吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (5): 1323-1331.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220744
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
山区双车道公路货车移动遮断小客车跟驰风险预测模型
戢晓峰1,2( ),徐迎豪1,2,普永明1,2,郝京京1,2,覃文文1,2(
),徐迎豪1,2,普永明1,2,郝京京1,2,覃文文1,2( )
)
- 1.昆明理工大学 交通工程学院,昆明 650504
2.云南省现代物流工程研究中心,昆明 650604
Risk prediction model of passenger car following behavior under truck movement interruption of two-lane highway in mountainous area
Xiao-feng JI1,2( ),Ying-hao XU1,2,Yong-ming PU1,2,Jing-jing HAO1,2,Wen-wen QIN1,2(
),Ying-hao XU1,2,Yong-ming PU1,2,Jing-jing HAO1,2,Wen-wen QIN1,2( )
)
- 1.School of Transportation Engineering, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming 650504, China
2.Yunnan Modern Logistics Engineering Research Center, Kunming 650604, China
摘要:
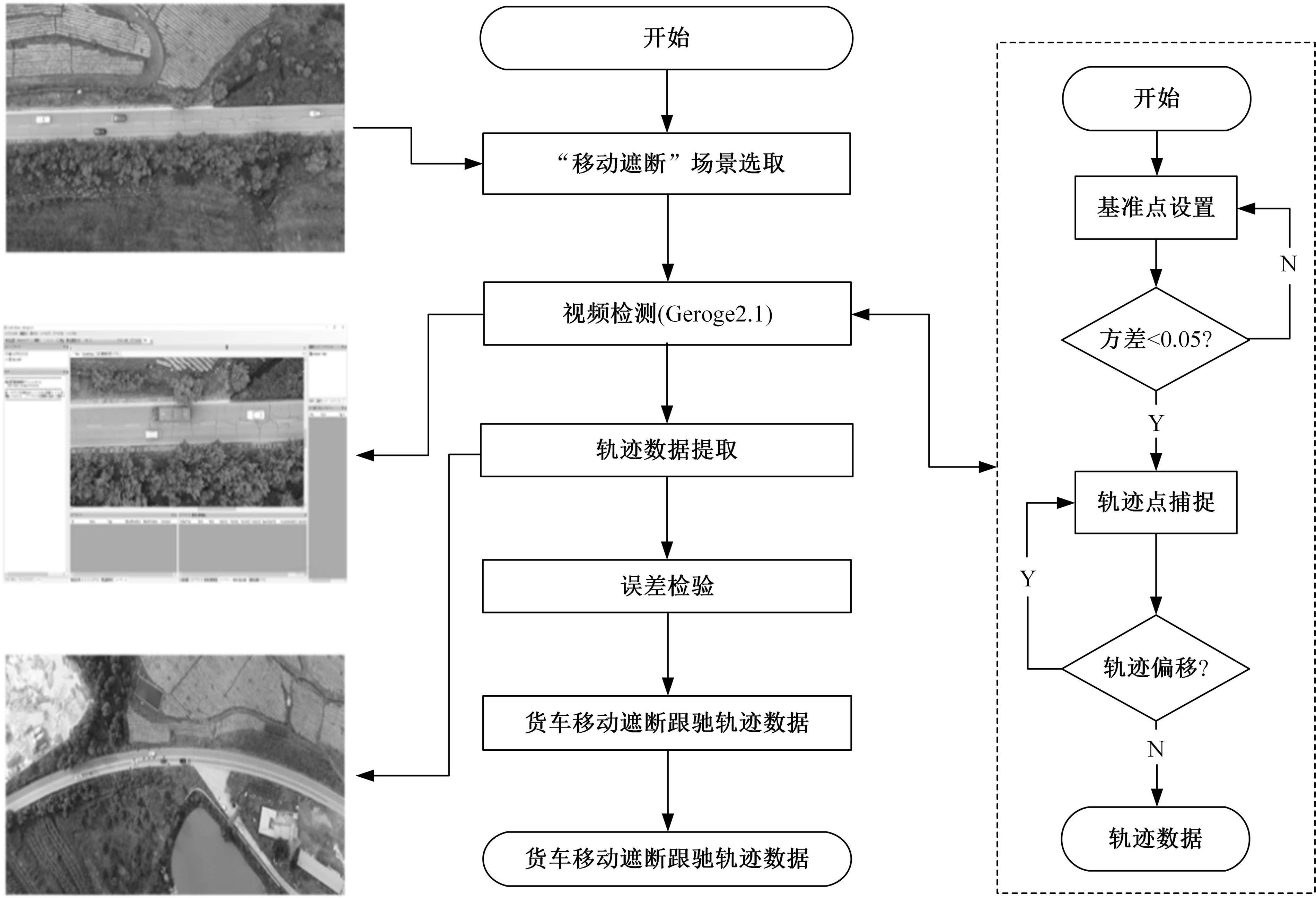
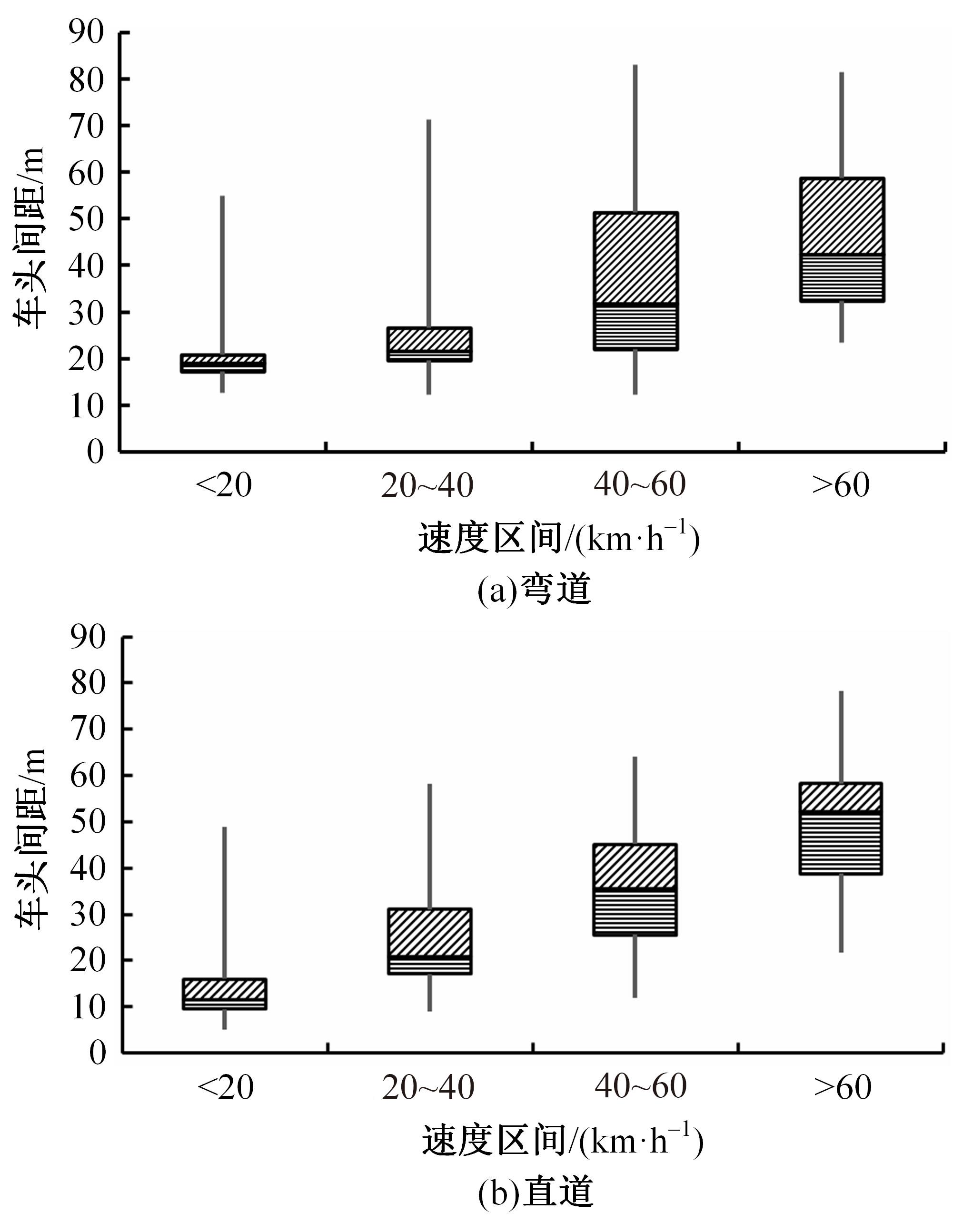
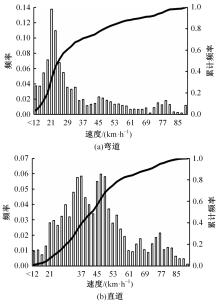
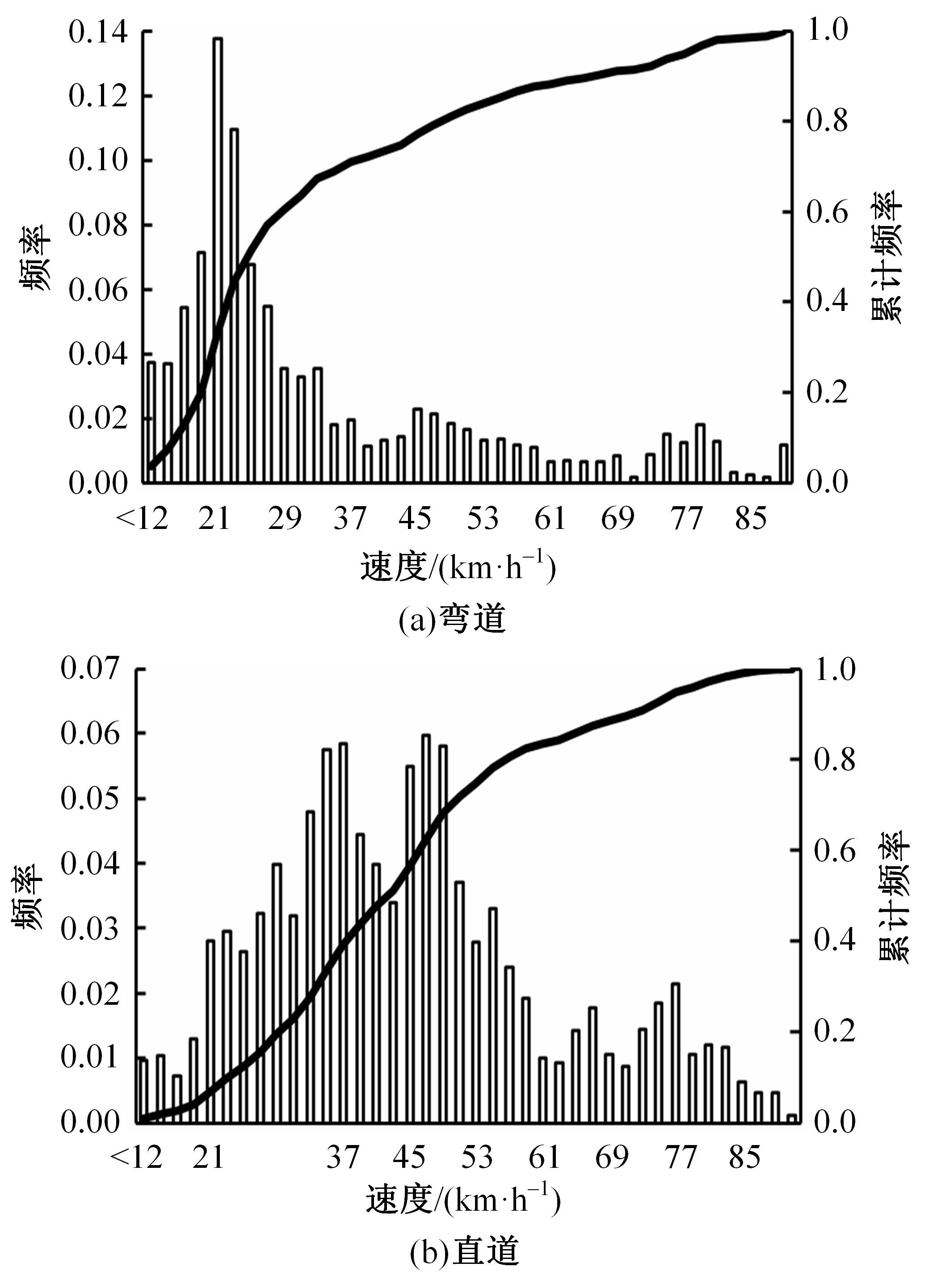
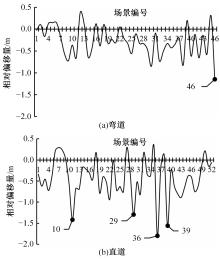
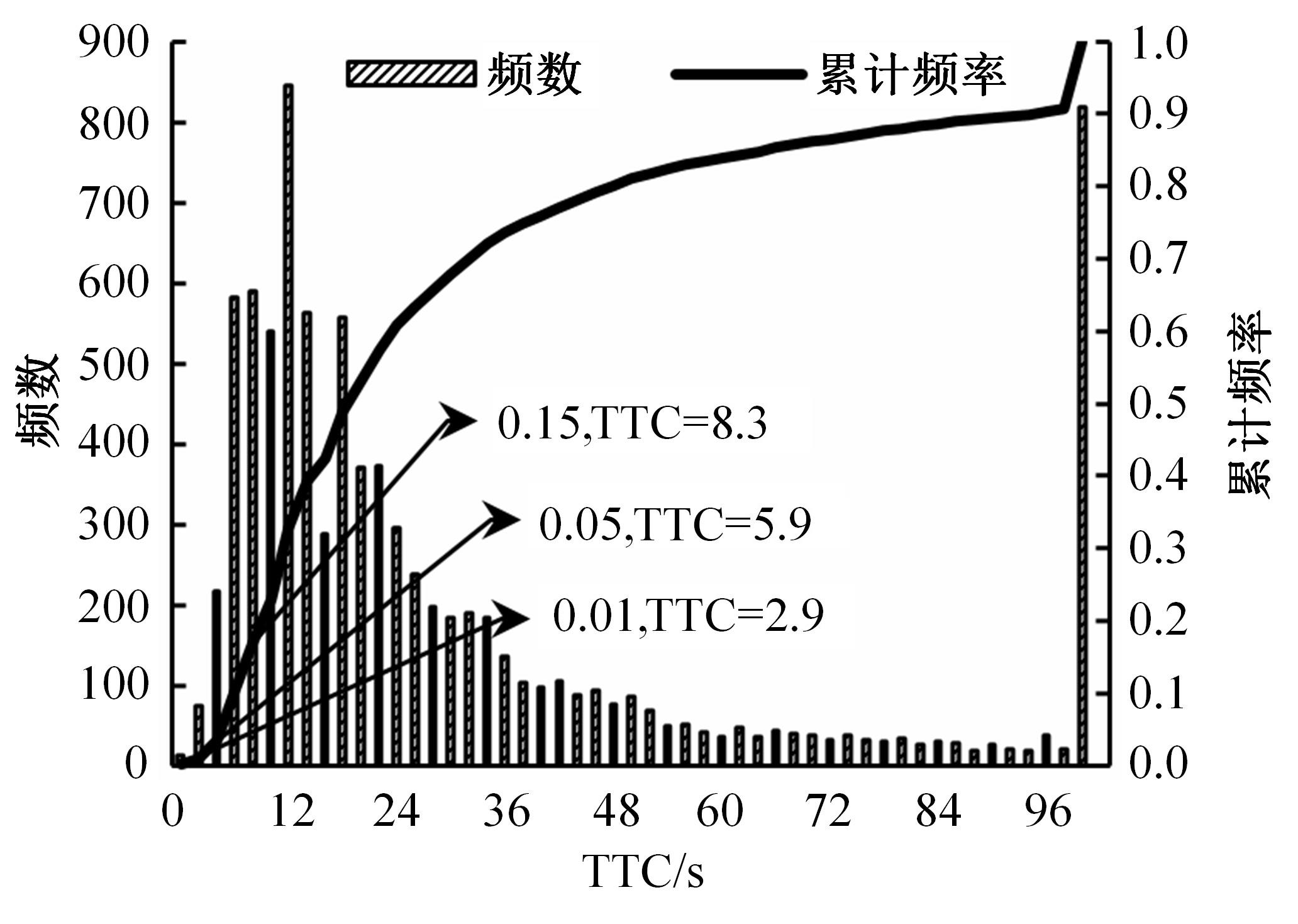
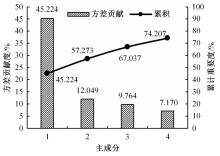
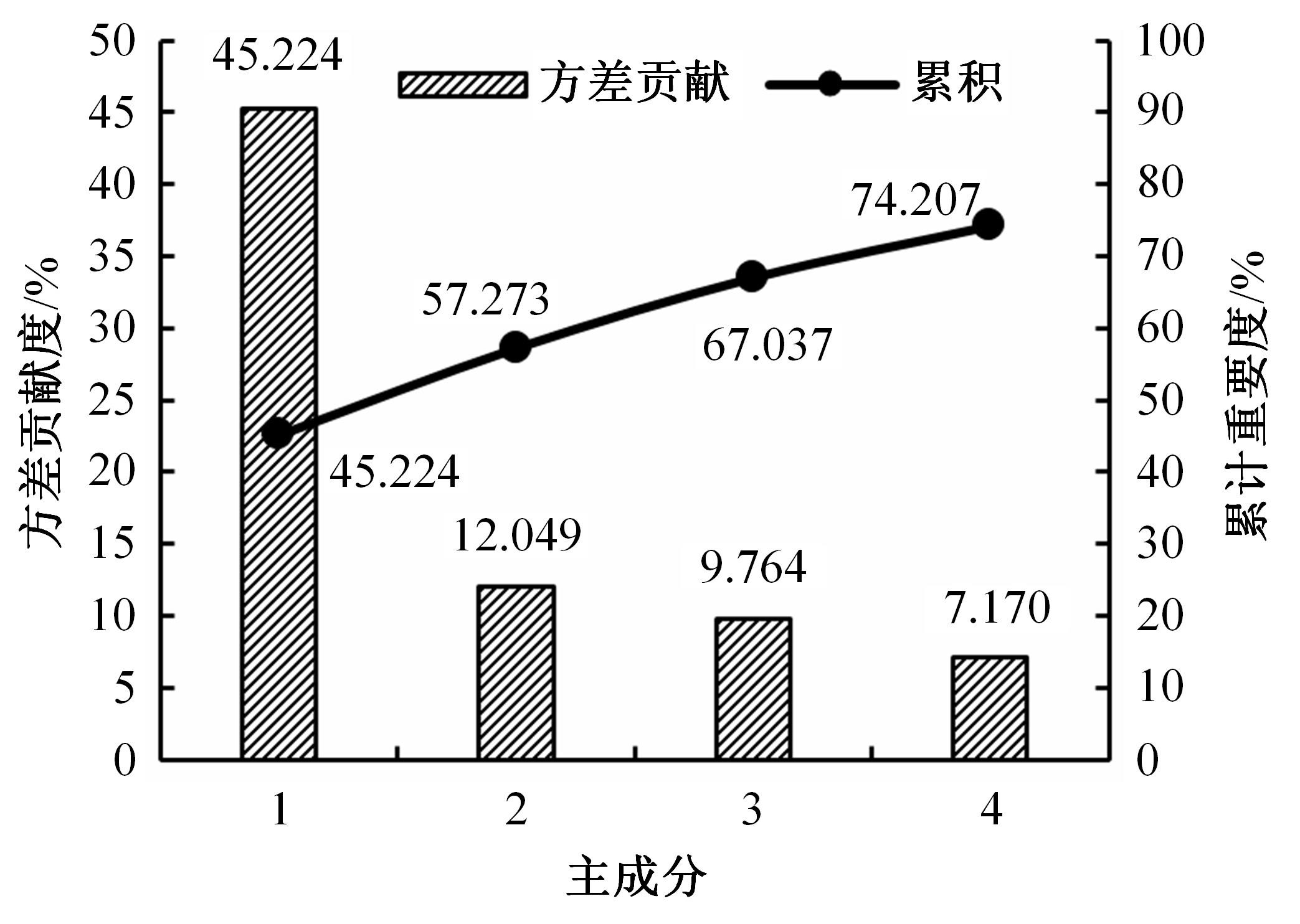
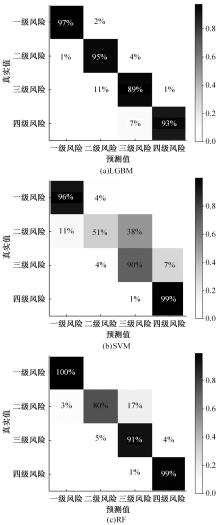
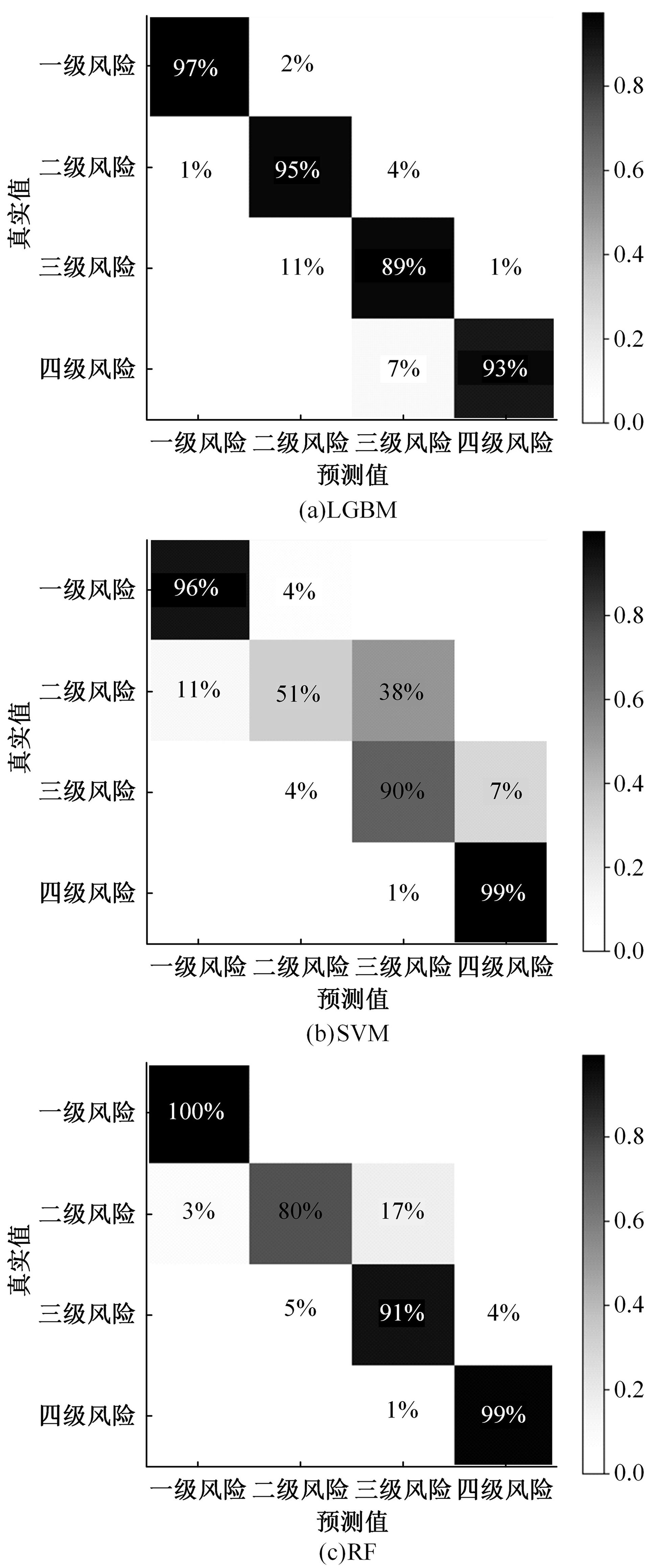
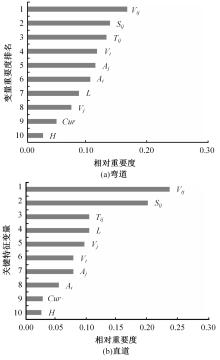
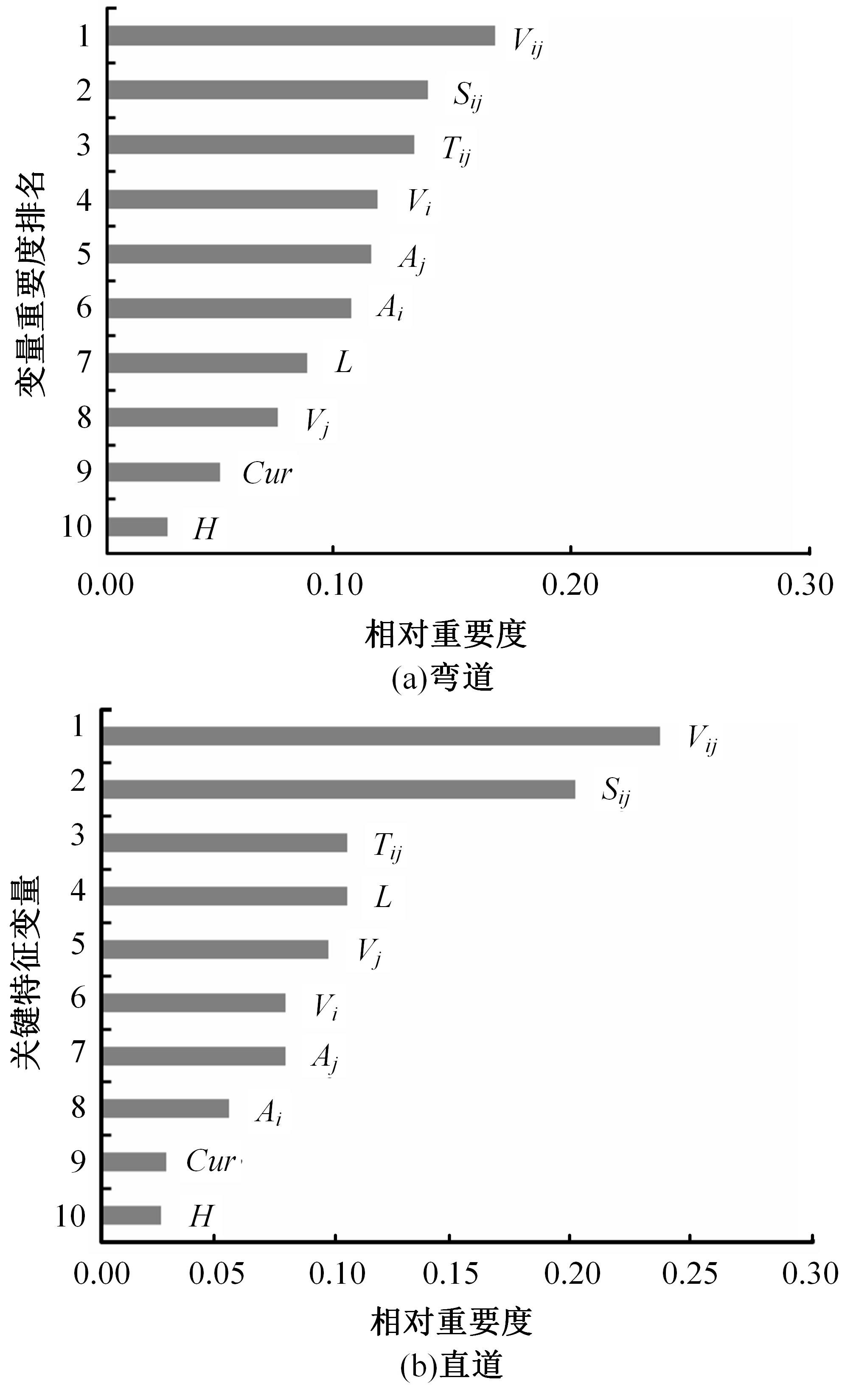
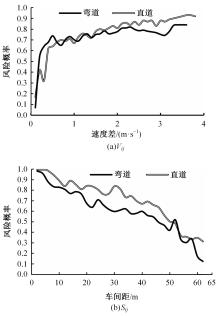
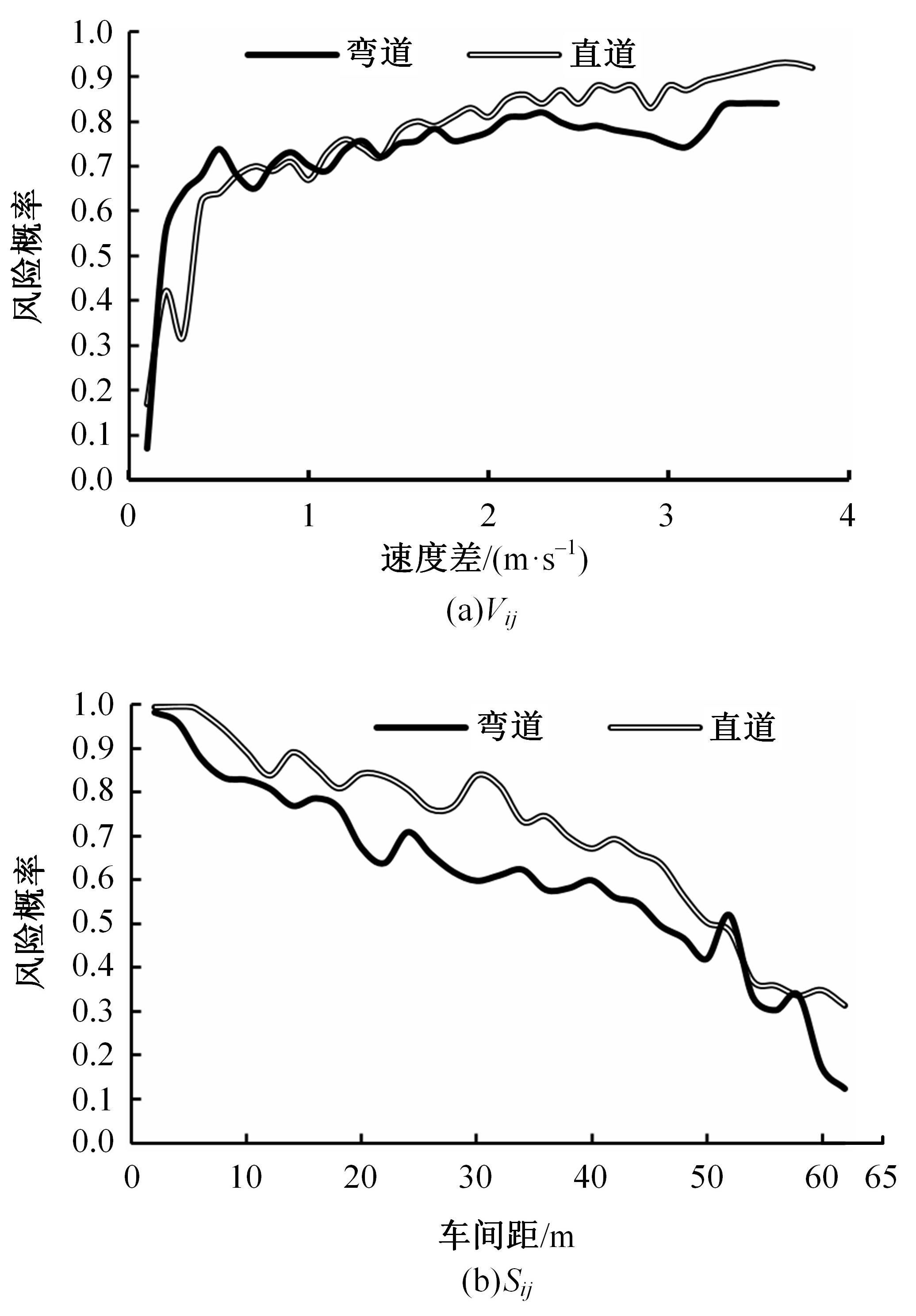
选取典型山区双车道公路弯道和直道为研究对象,基于无人机航拍视频提取的交通轨迹数据,通过轻度提升机算法构建了货车移动遮断下小客车跟驰风险预测模型,采用支持向量机、随机森林验证了模型有效性,分析了模型关键特征参数风险作用机制。实验结果表明:基于轻度提升机算法的风险预测模型准确率达96.9%,具有优越性,速度差、跟驰间距是模型关键特征参数,直道上单因子重要度更大;相比弯道,直道路段危险驾驶行为突出,大幅横向偏移等不稳定跟驰特征明显;由模型解释器结果可知,当速度差小于0.5 m/s、跟驰间距大于40 m时,是较为安全的跟驰状态。
中图分类号:
- U491.31
| 1 | 戢晓峰,卢梦媛,覃文文.货车移动遮断影响下的小客车驾驶行为识别[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2021, 21(5):174-182. |
| Ji Xiao-feng, Lu Meng-yuan, Qin Wen-wen. Identification of passenger car driving behavior under the influence of truck moving interruption[J]. Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2021,21(5): 174-182. | |
| 2 | Moridpour S, Mazloumi E, Mesbah M. Impact of heavy vehicles on surrounding traffic characteristics[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2015, 49(4): 535-552. |
| 3 | Gazis D C, Herman R. The moving and "phantom" bottlenecks[J]. Transportation Science, 1992, 26(3): 223-229. |
| 4 | Aghabayk K, Sarvi M, Young W. Understanding the dynamics of heavy vehicle interactions in car-following[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2012, 138(12): 1468-1475. |
| 5 | Sarvi M. Heavy commercial vehicles‐following behavior and interactions with different vehicle classes[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2013, 47(6): 572-580. |
| 6 | Xu C, Liu P, Wang W, et al. Evaluation of the impacts of traffic states on crash risks on freeways[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2012, 47: 162-171. |
| 7 | Hossain M, Muromachi Y. A Bayesian network based framework for real-time crash prediction on the basic freeway segments of urban expressways[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2012, 45: 373-381. |
| 8 | 杨奎,余荣杰,王雪松.基于车道集计交通流数据的事故风险评估分析[J].同济大学学报,2016,44(10): 1567-1572. |
| Yang Kui, Yu Rong-jie, Wang Xue-song. Application of aggregated lane data from dual-loop detector to crash risk evaluation[J]. Journal of Tongji University, 2016, 44(10): 1567-1572. | |
| 9 | Song Y, Kou S, Wang C. Modeling crash severity by considering risk indicators of driver and roadway: a Bayesian network approach[J]. Journal of Safety Research, 2021, 76: 64-72. |
| 10 | 李志慧,孙雅倩,陶鹏飞,等.交通事故后的交通运行风险状态等级预测方法[J].吉林大学学报:工学版,2022,52(1):127-135. |
| Li Zhi-hui, Sun Ya-qian, Tao Peng-fei, et al. Forecasting method of traffic operation risk level after traffic accident[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(1): 127-135. | |
| 11 | Sayed T, Zaki M H, Autey J. Automated safety diagnosis of vehicle-bicycle interactions using computer vision analysis[J]. Safety Science, 2013 59(11): 163-172. |
| 12 | 朱顺应,蒋若曦,王红,等.机动车交通冲突技术研究综述[J].中国公路学报,2020,33(2):15-33. |
| Zhu Shun-ying, Jiang Ruo-xi, Wang Hong, et al. Summary of research on vehicle traffic conflict technology[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2020, 33(2): 15-33. | |
| 13 | 戢晓峰,谢世坤,覃文文,等.基于轨迹数据的山区危险性弯道路段交通事故风险动态预测[J].中国公路学报,2022,35(4):277-285. |
| Ji Xiao-feng, Xie Shi-kun, Qin Wen-wen, et al. Dynamic prediction of traffic accident risk in dangerous mountain bends based on trajectory data[J]. China Journal of Highways, 2022, 35(4): 277-285. |
| [1] | 邬岚,赵乐,李根. 基于方差异质性随机参数模型的汇合行为分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 883-889. |
| [2] | 王宏志,宋明轩,程超,解东旋. 基于改进YOLOv4-tiny算法的车距预警方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 741-748. |
| [3] | 何杰,张长健,严欣彤,王琛玮,叶云涛. 基于微观动力学参数的高速公路特征路段事故风险分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 162-172. |
| [4] | 潘恒彦,张文会,梁婷婷,彭志鹏,高维,王永岗. 基于MIMIC与机器学习的出租车驾驶员交通事故诱因分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 457-467. |
| [5] | 贺宜,孙昌鑫,彭建华,吴超仲,江亮,马明. 电动载货三轮车风险行为及影响因素分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 413-420. |
| [6] | 朱洁玉,马艳丽. 合流区域多车交互风险实时评估方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1574-1581. |
| [7] | 彭涛,方锐,刘兴亮,王海玮,庞彦伟,许洪国,刘福聚,王涛. 基于典型事故场景的雪天高速换道自动驾驶策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2558-2567. |
| [8] | 程国柱,程瑞,徐亮,张文会. 基于乘员伤害分析的公路路侧事故风险评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 875-885. |
| [9] | 王露,刘玉雯,陈红. 侧风下峡谷桥隧连接段汽车的行驶特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 736-748. |
| [10] | 代存杰,李引珍,马昌喜,柴获,牟海波. 不确定条件下危险品配送路线多准则优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1694-1702. |
| [11] | 王芳荣, 郭柏苍, 金立生, 高琳琳, 岳欣羽. 次任务驾驶安全评价指标筛选及其权值计算[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1710-1715. |
| [12] | 谭立东, 刘丹, 李文军. 基于蝇复眼的交通事故现场全景图像阵列仿生设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1738-1744. |
| [13] | 李显生, 孟祥雨, 郑雪莲, 程竹青, 任圆圆. 非满载罐体内液体冲击动力学特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 737-743. |
| [14] | 王占中, 赵利英, 曹宁博. 基于多层编码遗传算法的危险品运输调度模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 751-755. |
| [15] | 徐进, 陈薇, 周佳, 罗骁, 邵毅明. 汽车转向盘操作与驾驶负荷的相关性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 438-445. |
|
||