吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (1): 118-126.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200728
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
基于MADYMO的大客车追尾碰撞事故乘员损伤机理
- 东北林业大学 交通学院,哈尔滨 150040
Injury mechanism of occupants in bus during rear-end crash based on MADYMO
Wen-hui ZHANG( ),Jing YI,Wei LIU,Qiu-ying YU,Lian-zhen WANG(
),Jing YI,Wei LIU,Qiu-ying YU,Lian-zhen WANG( )
)
- School of Traffic and Transportation,Northeast Forestry University,Harbin 150040,China
摘要:
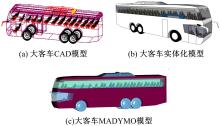
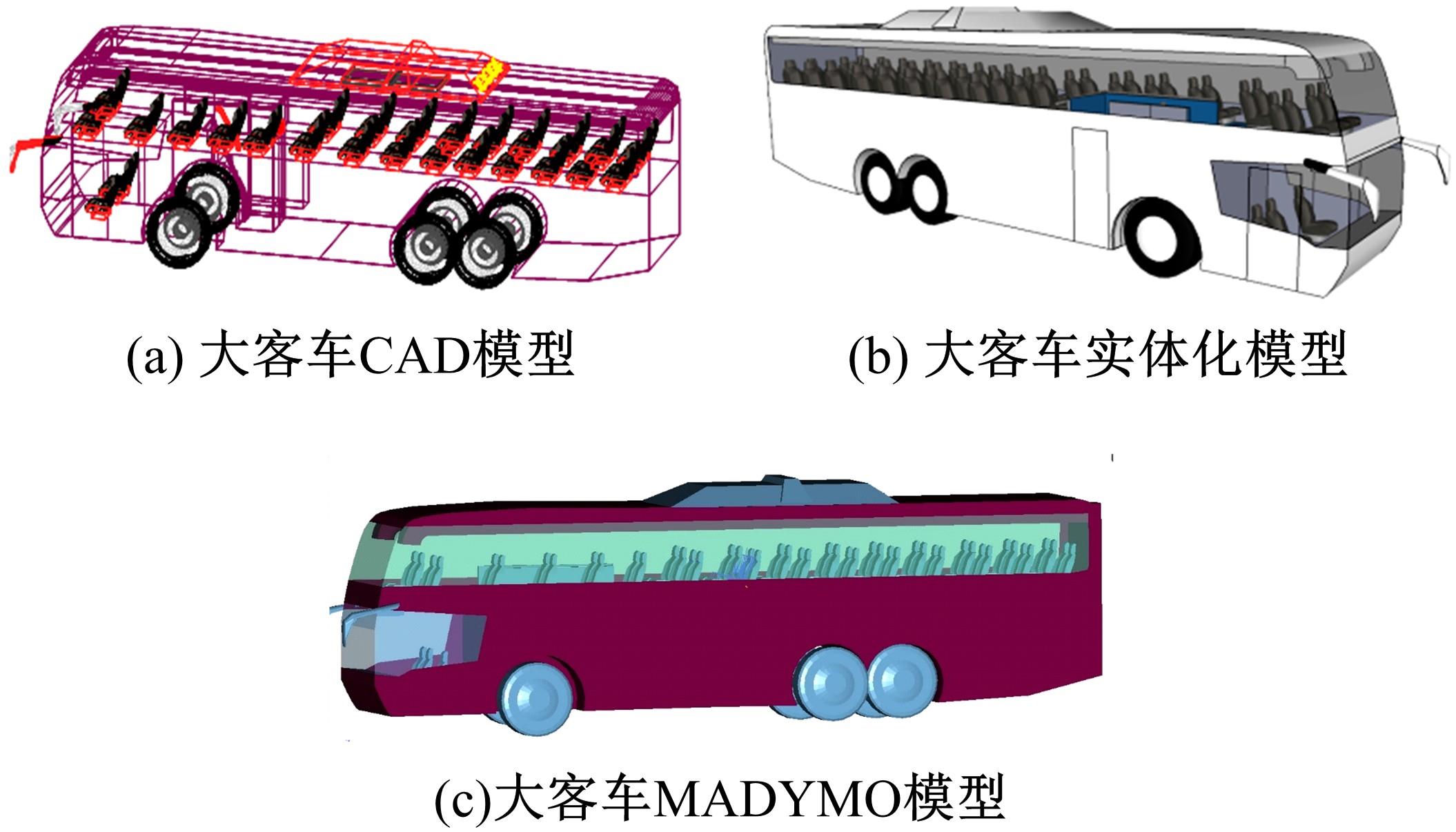
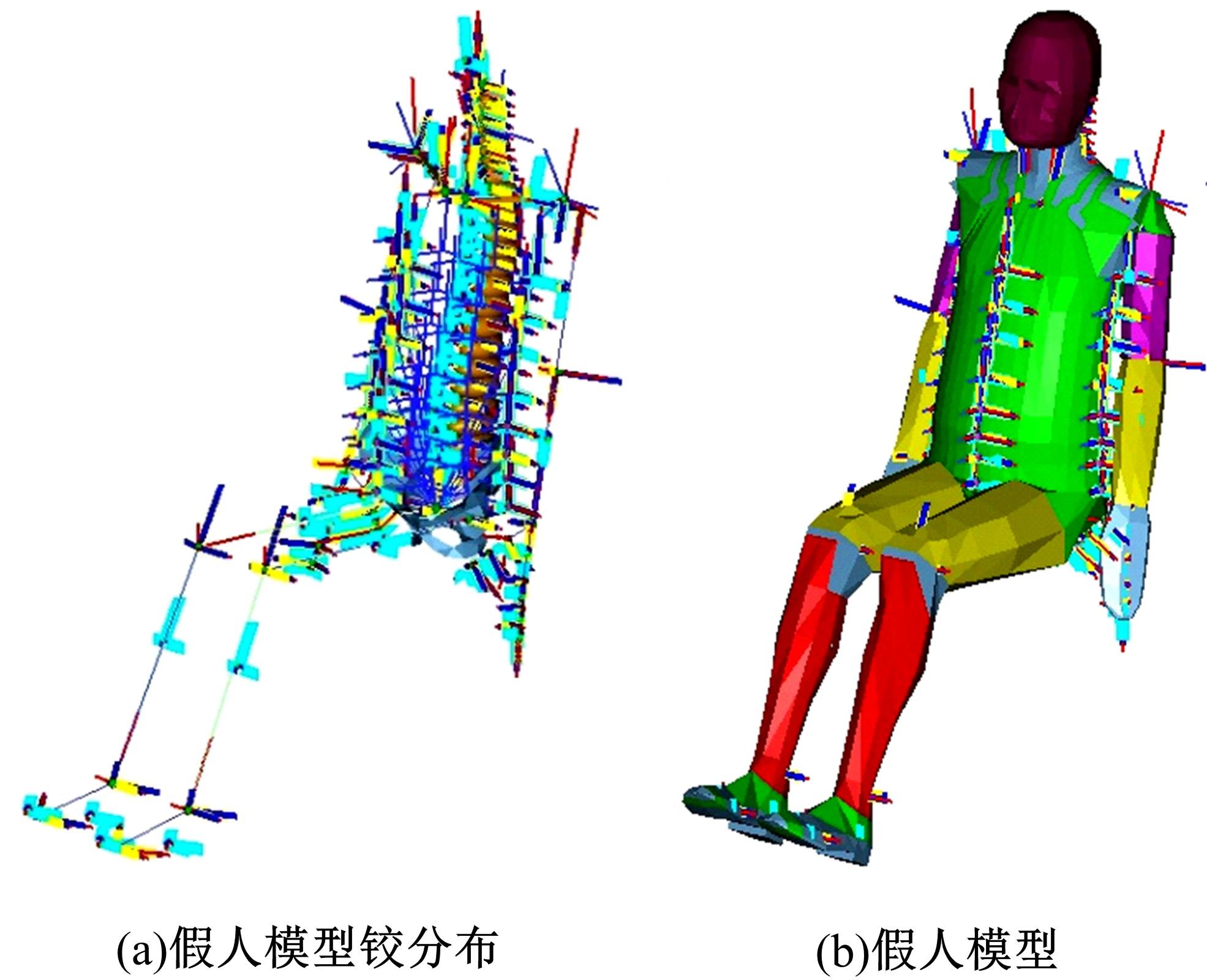
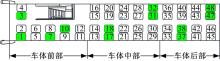
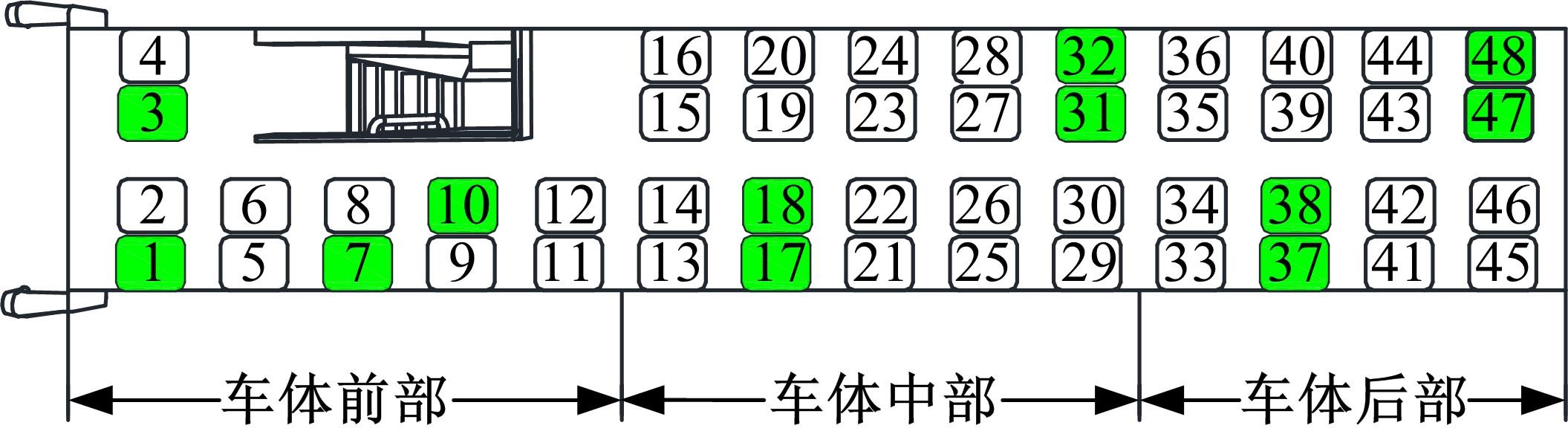
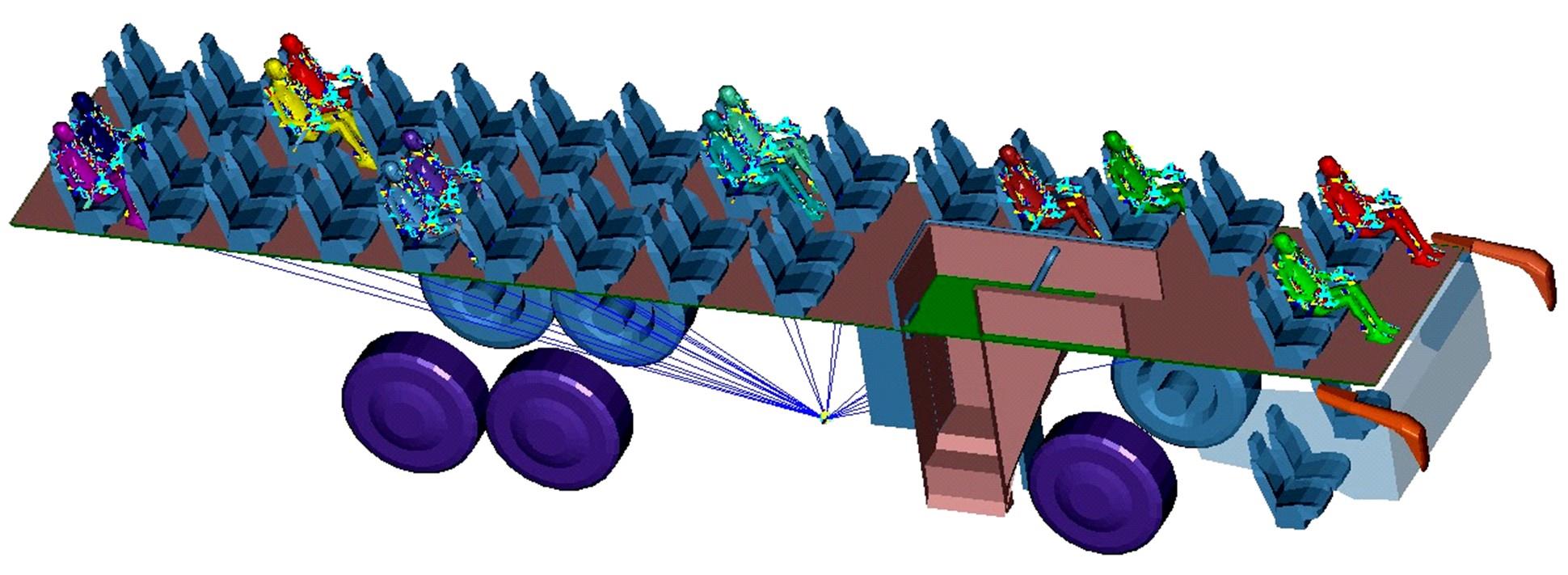
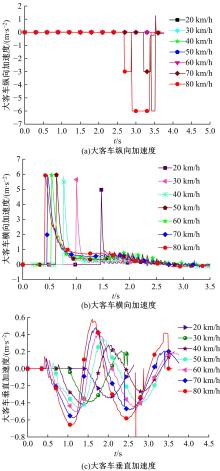
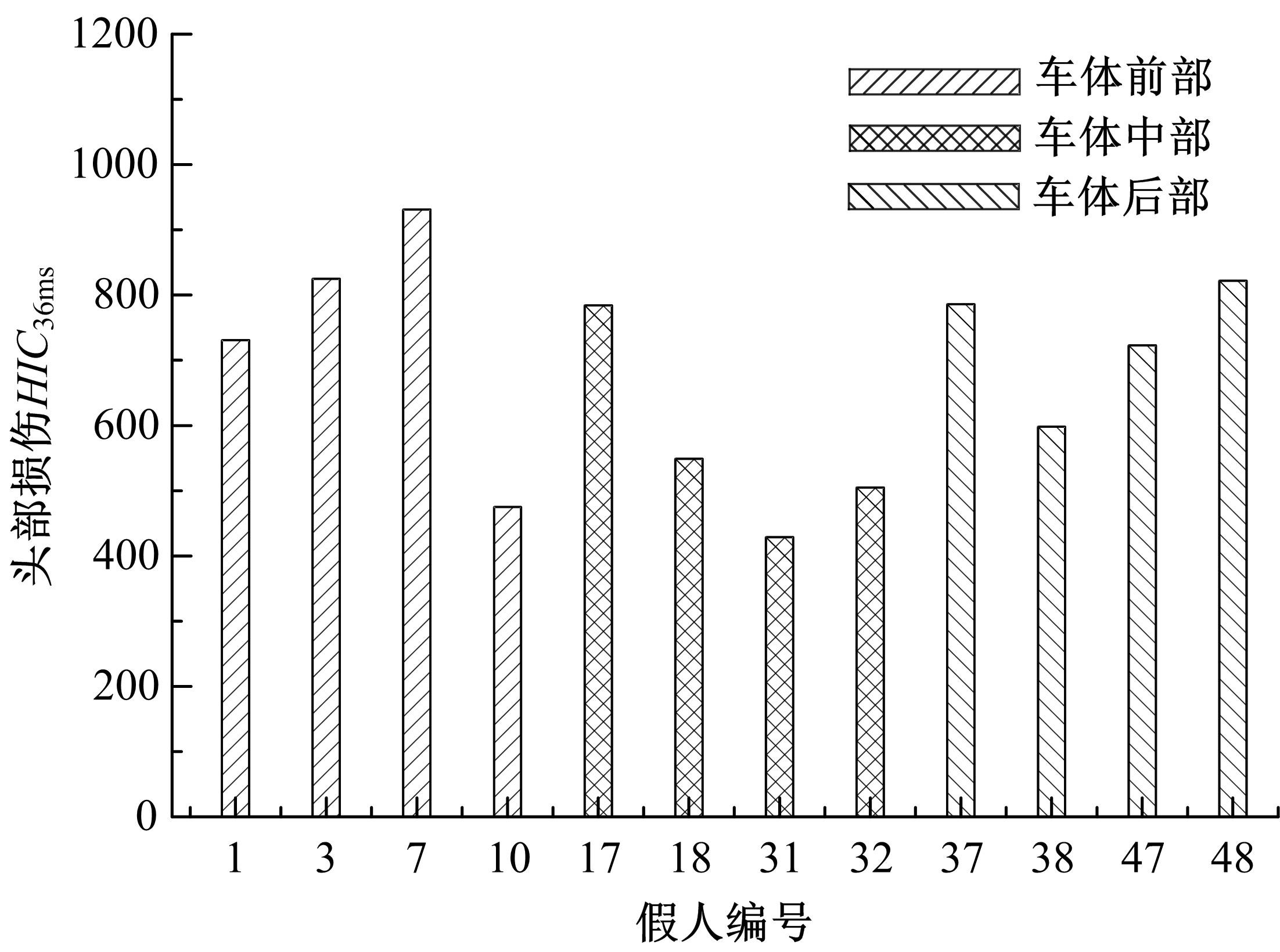
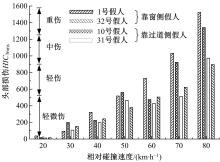
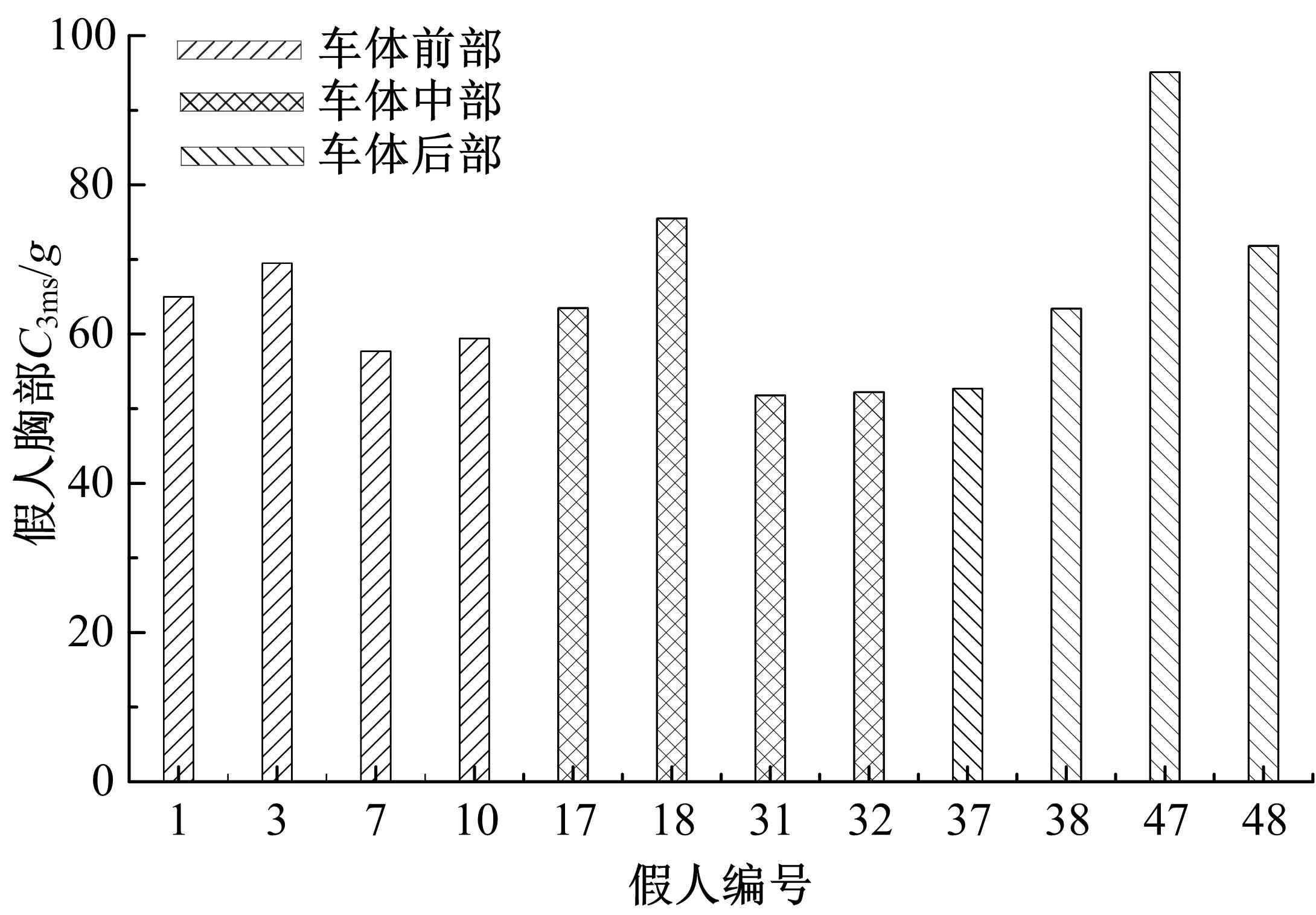
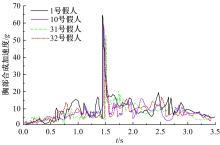
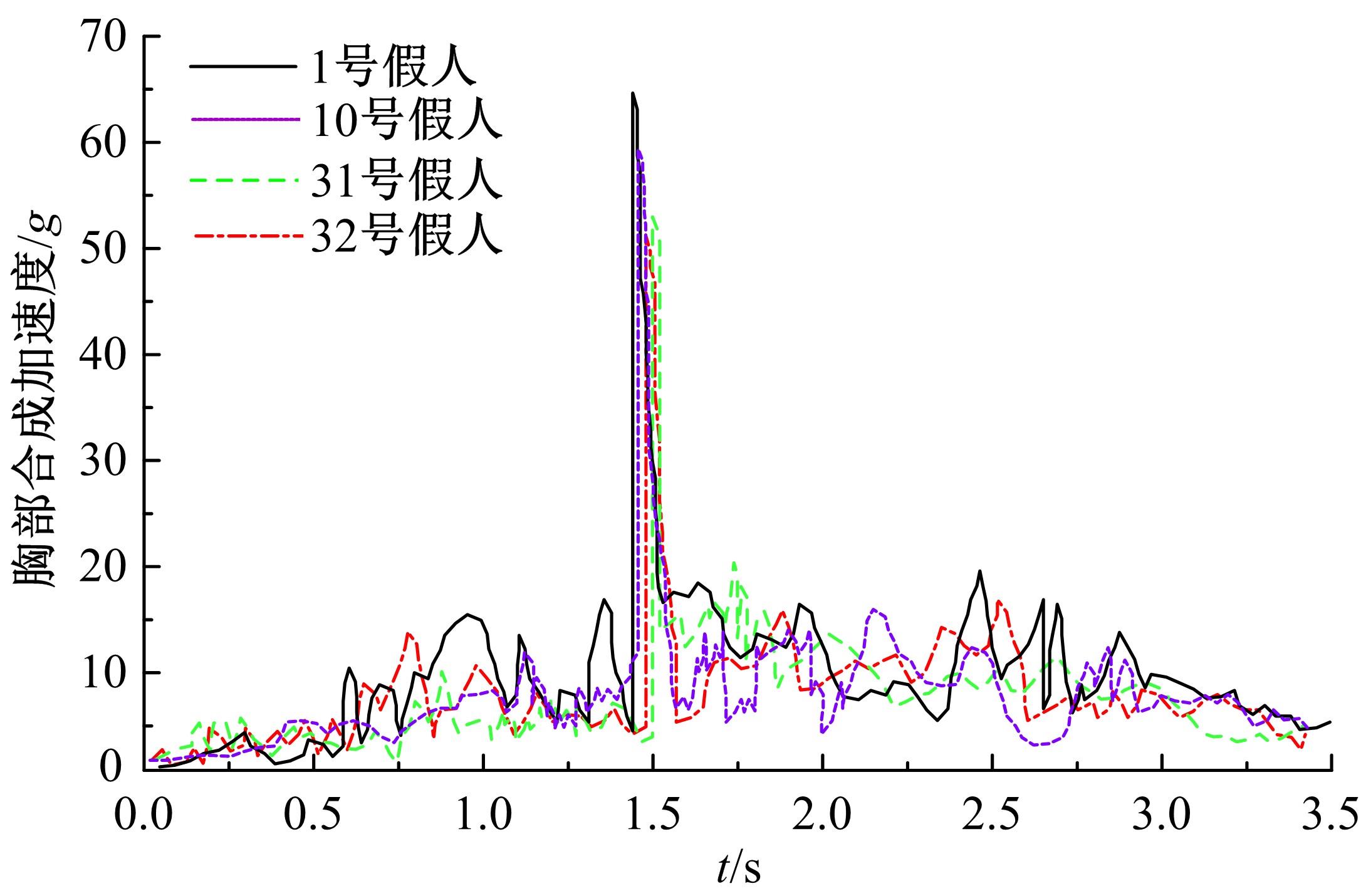
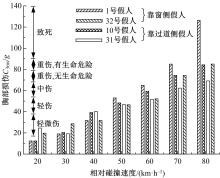
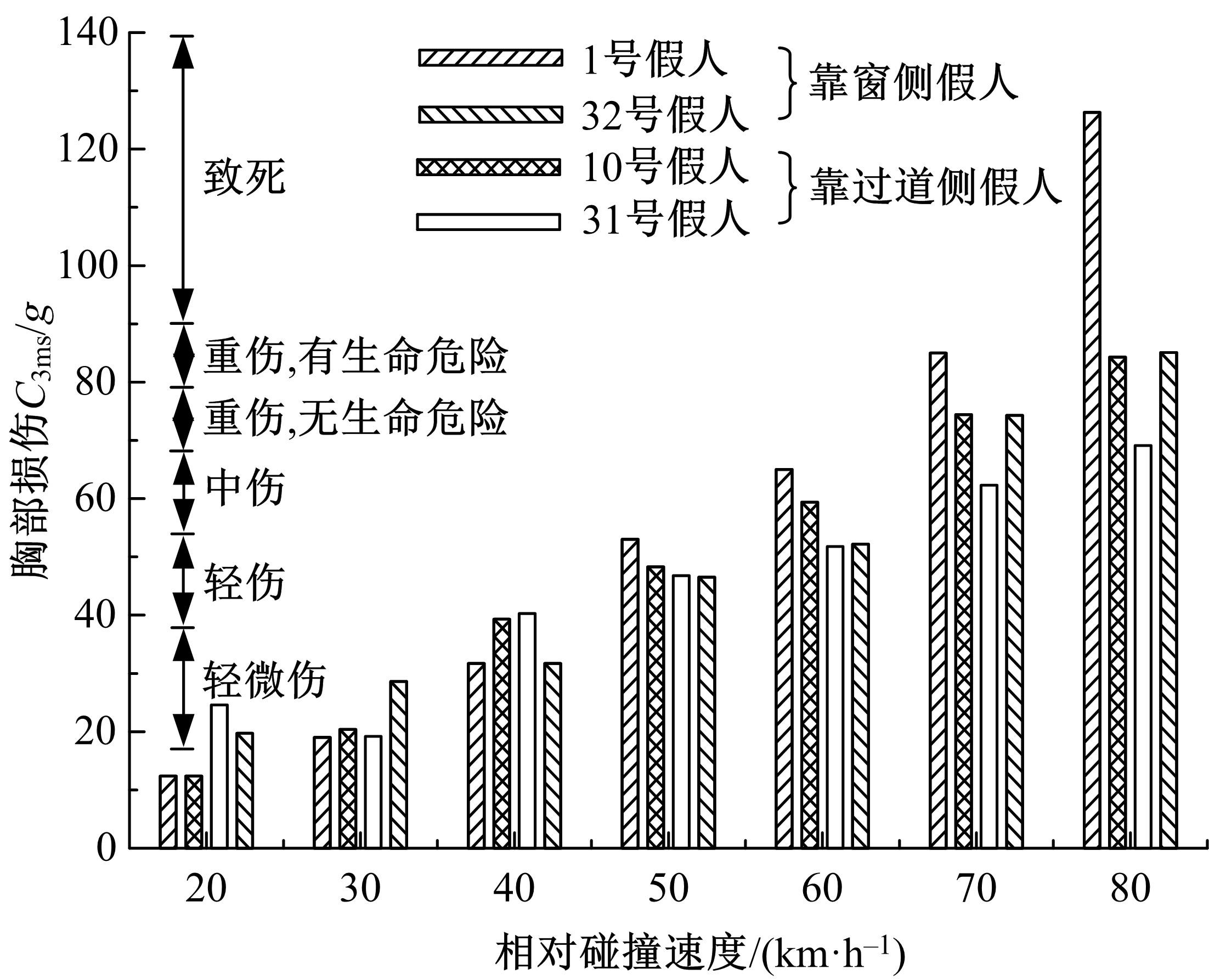
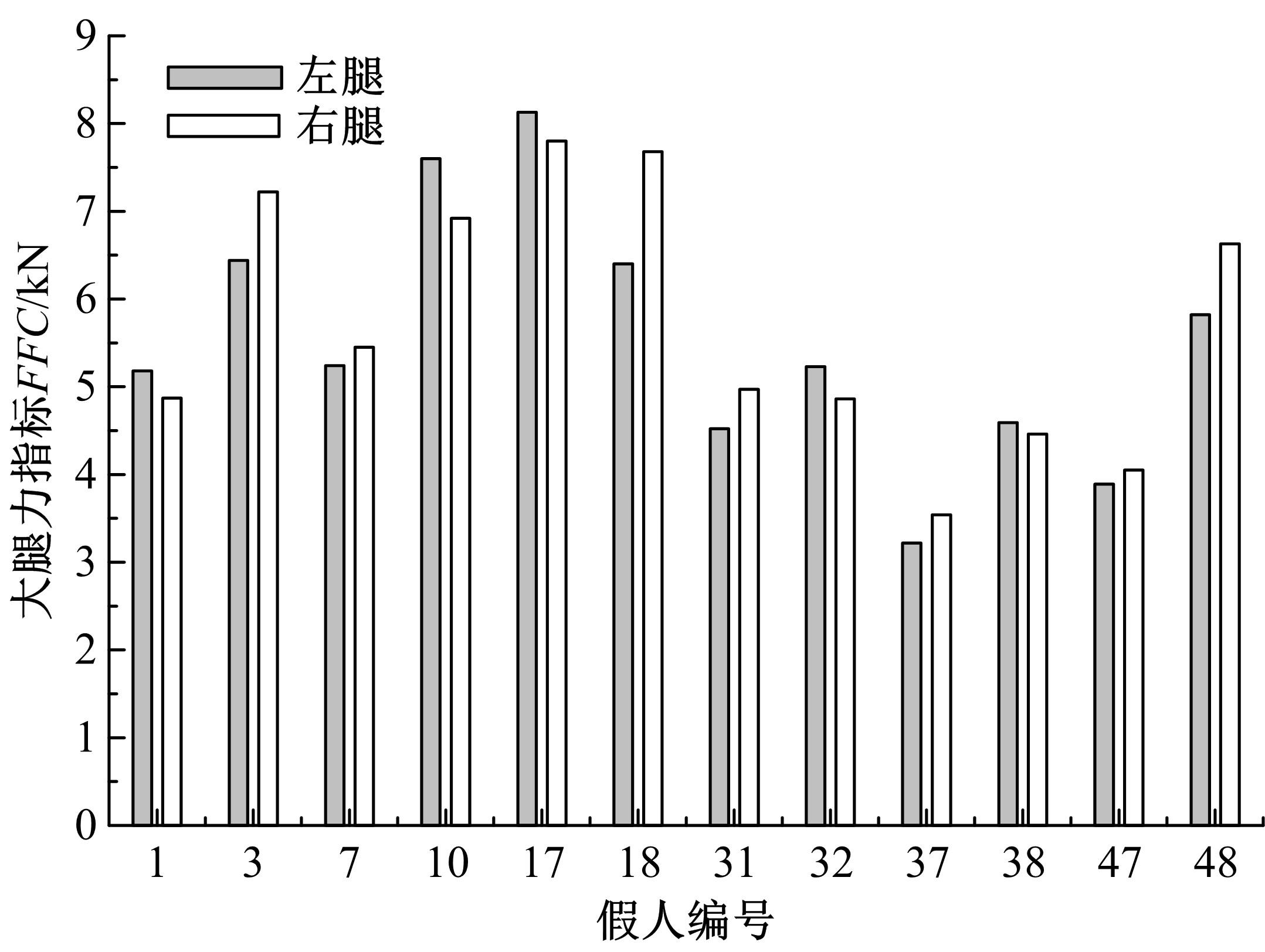
为使乘员在大客车追尾事故发生时可以根据不同位置进行有针对性的保护,利用有限元和多刚体动力学软件,构建了大客车模型、12个假人模型和安全带模型,并分配假人模型于大客车的不同位置。加载重力加速度、碰撞波形和相对碰撞速度等参数到仿真模型中,最终得到不同相对碰撞速度下假人的头部、胸部、腿部损伤指标值。研究结果表明,相对碰撞速度越大,乘员的头部、胸部、腿部损伤指标值越大,相对碰撞速度大于60 km/h,部分乘员的头部和胸部会受到4级或4级以上程度的严重损伤;车体前部和后部座椅上乘员的加权损伤值(WIC)较中部座椅上乘员的加权损伤值更大;靠近挡风玻璃侧乘员的WIC比同排座椅靠近过道侧乘员的WIC更大。
中图分类号:
- U491.31
| 1 | 杨亚东. 基于突变理论的道路交通事故致因机理研究[J]. 交通工程, 2018, 18(3): 40-45. |
| Yang Ya-dong. Study on the cause mechanism of road traffic accidents based on catastrophe theory[J]. Traffic Engineering, 2018, 18(3): 40-45. | |
| 2 | Chen C, Liu X M, Chen H H. A rear-end collision risk evaluation and control scheme using a bayesian network model[J]. Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2019, 20(1): 264-284. |
| 3 | 江亮,贺宜.电动两轮车风险驾驶行为及事故影响因素分析[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(4): 1107-1113. |
| Jiang Liang, He Yi. Analysis of risky driving behavior and accident influencing factors of electric two-wheeled vehicles[J]. Journal of Jilin University( Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1107-1113. | |
| 4 | 张文会, 于秋影, 沈航先. 基于SEM的高速公路事故路段行车风险因素辨识[J]. 森林工程, 2021, 37(2): 95-103. |
| Zhang Wen-hui, Yu Qiu-ying, Shen Hang-xian. SEM-based identification of driving risk factors in highway accident sections[J]. Forest Engineering,2021, 37(2): 95-103. | |
| 5 | 兰凤崇,王俊峰,曾子聪,等. 人-车碰撞事故再现及头部损伤生物力学分析[J]. 重庆理工大学学报: 自然科学, 2019, 33(8): 8-15. |
| Lan Feng-chong, Wang Jun-feng, Zeng Zi-cong, et al. Reconstruction of human vehicle collision and biomechanical analysis of head injury[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology: Natural Science, 2019,33(8): 8-15. | |
| 6 | Ge Ru-hai, Zhang Su-xiu, Hong Liang. Optimization of front-row occupant restraint system with NSGA-Ⅱ genetic algorithm[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2017, 39(12):1382-1389. |
| 7 | 陈吉清,杜天亚,兰凤崇,等. 汽车碰撞中乘员腹部损伤机理及生物力学响应研究进展[J]. 汽车工程学报, 2015, 5(2): 79-89. |
| Chen Ji-qing, Du Tian-ya, Lan Feng-chong, et al. Research progress on mechanism and biomechanical response of occupant abdominal injury in vehicle collision[J]. Acta Automotive Engineering, 2015, 5(2): 79-89. | |
| 8 | Jost R, Nurick G N. Finite element modelling of the human body in vehicle side impact[J]. International Journal of Crashworthiness, 1999, 4(1):31-37. |
| 9 | Xu J J, Wali B H, Li X B, et al. Injury severity and contributing driver actions in passenger vehicle-truck collisions[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2019, 16(19): 3542. |
| 10 | Zou Tie-fang, Yu Zhi, Cai Ming, et al. Car-pedestrian accident reconstruction based on Pc-Crash[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2011, 30(3): 215-219. |
| 11 | 周华,彭一峻,刘卓异,等. 约束系统对不同体型女性驾驶人的保护研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(4): 76-82. |
| Zhou Hua, Peng Yi-jun, Liu Zhuo-yi, et al. Study on the protection of restraint system for female drivers with different body sizes[J]. Chinese Journal of safety Sciences, 2019, 29(4): 76-82. | |
| 12 | 周鸣昊,李傲,谷先广. 考虑多种工况的乘员约束系统可靠性优化设计[J]. 合肥工业大学学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 42(7): 888-894. |
| Zhou Ming-hao, Li Ao, Gu Xian-guang. Reliability optimization design of occupant restraint system considering various working conditions[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 42(7): 888-894. | |
| 13 | 张鹏,张道文,肖凌云,等. 男性行人与SUV正碰后的运动形态及损伤研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2019, 29(1): 25-30. |
| Zhang Peng, Zhang Dao-wen, Xiao Ling-yun, et al. Study on the movement pattern and injury of male pedestrian after frontal collision with SUV[J]. Chinese Journal of Safety Sciences, 2019, 29(1): 25-30. | |
| 14 | 王波, 何洋扬, 聂冰冰,等. 底部爆炸条件下车内乘员的腹部损伤[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2021, 51(3): 792-798. |
| Wang Bo, He Yang-yang, Nie Bing-bing, et al. Abdominal injury of occupants in a car under the condition of bottom explosion[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 792-798. | |
| 15 | 洪汉池,黄红武. 客车侧翻碰撞中安全带对乘员损伤的影响分析[J]. 重庆大学学报, 2016, 39(3): 140-146. |
| Hong Han-chi, Huang Hong-wu. Analysis of the impact of seat belt on occupant injury in rollover crash[J]. Journal of Chongqing University, 2016, 39(3): 140-146. | |
| 16 | 曹立波,欧阳志高,徐哲,等. 可逆约束系统参数匹配优化研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2016, 52(10): 133-141. |
| Cao Li-bo, Ouyang Zhi-gao, Xu Zhe, et al. Study on parameter matching optimization of reversible constrained systems[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2016, 52(10): 133-141. |
| [1] | 曲大义,黑凯先,郭海兵,贾彦峰,王韬. 车联网环境下车辆换道博弈行为及模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 101-109. |
| [2] | 李明,薛庆峰,张可欣,吕然,韦长华. 电动汽车热泵空调系统性能分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 1943-1952. |
| [3] | 刘志伟,刘建荣,邓卫. 基于潜在类别的无人驾驶汽车选择行为[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1261-1268. |
| [4] | 徐进,潘存书,符经厚,刘俊,王郸祁. 典型道路场景以及场景切换时的速度行为特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1331-1341. |
| [5] | 查伟雄,蔡其燕,李剑,严利鑫. 边路车辆出入条件下城市干线信号协调相位差优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 565-574. |
| [6] | 陈学深,黄柱健,马旭,齐龙,方贵进. 水稻机械除草避苗控制系统设计与试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 386-396. |
| [7] | 王扬, 王晓梅, 陈泽仁, 于建群. 基于离散元法的玉米籽粒建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1537-1547. |
| [8] | 王扬, 吕凤妍, 徐天月, 于建群. 大豆籽粒形状和尺寸分析及其建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 507-517. |
| [9] | 李俊烨, 乔泽民, 杨兆军, 张心明. 介观尺度下磨料浓度对磨粒流加工质量的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 837-843. |
| [10] | 孙轶轩, 邵春福, 岳昊, 朱亮. 基于SVM灵敏度的城市交通事故严重程度影响因素分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(5): 1315-1320. |
| [11] | 李志斌, 刘攀, 金茂菁, 徐铖铖. 高速公路常发拥堵路段追尾事故风险实时预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(06): 1482-1487. |
| [12] | 姚亮, 初亮, 周飞鲲, 刘明辉, 张永生, 魏文若. 纯电动轿车制动能量回收节能潜力仿真分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(01): 6-11. |
| [13] | 王登峰, 季枫, 陈书明, 苏丽俐, 郝赫. 多轴重型汽车气动制动防抱死系统性能仿真与试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(增刊1): 7-12. |
| [14] | 陈晋市, 元万荣, 袁华山, 刘昕晖, 王展. 基于AMESim的滑移装载机自动调平系统[J]. , 2012, (06): 1390-1395. |
| [15] | 陈立军, 孙博, 薛宏, 刁建超. 燃烧控制系统H∞鲁棒控制器设计 [J]. , 2012, (03): 726-731. |
|
||