吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (6): 1767-1776.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220851
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
联合时空注意力的视频显著性预测
孙铭会1,2( ),薛浩1,2,金玉波3(
),薛浩1,2,金玉波3( ),曲卫东4,秦贵和1,2
),曲卫东4,秦贵和1,2
- 1.吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
2.吉林大学 符号计算与知识工程教育部重点实验室,长春 130012
3.上海爱思博特管理咨询有限公司,上海 200050
4.光电对抗测试评估技术重点实验室,河南 洛阳 471000
Video saliency prediction with collective spatio-temporal attention
Ming-hui SUN1,2( ),Hao XUE1,2,Yu-bo JIN3(
),Hao XUE1,2,Yu-bo JIN3( ),Wei-dong QU4,Gui-he QIN1,2
),Wei-dong QU4,Gui-he QIN1,2
- 1.College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
2.Key Laboratory of Symbolic Computation and Knowledge Engineering of Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
3.EXPERT Management Consulting Co. Ltd. ,Shanghai 200050,China
4.Key Laboratory of Optical Countermeasure Test and Evaluation Technology,Luoyang 471000,China
摘要:
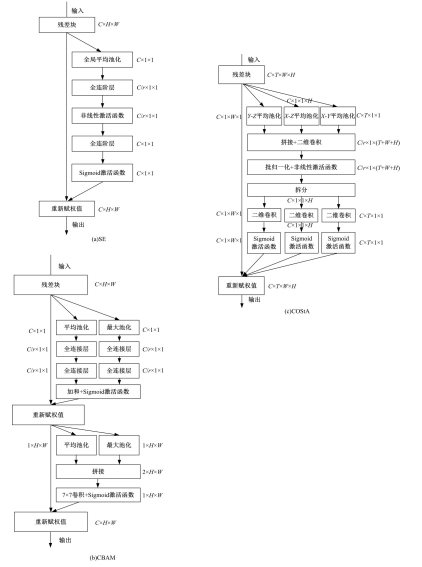
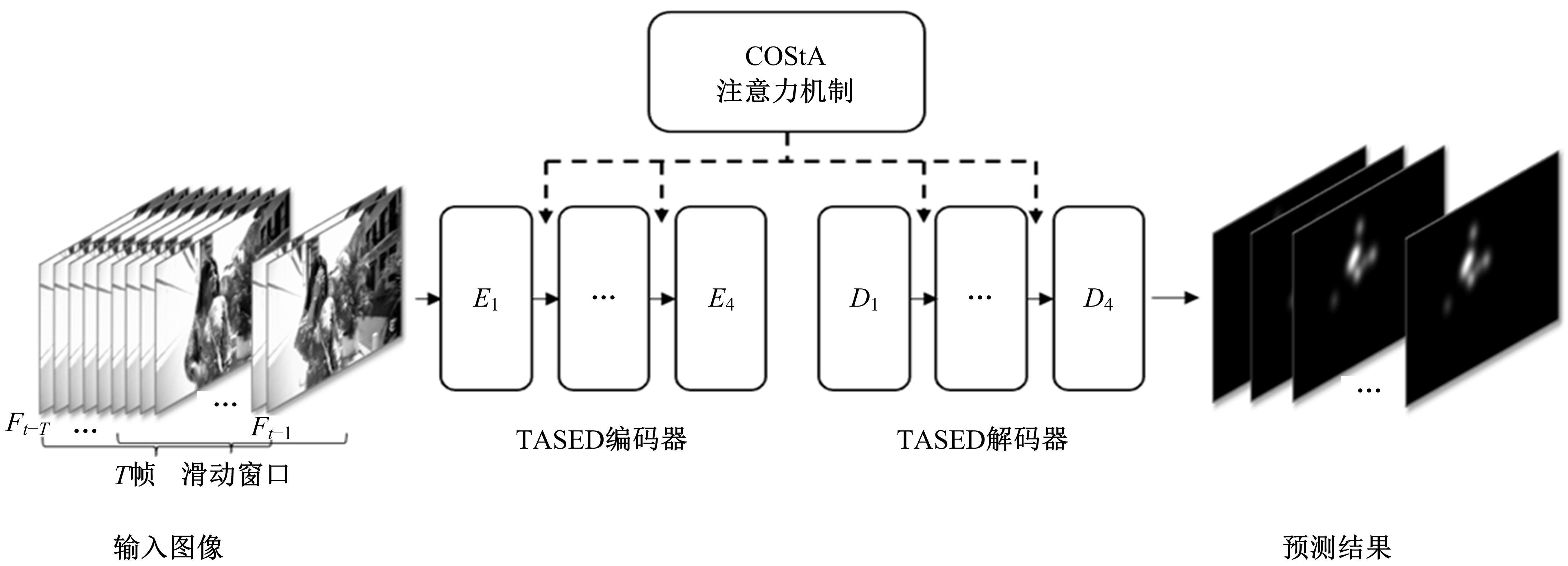
为了解决视频显著性预测任务中时间与空间特征联合建模的问题,提出联合时空注意力机制(COStA),共同提取时间和空间维度的注意信息,突出特定时间和区域的特征供模型来感知。基于该机制,进一步提出视频显著性预测模型TASED-COStA,对比实验表明:COStA机制能为神经网络模型在CC、NSS与SIM三个评价指标上获得大于8%的性能提升,TASED-COStA模型能有效地建模视频信息中的时间与空间关系,并给出准确的预测结果。
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | Guo Q, Feng W, Zhou C, et al. Learning dynamic siamese network for visual object tracking[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 1763-1771. |
| 2 | Feng W, Han R Z, Guo Q, et al. Dynamic saliency-aware regularization for correlation filter-based object tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(7): 3232-3245. |
| 3 | Wang H Y, Xu Y J, Han Y H. Spotting and aggregating salient regions for video captioning[C]∥Proce-edings of the 26th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seoul, Korea, 2018: 1519-1526. |
| 4 | Chen Y, Zhang G, Wang S H, et al. Saliency-based spatiotemporal attention for video captioning[C]∥2018 IEEE Fourth International Conference on Multimedia Big Data, Xi'an, China, 2018: 1-8. |
| 5 | Guo C L, Zhang L M. A novel multiresolution spatiotemporal saliency detection model and its applications in image and video compression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2009, 19(1): 185-198. |
| 6 | Itti L, Dhavale N, Pighin F. Realistic avatar eye and head animation using a neurobiological model of visu-al attention[J/OL]. [2022-06-28]. |
| 7 | Zhong S H, Liu Y, Ren F F, et al. Video saliency detection via dynamic consistent spatio-temporal attention modelling[C]∥Twenty-seventh AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Bellevue, USA, 2013: 1063-1069. |
| 8 | Wang W G, Shen J B, Guo F, et al. Revisiting video saliency: a large-scale benchmark and a new model[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 4894-4903. |
| 9 | Bak C, Kocak A, Erdem E, et al. Spatio-temporal saliency networks for dynamic saliency prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2017, 20(7): 1688-1698. |
| 10 | Tran H D, Bak S, Xiang W, et al. Verification of deep convolutional neural networks using imagestars[J/OL]. [2022-06-28]. |
| 11 | Mathe S, Sminchisescu C. Actions in the eye: dynamic gaze datasets and learnt saliency models for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2014, 37(7): 1408-1424. |
| 12 | Bazzani L, Larochelle H, Torresani L. Recurrent mixture density network for spatiotemporal visual attention[J/OL]. [2022-06-28]. |
| 13 | Droste R, Jiao J, Noble J A. Unified image and video saliency modeling[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 419-435. |
| 14 | Wu X Y, Wu Z Y, Zhang J L, et al. SalSAC: a video saliency prediction model with shuffled attentions and correlation-based ConvLSTM[C]∥Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2020, 34(7): 12410-12417. |
| 15 | Min K, Corso J J. Tased-net: temporally-aggregating spatial encoder-decoder network for video saliency detection[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 2019: 2394-2403. |
| 16 | Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]∥Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Los Angeles, USA, 2017: 5998-6008. |
| 17 | Hu J, Shen L, Sun G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7132-7141. |
| 18 | Woo S, Park J, Lee J Y, et al. Cbam: convolutional block attention module[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 2018: 3-19. |
| 19 | Riche N, Duvinage M, Mancas M, et al. Saliency and human fixations: state-of-the-art and study of comparison metrics[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, Australia, 2013: 1153-1160. |
| 20 | Bylinskii Z, Judd T, Oliva A, et al. What do different evaluation metrics tell us about saliency models?[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 41(3): 740-757. |
| 21 | Wang W G, Shen J B. Deep visual attention prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 27(5): 2368-2378. |
| 22 | Kay W, Carreira J, Simonyan K, et al. The kinetics human action video dataset[J/OL]. [2022-06-28]. |
| 23 | He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, et al. Delving deep into rectifiers: surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1026-1034. |
| 24 | Huang X, Shen C Y, Boix X, et al. Salicon: reducing the semantic gap in saliency prediction by adapting deep neural networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 262-270. |
| 25 | Cornia M, Baraldi L, Serra G, et al. Predicting human eye fixations via an LSTM-based saliency attentive model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(10): 5142-5154. |
| 26 | Jiang L, Xu M, Wang Z L. Predicting video saliency with object-to-motion CNN and two-layer convolutional LSTM[J/OL]. [2022-06-28]. |
| 27 | Lai Q X, Wang W G, Sun H Q, et al. Video saliency prediction using spatiotemporal residual attentive networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 29: 1113-1126. |
| 28 | Wang L M, Tong Z, Ji B, et al. TDN: temporal difference networks for efficient action recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 2021: 1895-1904. |
| 29 | Chen C F R, Panda R, Ramakrishnan K, et al. Deep analysis of CNN-based spatio-temporal representations for action recognition[J/OL]. [2022-06-30]. |
| [1] | 魏晓辉,王晨洋,吴旗,郑新阳,于洪梅,岳恒山. 面向脉动阵列神经网络加速器的软错误近似容错设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1746-1755. |
| [2] | 张丽平,刘斌毓,李松,郝忠孝. 基于稀疏多头自注意力的轨迹kNN查询方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1756-1766. |
| [3] | 陆玉凯,袁帅科,熊树生,朱绍鹏,张宁. 汽车漆面缺陷高精度检测系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1205-1213. |
| [4] | 高云龙,任明,吴川,高文. 基于注意力机制改进的无锚框舰船检测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1407-1416. |
| [5] | 王宇,赵凯. 基于亚像素定位的人体姿态热图后处理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1385-1392. |
| [6] | 王殿伟,张池,房杰,许志杰. 基于高分辨率孪生网络的无人机目标跟踪算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1426-1434. |
| [7] | 夏超,王梦佳,朱剑月,杨志刚. 基于分层卷积自编码器的钝体湍流流场降阶分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 874-882. |
| [8] | 梁礼明,周珑颂,尹江,盛校棋. 融合多尺度Transformer的皮肤病变分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 1086-1098. |
| [9] | 张云佐,郭威,李文博. 遥感图像密集小目标全方位精准检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 1105-1113. |
| [10] | 杨国俊,齐亚辉,石秀名. 基于数字图像技术的桥梁裂缝检测综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 313-332. |
| [11] | 李雄飞,宋紫萱,朱芮,张小利. 基于多尺度融合的遥感图像变化检测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 516-523. |
| [12] | 陈岳林,高铸成,蔡晓东. 基于BERT与密集复合网络的长文本语义匹配模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 232-239. |
| [13] | 霍光,林大为,刘元宁,朱晓冬,袁梦,盖迪. 基于多尺度特征和注意力机制的轻量级虹膜分割模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2591-2600. |
| [14] | 何颖,王卓然,周旭,刘衍珩. 融合社交地理信息加权矩阵分解的兴趣点推荐算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2632-2639. |
| [15] | 张云佐,董旭,蔡昭权. 拟合下肢几何特征的多视角步态周期检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2611-2619. |
|
||