吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (9): 2638-2645.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230446
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于RGHS图像增强和改进YOLOv5网络的黄颡鱼目标提取
李路1,2( ),宋均琦1,朱明1,2,谭鹤群1,2,周玉凡1,孙超奇1,周铖钰1
),宋均琦1,朱明1,2,谭鹤群1,2,周玉凡1,孙超奇1,周铖钰1
- 1.华中农业大学 工学院,武汉 430070
2.农业农村部 水产养殖设施工程重点实验室,武汉 430070
Object extraction of yellow catfish based on RGHS image enhancement and improved YOLOv5 network
Lu Li1,2( ),Jun-qi Song1,Ming Zhu1,2,He-qun Tan1,2,Yu-fan Zhou1,Chao-qi Sun1,Cheng-yu Zhou1
),Jun-qi Song1,Ming Zhu1,2,He-qun Tan1,2,Yu-fan Zhou1,Chao-qi Sun1,Cheng-yu Zhou1
- 1.College of Engineering,Huazhong Agricultural University,Wuhan 430070,China
2.Key Laboratory of Aquaculture Facilities Engineering,Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs,Wuhan 430070,China
摘要:
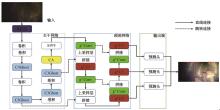
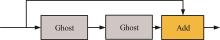
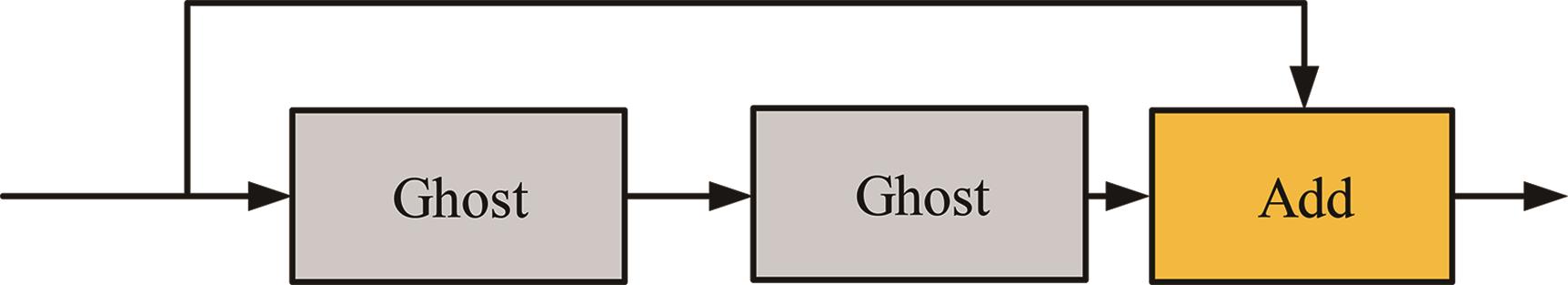
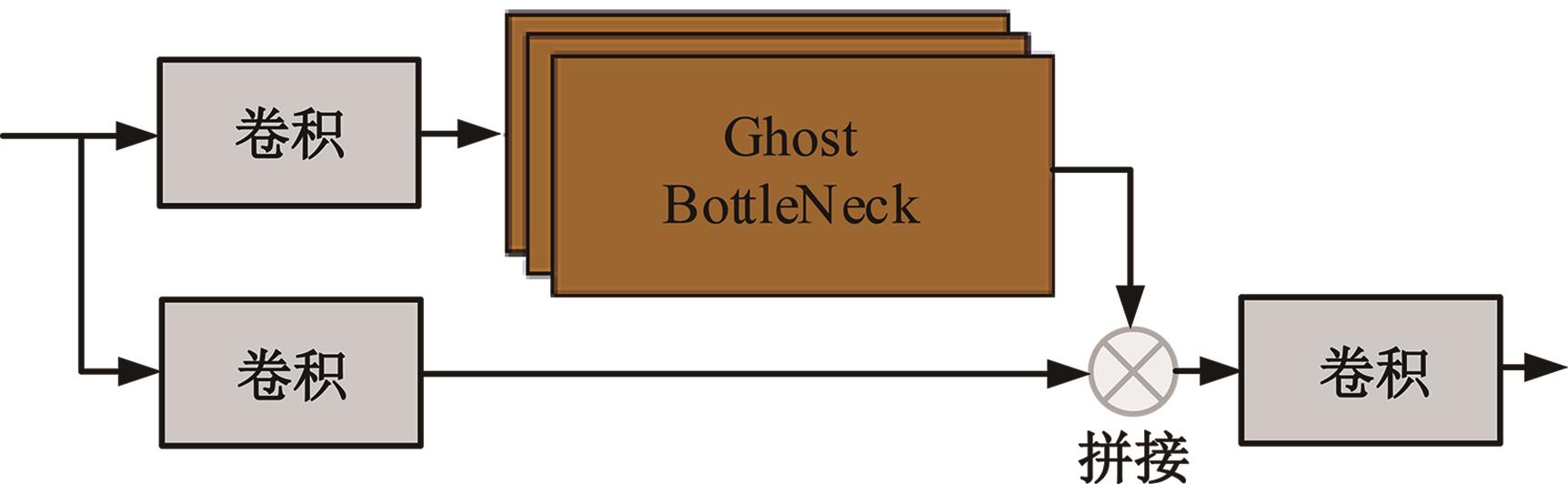
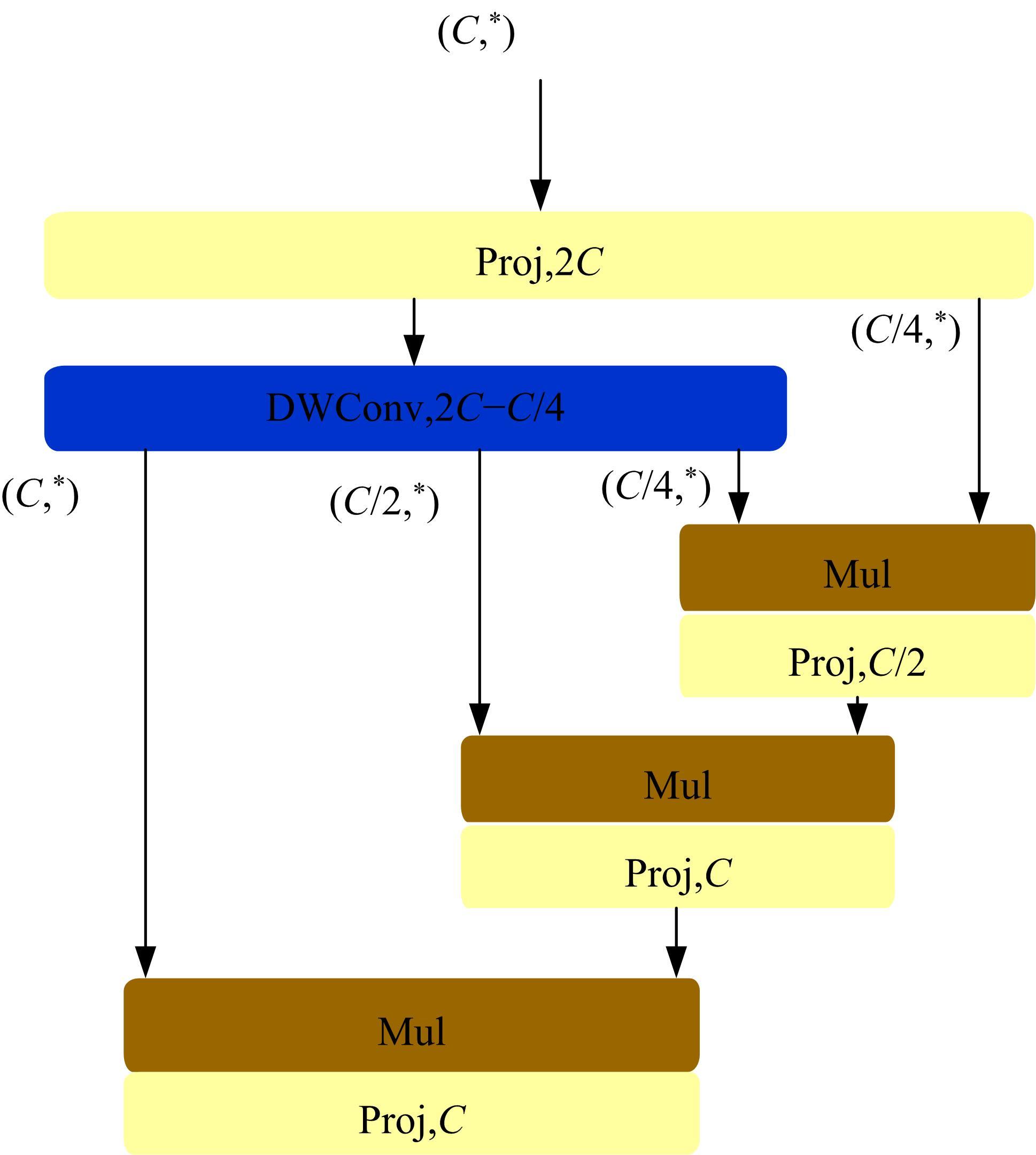
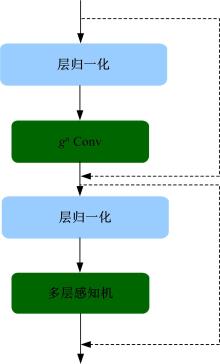
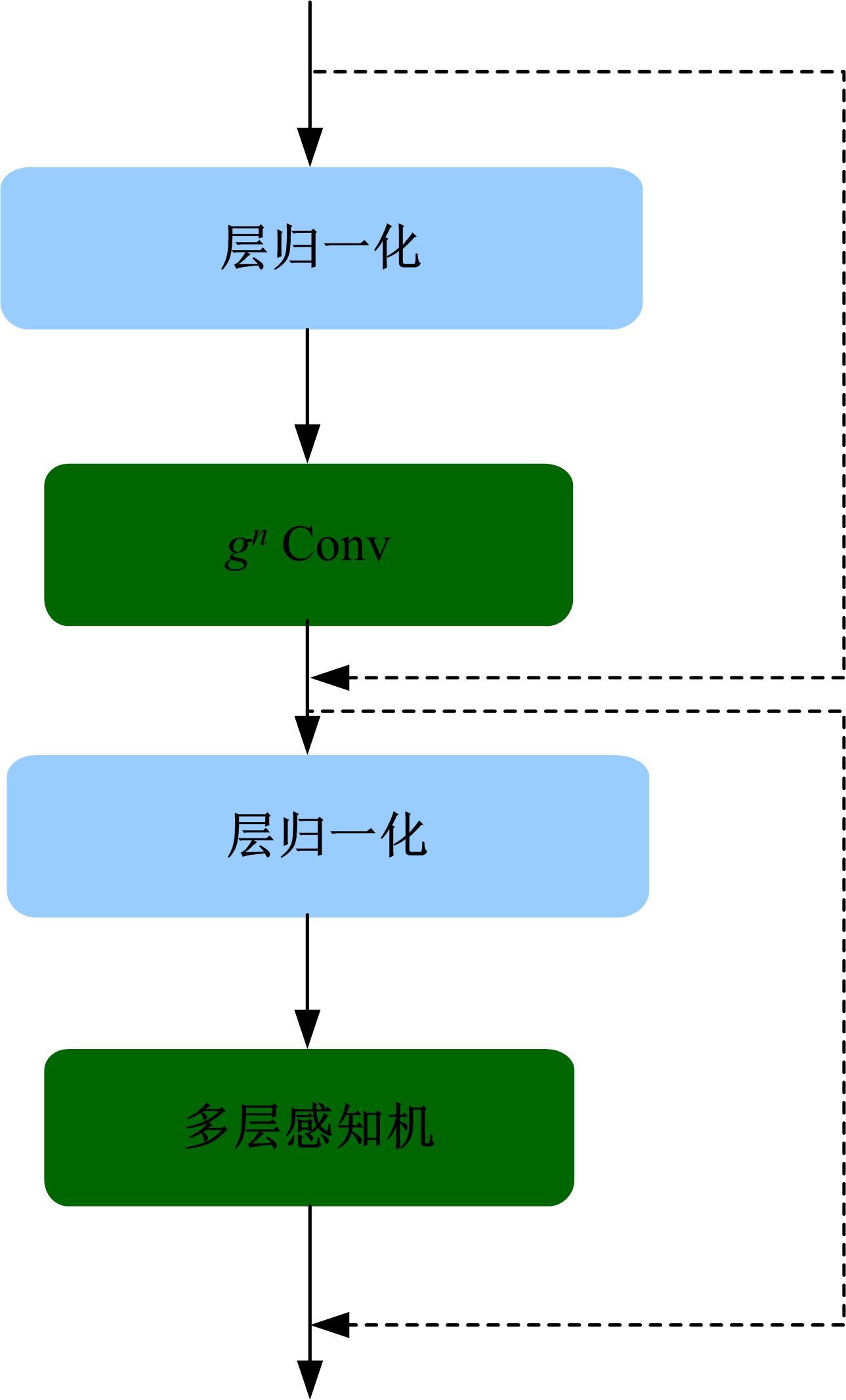
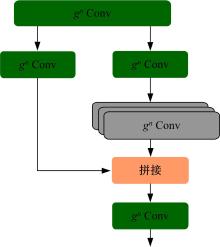
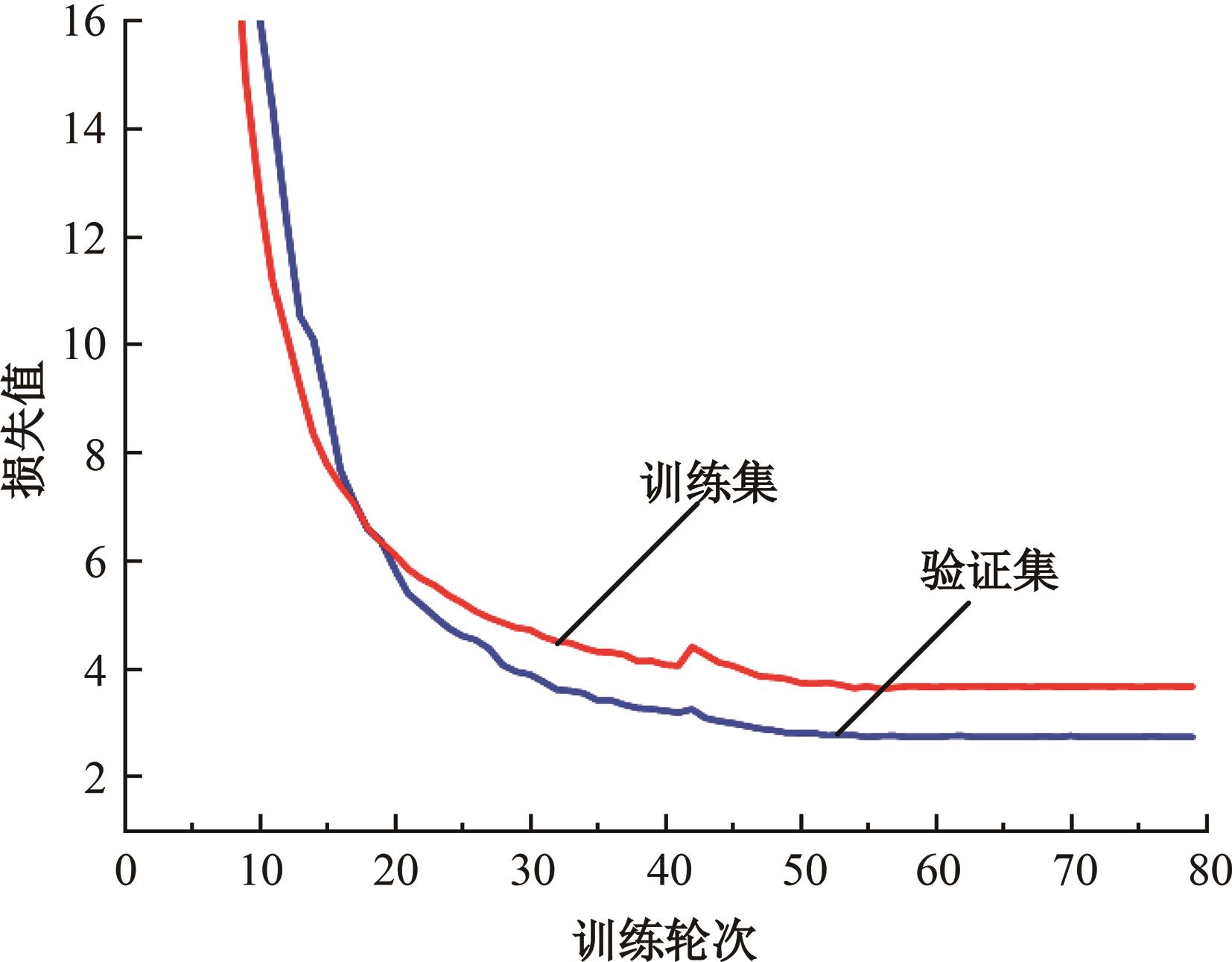
针对水下能见度不佳,黄颡鱼目标提取精度低、速度慢等问题,提出了基于相对全局直方图拉伸(RGHS)算法和改进YOLOv5的黄颡鱼目标提取模型。首先,为解决光照不均、噪声大等因素带来的图像质量问题,采用RGHS算法对黄颡鱼图像进行亮度增强。然后,在YOLOv5主干网络中引入C3ghost模块和坐标注意力(CA)机制,在颈部网络中用
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | Jiao L C, Zhang R H, Liu F, et al. New generation deep learning for video object detection: a survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(8): 3195-3215. |
| 2 | Zhang L, Li W, Liu C, et al. Automatic fish counting method using image density grading and local regression[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2020, 179: No.105844. |
| 3 | Aliyu I, Gana K J, Musa A A, et al. Incorporating recognition in catfish counting algorithm using artificial neural network and geometry[J]. KSII Transactions on Internet and Information Systems, 2020, 14(12): 4866-4888. |
| 4 | Garcia R, Prados R, Quintana J, et al. Automatic segmentation of fish using deep learning with application to fish size measurement[J]. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 2020, 77(4): 1354-1366. |
| 5 | Yu C, Liu Y, Hu Z, et al. Precise segmentation and measurement of inclined fish's features based on U-net and fish morphological characteristics[J]. Applied Engineering in Agriculture, 2022, 38(1): 37-48. |
| 6 | Yasruddin M L, Ismail M A H, Husin Z, et al. Feasibility study of fish disease detection using computer vision and deep convolutional neural network (dcnn) algorithm[C]∥2022 IEEE 18th International Colloquium on Signal Processing & Applications, Selangor, Malaysia, 2022: 272-276. |
| 7 | Zhang J, Pang H, Cai W, et al. Using image processing technology to create a novel fry counting algorithm[J]. Aquaculture and Fisheries, 2022, 7(4): 441-449. |
| 8 | Guillaud A, Troadec H, Benzinou A, et al. A multiagent system for edge detection and continuity perception on fish otolith images[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2002, 7: 746-753. |
| 9 | Deka J, Laskar S. Comparative Analysis of FOD based prewitt, sobel & laplacian operators for edge detection on freshwater fish images[C]∥2020 International Conference on Emerging Smart Computing and Informatics, Madurai, India, 2020: 65-70. |
| 10 | Gao T S, Sheng D B, Nguyen T H, et al. Measurement of the fish body wound depth based on a depth map inpainting method[C]∥AETA 2016: Recent Advances in Electrical Engineering and Related Sciences: Theory and Application, Busan, Korea, 2017: 289-299. |
| 11 | Abdeldaim A M, Houssein E H, Hassanien A E. Color image segmentation of fishes with complex background in water[C]∥The International Conference on Advanced Machine Learning Technologies and Applications,Cairo, Egypt, 2018: 634-643. |
| 12 | Xu G, Chen Q, Yoshida T, et al. Detection of bluefin tuna by cascade classifier and deep learning for monitoring fish resources[C]∥Global Oceans 2020: Singapore-US Gulf Coast, Biloxi, MS, USA, 2020: 1-4. |
| 13 | 谭鹤群,李玉祥,朱明,等. 通过图像增强与改进Faster-RCNN网络的重叠鱼群尾数检测[J]. 农业工程学报,2022,38(13):167-176. |
| TAN He-qun, Li Yu-xiang, ZHU Ming, et al. Detecting overlapping fish population using image enhancement and improved Faster-RCNN networks[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2022, 38(13):167-176. | |
| 14 | Zhang W, Dong L, Pan X, et al. Single image defogging based on multi-channel convolutional MSRCR[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 72492-72504. |
| 15 | 郝琨,王阔,赵璐,等. 基于图像增强与改进YOLOv3的水下生物检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(5):1088-1097. |
| Hao Kun, Wang Kuo, Zhao Lu, et al. Underwater biological detection algorithm based on image enhancement and improved YOLOv3[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(5):1088-1097. | |
| 16 | Cai K, Miao X, Wang W, et al. A modified YOLOv3 model for fish detection based on MobileNetv1 as backbone[J]. Aquacultural Engineering, 2020, 91: No.102117. |
| 17 | Li J, Liu C, Lu X, et al. CME-YOLOv5: an efficient object detection network for densely spaced fish and small targets[J]. Water, 2022, 14(15): 2412. |
| 18 | Huang D, Wang Y, Song W, et al. Shallow-water image enhancement using relative global histogram stretching based on adaptive parameter acquisition[C]∥MultiMedia Modeling: 24th International Conference, Bangkok, Thailand, 2018: 453-465. |
| 19 | 刘彦呈,董张伟,朱鹏莅,等. 基于特征解耦的无监督水下图像增强[J]. 电子与信息学报,2022,44(10):3389-3398. |
| Liu Yan-chen, Dong Zhang-wei, Zhu Peng-li, et al. Unsupervised underwater image enhancement based on feature decoupling[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(10):3389-3398. | |
| 20 | Bochkovskiy A, Wang C Y, Liao H Y M. Yolov4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection[J/OL]. [2023-04-20]. |
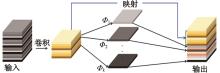
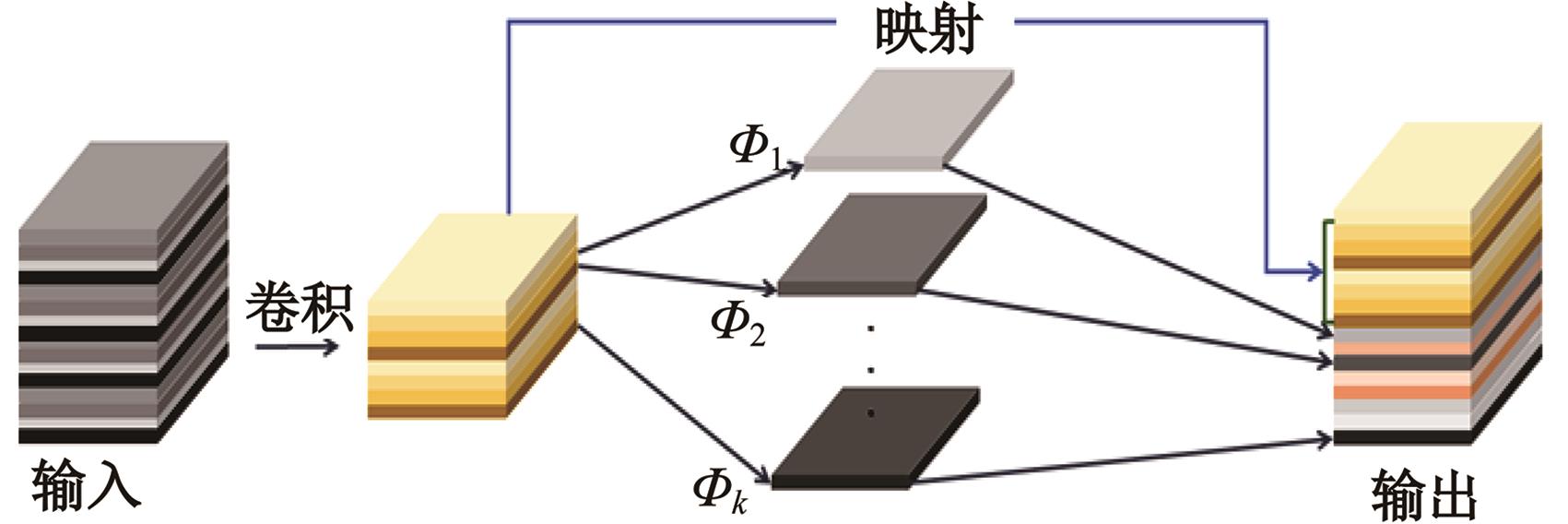
| 21 | Han K, Wang Y, Tian Q, et al. Ghostnet: more features from cheap operations[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle USA, 2020: 1580-1589. |
| 22 | Hou Q, Zhou D, Feng J. Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Online Conference, 2021: 13713-13722. |
| 23 | Rao Y M, Zhao W L, Tang Y S, et al. Hornet: efficient high-order spatial interactions with recursive gated convolutions[J/OL]. [2023-04-22]. |
| 24 | Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, et al. SSD: single shot multibox detector[C]∥Computer Vision-ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 21-37. |
| 25 | Ge Z, Liu S, Wang F, et al. Yolox: exceeding yolo series in 2021[J/OL]. [2023-04-22]. |
| [1] | 张磊,焦晶,李勃昕,周延杰. 融合机器学习和深度学习的大容量半结构化数据抽取算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2631-2637. |
| [2] | 余萍,赵康,曹洁. 基于优化A-BiLSTM的滚动轴承故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2156-2166. |
| [3] | 郭昕刚,程超,沈紫琪. 基于卷积网络注意力机制的人脸表情识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2319-2328. |
| [4] | 赵宏伟,武鸿,马克,李海. 基于知识蒸馏的图像分类框架[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2307-2312. |
| [5] | 张云佐,郑宇鑫,武存宇,张天. 基于双特征提取网络的复杂环境车道线精准检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 1894-1902. |
| [6] | 乔百友,武彤,杨璐,蒋有文. 一种基于BiGRU和胶囊网络的文本情感分析方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 2026-2037. |
| [7] | 郭昕刚,何颖晨,程超. 抗噪声的分步式图像超分辨率重构算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 2063-2071. |
| [8] | 张丽平,刘斌毓,李松,郝忠孝. 基于稀疏多头自注意力的轨迹kNN查询方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1756-1766. |
| [9] | 孙铭会,薛浩,金玉波,曲卫东,秦贵和. 联合时空注意力的视频显著性预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1767-1776. |
| [10] | 李延风,刘名扬,胡嘉明,孙华栋,孟婕妤,王奥颖,张涵玥,杨华民,韩开旭. 基于梯度转移和自编码器的红外与可见光图像融合[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1777-1787. |
| [11] | 陆玉凯,袁帅科,熊树生,朱绍鹏,张宁. 汽车漆面缺陷高精度检测系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1205-1213. |
| [12] | 高云龙,任明,吴川,高文. 基于注意力机制改进的无锚框舰船检测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1407-1416. |
| [13] | 梁礼明,周珑颂,尹江,盛校棋. 融合多尺度Transformer的皮肤病变分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 1086-1098. |
| [14] | 张云佐,郭威,李文博. 遥感图像密集小目标全方位精准检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 1105-1113. |
| [15] | 李晓旭,安文娟,武继杰,李真,张珂,马占宇. 通道注意力双线性度量网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 524-532. |
|
||