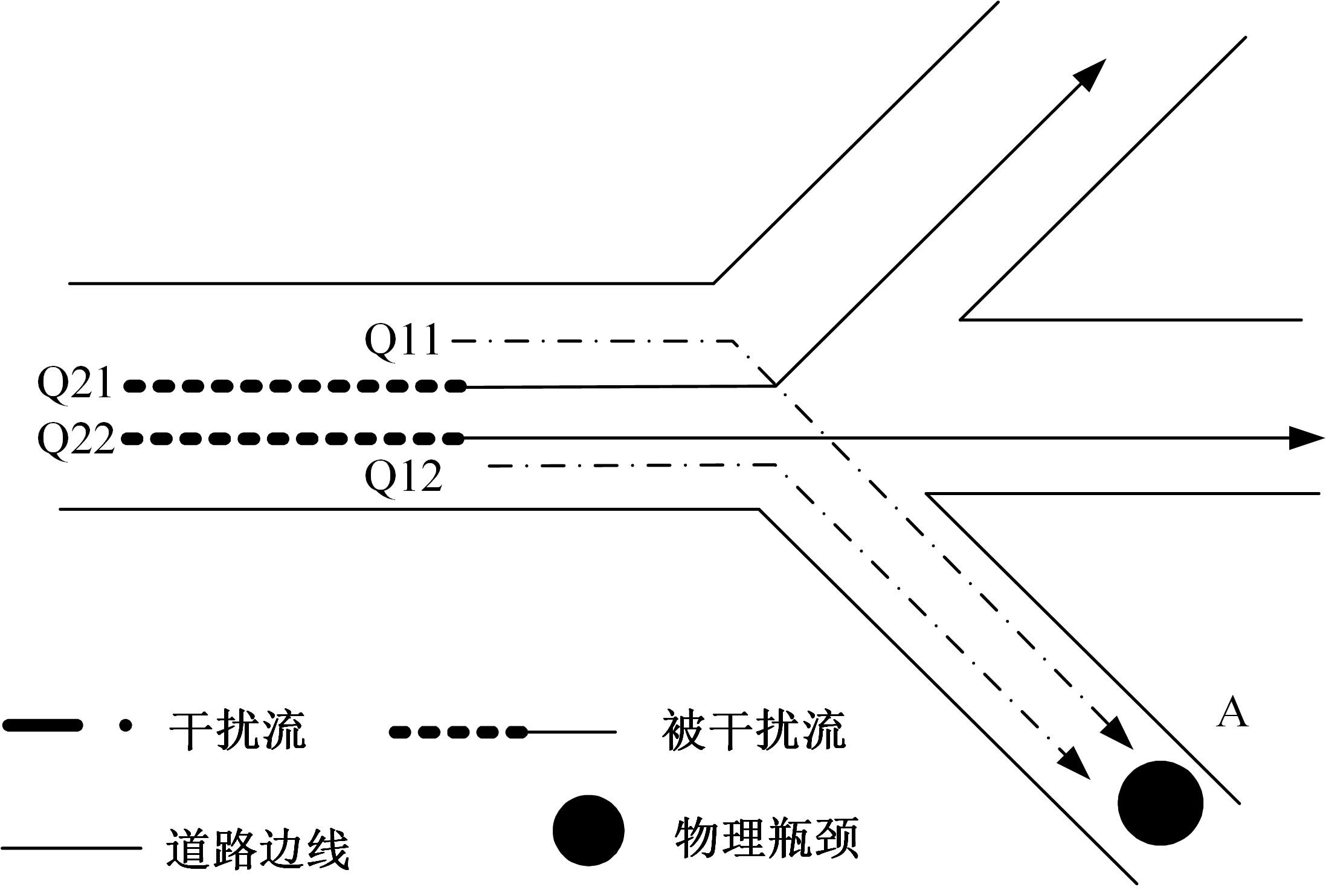
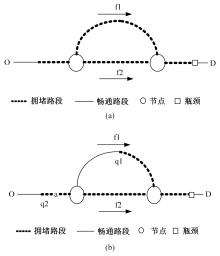
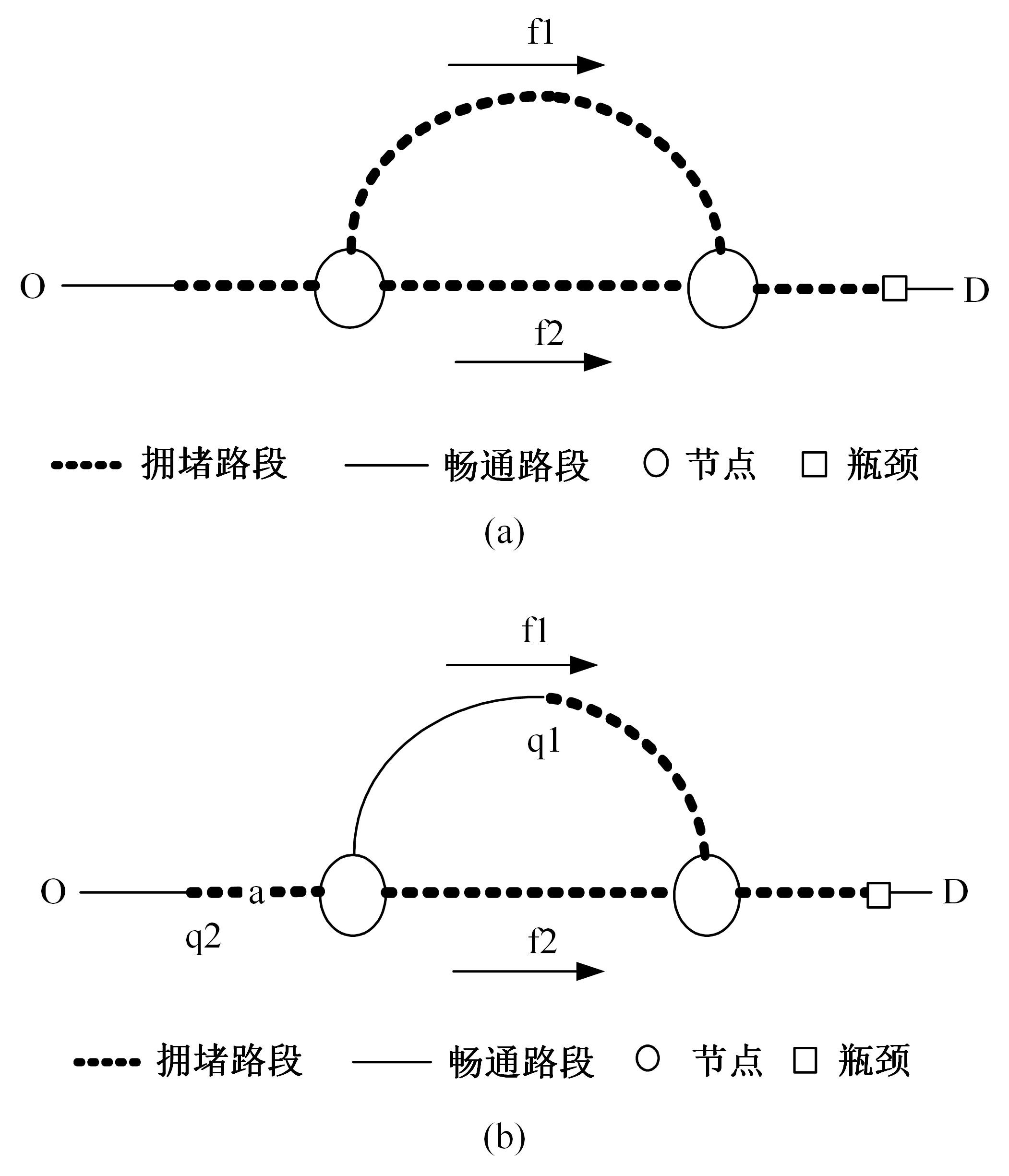
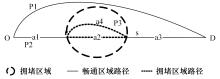
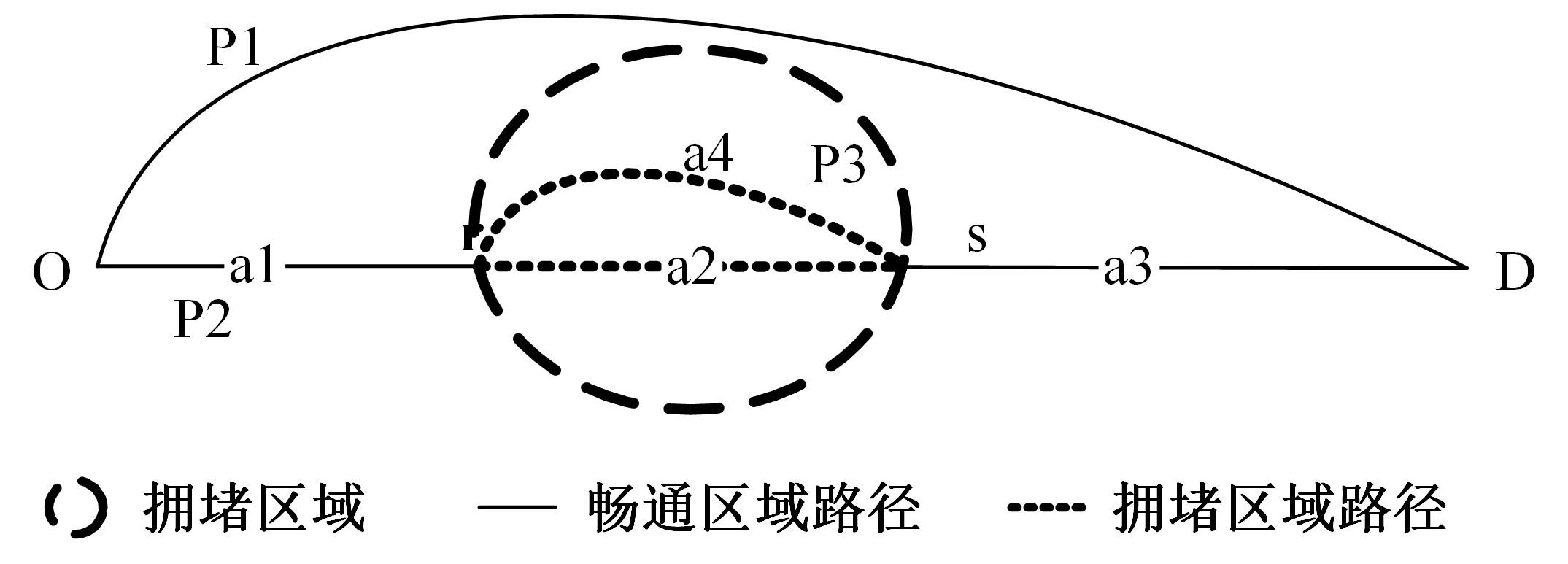
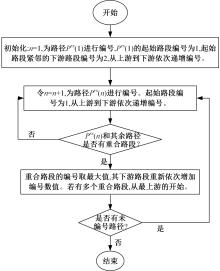
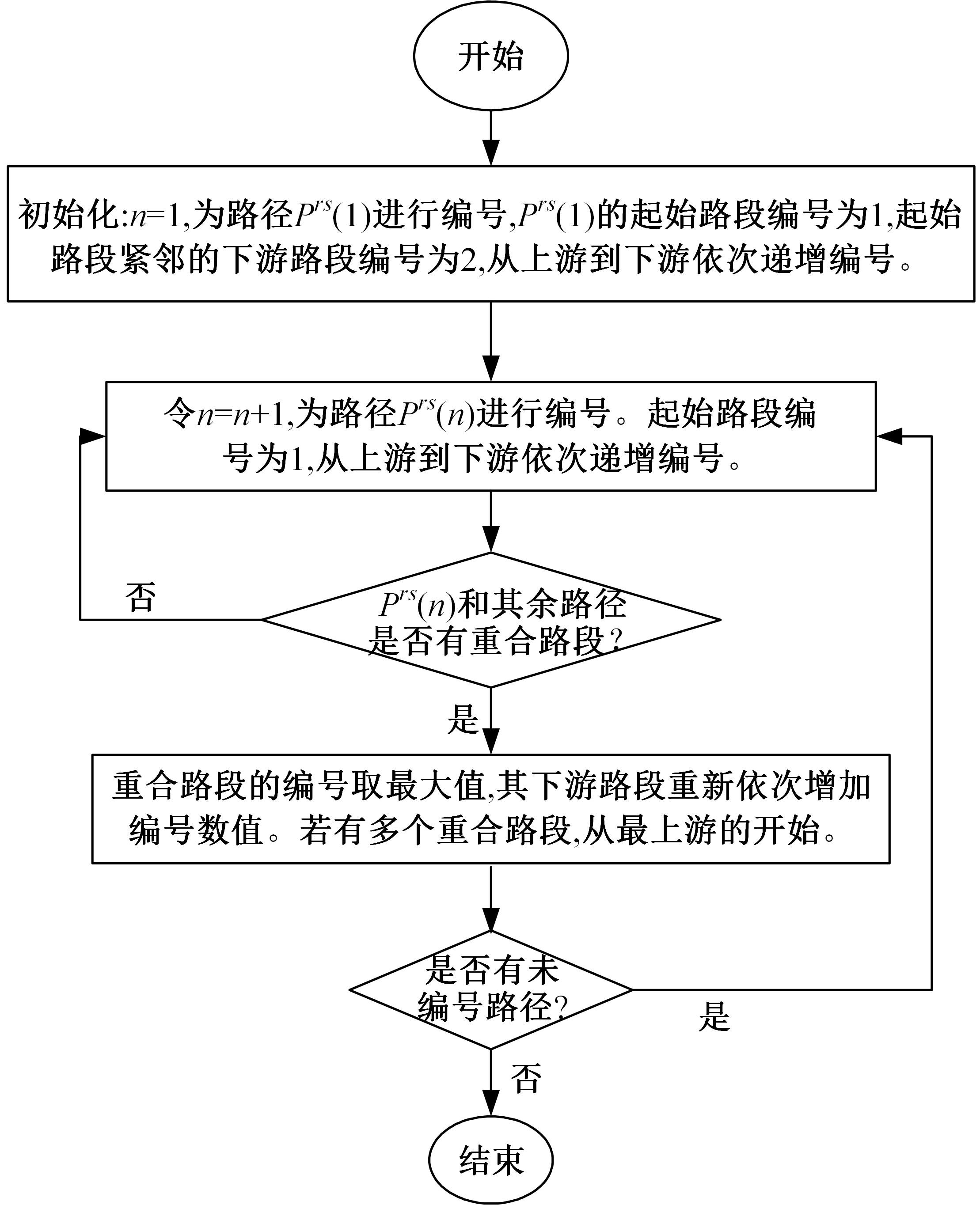
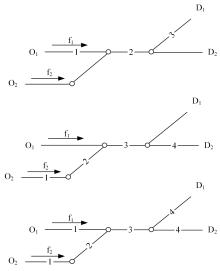
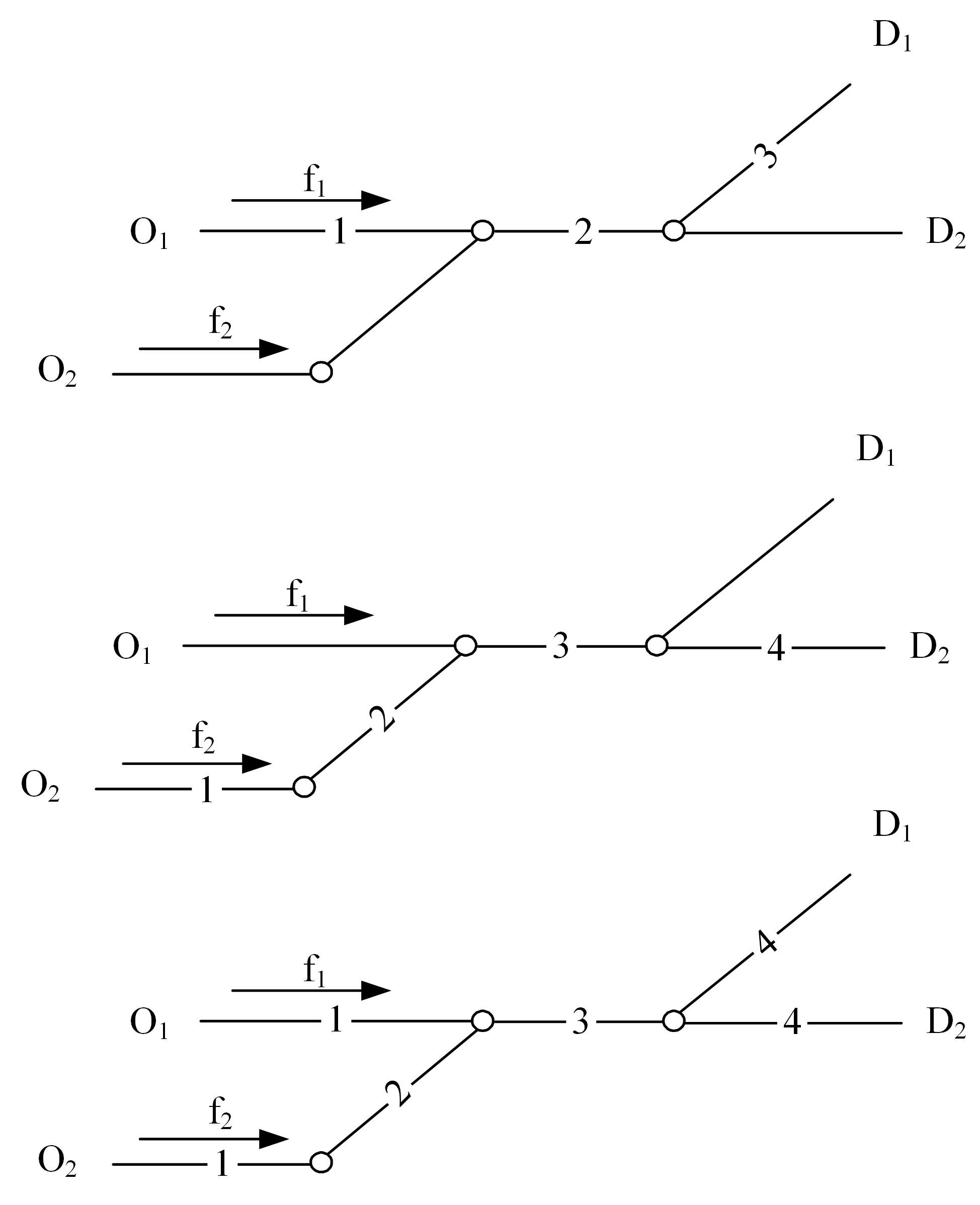
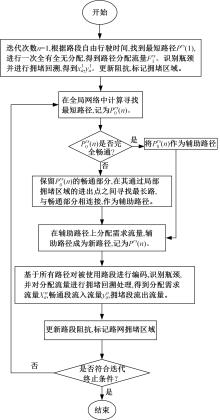
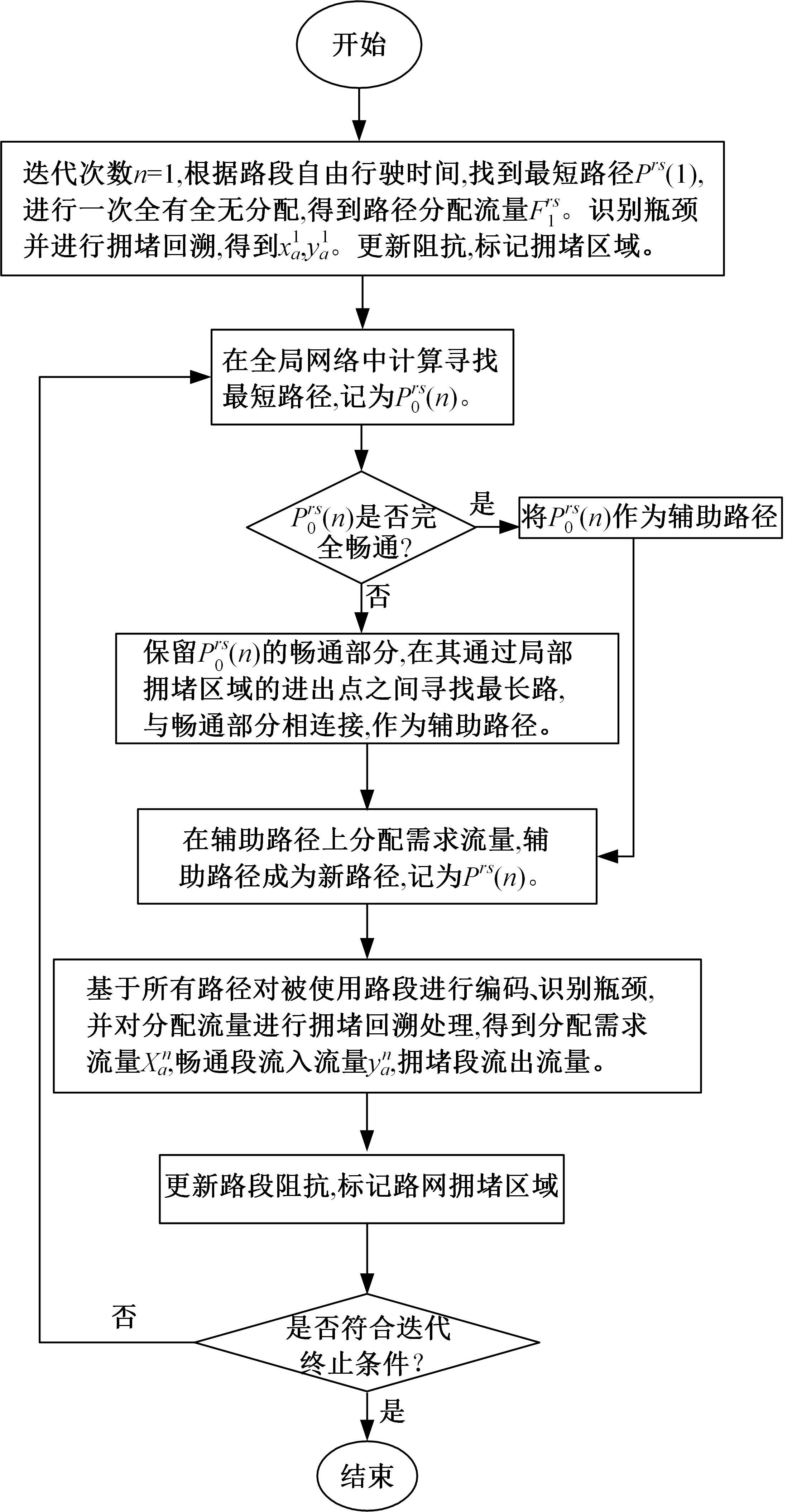
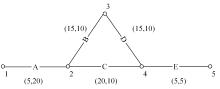
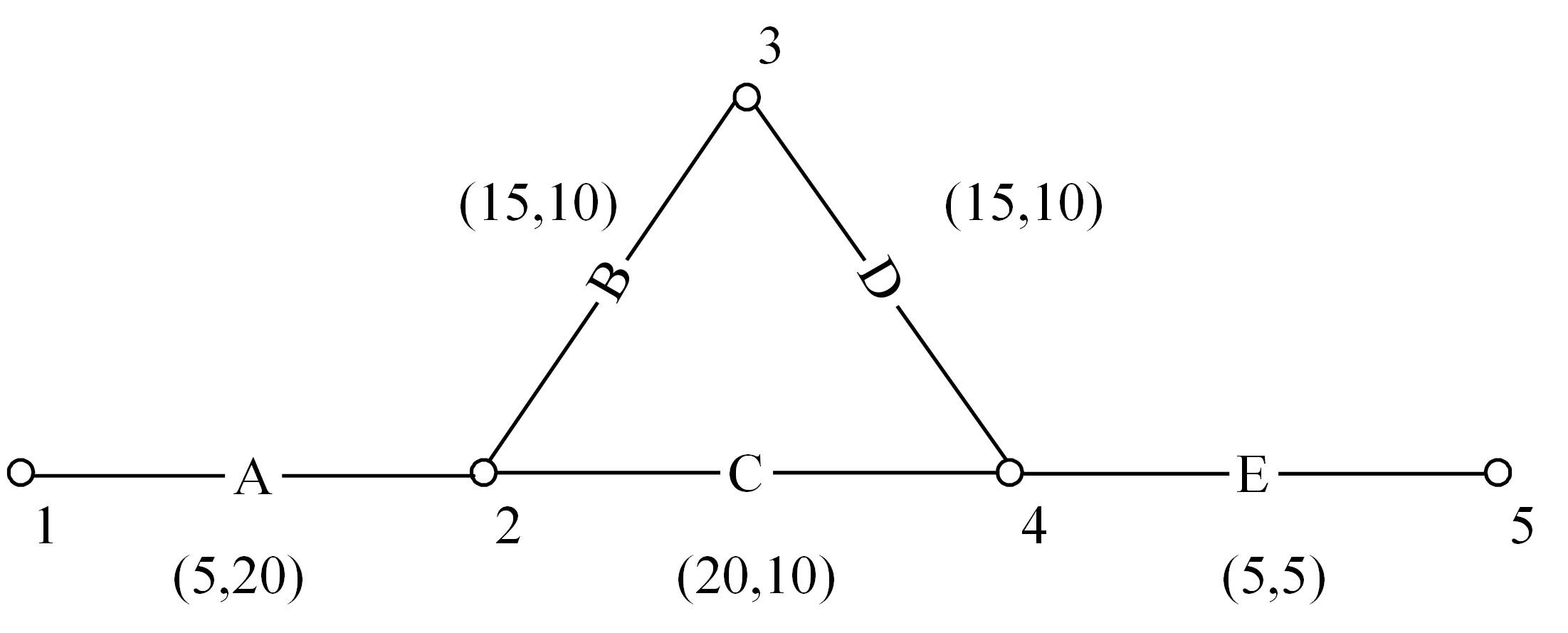
为求解考虑拥堵空间排队与溢出的道路网静态交通流分配问题,首先,基于拥堵空间排队将道路网络划分为局部拥堵区域与局部畅通区域,证明了存在拥堵干扰条件下不同队尾通过瓶颈时间相等;其次,提出了在全局区域内选择最短路而在局部拥堵区域内选择最长路的极小极大需求加载路径选择机制;然后,基于路段编码改进了需求压缩与拥堵回溯算法,提出了拥堵区识别算法并构建了迭代加权求解算法;最后,通过算例验证了求解算法的有效性。本文提出并解决了拥堵区识别、用户均衡原理、需求加载机制、迭代加权算法这4个核心问题,丰富和发展了考虑拥堵空间排队的静态交通流分配理论。
中图分类号:
- U491
| 1 | Thompson W A, Payne H J. Traffic assignment on a transportation network with capacity constraints and queueing[C]∥The 47th National ORSA/TIMS North American Meeting, Washington DC, USA, 1975:232-239. |
| 2 | Smith M J. Traffic control and traffic assignment in a signal-controlled network with queueing[C]∥International Symposium on the Theory of Traffic Flow and Transportation, Berkeley, USA, 1987: 61-77. |
| 3 | Bliemer M C J, Raadsen M P H, Smits E S, et al. Quasi-dynamic traffic assignment with residual point queues incorporating a first order node mode[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2014, 68: 363-384. |
| 4 | Michiel Bliemer, Luuk Brederodel, Luc Wismans, et al. Quasi-dynamic network loading: adding queuing and spillback to static traffic assignment[J]. ITLS Working Paper, 2012, 2: 1-20. |
| 5 | Smith M J. Traffic assignment and traffic control on a capacity constrained network with queueing[C]∥Annual Meeting of the Italian Operations Research Society, Rome, Italy, 1983. |
| 6 | Smith M J. A link-based elastic demand equilibrium in capacitated network models with queueing delays[J]. Transportation Research Part C, 2013, 29: 131-147. |
| 7 | Yang H, Yager S. Traffic assignment and traffic control in general freeway-arterial corridor systems[J]. Transportation Research Part B, 1994, 28(4): 463-486. |
| 8 | Larsson T, Patriksson M. An augment lagrangean dual algorithm gor link capacity side constrained traffic assignment problems[J]. Transportation Research Part B, 1995, 29(6): 433-455. |
| 9 | Bell M G H. Stochastic user equilibrium in networks with queues[J]. Transportation Research Part B, 1995, 29(2): 125-137. |
| 10 | Nesterow Y, de Palma A. Stationary dynamic solutions in congested transportation networks: summary and perspectives[J]. Networks and Spatial Economics, 2003, 3(3): 371-395. |
| 11 | Smith M, Huang W, Viti F. Equilibrium in capacitated network models with queueing delays, queue-storage, blocking back and control[C]∥20th International Symposium on Transportation and Traffic Theory, Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 2013: 860-879. |
| 12 | Bifulco G, Crisalli U. Stochastic user equilibrium and link capacity constrains: formulation and theoretical evidence[C]∥Proceedings of Seminar Held at Aet European Transport Conference, Loughborough, UK, 1998: 424. |
| 13 | Lam W H K, Zhang Y. Capacity-constrained Traffic assignment in network with residual queues[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2000, 126(2): 121-128. |
| 14 | Bliemer M C J, Raadsen M P H, Smits E S, et al. Quasi-dynamic traffic assignment with residual point queues incorporating a first order node model[J]. Transportation Research Part B, 2014, 68: 363-384. |
| 15 | Jin Wen-long. The traffic statics problem in a road network[J]. Transportation Research Part B, Methodological, Elsevier, 2012, 46(10): 1360-1373. |
| 16 | 岳昊,刘晓玲,孟晓雨,等. 拥堵道路网的静态交通流非均衡分配方法[J]. 北京交通大学学报,2017,41(03): 1-6. |
| Yue Hao, Liu Xiao-ling, Meng Xiao-yu, et al. A non-equilibrium method to solve static traffic assignment problem at the congested road network[J]. Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University, 2017, 41(3): 1-6. | |
| 17 | 岳昊,张鹏,刘晓玲,等. 拥堵路网交通流均衡分配模型[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2019, 51(9): 103-109. |
| Yue Hao, Zhang Peng, Liu Xiao-ling, et al. The equilibrium model for congested traffic assignment in road networks[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019, 51(9): 103-109. | |
| 18 | Bliemer M C J, Raadsen M P H. Static traffic assignment with residual queues and spillback[J]. Transportation Research Part B, 2020, 132: 303-319. |
| 19 | 岳昊,任孟杰,杨子玉,等. 考虑拥堵空间排队与溢出的道路网静态交通流分配[J]. 中国公路学报, 2022, 35(7): 241-250. |
| Yue Hao, Ren Meng-jie, Yang Zi-yu, et al. Static traffic assignment on road network with congestion spatial queuing and spillback[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2022, 35(7): 241-250. |
| [1] | 杜筱婧,姚荣涵. 智能网联公交车出站强制换道的演化博弈机制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 124-135. |
| [2] | 马壮林,崔姗姗,胡大伟,王晋. 限行政策下传统小汽车出行者出行方式选择[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 1981-1993. |
| [3] | 张雅丽,付锐,袁伟,郭应时. 考虑能耗的进出站驾驶风格分类及识别模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2029-2042. |
| [4] | 尹超英,陆颖,邵春福,马健霄,许得杰. 考虑空间自相关的建成环境对通勤方式选择的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 1994-2000. |
| [5] | 潘恒彦,王永岗,李德林,陈俊先,宋杰,杨钰泉. 基于交通冲突的长纵坡路段追尾风险评估及预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1355-1363. |
| [6] | 宋灿灿,荆迪菲,谢俊峰,康可心. 设置广告牌的高速公路平曲线路段驾驶行为分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1345-1354. |
| [7] | 卢凯,徐广辉,叶志宏,林永杰. 考虑清空时间的双向队首绿波协调控制数解算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 421-429. |
| [8] | 曹倩,李志慧,陶鹏飞,马永建,杨晨曦. 考虑风险异质特性的路网交通事故风险评估方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(10): 2817-2825. |
| [9] | 张鑫,张卫华. 快速路合流区主线不同交通状态下的安全性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1308-1314. |
| [10] | 曲大义,赵梓旭,贾彦峰,王韬,刘琼辉. 基于Lennard-Jones势的车辆跟驰动力学特性及模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2549-2557. |
| [11] | 董春娇,董黛悦,诸葛承祥,甄理. 电动自行车出行特性及骑行决策行为建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2618-2625. |
| [12] | 曲大义,黑凯先,郭海兵,贾彦峰,王韬. 车联网环境下车辆换道博弈行为及模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 101-109. |
| [13] | 张文会,伊静,刘委,于秋影,王连震. 基于MADYMO的大客车追尾碰撞事故乘员损伤机理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 118-126. |
| [14] | 刘志伟,刘建荣,邓卫. 基于潜在类别的无人驾驶汽车选择行为[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1261-1268. |
| [15] | 徐进,潘存书,符经厚,刘俊,王郸祁. 典型道路场景以及场景切换时的速度行为特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1331-1341. |
|
||