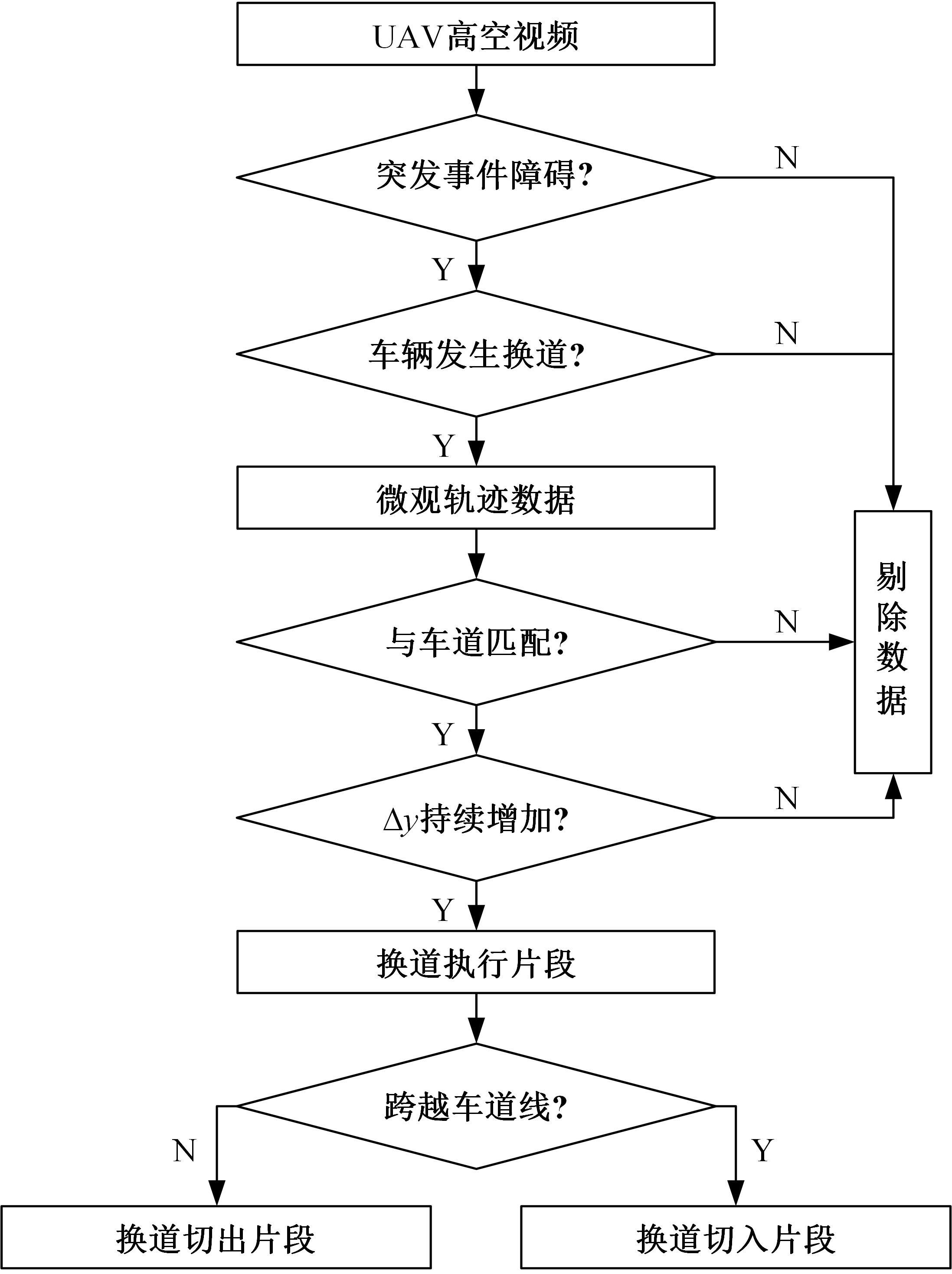
吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (5): 1311-1322.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220754
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
协同换道避障模型和轨迹数据驱动的车辆协同避障策略
- 昆明理工大学 交通工程学院,昆明 650500
Vehicle cooperative obstacle avoidance strategy driven by CLAM model and trajectory data
Ya-qin QIN( ),Zheng-fu QIAN,Ji-ming XIE(
),Zheng-fu QIAN,Ji-ming XIE( )
)
- Faculty of Transportation Engineering,Kunming University of Science and Technology,Kunming 650500,China
摘要:
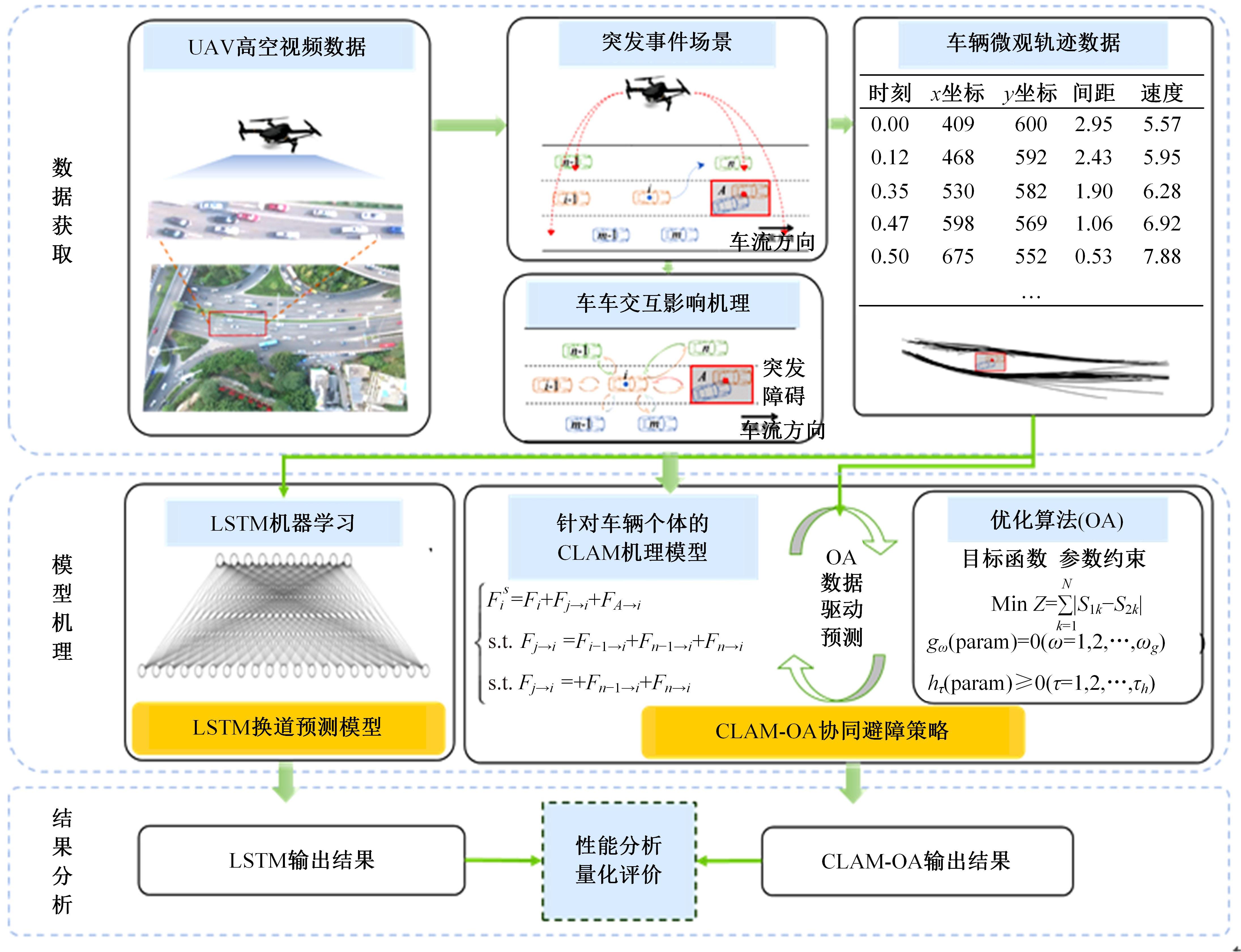
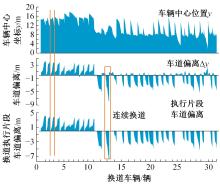
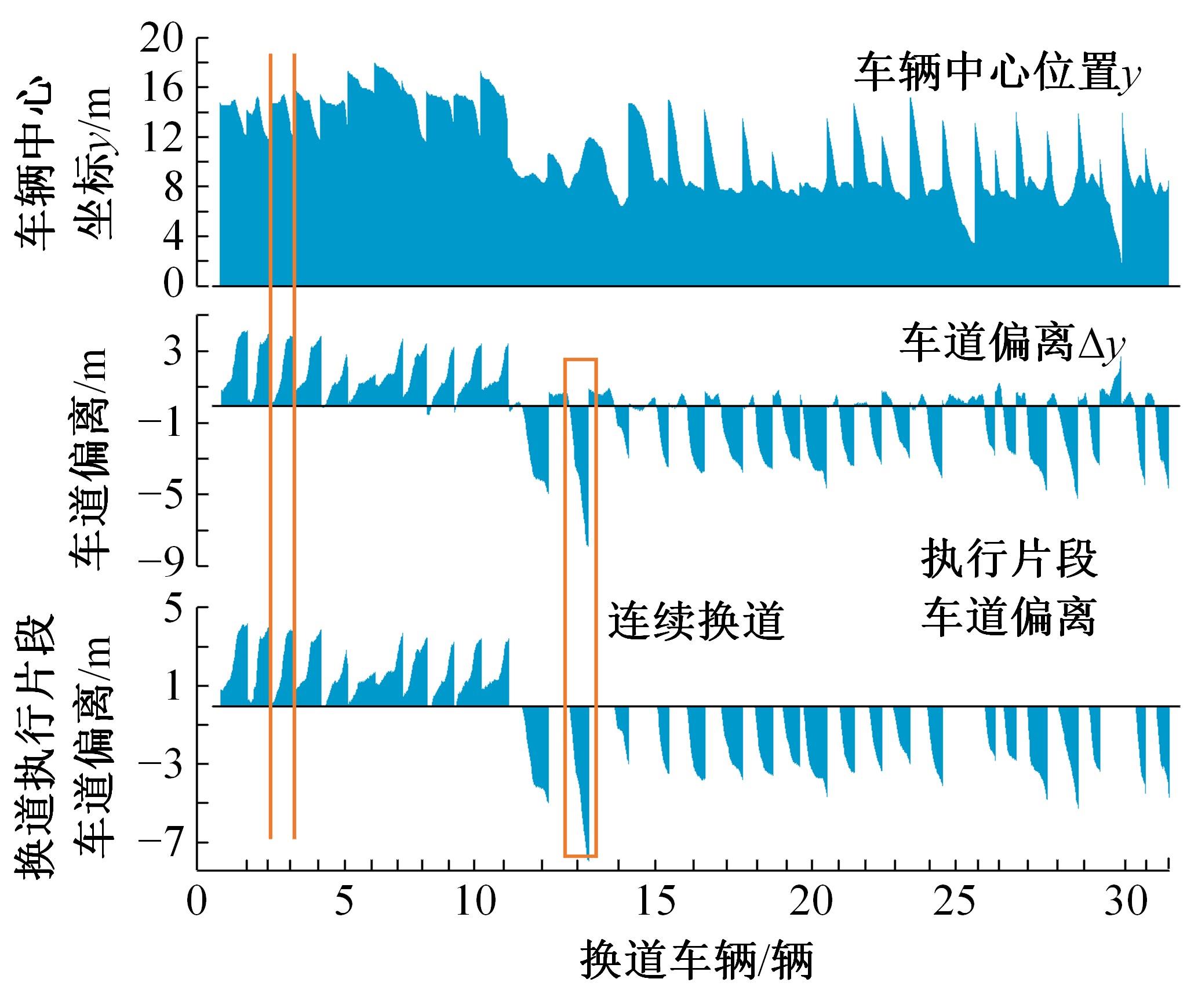
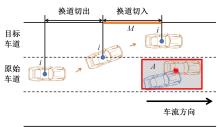
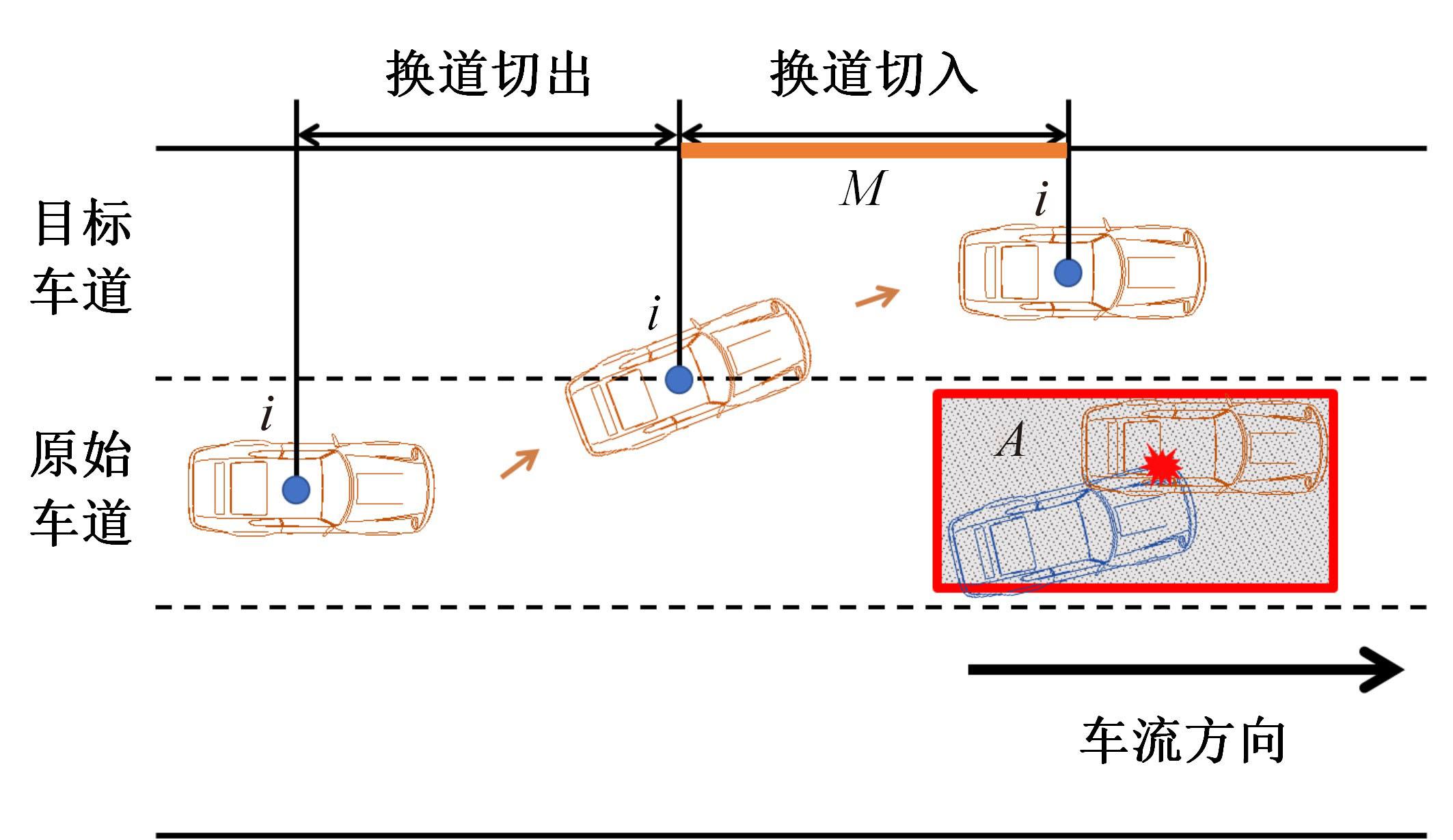
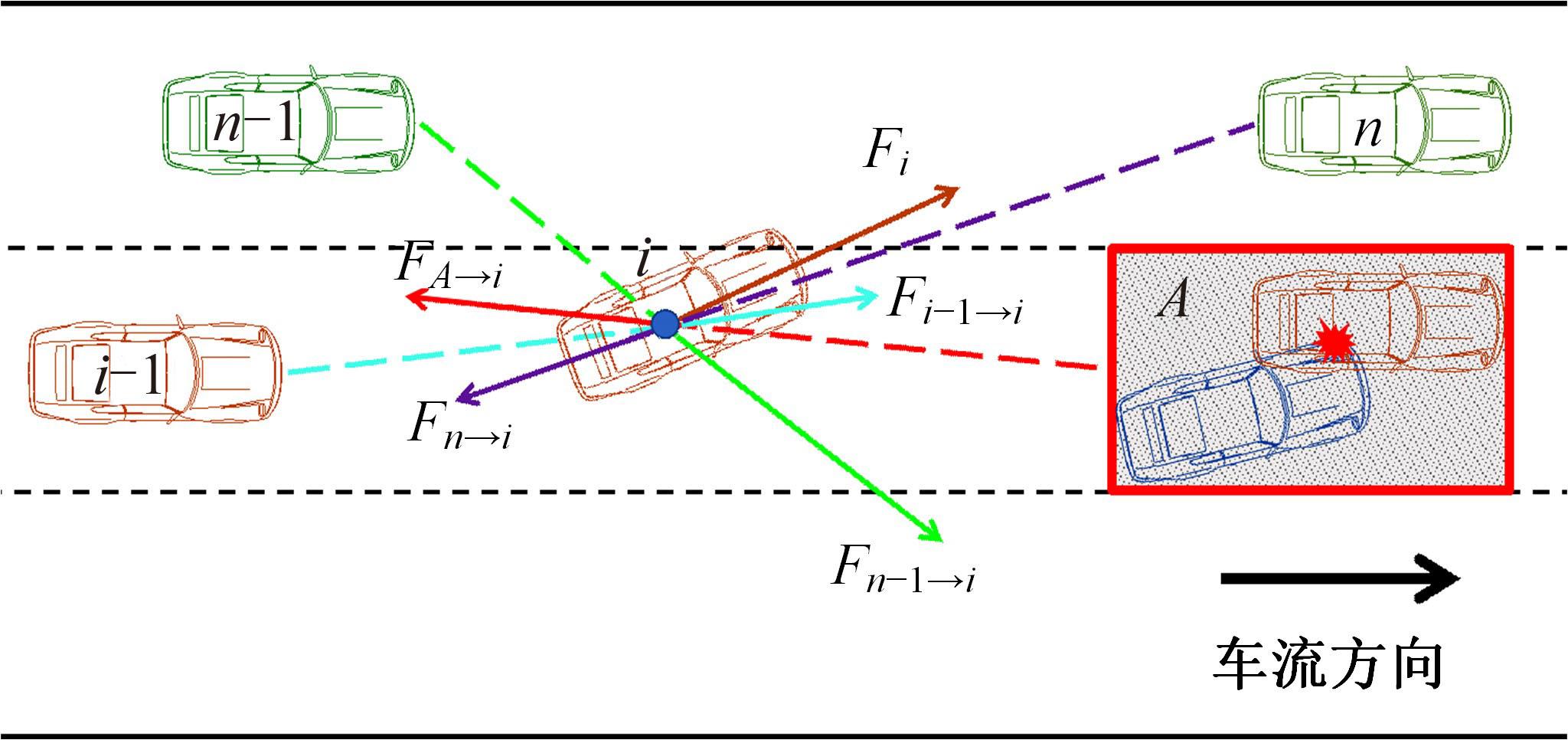
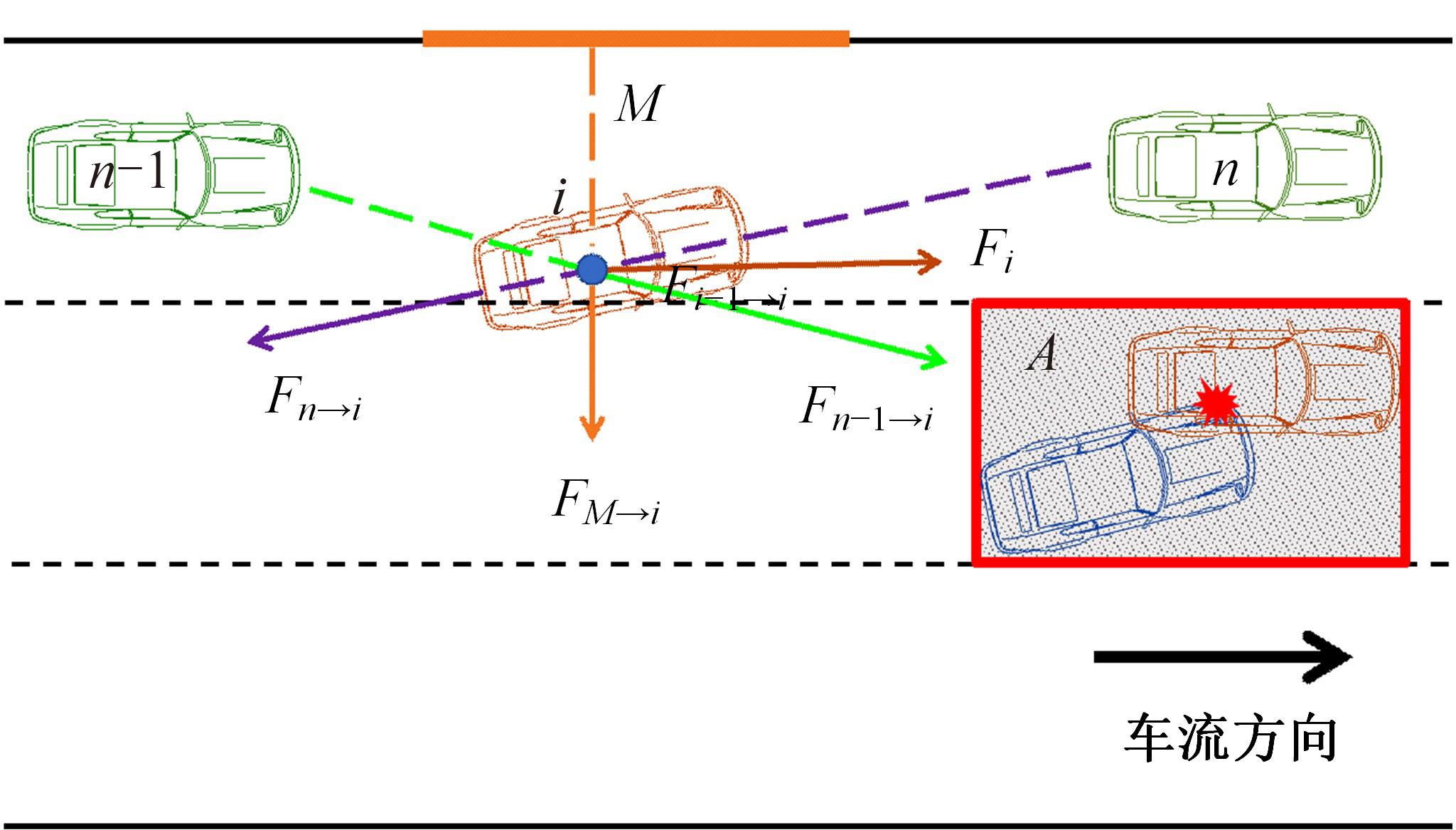
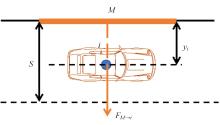
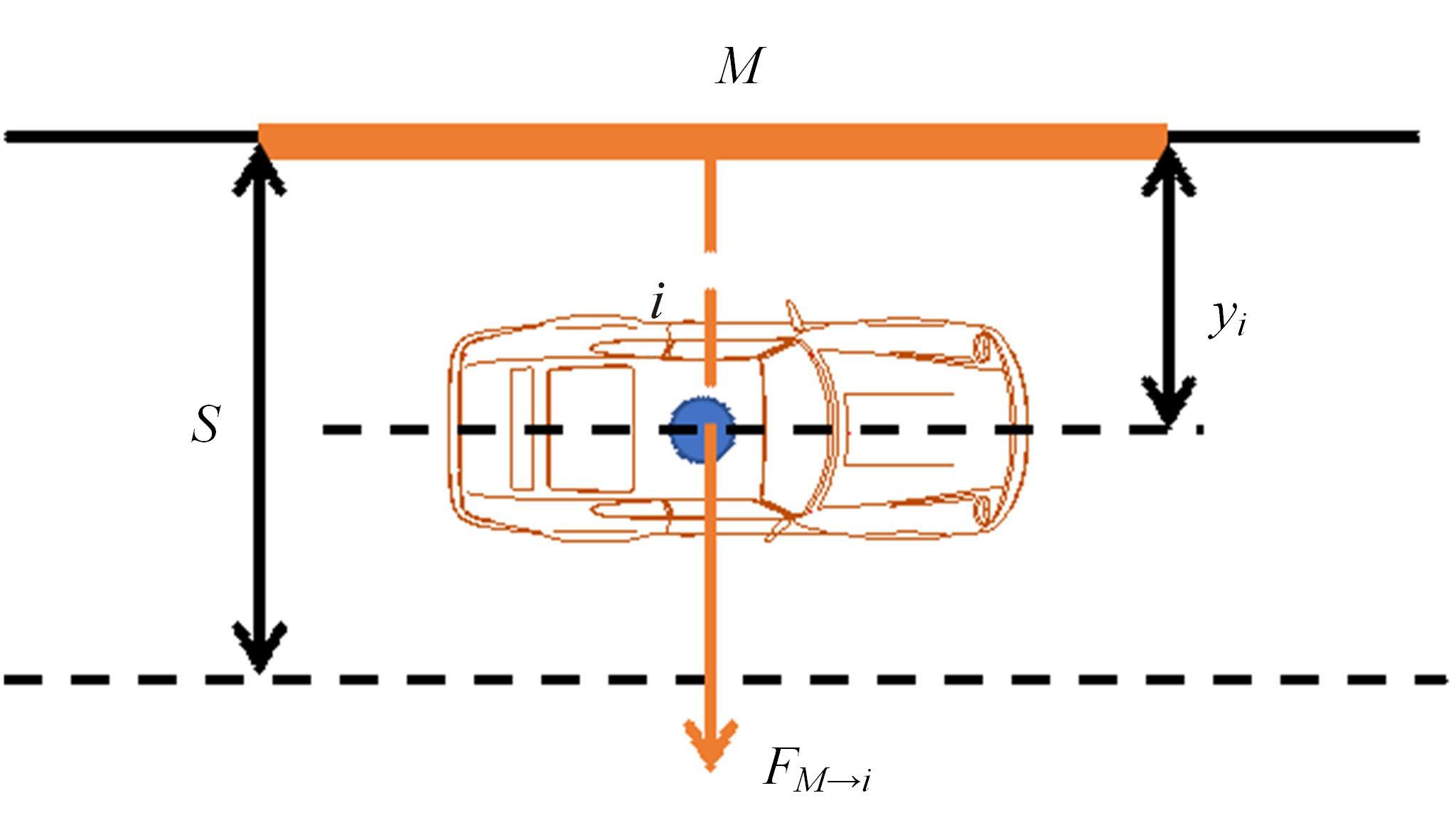
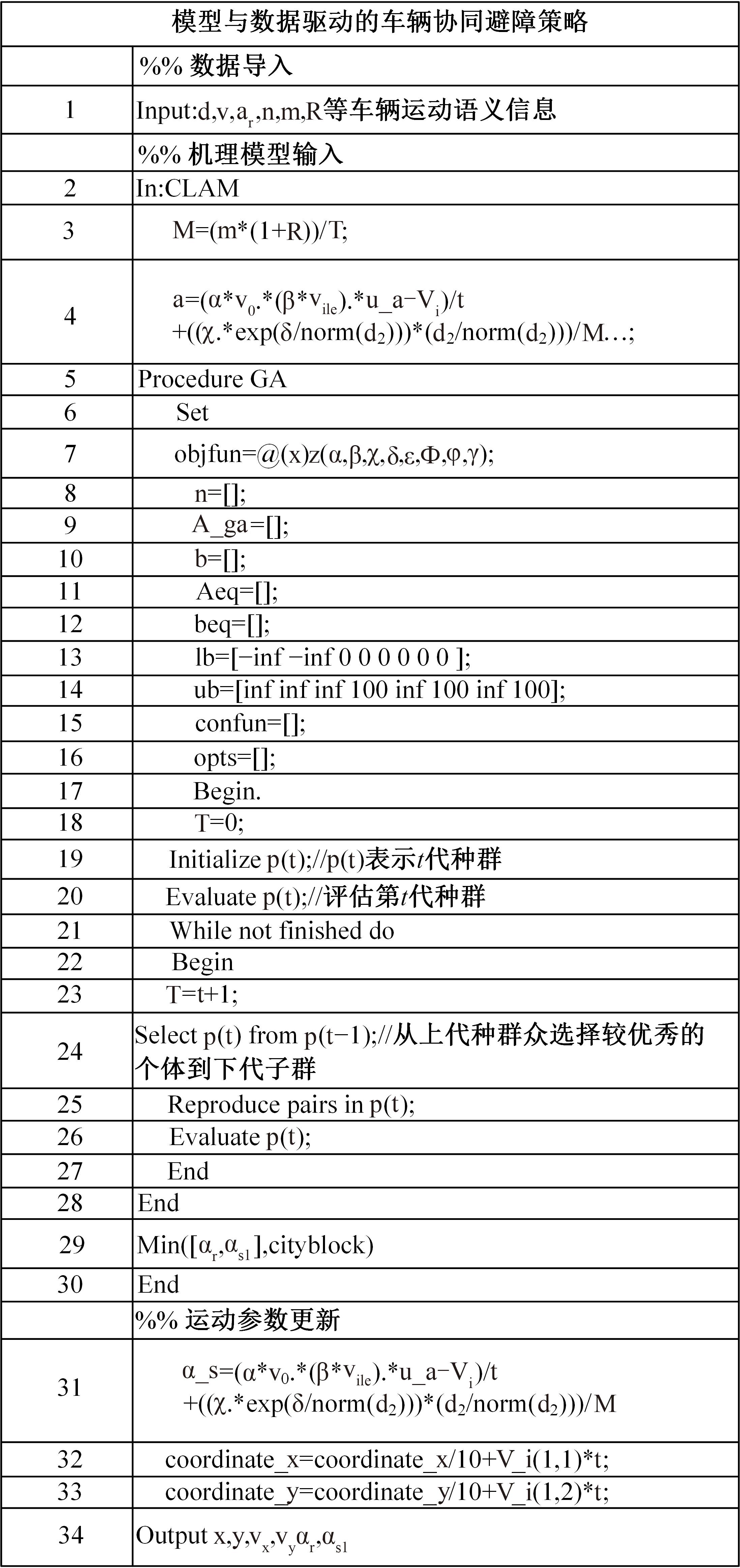
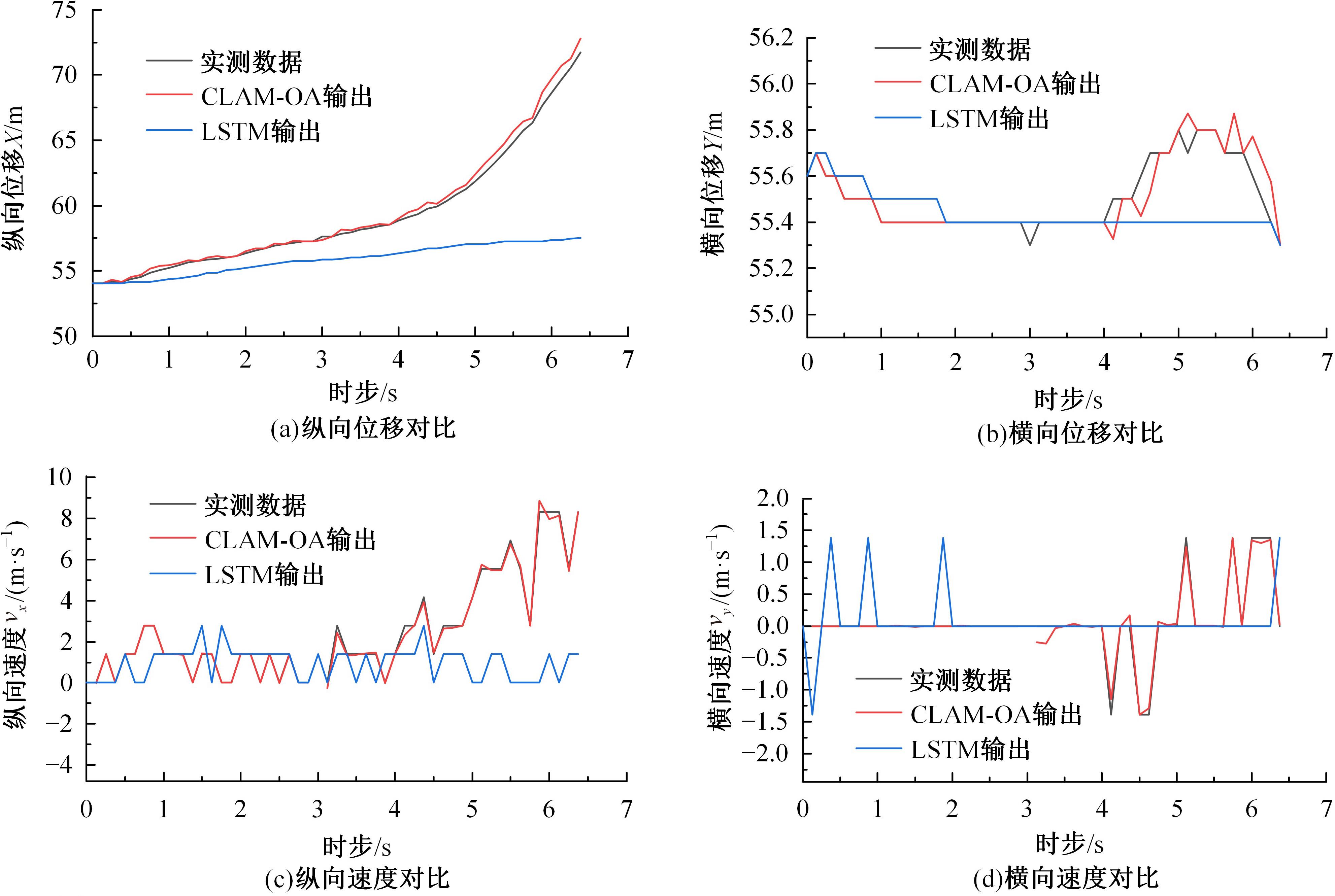
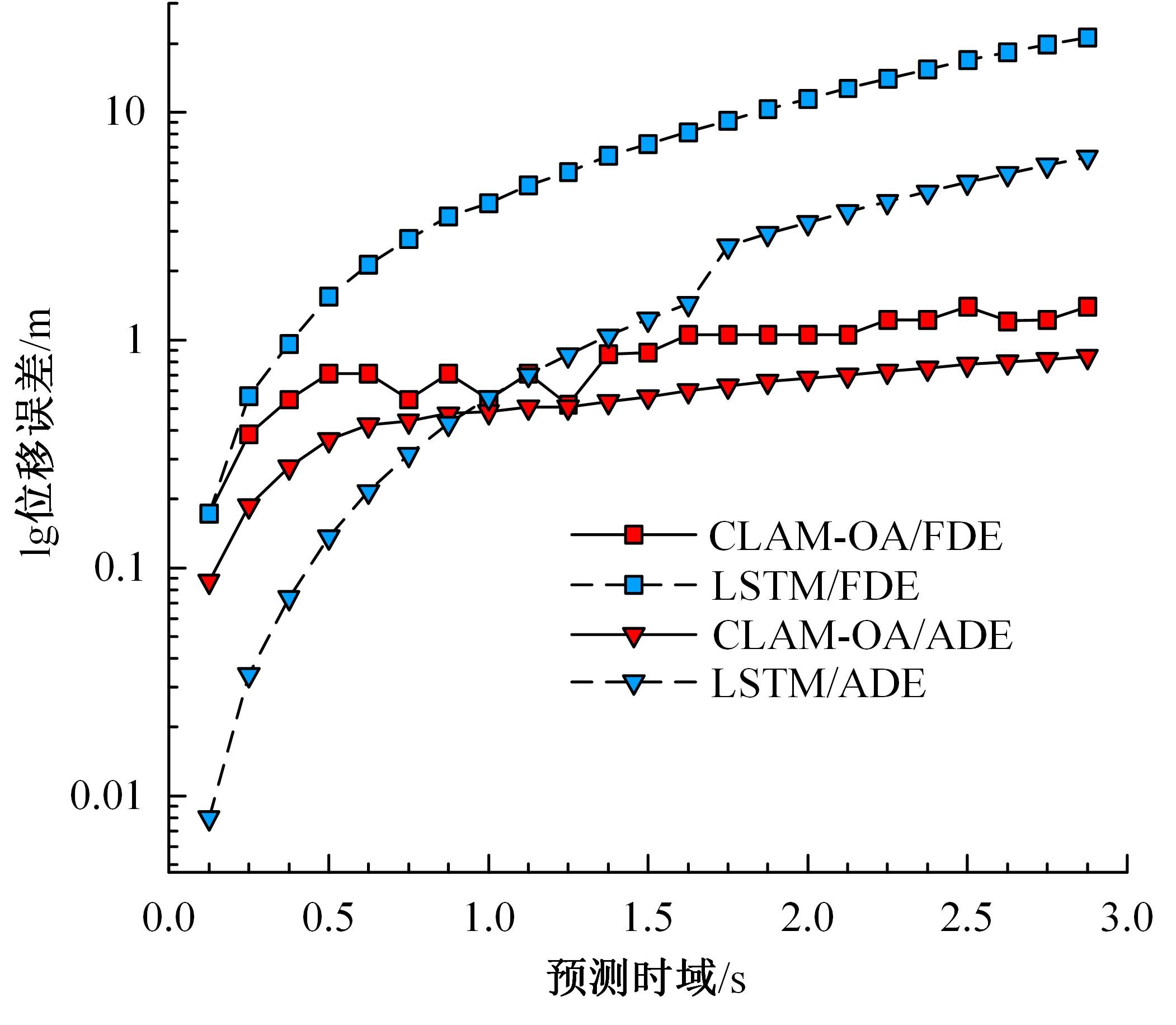
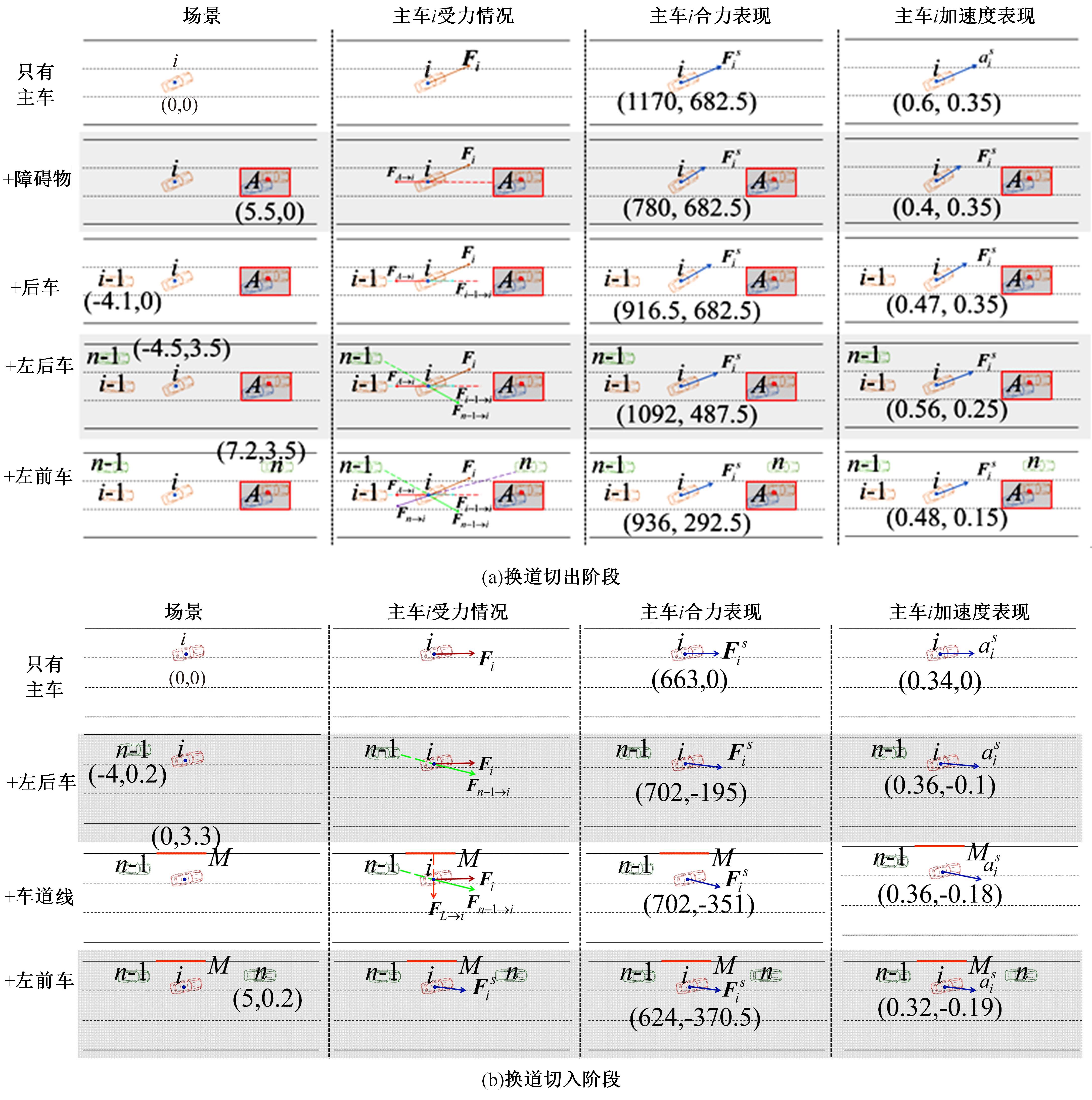
考虑车辆类型、驾驶风格及不同阶段影响车辆换道的关键目标,将车辆避障过程中的“车-车交互”机理描述为力的关系,构建协同换道避障模型(CLAM),提取并建立适用于突发事件的车辆避障微观轨迹数据集,将车辆避障转化为多约束优化控制问题,以优化算法(OA)为纽带,设计车辆协同避障控制(CLAM-OA)策略。结果表明:相较于数据驱动的长短时记忆模型,CLAM-OA策略输出的误差均显著减小、车速与位移在不同时域的输出结果也更加稳定。
中图分类号:
- U491
| 1 | Wang Z, Shi X W, Zhao X M, et al. Modeling decentralized mandatory lane change for connected and autonomous vehicles: an analytical method[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2021, 133: No. 103441. |
| 2 | Aradi S. Survey of deep reinforcement learning for motion planning of autonomous vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(2): 740-759. |
| 3 | Liu Q X, Xu S H, Lu C, et al. Early recognition of driving intention for lane change based on Recurrent Hidden Semi-Markov model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(10): 10545-10557. |
| 4 | Wang H, Lu B, Li J, et al. Risk assessment and mitigation in local path planning for autonomous vehicles with LSTM based predictive model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2022, 19(4): 2738-2749. |
| 5 | Wang J J, Li Y L, Gao R X, et al. Hybrid physics-based and data-driven models for smart manufacturing: modelling, simulation, and explainability[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2022, 63: 381-391. |
| 6 | 来飞, 叶心. 汽车高速行驶时自动紧急转向避撞的前馈与反馈跟踪控制的研究[J]. 汽车工程, 2020, 42(10): 1404-1411. |
| Lai Fei, Ye Xin. Research on feedforward and feedback tracking control for automatic emergency steering collision avoidance in vehicle high-speed driving[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2020, 42(10): 1404-1411. | |
| 7 | 王国栋, 刘立, 孟宇, 等. 一体式车辆避撞轨迹规划与跟踪控制[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2022, 22(2): 127-136, 162. |
| Wang Guo-dong, Liu Li, Meng Yu, et al. Integrated control of trajectory planning and tracking for vehicle collision avoidance[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2022, 22(2): 127-136, 162. | |
| 8 | 彭涛, 苏丽俐, 关志伟, 等. 高速公路弯道路段车辆紧急避撞安全换道模型[J]. 汽车工程, 2019, 41(9): 1013-1020. |
| Peng Tao, Su Li-li, Guan Zhi-wei, et al. A safe lane change model for vehicle emergent collision avoidance on curved section of highway[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2019, 41(9): 1013-1020. | |
| 9 | 韩月起, 张凯, 宾洋, 等. 基于凸近似的避障原理及无人驾驶车辆路径规划模型预测算法[J]. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(1): 153-167. |
| Han Yue-qi, Zhang Kai, Yang Bin, et al. Convex approximation based a voidance theory and path planning MPC for driver-less vehicles[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(1): 153-167. | |
| 10 | He X K, Liu Y L, Lyu C, et al. Emergency steering control of autonomous vehicle for collision avoidance and stabilisation[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2019, 57(8): 1163-1187. |
| 11 | Lee K, Kum D. Collision avoidance/mitigation system: motion planning of autonomous vehicle via predictive occupancy map[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 52846-52857. |
| 12 | 郭景华, 何智飞, 罗禹贡, 等. 人机混驾环境下基于深度学习的车辆切入轨迹预测[J]. 汽车工程, 2022, 44(2): 153-160, 214. |
| Guo Jing-hua, He Zhi-fei, Luo Yu-gong, et al. Vehicle cut-in trajectory prediction based on deep learning in a human-machine mixed driving environment[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2022, 44(2): 153-160, 214. | |
| 13 | 秦雅琴, 钱正富, 谢济铭, 等. 基于社会力的交织区突发瓶颈段协同换道决策模型[J]. 华南理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2022, 50(7): 66-75. |
| Qin Ya-qin, Qian Zheng-fu, Xie Ji-ming, et al. Cooperative lane change decision-making model of bottleneck emergency section in weaving area based on social force[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(7): 66-75. | |
| 14 | Yang D, Zhou X, Su G, et al. Model and simulation of the heterogeneous traffic flow of the urban signalized intersection with an island work zone[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2019, 20(5): 1719-1727. |
| 15 | Yang X L, Yang X X, Li Y X, et al. Obstacle avoidance in the improved social force model based on ant colony optimization during pedestrian evacuation[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2021, 583: No. 126256. |
| 16 | Liu S, Wang X S, Hassanin O, et al. Calibration and evaluation of responsibility-sensitive safety (RSS) in automated vehicle performance during cut-in scenarios[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2021, 125: No. 103037. |
| 17 | Katoch S, Chauhan S S, Kumar V. A review on genetic algorithm: past, present, and future[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2021, 80(5): 8091-8126. |
| 18 | 谢济铭, 彭博, 秦雅琴. 基于换道概率分布的多车道交织区元胞自动机模型[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2022, 22(3): 276-285. |
| Xie Ji-ming, Peng Bo, Qin Ya-qin. Cellular automata model of multi-lane weaving area based on lane-changing probability distribution[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2022, 22(3): 276-285. |
| [1] | 张明业,杨敏,黎彧,黄世玉,李清韵. 考虑有序充电策略的多车型电动公交调度优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1293-1301. |
| [2] | 马潇驰,陆建. 基于基因表达式编程的高架道路事故实时预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 719-726. |
| [3] | 严利鑫,冯进培,郭军华,龚毅轲. 不同险态情景下共驾型智能车辆接管行为特征分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 683-691. |
| [4] | 曲大义,张可琨,顾原,王韬,宋慧,戴守晨. 自动驾驶车辆换道决策行为分析及分子动力学建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 700-710. |
| [5] | 涂辉招,王万锦,乔鹏,郭静秋,鹿畅,吴海飞. 自动驾驶卡车路测安全员接管干预行为解析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 727-740. |
| [6] | 张健,李青扬,李丹,姜夏,雷艳红,季亚平. 基于深度强化学习的自动驾驶车辆专用道汇入引导[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2508-2518. |
| [7] | 郑植,袁佩,金轩慧,魏思斯,耿波. 桥墩复合材料柔性防撞护舷试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2581-2590. |
| [8] | 郑皓,余立均,智鹏鹏,汪忠来. 仿生扑翼微型飞行器动态避障策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2732-2740. |
| [9] | 李建华,王泽鼎. 考虑路径耗时的城市汽车分布式充电桩选点规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2298-2303. |
| [10] | 李洪涛,王琳虹,李俊达. 公路交叉口照明和限速对视觉搜索能力的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2287-2297. |
| [11] | 巫威眺,曾坤,周伟,李鹏,靳文舟. 基于多源数据和响应面优化的公交客流预测深度学习方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2001-2015. |
| [12] | 程国柱,盛林,赵浩,冯天军. 基于危险度分析的信号交叉口专用相位设置条件[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 1962-1969. |
| [13] | 何永明,陈世升,冯佳,万亚楠. 基于高精地图的超高速公路虚拟轨道系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2016-2028. |
| [14] | 薛志佳,王召阳,张久鹏,晏长根,许子凯,张英立,黄晓明,马涛. 泥石流作用下道路结构韧性分析及提升[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1773-1781. |
| [15] | 刘振亮,赵存宝,吴云鹏,马迷娜,马龙双. 数据驱动的公路桥梁网络全寿命抗震韧性评估[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1695-1701. |
|
||