吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (12): 3423-3432.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230087
• 车辆工程·机械工程 • 下一篇
基于注意力机制的机械臂目标抓取网络技术
赵彬1,2,3( ),吴成东1,3,张雪娇3,孙若怀1,姜杨3
),吴成东1,3,张雪娇3,孙若怀1,姜杨3
- 1.东北大学 信息科学与工程学院,沈阳 110819
2.新松机器人自动化股份有限公司,沈阳 110168
3.东北大学 机器人科学与工程学院,沈阳 110169
Target grasping network technology of robot manipulator based on attention mechanism
Bin ZHAO1,2,3( ),Cheng-dong WU1,3,Xue-jiao ZHANG3,Ruo-huai SUN1,Yang JIANG3
),Cheng-dong WU1,3,Xue-jiao ZHANG3,Ruo-huai SUN1,Yang JIANG3
- 1.College of Information Science and Engineering Northeastern University,Shenyang 110819,China
2.SIASUN Robot & Automation Co. ,Ltd. ,Shenyang 110168,China
3.Faculty of Robot Science and Engineering Northeastern University,Shenyang 110169,China
摘要:
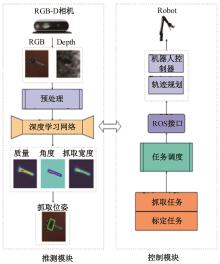
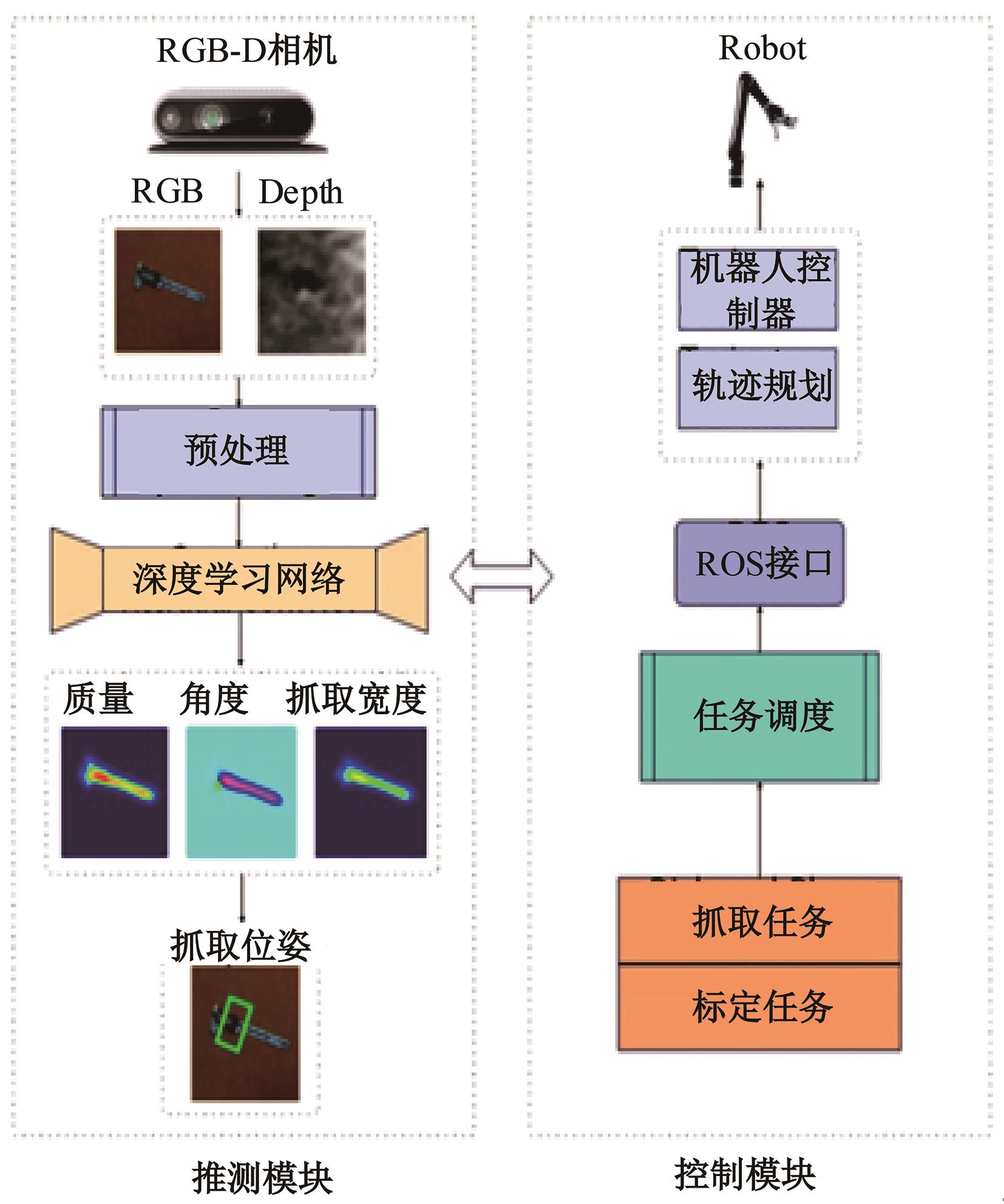
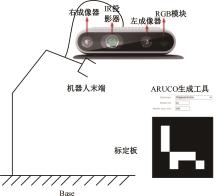
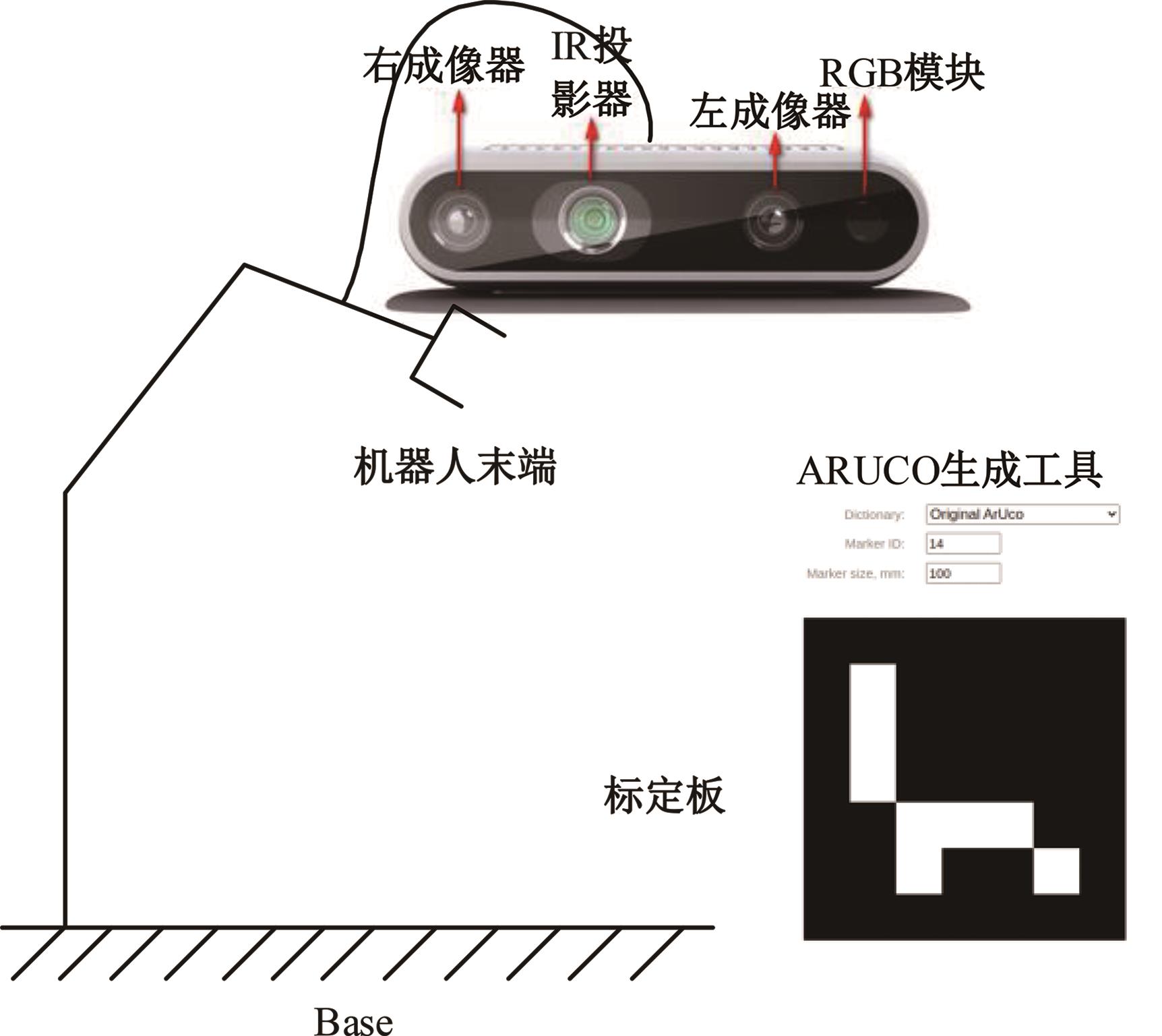
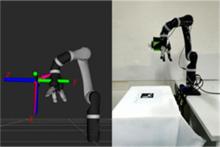
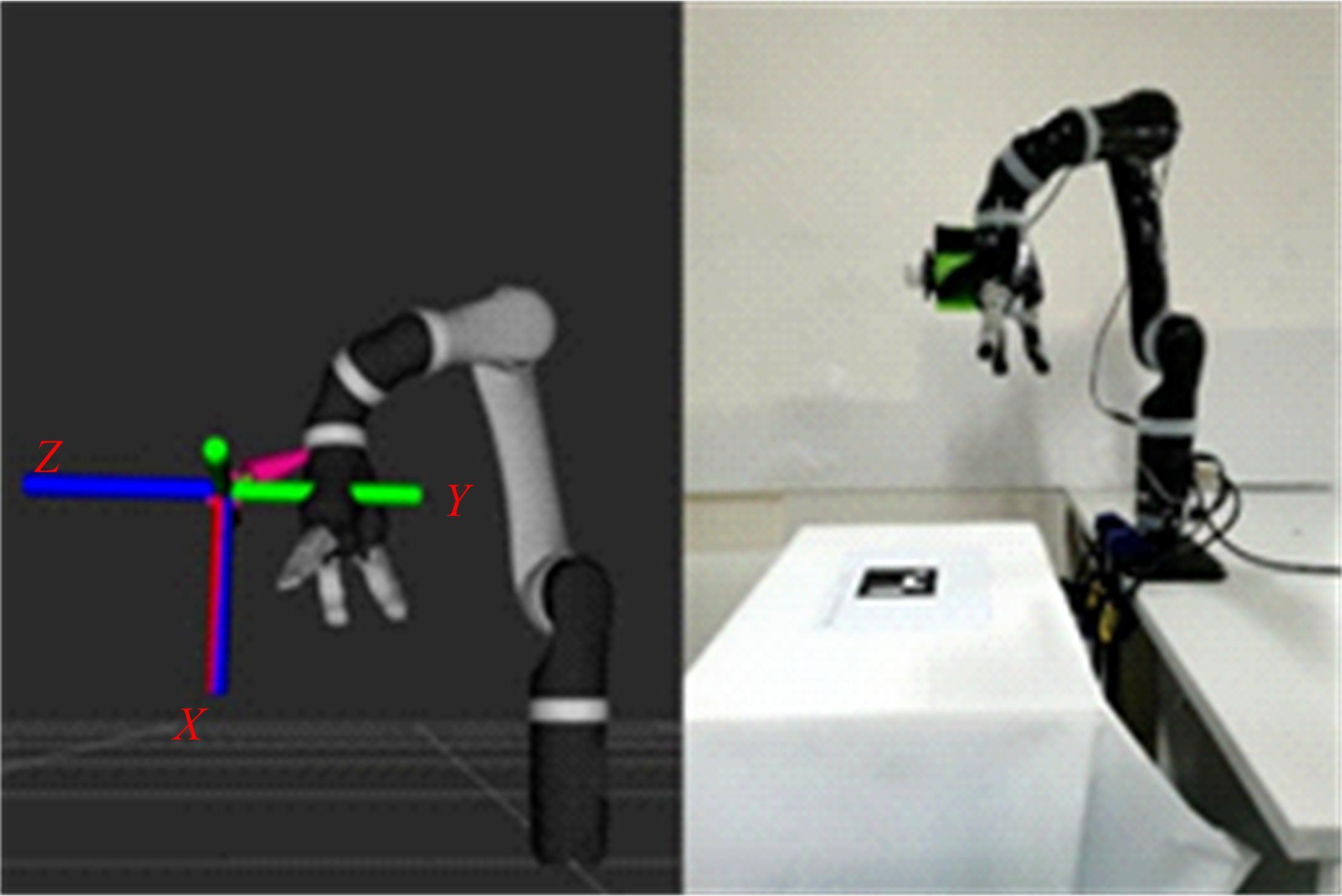
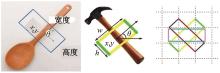
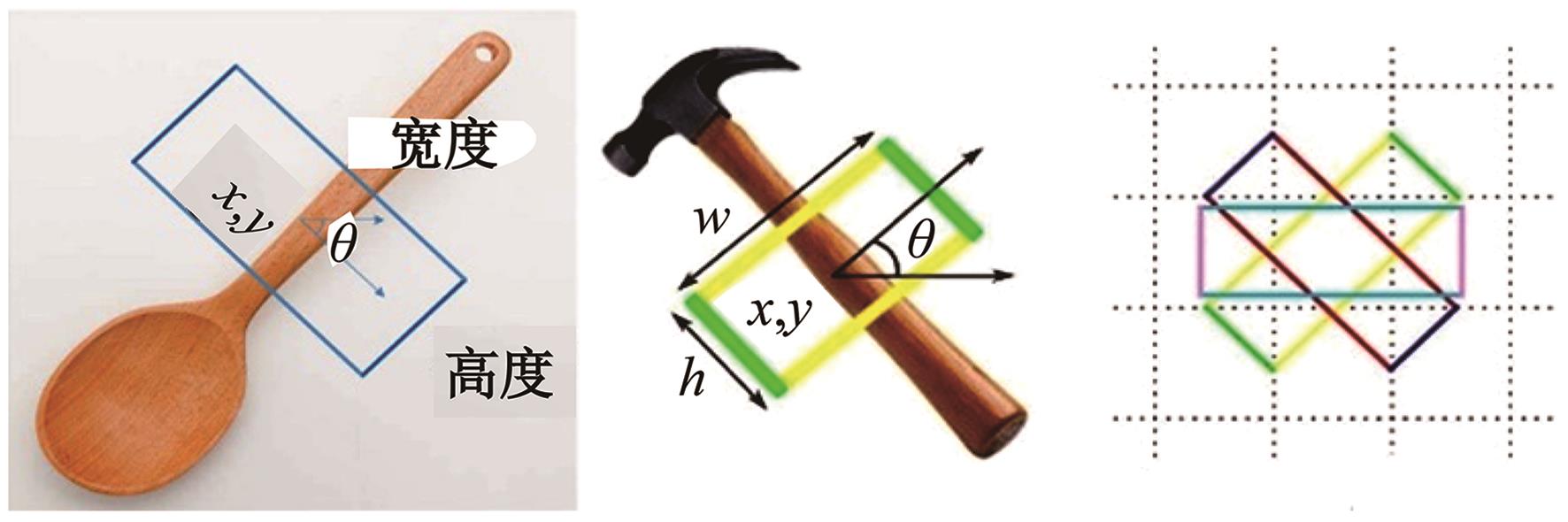
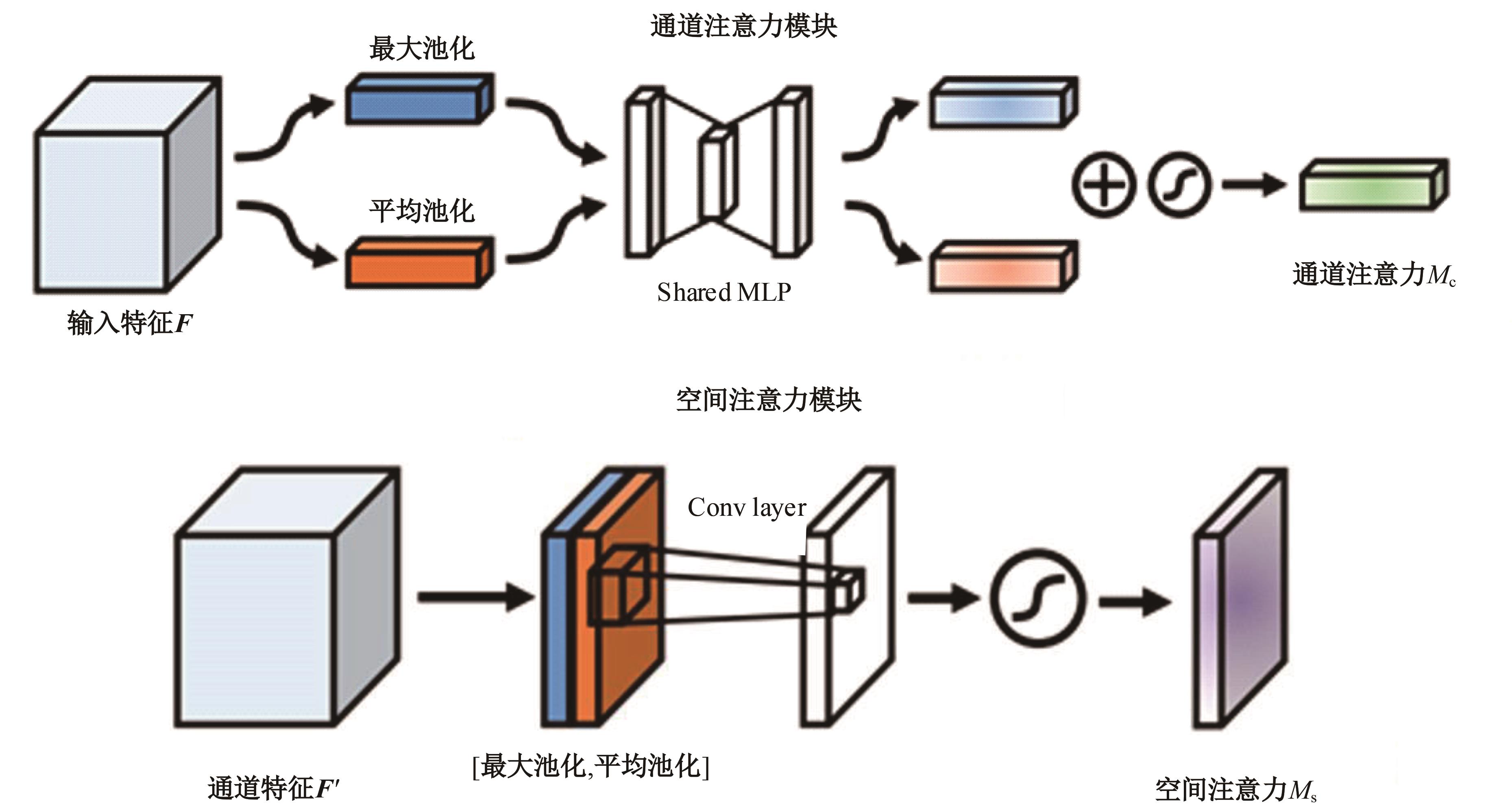
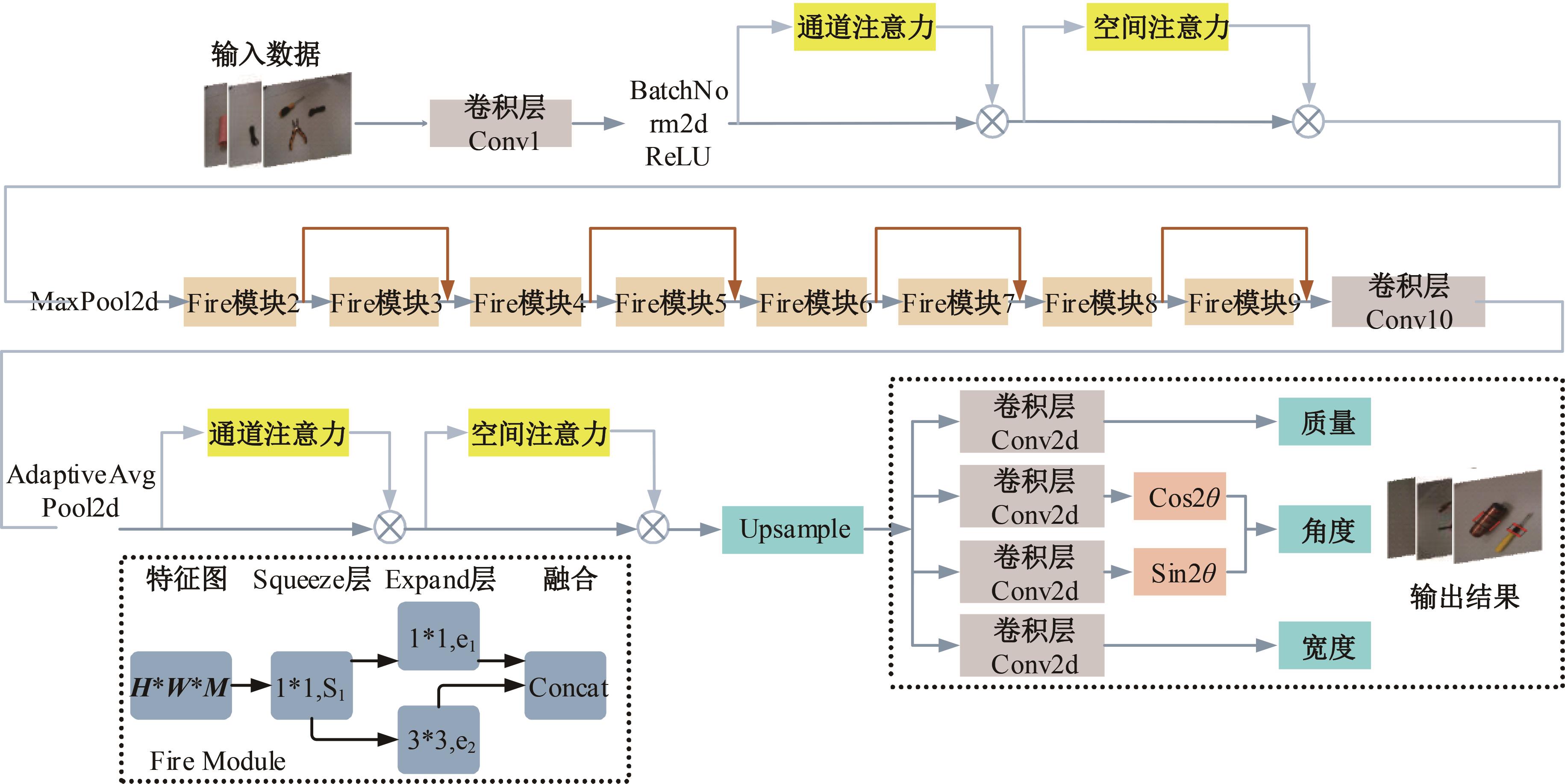
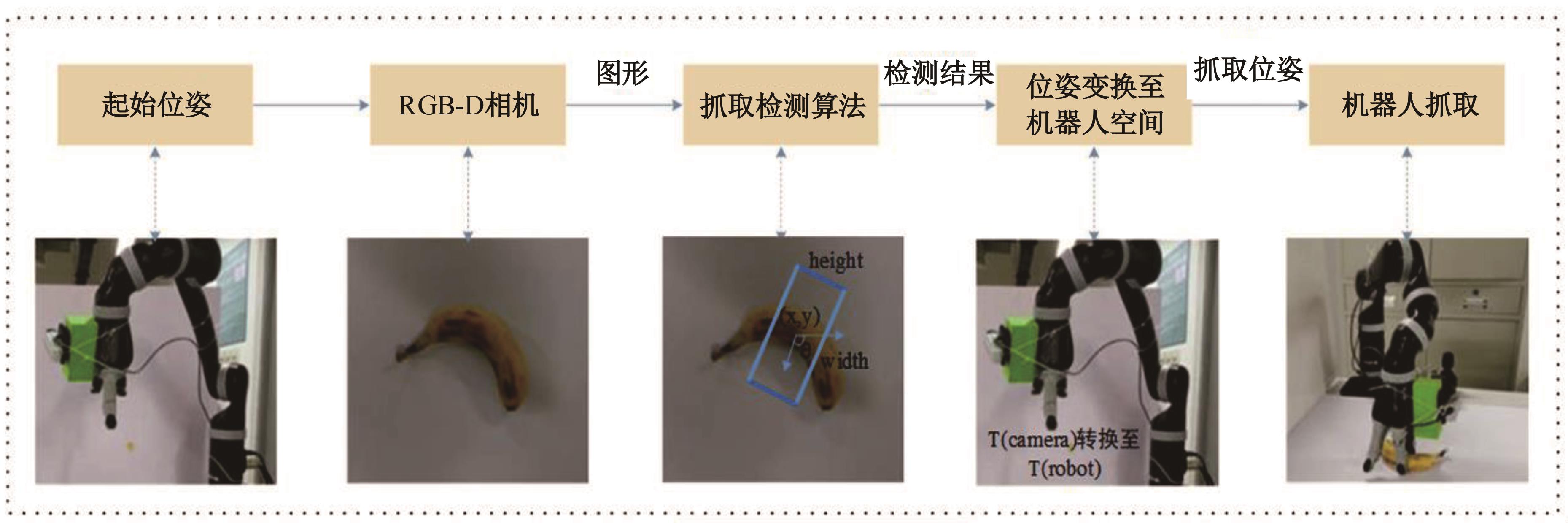
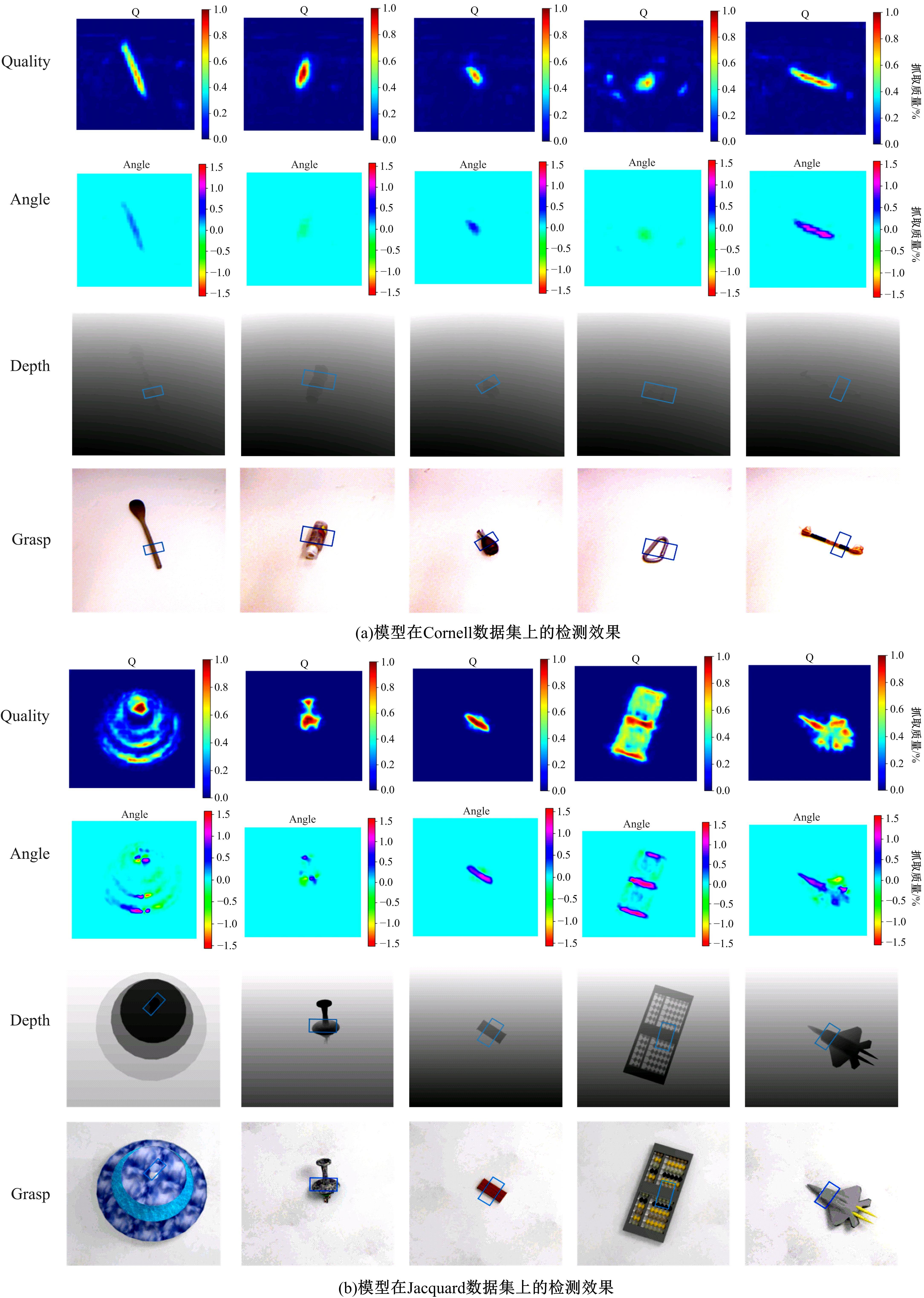
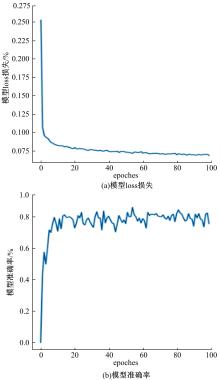
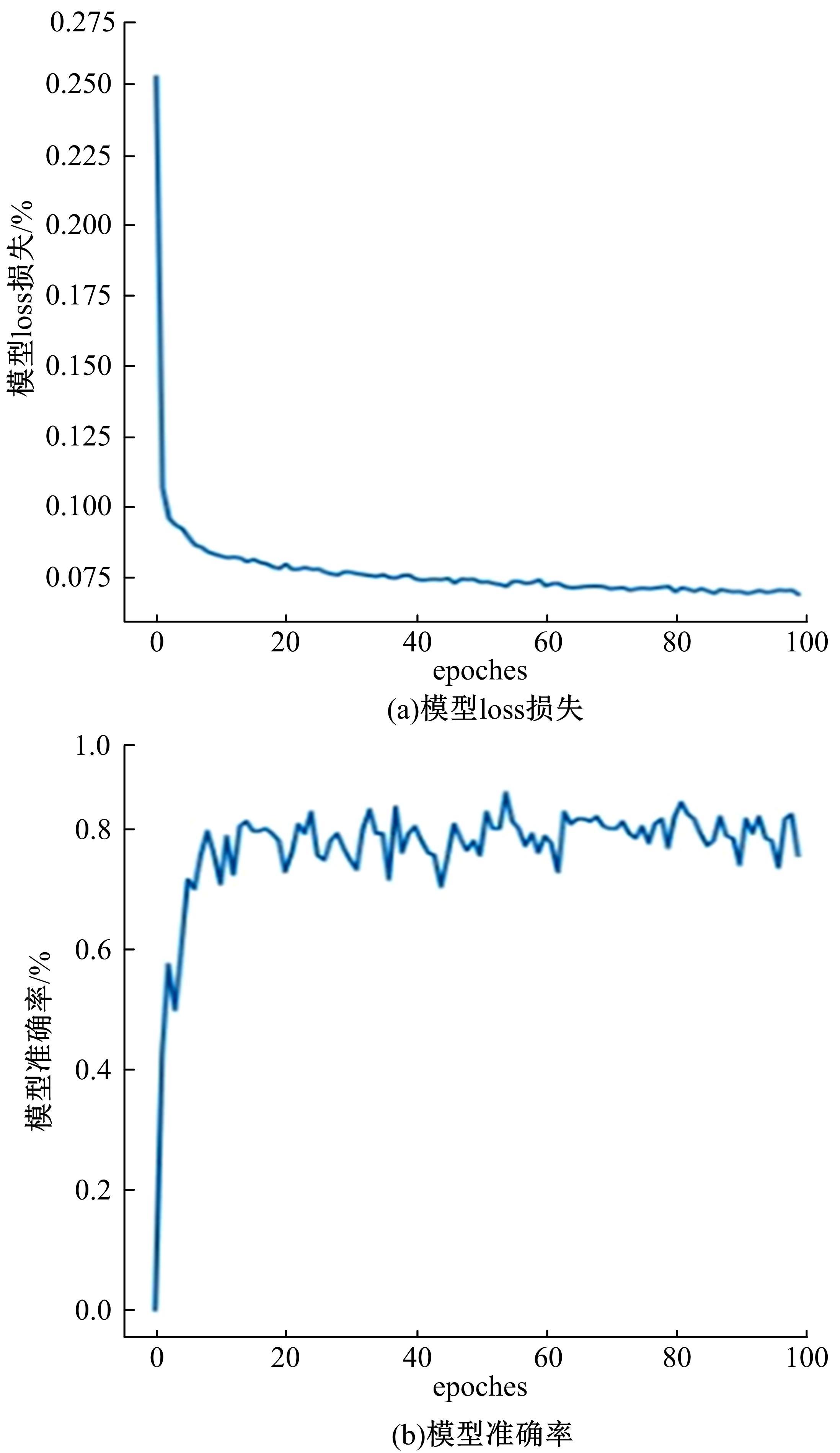
为解决机械臂的单物体抓取检测问题,提出了一种基于注意力机制(CBAM)的SqueezeNet网络模型。首先,对深度视觉抓取系统进行阐述,完成了抓取系统的手眼标定。采用随机裁剪、翻转、调节对比度和增加噪声等方式有效扩充了物体抓取检测数据集。其次,引入轻量化SqueezeNet模型,采用五参数法表征二维抓取框,在不加大网络设计难度的前提下即可完成对目标的抓取。再次,引入“即插即用”的带有注意力机制的网络在通道维度上和空间维度上对传进来的特征图进行加权处理,对SqueezeNet模型抓取网络进行优化改进。最后,将改进后的CBAM-SqueezeNet算法在公开的数据集Cornell grasping dataset和Jacquard dataset上进行验证,抓取检测准确率分别为94.8%和96.4%,比SqueezeNet的准确率提升了2%。CBAM-SqueezeNet网络抓取方法的推理速度为15 ms,达到了抓取精度和运行速度的平衡。将本文方法在Kinova和新松手臂上进行了试验,网络抓取的成功率为93%,速度更快、效率更高。
中图分类号:
- TP242.6
| 1 | Zhang H B, Zhou X W, Lan X G, et al. A real-time robotic grasping approach with oriented anchor box[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics Systems, 2021, 50(5): 3014-3025. |
| 2 | Patten T, Park K, Vincze M. DGCM-Net: dense geometrical correspondence matching network for incremental experience-based robotic grasping[J/OL]. [2023-01-20]. |
| 3 | Valarezo Añazco E, Rivera Lopez P, Park N, et al. Natural object manipulation using anthropomorphic robotic hand through deep reinforcement learning and deep grasping probability network[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2021,51(2): 1041-1055. |
| 4 | Lan R, Sun L, Liu Z, et al. MADNet: a fast and lightweight network for single-image super resolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021,51(3): 1443-1453. |
| 5 | Xiao Z J, Yang X D, Wei X, et al. Improved lightweight network in image recognition[J]. Jisuanji Kexue Yu Tansuo, 2021, 15(4): 743-753. |
| 6 | Li M, He Z, Zhu Y, et al. A method of grasping detection for kiwifruit harvesting robot based on deep learning[J]. Agronomy, 2022, 12(12): No.3096. |
| 7 | Li H, Cheng H. Lightweight neural network design for complex verification code recognition task[J]. Computer Systems and Applications, 2021, 4: No.247. |
| 8 | Song T N, Qin W W, Liang Z, et al. Improved dual-channel attention mechanism image classification method for lightweight network[J]. Hangkong Bingqi, 2021, 28(5): 81-85. |
| 9 | Zhao B, Wu C D, Zou F S, et al. Research on small sample multi-target grasping technology based on transfer learning[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(13): No.5826. |
| 10 | Kim D, Jo H, Song J. Irregular depth tiles: automatically generated data used for network-based robotic grasping in 2D dense clutter[J]. International Journal of Control, Automation, and Systems, 2021, 19(10): 3428-3434. |
| 11 | Kumra S, Joshi S, Sahin F. GR-ConvNet v2: a real-time multi-grasp detection network for robotic grasping[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(16): No.6208. |
| 12 | Wang D, Liu C, Chang F, et al. High-performance pixel-level grasp detection based on adaptive grasping and grasp-aware network[J].IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022,69(11): 11611-11621. |
| 13 | Himeur C, Lejemble T, Pellegrini T, et al. PCEDNet: a lightweight neural network for fast and interactive edge detection in 3D point clouds[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2022, 41(1):No. 3481804. |
| [1] | 张磊,焦晶,李勃昕,周延杰. 融合机器学习和深度学习的大容量半结构化数据抽取算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2631-2637. |
| [2] | 李路,宋均琦,朱明,谭鹤群,周玉凡,孙超奇,周铖钰. 基于RGHS图像增强和改进YOLOv5网络的黄颡鱼目标提取[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2638-2645. |
| [3] | 郭昕刚,程超,沈紫琪. 基于卷积网络注意力机制的人脸表情识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2319-2328. |
| [4] | 余萍,赵康,曹洁. 基于优化A-BiLSTM的滚动轴承故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2156-2166. |
| [5] | 乔百友,武彤,杨璐,蒋有文. 一种基于BiGRU和胶囊网络的文本情感分析方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 2026-2037. |
| [6] | 郭昕刚,何颖晨,程超. 抗噪声的分步式图像超分辨率重构算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 2063-2071. |
| [7] | 张丽平,刘斌毓,李松,郝忠孝. 基于稀疏多头自注意力的轨迹kNN查询方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1756-1766. |
| [8] | 孙铭会,薛浩,金玉波,曲卫东,秦贵和. 联合时空注意力的视频显著性预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1767-1776. |
| [9] | 陆玉凯,袁帅科,熊树生,朱绍鹏,张宁. 汽车漆面缺陷高精度检测系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1205-1213. |
| [10] | 高云龙,任明,吴川,高文. 基于注意力机制改进的无锚框舰船检测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1407-1416. |
| [11] | 李雄飞,宋紫萱,朱芮,张小利. 基于多尺度融合的遥感图像变化检测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 516-523. |
| [12] | 杨国俊,齐亚辉,石秀名. 基于数字图像技术的桥梁裂缝检测综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 313-332. |
| [13] | 李晓旭,安文娟,武继杰,李真,张珂,马占宇. 通道注意力双线性度量网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 524-532. |
| [14] | 苏育挺,景梦瑶,井佩光,刘先燚. 基于光度立体和深度学习的电池缺陷检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(12): 3653-3659. |
| [15] | 王勇,边宇霄,李新潮,徐椿明,彭刚,王继奎. 基于多尺度编码-解码神经网络的图像去雾算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(12): 3626-3636. |
|