吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (12): 3505-3512.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230184
基于手环数据的愤怒驾驶行为实时检测方法
- 1.长安大学 汽车运输安全保障技术交通行业重点实验室,西安 710064
2.长安大学 汽车学院,西安 710064
Real-time detection method of angry driving behavior based on bracelet data
Shi-feng NIU1,2( ),Shi-jie YU2,Yan-jun LIU2,Chong MA2
),Shi-jie YU2,Yan-jun LIU2,Chong MA2
- 1.Key Laboratory of Automotive Transportation Safety Assurance Technology for Transportation Industry,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
2.School of Automobile,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
摘要:
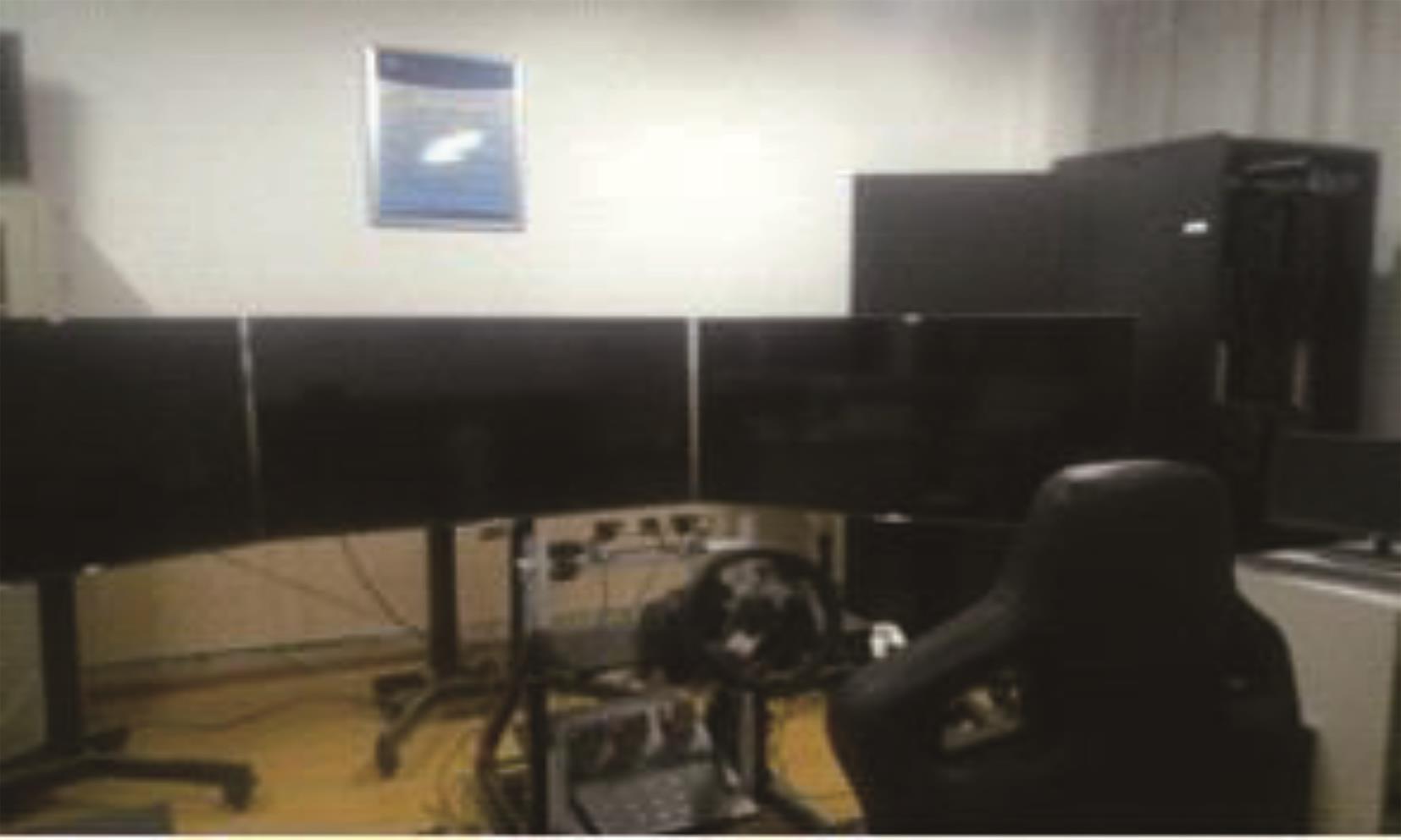
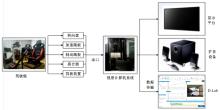
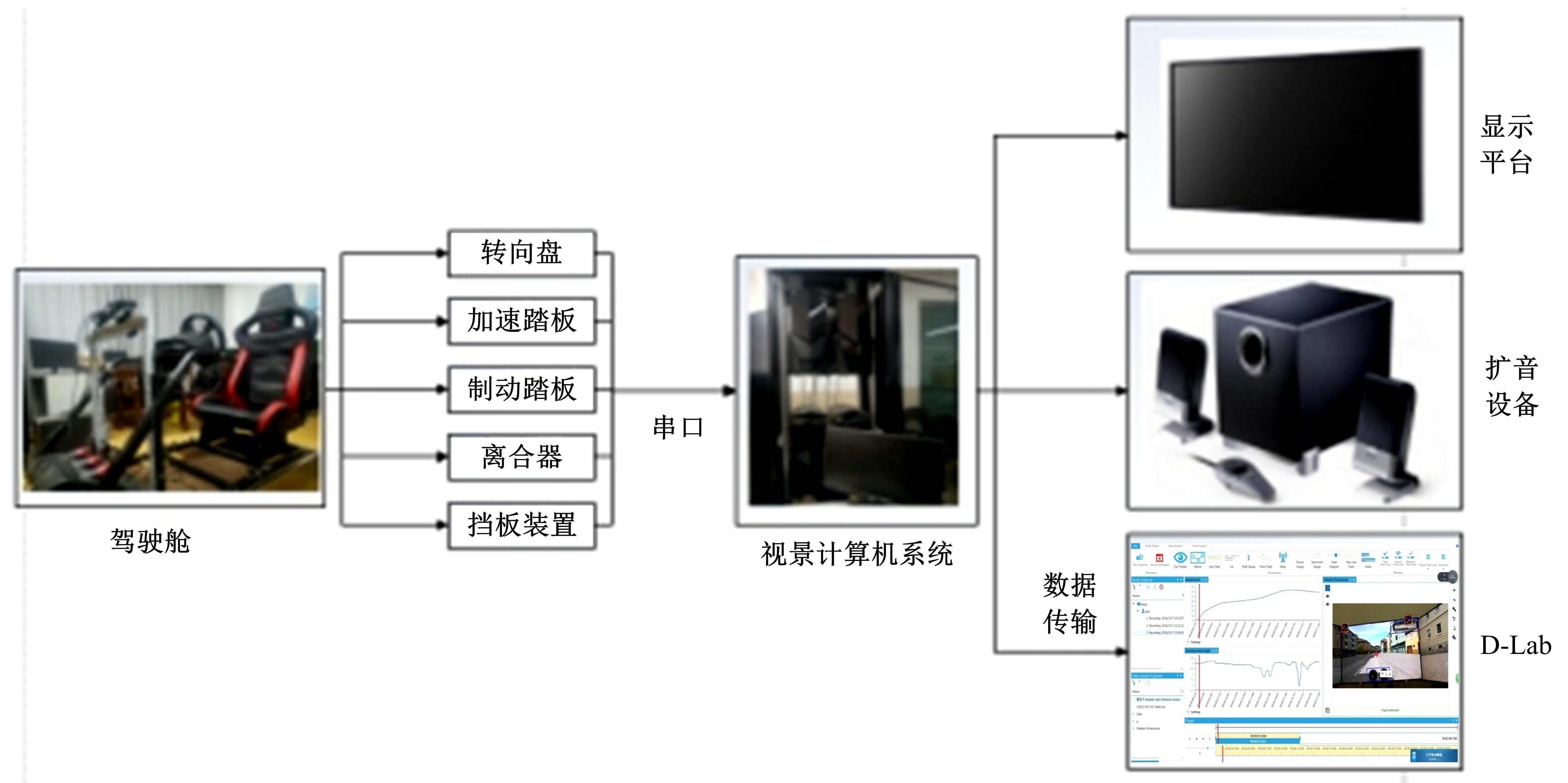
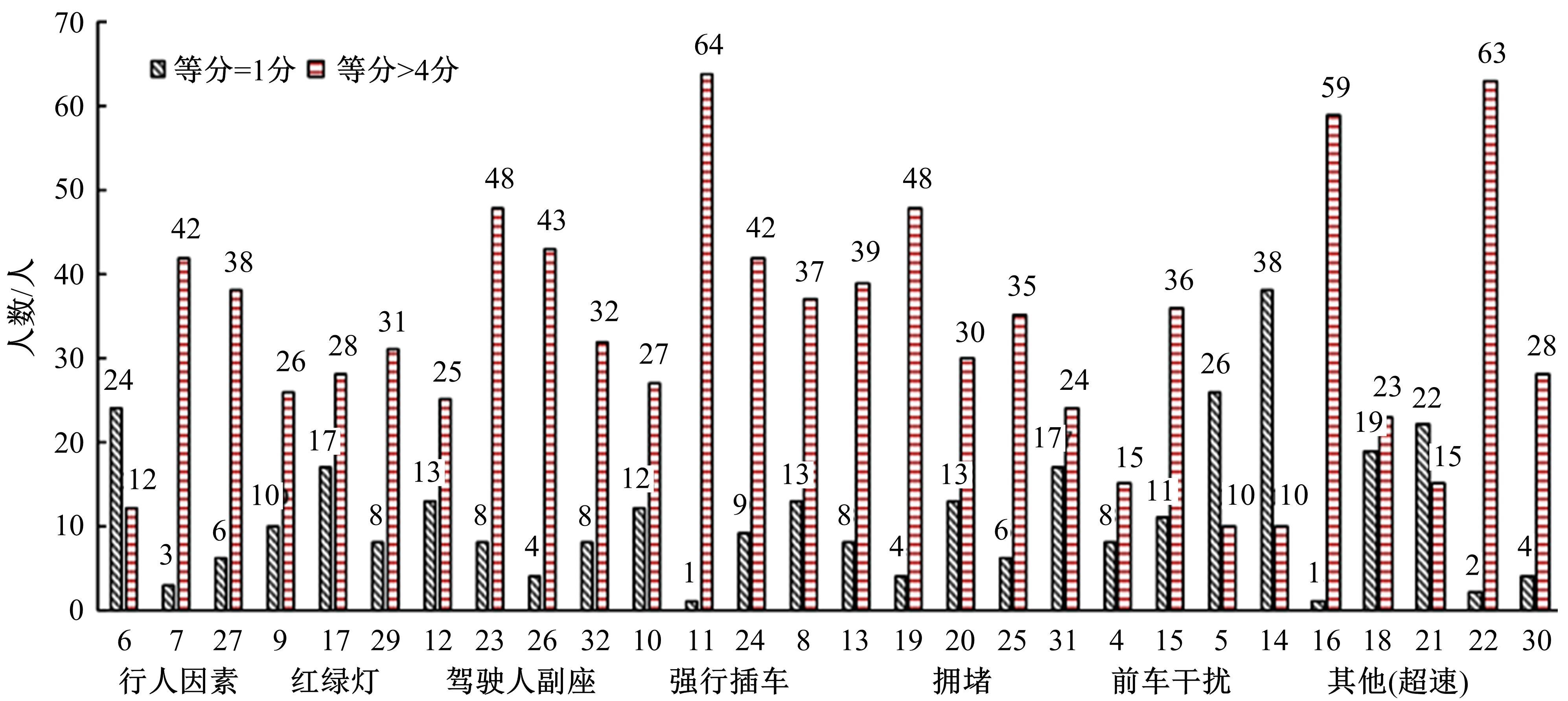
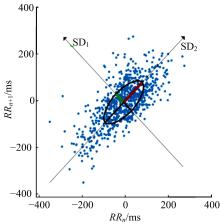
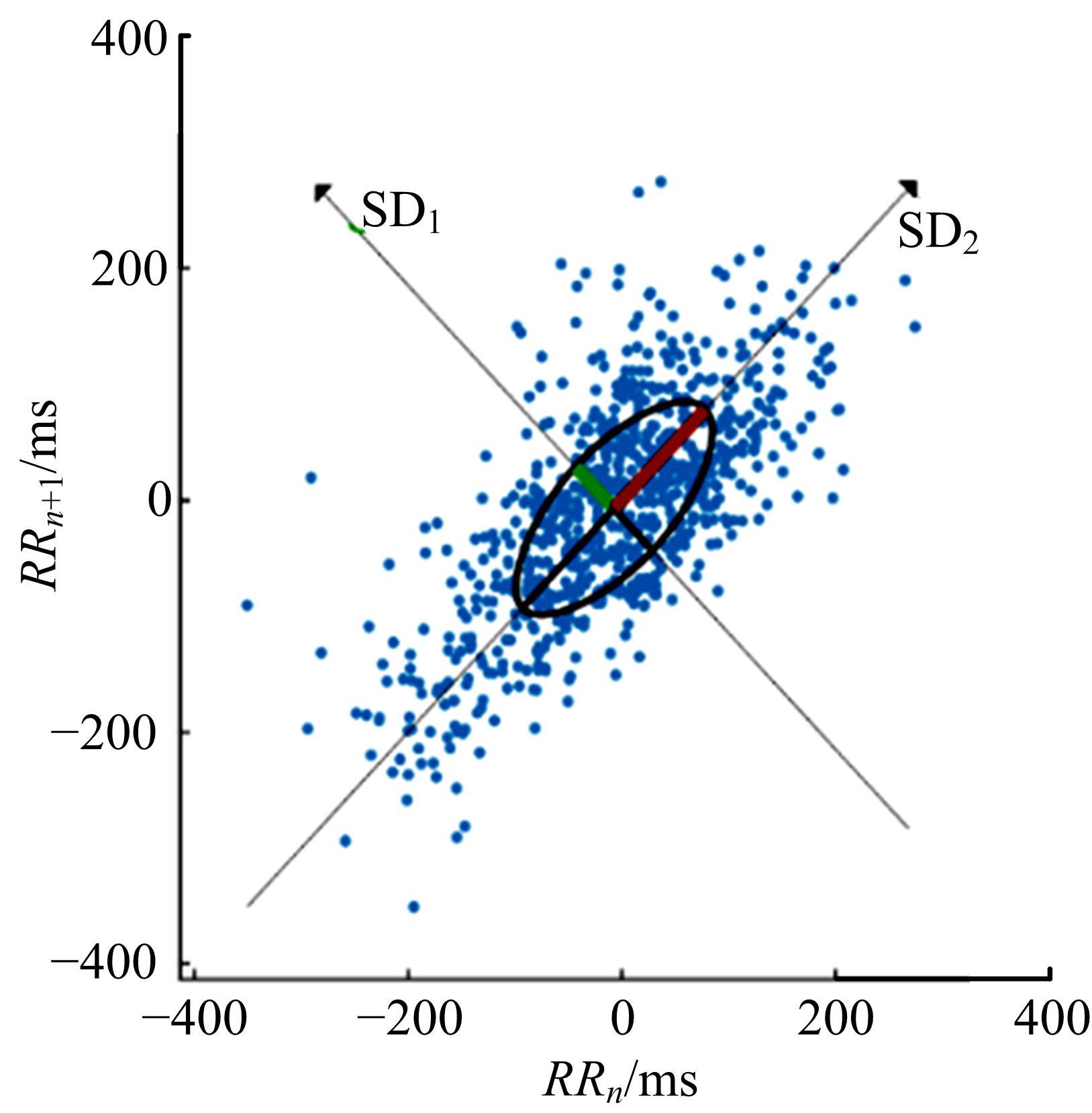
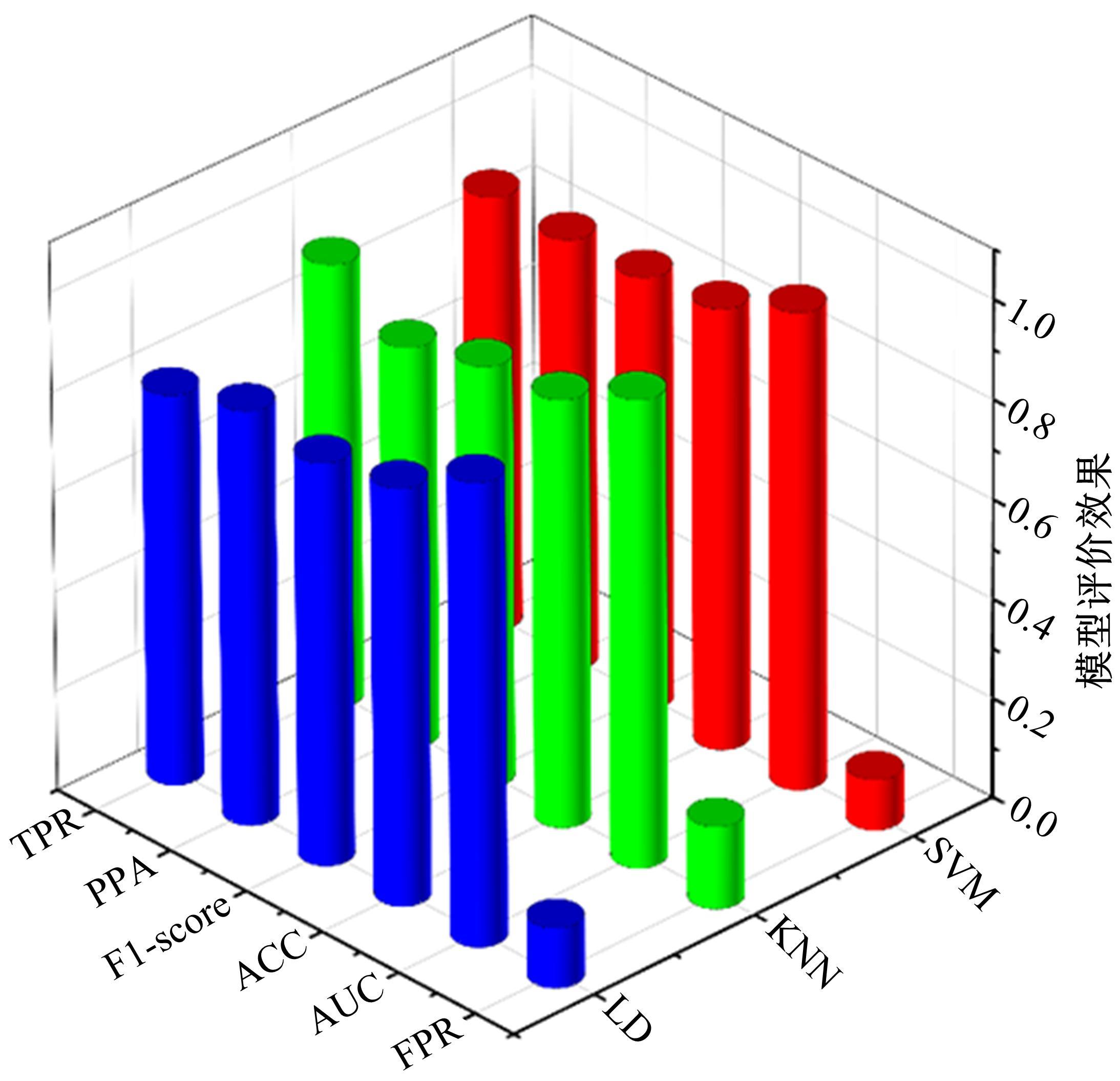
利用大众普遍使用的智能手环设计了驾驶人愤怒驾驶行为检测方法,为愤怒驾驶行为有效监测提供了新的途径和方法。本文招聘50名驾驶人开展模拟驾驶实验,设计了引发愤怒的模拟驾驶场景,利用手环采集数据获取心率指标HR和RR.mean、SDNN、RMSSD、PNN50、SDSD、HF、LF、LF/HF八个心率变异性(HRV)指标,对采集指标与愤怒驾驶行为进行关联研究,筛选显著性影响指标,利用支持向量机(SVM)、K-近邻(KNN)和线性判别分析(LDA)3种方法建立愤怒驾驶行为检测模型,并对其进行验证。结果表明:KNN算法的模型愤怒识别效果最好,对愤怒强度识别的准确率能达到75%,对愤怒状态识别的准确率为86%。结果表明:可穿戴式设备(智能手环)可以合理地检测驾驶人的愤怒情绪状态及愤怒情绪强度。
中图分类号:
- U492.8
| 1 | 陈安光. 浅议驾驶员情绪对安全行车的影响[J]. 现代交通管理, 2001 (6): 35-35. |
| Chen An-guang. A brief discussion on the influence of driver's emotion on safe driving[J]. Modern Traffic Management, 2001 (6): 35-35. | |
| 2 | Blanchette I, Richards A. Reasoning about emotional and neutral materials: is logic affected by emotion?[J]. Psychological Science, 2004, 15(11): 745-752. |
| 3 | Mesken J, Hagenzieker M P, Rothengatter T, et al. Frequency, determinants, and consequences of different drivers´ emotions: an on-the-road study using self-reports, (observed) behaviour, and physiology[J].Transportation Research Part F Traffic Psychology & Behaviour, 2007, 10(6): 458-475. |
| 4 | Lajunen T, Parker D. Are aggressive people aggressive drivers? A study of the relationship between self-reported general aggressiveness, driver anger and aggressive driving[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2001, 33(2): 243-255. |
| 5 | Wells-Parker E, Ceminsky J, Hallberg V, et al. An exploratory study of the relationship between road rage and crash experience in a representative sample of US drivers[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2002, 34(3): 271-278. |
| 6 | Stephens A N, Groeger J A. Anger-congruent behaviour transfers across driving situations[J]. Cognition & Emotion, 2011, 25(8): 1423-1438. |
| 7 | Paschero M, Del Vescovo G, Benucci L, et al. A real time classifier for emotion and stress recognition in a vehicle driver[C]∥2012 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, New York, USA, 2012: 1690-1695. |
| 8 | Kolli A, Fasih A, Al Machot F, et al. Non-intrusive car driver's emotion recognition using thermal camera[C]∥2011 IEEE Intellige Proceedings of the Joint INDS'11 & ISTET'11nt Vehicles Symposium. New York, USA, 2011:No.6024802. |
| 9 | Tawari A, Trivedi M. Speech based emotion classification framework for driver assistance system[C]∥2010 IEEE Intellige Proceedings of the Joint INDS'11 & ISTET'11nt Vehicles Symposium, New York, USA, 2010: 174-178. |
| 10 | Jones C M. Using Paralinguistic Cues in Speech to Recognise Emotions in Older Car Drivers[M].Berlin:Springer-Verlag, 2008. |
| 11 | Gunes H, Piccardi M. Fusing face and body gesture for machine recognition of emotions[C]∥ROMAN 2005. IEEE International Workshop on Robot and Human Interactive Communication, New York, USA, 2005: 306-311. |
| 12 | Kessous L, Castellano G, Caridakis G. Multimodal emotion recognition in speech-based interaction using facial expression, body gesture and acoustic analysis[J]. Journal on Multimodal User Interfaces, 2010, 3: 33-48. |
| 13 | 牛晓伟, 刘光远. 基于遗传算法的生理信号情感识别[J]. 西南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2007 29(9):134-138. |
| Niu Xiao-wei, Liu Guang-yuan. Emotion recognition with physiological signals based on genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Southwest University(Natural Science Edition), 2007, 29(9): 134-138. | |
| 14 | Katsis C D, Katertsidis N, Ganiatsas G, et al. Toward emotion recognition in car-racing drivers: a biosignal processing approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics—Part A: Systems and Humans, 2008, 38(3): 502-512. |
| 15 | 万平, 吴超仲, 林英姿, 等. 基于置信规则库的驾驶人愤怒情绪识别模型[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2015, 15(5): 96-102. |
| Wan Ping, Wu Chao-zhong, Lin Ying-zi, et al. A recognition model of driving anger based on belief rule base[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2015, 15(5): 96-102. | |
| 16 | Lisetti C L, Nasoz F. Using noninvasive wearable computers to recognize human emotions from physiological signals[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2004, 2004(11): 1672-1687. |
| 17 | 严利鑫. 驾驶愤怒情绪诱导实验方法研究及应用[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学交通与物流工程学院, 2014. |
| Yan Li-xin. The research and application of the driving anger induced method[D]. Wuhan: School of Transportation and Logistics Engineering, Wuhan University of Technology, 2014. | |
| 18 | Kreibig S D. Autonomic nervous system activity in emotion: a review[J]. Biological Psychology, 2010, 84(3): 394-421. |
| [1] | 张磊,焦晶,李勃昕,周延杰. 融合机器学习和深度学习的大容量半结构化数据抽取算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2631-2637. |
| [2] | 陈城,史培新,贾鹏蛟,董曼曼. 基于MK-LSTM算法的盾构掘进参数相关性分析及结构变形预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1624-1633. |
| [3] | 付忠良,陈晓清,任伟,姚宇. 带学习过程的随机K最近邻算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 209-220. |
| [4] | 耿庆田,刘植,李清亮,于繁华,李晓宁. 基于一种深度学习模型的土壤湿度预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2430-2436. |
| [5] | 潘恒彦,张文会,梁婷婷,彭志鹏,高维,王永岗. 基于MIMIC与机器学习的出租车驾驶员交通事故诱因分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 457-467. |
| [6] | 袁伟,袁小慧,高岩,李坤宸,赵登峰,刘朝辉. 基于自然驾驶数据的电动公交踏板误操作辨识方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(12): 3342-3350. |
| [7] | 周丰丰,颜振炜. 基于混合特征的特征选择神经肽预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(11): 3238-3245. |
| [8] | 耿庆田,赵杨,李清亮,于繁华,李晓宁. 基于注意力机制的LSTM和ARIMA集成方法在土壤温度中应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(10): 2973-2981. |
| [9] | 段亮,宋春元,刘超,魏苇,吕成吉. 基于机器学习的高速列车轴承温度状态识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 53-62. |
| [10] | 李洪雪,李世武,孙文财,李玮,郭梦竹. 重型危险品半挂列车行驶工况的构建[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1700-1707. |
| [11] | 李光松,李文清,李青. 基于随机性特征的加密和压缩流量分类[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1375-1386. |
| [12] | 朱小龙,谢忠. 基于机器学习的地理空间数据抽取算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1011-1016. |
| [13] | 李阳,李硕,井丽巍. 基于贝叶斯模型与机器学习算法的金融风险网络评估模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1862-1869. |
| [14] | 方伟,黄羿,马新强. 基于机器学习的虚拟网络感知数据缺陷自动检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1844-1849. |
| [15] | 刘洲洲,尹文晓,张倩昀,彭寒. 基于离散优化算法和机器学习的传感云入侵检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 692-702. |
|