吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (3): 719-726.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221029
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
基于基因表达式编程的高架道路事故实时预测
- 1.东南大学 江苏省城市智能交通重点实验室,南京 211189
2.东南大学 现代城市交通技术江苏高校协同创新中心,南京 211189
3.东南大学 交通学院,南京 211189
Real⁃time crash prediction of elevated expressway based on gene expression programming algorithm
Xiao-chi MA1,2,3( ),Jian LU1,2,3(
),Jian LU1,2,3( )
)
- 1.Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Urban ITS,Southeast University,Nanjing 211189,China
2.Jiangsu Province Collaborative Innovation Center of Modern Urban Traffic Technologies,Southeast University,Nanjing 211189,China
3.School of Transportation,Southeast University,Nanjing 211189,China
摘要:
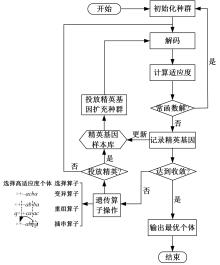
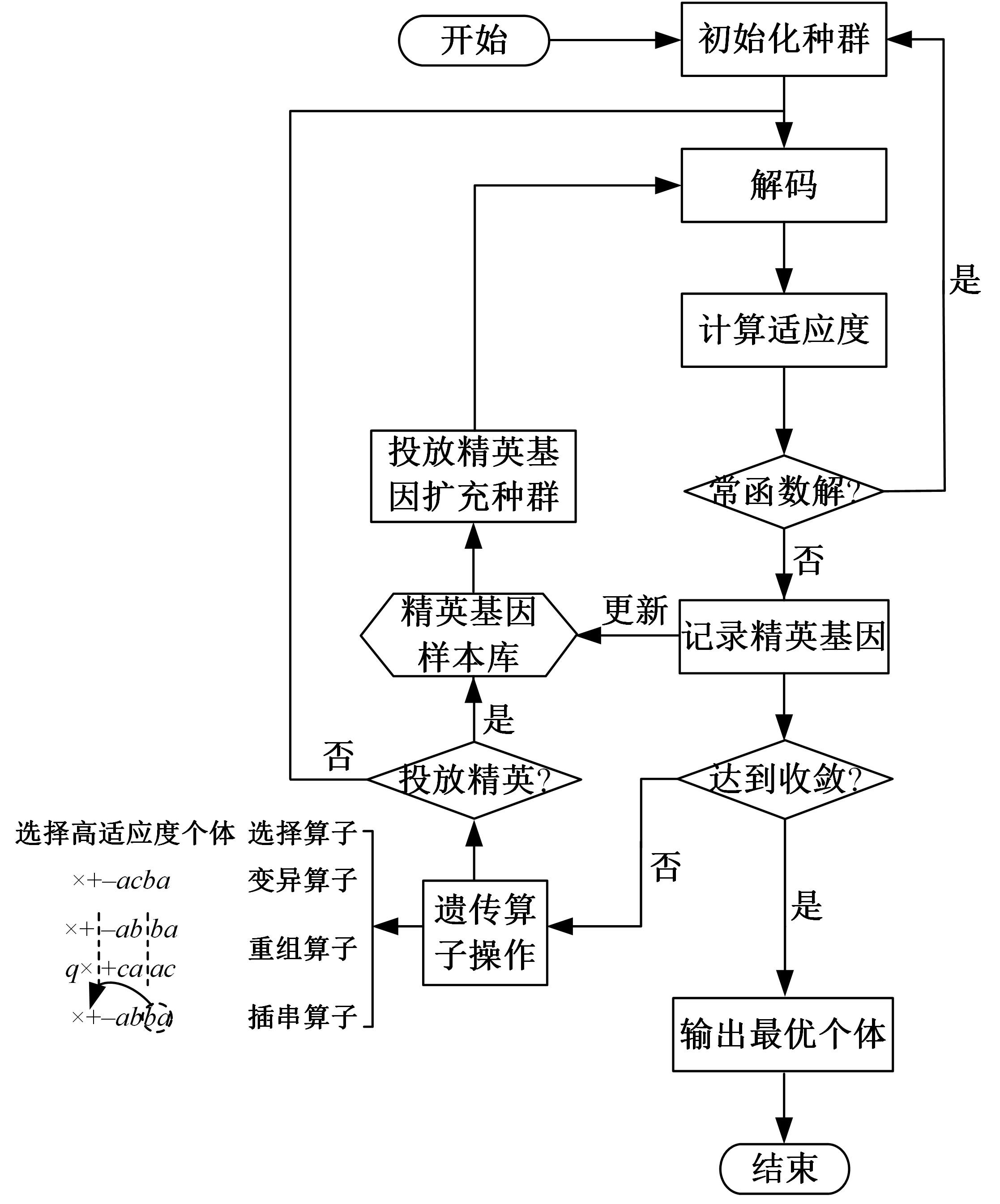
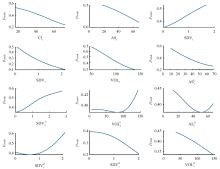
为在城市高架道路场景下有效预测交通事故,基于上海市延安高架道路交通流和事故数据,利用附加精英基因库和灭绝机制的改进型基因表达式编程算法,提出了高架道路事故预测经验公式。通过与传统建模方法的结果进行对比,验证了经验公式的预测精度和可理解性;在不进行重新训练和标定的前提下直接应用经验公式对其他高架道路的事故数据集进行预测,验证了其可移植性。结果表明:在延安高架道路数据集上,经验公式的预测性能较传统Logistics回归有较大提升,受试者工作特征曲线面积指标和F1-score指标达到与人工神经网络模型一致的水平,能正确识别74%的事故。经验公式在杭州市上塘高架道路数据集上的良好性能表明其具有基本的可移植性。综上,基因表达式编程算法针对事故风险预测问题兼顾了高精度和可理解性,并表现出可移植性,有助于建设低成本、高效率的事故预测系统。
中图分类号:
- U491.31
| 1 | Hossain M, Abdel-Aty M, Quddus M A, et al. Real-time crash prediction models: state-of-the-art, design pathways and ubiquitous requirements[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2019, 124: 66-84. |
| 2 | Mannering F, Bhat C R, Shankar V, et al. Big data, traditional data and the tradeoffs between prediction and causality in highway-safety analysis[J]. Analytic Methods in Accident Research, 2020, 25: No. 100113. |
| 3 | Abdel-Aty M, Uddin N, Pande A, et al. Predicting freeway crashes from loop detector data by matched case-control logistic regression[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2004, 1897(1): 88-95. |
| 4 | 郑来, 顾鹏, 卢健. 基于T-S模糊故障树和贝叶斯网络的重特大交通事故成因分析[J]. 交通信息与安全, 2021, 39(4): 43-51. |
| Zheng Lai, Gu Peng, Lu Jian. A cause analysis of extraordinarily severe traffic crashes based on T-S fuzzy fault tree and bayesian network[J]. Journal of Transport Information and Safety, 2021, 39(4): 43-51. | |
| 5 | Yu R J, Zheng Y, Abdel-Aty M, et al. Exploring crash mechanisms with microscopic traffic flow variables: a hybrid approach with latent class logit and path analysis models[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2019, 125: 70-78. |
| 6 | Li L C, Sheng X, Du B, et al. A deep fusion model based on restricted Boltzmann machines for traffic accident duration prediction[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 93: No. 103686. |
| 7 | Wang L, Abdel-Aty M, Lee J, et al. Analysis of real-time crash risk for expressway ramps using traffic, geometric, trip generation, and socio-demographic predictors[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2019, 122: 378-384. |
| 8 | 陈荔, 李聪颖, 詹立, 等. 城市道路交通事故形态影响因素分析与预测[J]. 长安大学学报: 自然科学版, 2022, 42(4): 98-107. |
| Chen Li, Li Cong-ying, Zhan Li, et al. Influencing factors analysis and prediction of urban road traffic accident patterns[J]. Journal of Chang'an University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 42(4): 98-107. | |
| 9 | Yu R J, Abdel-Aty M. Utilizing support vector machine in real-time crash risk evaluation[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2013, 51: 252-259. |
| 10 | Guo Miao, Zhao Xiao-hua, Yao Ying, et al. A study of freeway crash risk prediction and interpretation based on risky driving behavior and traffic flow data[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2021, 160: No. 106328. |
| 11 | Eboli L, Mazzulla G, Pungillo G. How to define the accident risk level of car drivers by combining objective and subjective measures of driving style[J]. Transportation Research Part F: Traffic Psychology and Behaviour, 2017, 49: 29-38. |
| 12 | Dingus T A, Guo F, Lee S, et al. Driver crash risk factors and prevalence evaluation using naturalistic driving data[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(10): 2636-2641. |
| 13 | 王海晓, 李永翔, 丁旭, 等. 基于边缘智能的城市下穿隧道车辆行车安全预测[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(6): 1337-1343. |
| Wang Hai-xiao, Li Yong-xiang, Ding Xu, et al. Traffic safety prediction of urban underpass tunnel vehicles based on edge intelligence[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1337-1343. | |
| 14 | 高珍, 高屹, 余荣杰, 等. 连续数据环境下的道路交通事故风险预测模型[J]. 中国公路学报, 2018, 31(4): 280-287. |
| Gao Zhen, Gao Yi, Yu Rong-jie, et al. Road crash risk prediction model for continuous streaming data environment[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2018, 31(4): 280-287. | |
| 15 | 李思瑶. 考虑交通异质性的城市快速路事故预测方法[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学能源与动力工程学院, 2020. |
| Li Si-yao. Study on urban expressway crash prediction method considering traffic heterogeneity[D]. Wuhan: School of Energy and Power Engineering, Wuhan University of Technology, 2020. | |
| 16 | Xu Chuan, Wang Xue-song, Yang Hong, et al. Exploring the impacts of speed variances on safety performance of urban elevated expressways using GPS data[J]. Accident Analysis And Prevention, 2019, 123: 29-38. |
| 17 | Xu Cheng-cheng, Liu Pan, Wang Wei, et al. Real-time identification of traffic conditions prone to injury and non-injury crashes on freeways using genetic programming[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2016, 50(5): 701-716. |
| 18 | Candida F. Gene expression programming: a new adaptive algorithm for solving problems[J]. Complex Systems, 2000, 13(2): 87-129. |
| 19 | Yang Kui, Yu Rong-jie, Wang Xue-song, et al. How to determine an optimal threshold to classify real-time crash-prone traffic conditions?[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2018, 117: 250-261. |
| 20 | Behnood A, Al-Bdairi N S S. Determinant of injury severities in large truck crashes: a weekly instability analysis[J]. Safety Science, 2020, 131: No. 104911. |
| 21 | Chand A, Jayesh S, Bhasi A B. Road traffic accidents: an overview of data sources, analysis techniques and contributing factors[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2021, 47: 5135-5141. |
| [1] | 严利鑫,冯进培,郭军华,龚毅轲. 不同险态情景下共驾型智能车辆接管行为特征分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 683-691. |
| [2] | 曲大义,张可琨,顾原,王韬,宋慧,戴守晨. 自动驾驶车辆换道决策行为分析及分子动力学建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 700-710. |
| [3] | 张健,李青扬,李丹,姜夏,雷艳红,季亚平. 基于深度强化学习的自动驾驶车辆专用道汇入引导[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2508-2518. |
| [4] | 郑植,袁佩,金轩慧,魏思斯,耿波. 桥墩复合材料柔性防撞护舷试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2581-2590. |
| [5] | 李洪涛,王琳虹,李俊达. 公路交叉口照明和限速对视觉搜索能力的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2287-2297. |
| [6] | 李建华,王泽鼎. 考虑路径耗时的城市汽车分布式充电桩选点规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2298-2303. |
| [7] | 巫威眺,曾坤,周伟,李鹏,靳文舟. 基于多源数据和响应面优化的公交客流预测深度学习方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2001-2015. |
| [8] | 何永明,陈世升,冯佳,万亚楠. 基于高精地图的超高速公路虚拟轨道系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2016-2028. |
| [9] | 程国柱,盛林,赵浩,冯天军. 基于危险度分析的信号交叉口专用相位设置条件[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 1962-1969. |
| [10] | 薛志佳,王召阳,张久鹏,晏长根,许子凯,张英立,黄晓明,马涛. 泥石流作用下道路结构韧性分析及提升[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1773-1781. |
| [11] | 刘振亮,赵存宝,吴云鹏,马迷娜,马龙双. 数据驱动的公路桥梁网络全寿命抗震韧性评估[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1695-1701. |
| [12] | 贾洪飞,徐英俊,杨丽丽,王楠. 商品车多式联运联盟成员选择及利益分配[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1060-1069. |
| [13] | 孙超,尹浩为,汤文蕴,褚昭明. 交通需求估计下的检测器布局和手机数据扩样推断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1070-1077. |
| [14] | 常玉林,徐文倩,孙超,张鹏. 车联网环境下考虑遵从程度的混合流量逐日均衡[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1085-1093. |
| [15] | 肖雪,李克平,彭博,昌满玮. 基于决策-规划迭代框架的智驾车换道行为建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 746-757. |
|
||