吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (4): 883-889.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220614
基于方差异质性随机参数模型的汇合行为分析
- 南京林业大学 汽车与交通工程学院,南京 210037
Analysis of merging behavior based on random parameter model with heterogeneity in variances
- College of Automobile and Traffic Engineering,Nanjing Forestry University,Nanjing 210037,China
摘要:
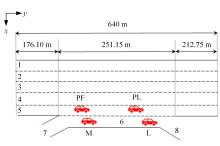
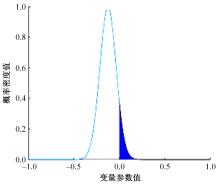
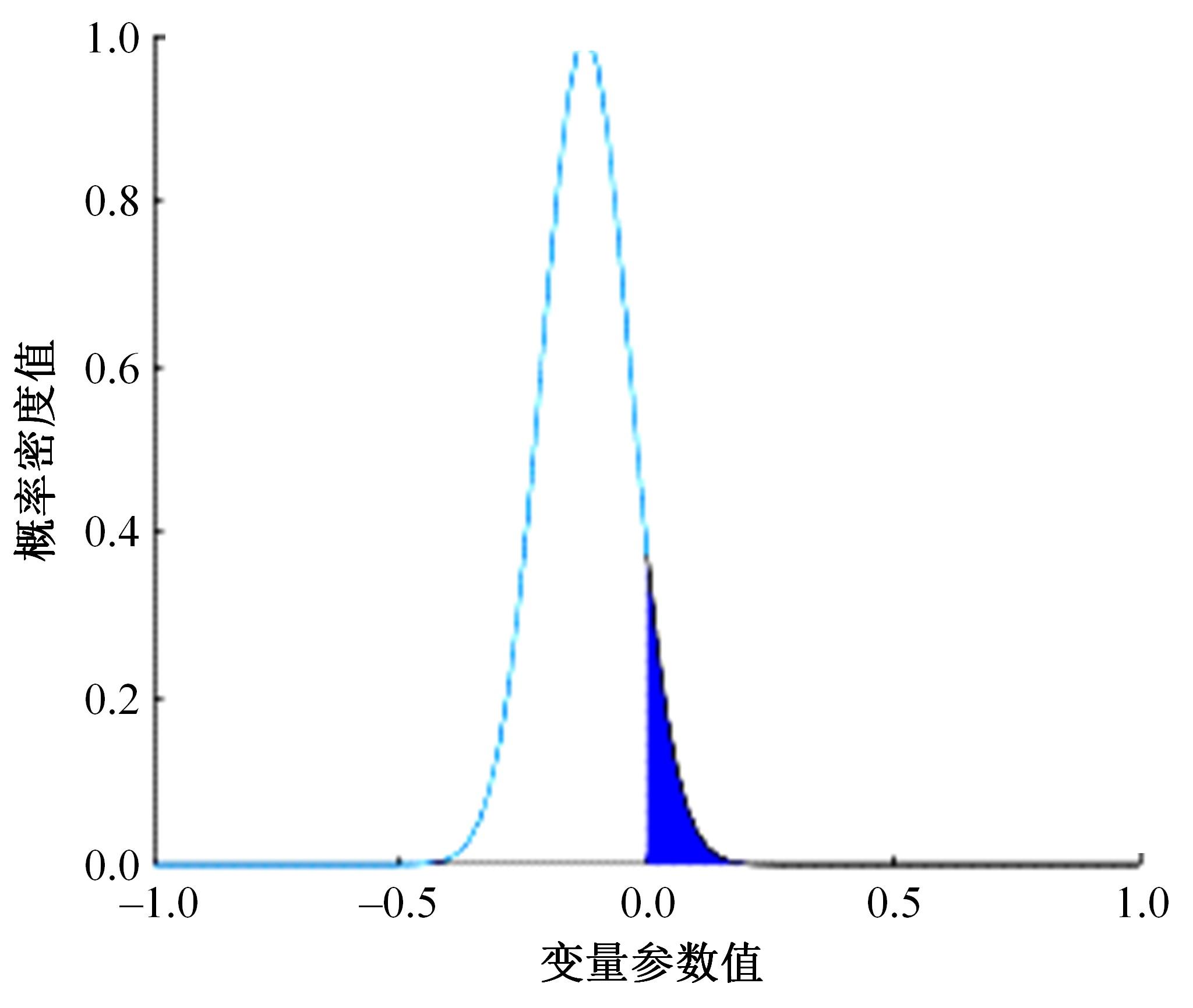
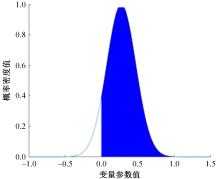
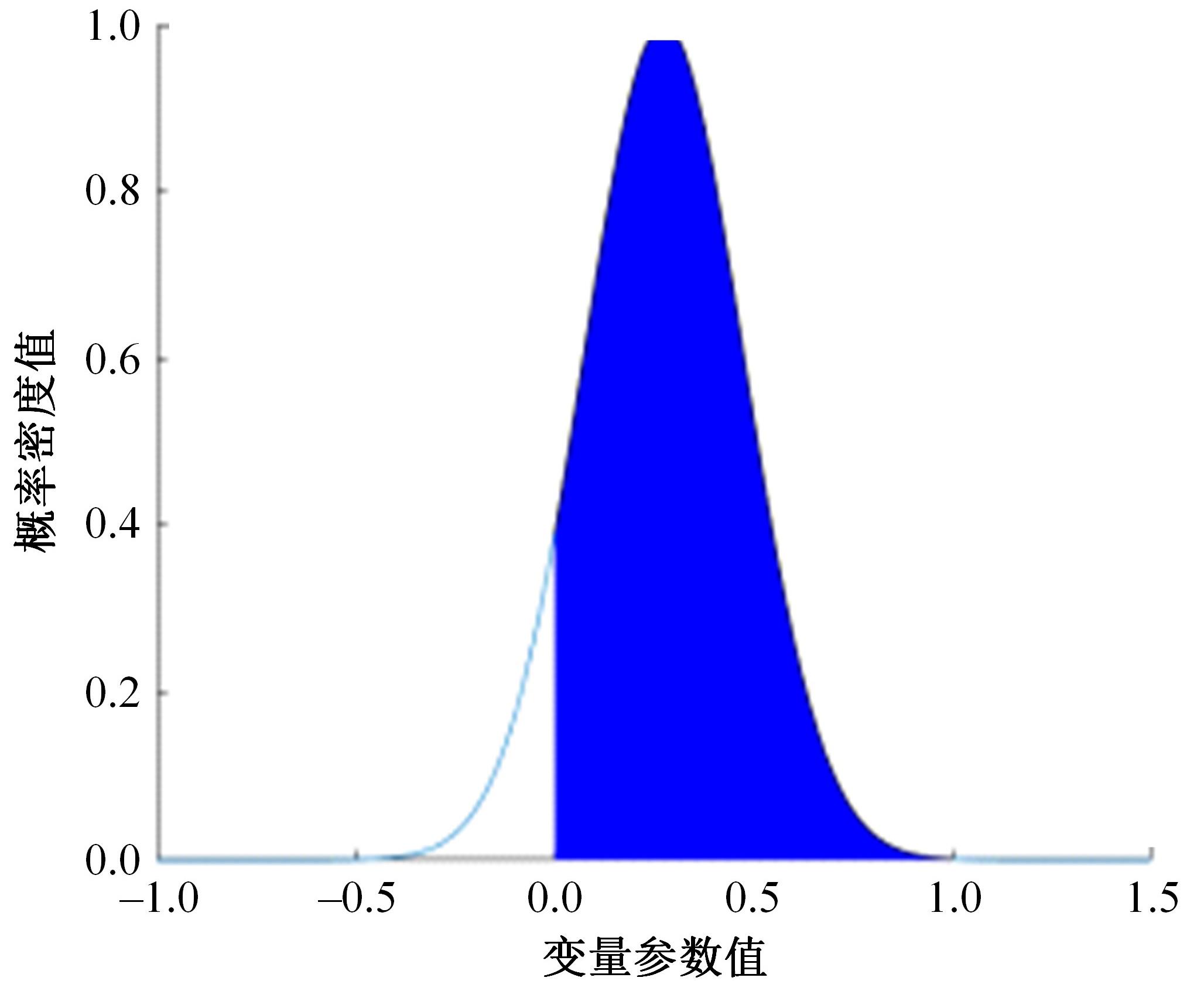
为研究高速公路交织区入口匝道车辆汇入主线的换道行为,基于方差异质性随机参数模型构建了车辆汇入换道模型,先从NGSIM数据集中提取7个在统计上显著且对换道行为有影响的解释变量,然后将其引入方差异质性随机参数模型探索潜在异质性,计算各变量平均边际效应量化对换道行为的影响,最后提出了“个体样本精度”指标对模型进行比较。研究结果表明:汇入车辆与目标车道领车的车头间距、目标车道领车宽度、辅助车道领车速度对换道行为产生了显著的影响,且汇入车辆在辅助车道上的纵向位置显著影响汇入车辆与目标车道领车的车头间距,方差异质性随机参数模型比未考虑方差异质性的随机参数模型和二元Logit模型具有更高的拟合优度和模型精度,能够更好地解释车辆汇入行为中的潜在异质性。本文的研究成果可应用于自动驾驶辅助系统和交通流仿真软件中,对阐明车道变换行为的机理有一定的参考价值。
中图分类号:
- U491.2
| 1 | 孙剑,李克平,杨晓光.拥挤交通流交织区车道变换行为仿真[J].系统仿真学报,2009,21(13):4174-4178, 4182. |
| Sun Jian, Li Ke-Ping, Yang Xiao-guang. Simulation of lane-changing behavior in congested traffic flow of the interweaving area[J]. Journal of System Engineering Simulation, 2009, 21(13): 4174-4178, 4182. | |
| 2 | Chang G L, Kao Y M. An empirical investigation of macroscopic lane-changing characteristics on uncongested multilane freeways[J]. Transportation Research Part A: General, 1991, 25(6): 375-389. |
| 3 | Laval J A, Leclercq L. Microscopic modeling of the relaxation phenomenon using a macroscopic lane-changing model[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2008, 42(6): 511-522. |
| 4 | Bham G H. A simple lane change model for microscopic traffic flow simulation in weaving sections[J]. Transportation Letters: the International Journal of Transportation Research, 2011, 3(4): 231-251. |
| 5 | Hou Y, Edara P, Sun C. A genetic fuzzy system for modeling mandatory lane changing[C]//The 15th International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), New York, United States, 2012: 1044-1048. |
| 6 | Rahman M, Chowdhury M, Xie Y, et al. Review of microscopic lane-changing models and future research opportunities[J]. Ieee Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2013, 14(4): 1942-1956. |
| 7 | Li G, Yang Z, Yu Q, et al. Characterizing heterogeneity among merging positions: comparison study between random parameter and latent class accelerated hazard model[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, Part A: Systems, 2021, 147(6):No. 4021029. |
| 8 | Zhou H, Sun Y, Qin X, et al. Modeling discretionary lane-changing behavior on urban streets considering drivers' heterogeneity[J]. Transportation Letters, 2020, 12(3): 213-222. |
| 9 | Keyvan-Ekbatani M, Knoop V L, Daamen W. Categorization of the lane change decision process on freeways[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2016, 69: 515-526. |
| 10 | Li G. Application of finite mixture of logistic regression for heterogeneous merging behavior analysis[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2018(7): No.1436521. |
| 11 | Li G, Pan Y Y, Yang Z, et al. Modeling vehicle merging position selection behaviors based on a finite mixture of linear regression models[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 158445-158458. |
| 12 | Mannering F, Shankar V, Bhat C R. Unobserved heterogeneity and the statistical analysis of highway accident data[J]. Analytic Methods in Accident Research, 2016, 11: 1-16. |
| 13 | Seraneeprakarn P, Huan G S, Shankar V, et al. Occupant injury severities in hybrid-vehicle involved crashes: A random parameters approach with heterogeneity in means and variances[J]. Analytic Methods in Accident Research, 2017, 15: 41-55. |
| 14 | Yu M, Zheng C J, Ma C X. Analysis of injury severity of rear-end crashes in work zones: A random parameters approach with heterogeneity in means and variances[J]. Analytic Methods in Accident Research, 2020, 27:No. 100126. |
| 15 | Chen T Y, Shi X P, Wong Y D. Key feature selection and risk prediction for lane-changing behaviors based on vehicles' trajectory data[J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2019, 129: 156-169 |
| 16 | 李华民, 黄海军, 刘剑锋. 混合Logit模型的参数估计与应用研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2010, 10(5): 73-78. |
| Li Hua-min, Huang Hai-jun, Liu Jian-feng. Parameter estimation and application research of mixed Logit model[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2010, 10(5): 73-78. | |
| 17 | 宋栋栋,杨小宝,祖兴水,等.基于均值异质性随机参数Logit模型的城市道路事故驾驶员受伤严重程度研究[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2021,21(3): 214-220. |
| Song Dong-dong, Yang Xiao-bao, Zu Xing-shui, et al. Research on the injury severity of drivers in urban road accidents based on mean heterogeneity random parameter Logit model[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2021, 21(3): 214-220. | |
| 18 | 王荣本,游峰,崔高健,等.车辆安全换道分析[J].吉林大学学报:工学版,2005,35(2):179-182. |
| Wang Rong-ben, You Feng, Cui Jian-gao, et al. Analysis on lane-changing safety of vehicle[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2005,35 (2): 179-182. | |
| 19 | 贾洪飞,谭云龙,李强,等.考虑驾驶员特征的快速路合流区间隙接受模型构建[J].吉林大学学报:工学版,2015,45(1):55-61. |
| Jia Hong-fei, Tan Yun-long, Li Qiang, et al. Gap acceptance model of expressway weaving area based on driver characteristics[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2015, 45(1): 55-61. |
| [1] | 王宏志,宋明轩,程超,解东旋. 基于改进YOLOv4-tiny算法的车距预警方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 741-748. |
| [2] | 张卫华,刘嘉茗,解立鹏,丁恒. 网联混合环境快速路交织区自动驾驶车辆换道模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 469-477. |
| [3] | 何杰,张长健,严欣彤,王琛玮,叶云涛. 基于微观动力学参数的高速公路特征路段事故风险分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 162-172. |
| [4] | 高海龙,徐一博,刘坤,李春阳,卢晓煜. 基于多源数据融合的高速公路路网短时交通流参数实时预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 155-161. |
| [5] | 张健,李青扬,李丹,姜夏,雷艳红,季亚平. 基于深度强化学习的自动驾驶车辆专用道汇入引导[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2508-2518. |
| [6] | 何永明,陈世升,冯佳,万亚楠. 基于高精地图的超高速公路虚拟轨道系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2016-2028. |
| [7] | 杨柳,王创业,王梦言,程阳. 设置自动驾驶小客车专用车道的六车道高速公路交通流特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2043-2052. |
| [8] | 李艳波,柳柏松,姚博彬,陈俊硕,渠开发,武奇生,曹洁宁. 考虑路网随机特性的高速公路换电站选址[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1364-1371. |
| [9] | 潘恒彦,张文会,梁婷婷,彭志鹏,高维,王永岗. 基于MIMIC与机器学习的出租车驾驶员交通事故诱因分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 457-467. |
| [10] | 贺宜,孙昌鑫,彭建华,吴超仲,江亮,马明. 电动载货三轮车风险行为及影响因素分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 413-420. |
| [11] | 朱洁玉,马艳丽. 合流区域多车交互风险实时评估方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1574-1581. |
| [12] | 彭涛,方锐,刘兴亮,王海玮,庞彦伟,许洪国,刘福聚,王涛. 基于典型事故场景的雪天高速换道自动驾驶策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2558-2567. |
| [13] | 马莹莹,陆思园,张晓明,魏文术. 考虑个体风险偏好差异的高速公路出行选择模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1673-1683. |
| [14] | 程国柱,程瑞,徐亮,张文会. 基于乘员伤害分析的公路路侧事故风险评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 875-885. |
| [15] | 王露,刘玉雯,陈红. 侧风下峡谷桥隧连接段汽车的行驶特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 736-748. |
|
||