吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (2): 524-532.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221176
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
通道注意力双线性度量网络
李晓旭1( ),安文娟1,武继杰1,李真1,张珂2,3,马占宇4
),安文娟1,武继杰1,李真1,张珂2,3,马占宇4
- 1.兰州理工大学 计算机与通信学院,兰州 730050
2.华北电力大学 电子与通信工程系,保定 071003
3.华北电力大学 河北省电力物联网技术重点实验室,保定 071003
4.北京邮电大学 人工智能学院模式识别与智能系统实验室,北京 100876
Channel attention bilinear metric network
Xiao-xu LI1( ),Wen-juan AN1,Ji-jie WU1,Zhen LI1,Ke ZHANG2,3,Zhan-yu MA4
),Wen-juan AN1,Ji-jie WU1,Zhen LI1,Ke ZHANG2,3,Zhan-yu MA4
- 1.School of Computer and Communication,Lanzhou University of Technology,Lanzhou 730050,China
2.Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering,North China Electric Power University,Baoding 071003,China
3.Hebei Key Laboratory of Power Internet of Things Technology,North China Electric Power University,Baoding 071003,China
4.Laboratory of Pattern Recognition and Intelligent System,School of Artificial Intelligence,Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications,Beijing 100876,China
摘要:
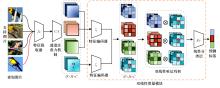
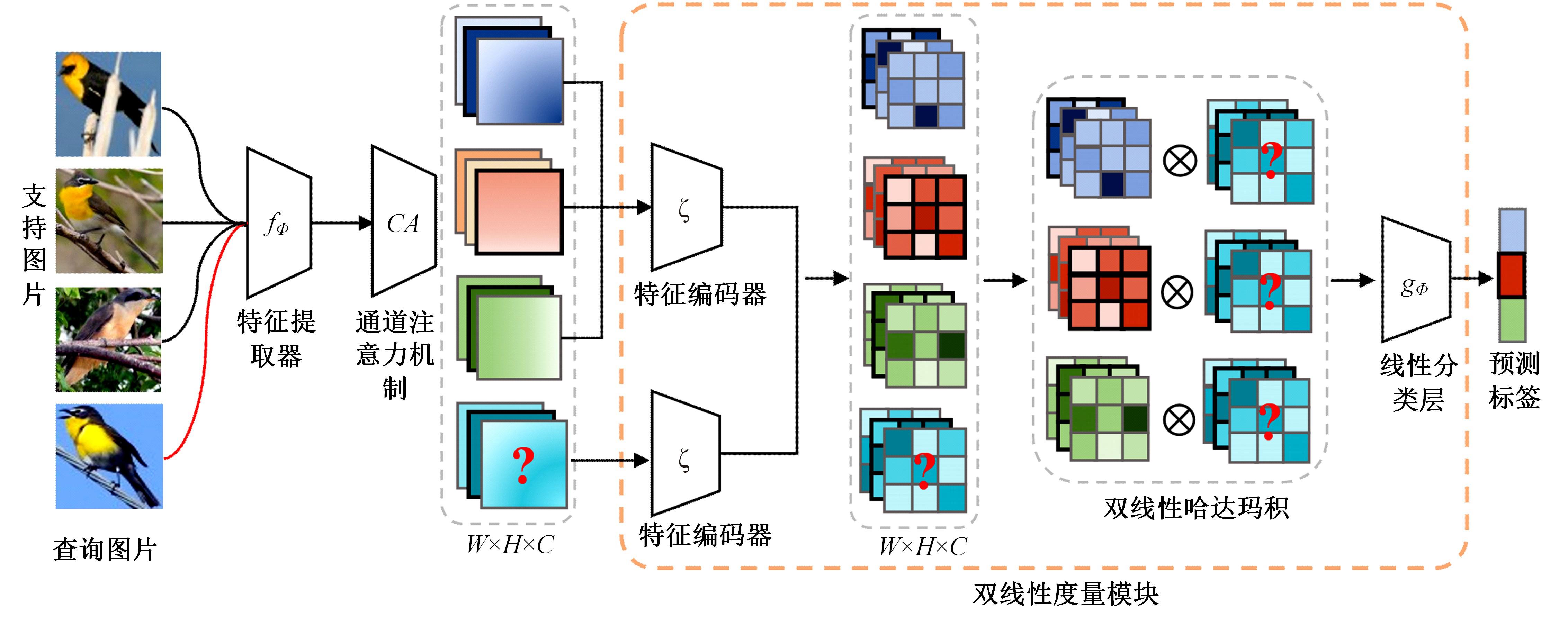
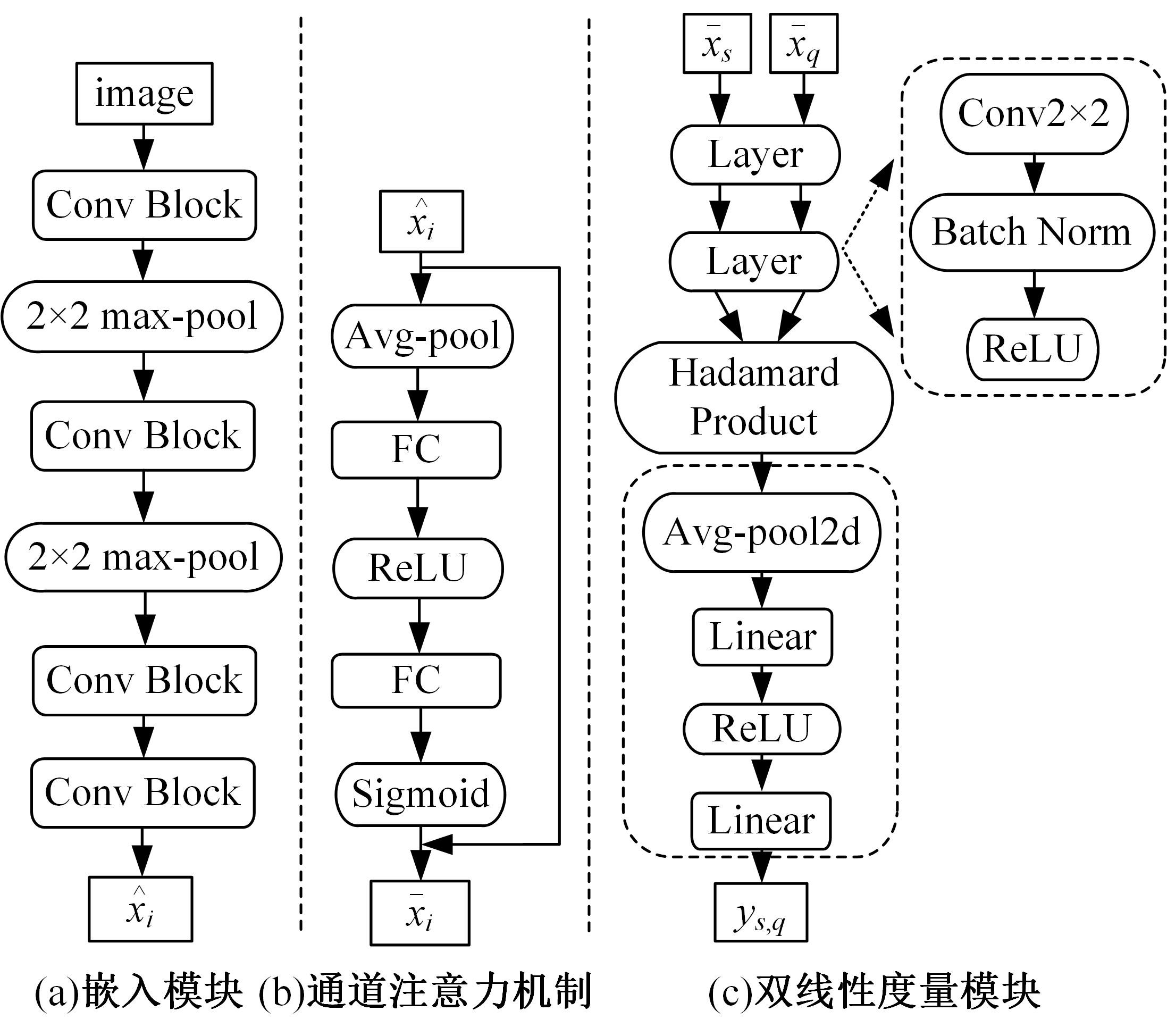
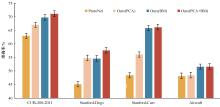
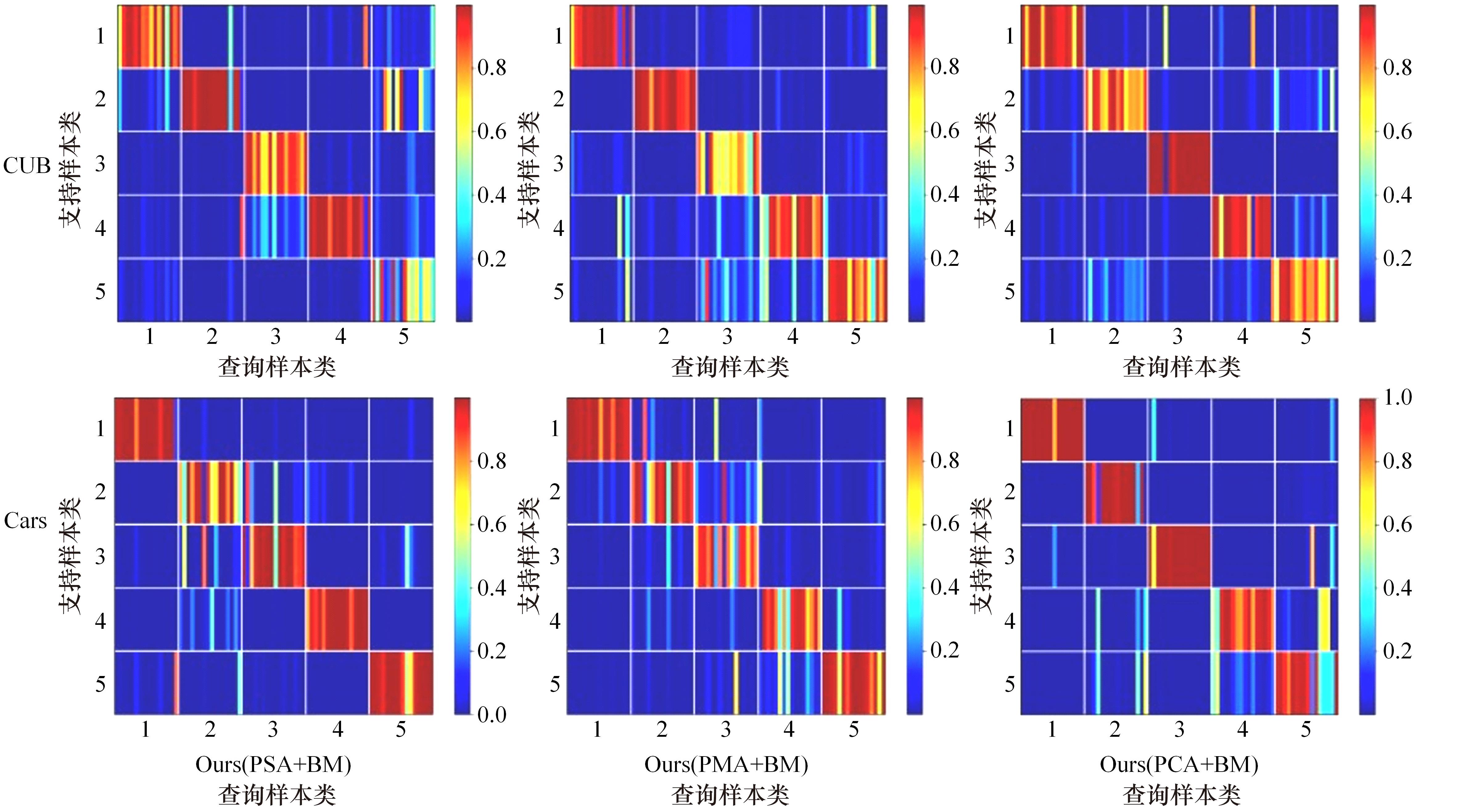
针对小样本图像分类任务中模型对不同类的相似图片进行度量时,由于缺少对样本局部重要特征的关注且难以捕捉相似图片间的细微差别,导致出现部分查询样本与正确类原型的分类边界较模糊的问题,提出了一种通道注意力双线性度量网络(CABMN)。该网络首先增加模型对图片局部重要区域的关注度,然后利用双线性哈达玛积操作挖掘该重要区域的深层次二阶特征信息,使模型对图片局部关键区域的定位更精准。对比实验结果表明:本文提出的CABMN在各数据集上的分类性能均有提高,尤其在细粒度数据集CUB-200-2011和Stanford-Cars上达到86.19%和81.51%的分类准确率。
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | Huang H, Zhang J, Zhang J, et al. Low-rank pairwise alignment bilinear network for few-shot fine-grained image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2020, 23: 1666-1680. |
| 2 | 曹洁, 屈雪, 李晓旭. 基于滑动特征向量的小样本图像分类方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(5): 1785-1791. |
| Cao Jie, Qu Xue, Li Xiao-xu. Few⁃shot image classification method based on sliding feature vectors[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(5): 1785-1791. | |
| 3 | Snell J, Swersky K, Zemel R. Prototypical networks for few-shot learning[C]∥Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach California, USA, 2017: 4080-4090. |
| 4 | Nguyen V N, Løkse S, Wickstrøm K, et al. Sen: a novel feature normalization dissimilarity measure for prototypical few-shot learning networks[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 118-134. |
| 5 | Vinyals O, Blundell C, Lillicrap T, et al. Matching networks for one shot learning[C]∥Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 3637-3645. |
| 6 | Zhang C, Cai Y, Lin G, et al. Deepemd: few-shot image classification with differentiable earth mover's distance and structured classifiers[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 12203-12213. |
| 7 | 刘萍萍, 赵宏伟, 耿庆田, 等. 基于局部特征和视皮层识别机制的图像分类[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2011, 41(5): 1401-1406. |
| Liu Ping-ping, Zhao Hong-wei, Geng Qing-tian, et al. Image classification method based on local feature and visual cortex recognition mechanism[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2011, 41(5): 1401-1406. | |
| 8 | Huang K, Geng J, Jiang W, et al. Pseudo-loss confidence metric for semi-supervised few-shot learning[C]∥IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 8671-8680. |
| 9 | Lin T Y, RoyChowdhury A, Maji S. Bilinear CNN models for fine-grained visual recognition[C]∥IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, USA, 2015: 1449-1457. |
| 10 | Wah C, Branson S, Welinder P, et al. The caltech-ucsd birds-200-2011 dataset[J]. California Institute of Technology, 2011, 7: 7138640. |
| 11 | Khosla A, Jayadevaprakash N, Yao B, et al. Novel dataset for fine-grained image categorization: Stanford dogs[J/OL]. [2022-09-12]. |
| 12 | Krause J, Stark M, Deng J, et al. 3D object representations for fine-grained categorization[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Sydney, Australia, 2013: 554-561. |
| 13 | Maji S, Rahtu E, Kannala J, et al. Fine-grained visual classification of aircraft[J]. ArXiv Preprint, 2013, 7:13065151. |
| 14 | Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, et al. ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 115(3): 211-252. |
| 15 | Liu Y, Lee J, Park M, et al. Transductive propagation network for few-shot learning[J]. arXiv E-prints, 2018, 5: 180510002. |
| 16 | Sung F, Yang Y, Zhang L, et al. Learning to compare: relation network for few-shot learning[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018:1199-1208. |
| 17 | Chen W Y, Liu Y C, Kira Z, et al. A closer look at few-shot classification[J]. arXiv E-prints, 2019, 4: 190404232. |
| 18 | Wu Z, Li Y, Guo L, et al. Parn: position-aware relation networks for few-shot learning[C]∥IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 6659-6667. |
| 19 | Zhu Y, Liu C, Jiang S. Multi-attention meta learning for few-shot fine-grained image recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence Main track, Yokohama, Japan, 2020: 1090-1096. |
| 20 | Li X, Wu J, Sun Z, et al. BSNet: bi-similarity network for few-shot fine-grained image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 30: 1318-1331. |
| 21 | Xu J, Le H, Huang M, et al. Variational feature disentangling for fine-Grained few-shot classification[C]∥IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 8792-8801. |
| 22 | Afrasiyabi A, Lalonde J F, Gagné C. Mixture-based feature space learning for few-shot image classification[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 9041-9051. |
| 23 | Ye H J, Hu H, Zhan D C, et al. Few-shot learning via embedding adaptation with set-to-set functions[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 8808-8817. |
| 24 | Kang D, Kwon H, Min J, et al. Relational embedding for few-shot classification[C]∥IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 8822-8833. |
| 25 | Finn C, Abbeel P, Lwvine S. Model-agnostic meta-learning for fast adaptation of deep networks[C]∥International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 2017: 1126-1135. |
| 26 | Cai Q, Pan Y, Yao T, et al. Memory matching networks for one-shot image recognition[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake, USA, 2018: 4080-4088. |
| 27 | Li X, Wu J, Chang D, et al. Mixed attention mechanism for small-sample fine-grained image classification[C]∥Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference, Lanzhou, China, 2019: 80-85. |
| [1] | 霍光,林大为,刘元宁,朱晓冬,袁梦,盖迪. 基于多尺度特征和注意力机制的轻量级虹膜分割模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2591-2600. |
| [2] | 郭晓新,李佳慧,张宝亮. 基于高分辨率网络的视杯和视盘的联合分割[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2350-2357. |
| [3] | 唐菲菲,周海莲,唐天俊,朱洪洲,温永. 融合动静态变量的滑坡多步位移预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1833-1841. |
| [4] | 田彦涛,黄兴,卢辉遒,王凯歌,许富强. 基于注意力与深度交互的周车多模态行为轨迹预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1474-1480. |
| [5] | 吕卫,韩镓泽,褚晶辉,井佩光. 基于多模态自注意力网络的视频记忆度预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1211-1219. |
| [6] | 田彦涛,许富强,王凯歌,郝子绪. 考虑周车信息的自车期望轨迹预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 674-681. |
| [7] | 刘桂霞,田郁欣,王涛,马明睿. 基于双输入3D卷积神经网络的胰腺分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(12): 3565-3572. |
| [8] | 刘晶红,邓安平,陈琪琪,彭佳琦,左羽佳. 基于多重注意力机制的无锚框目标跟踪算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(12): 3518-3528. |
| [9] | 江晟,王鹏朗,邓志吉,别一鸣. 基于深度学习的交通事故救援图像融合算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(12): 3472-3480. |
| [10] | 耿庆田,赵杨,李清亮,于繁华,李晓宁. 基于注意力机制的LSTM和ARIMA集成方法在土壤温度中应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(10): 2973-2981. |
| [11] | 欧阳继红,郭泽琪,刘思光. 糖尿病视网膜病变分期双分支混合注意力决策网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 648-656. |
| [12] | 李先通,全威,王华,孙鹏程,安鹏进,满永兴. 基于时空特征深度学习模型的路径行程时间预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 557-563. |
| [13] | 陈晓雷,孙永峰,李策,林冬梅. 基于卷积神经网络和双向长短期记忆的稳定抗噪声滚动轴承故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 296-309. |
| [14] | 周大可,张超,杨欣. 基于多尺度特征融合及双重注意力机制的自监督三维人脸重建[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(10): 2428-2437. |
| [15] | 曹洁,屈雪,李晓旭. 基于滑动特征向量的小样本图像分类方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1785-1791. |
|
||