吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (7): 1894-1902.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221129
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
基于双特征提取网络的复杂环境车道线精准检测
- 1.石家庄铁道大学 信息科学与技术学院,石家庄 050043
2.石家庄铁道大学 河北省电磁环境效应与信息处理重点实验室,石家庄 050043
Accurate lane detection of complex environment based on double feature extraction network
Yun-zuo ZHANG1,2( ),Yu-xin ZHENG1,Cun-yu WU1,Tian ZHANG1
),Yu-xin ZHENG1,Cun-yu WU1,Tian ZHANG1
- 1.School of Information Science and Technology,Shijiazhuang Tiedao University,Shijiazhuang 050043,China
2.Hebei Key Laboratory of Electromagnetic Environmental Effects and Information Processing,Shijiazhuang Tiedao University,Shijiazhuang 050043,China
摘要:
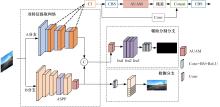
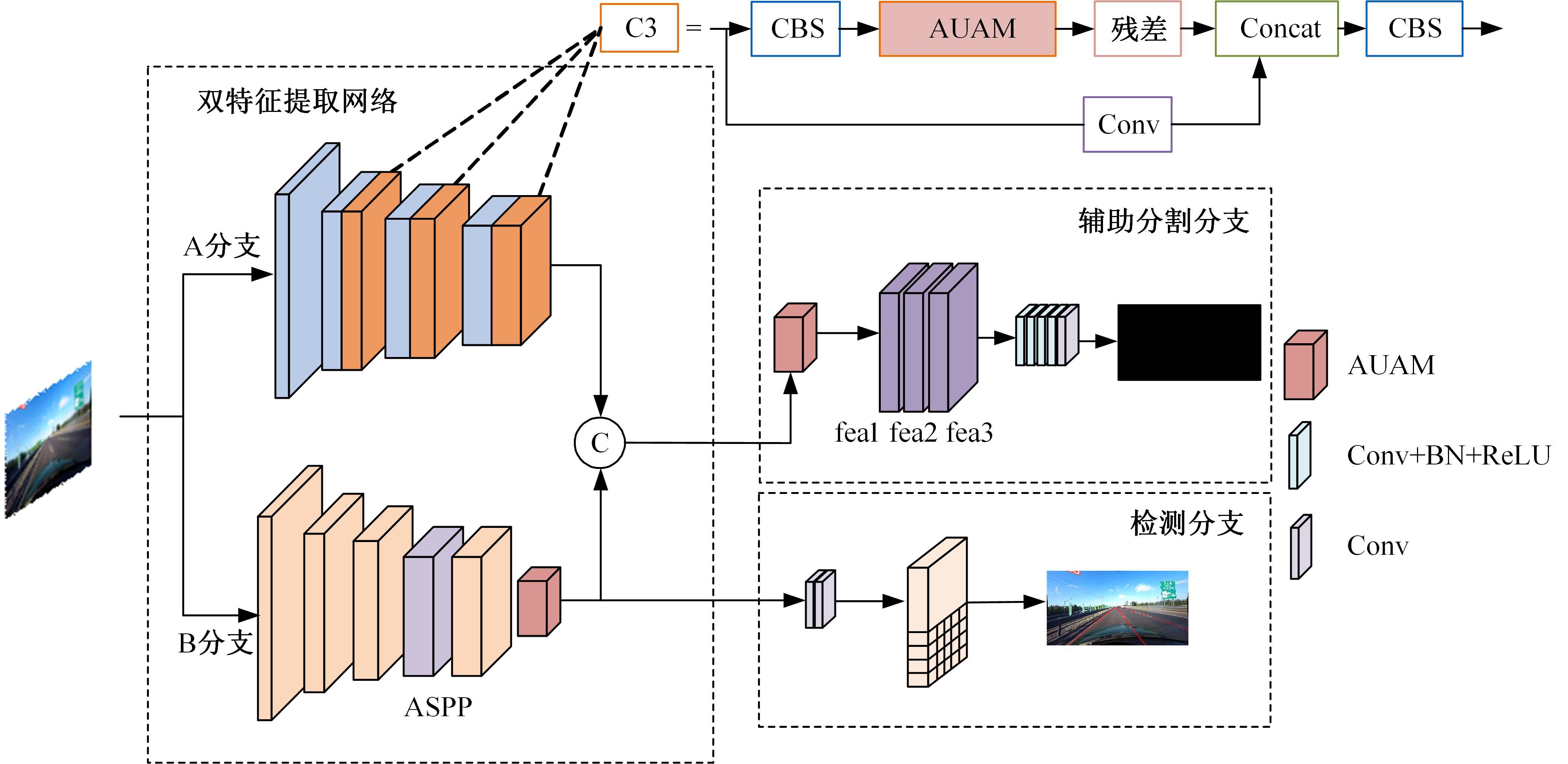
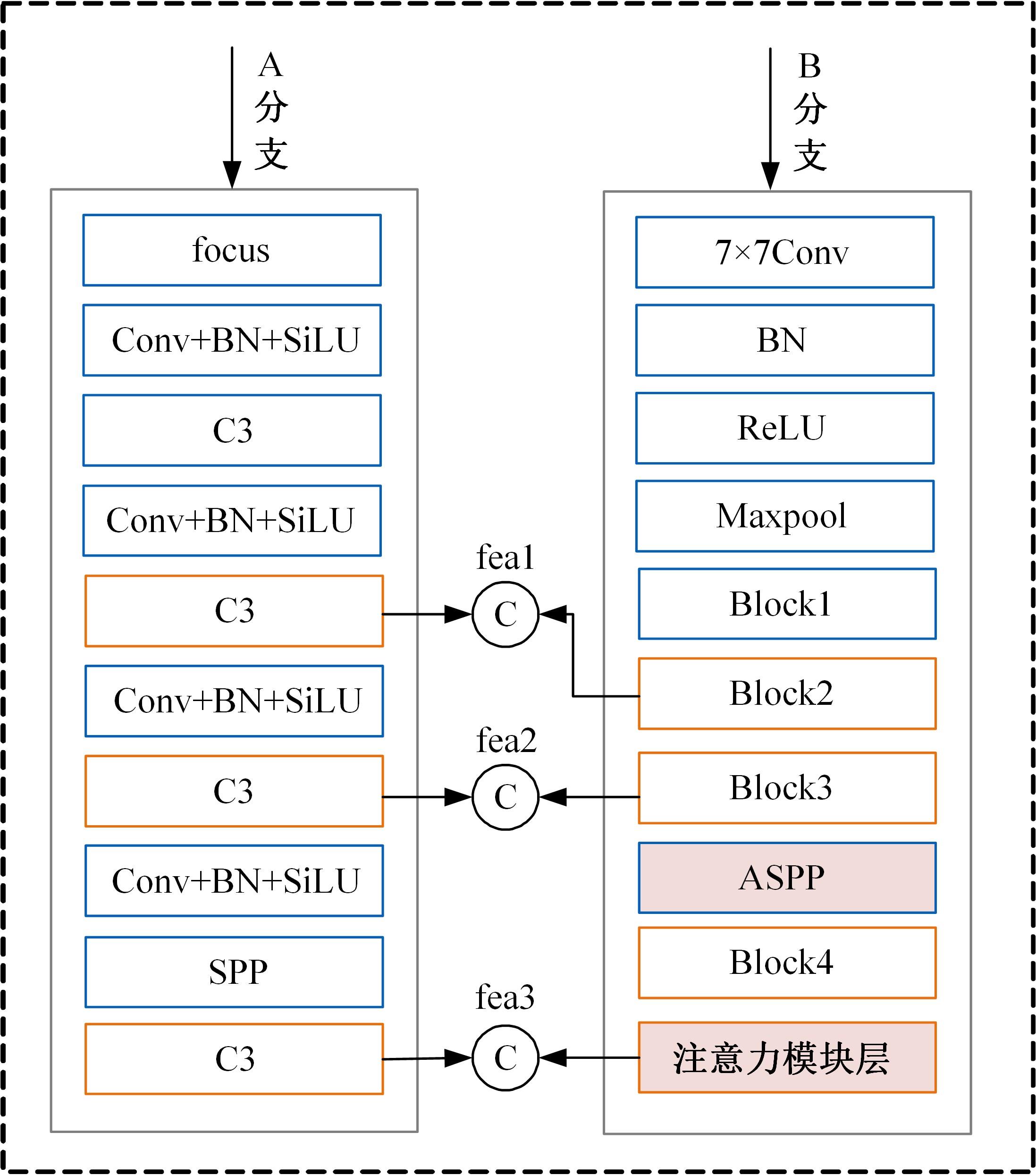
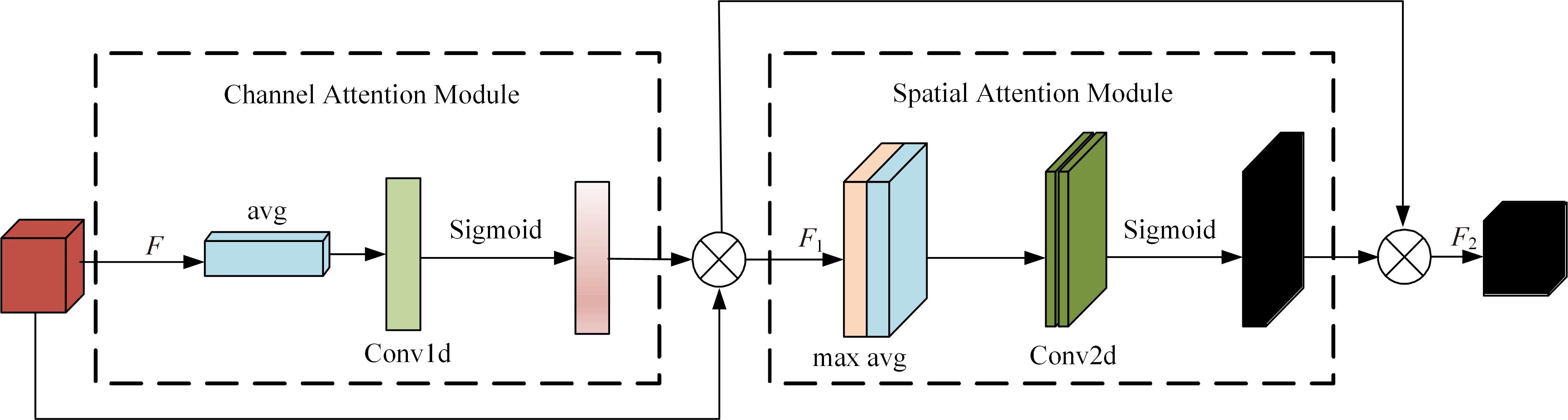
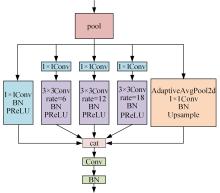
为解决现有方法在复杂环境中检测精度低的问题,提出了一种基于双特征提取网络的复杂环境车道线精准检测算法。首先,搭建双特征提取网络,获取不同尺度的特征图,提取更有效的特征,提高模型在复杂环境下的特征提取能力。然后,构建跨通道联合注意力模块,提高模型对车道线细节的关注度,抑制无用信息。最后,结合改进的空洞空间金字塔池化模块扩大图像感受野,提高模型对上下文信息的利用率,以强化算法的检测能力。经实验验证,本文算法在CULane数据集上的F1-measure达到了72.43%,相比于基线模型提升了4.03%,在复杂的场景中对车道线进行检测时效果提升明显。
中图分类号:
- TP391.4
| 1 | Kumar S, Jailia M, Varshney S. A comparative study of deep learning based lane detection methods[C]∥2022 9th International Conference on Computing for Sustainable Global Development (INDIACom), New Delhi, India, 2022: 579-584. |
| 2 | 时小虎, 吴佳琦, 吴春国, 等. 基于残差网络的弯道增强车道线检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022(2): 584-592. |
| Shi Xiao-hu, Wu Jia-qi, Wu Chun-guo, et al. Residual network based curve enhanced lane detection method[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022(2): 584-592. | |
| 3 | Tang J, Li S, Liu P. A review of lane detection methods based on deep learning[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2021, 111: No.107623. |
| 4 | 洪伟, 王吉通, 刘宇. 基于 DBSCAN 的复杂环境下车道线鲁棒检测及跟踪[J]. 吉林大学学报 :工学版, 2020, 50(6): 2122-2130. |
| Hong Wei, Wang Ji-tong, Liu Yu. Robust lane detection and tracking in complex environment based on DBSCAN[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(6): 2122-2130. | |
| 5 | Dang H S, Guo C J. Structure lane detection based on saliency feature of color and direction[C]∥Applied Mechanics and Materials, Trans Tech Publications Ltd, Xi´an, China,2014, 513: 2876-2879. |
| 6 | 都雪静, 张美欧. 基于光流法与背景建模法融合的车道线识别算法研究[J]. 重庆理工大学学报: 自然科学, 2021, 35(3): 29-35. |
| Du Xue-jing, Zhang Mei-ou. Based on fusing optical flow method and background modeling for lane line recomgnition[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology (Natural Science), 2021, 35(3): 29-35. | |
| 7 | Zhang Y, Lu Z, Zhang X, et al. Deep learning in lane marking detection: a survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(7): 5976-5992. |
| 8 | Yu F, Koltun V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions[DB/OL]. [2022-05-17]. . |
| 9 | Poudel R P K, Liwicki S, Cipolla R. Fast-scnn: fast semantic segmentation network[DB/OL]. [2022-05-23]. . |
| 10 | Borji A. Vanishing point detection with convolutional neural networks[DB/OL]. 2022-05-26]. . |
| 11 | Lee S, Kim J, Shin Yoon J, et al. Vpgnet: vanishing point guided network for lane and road marking detection and recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 1947-1955. |
| 12 | 崔文靓, 王玉静, 康守强, 等. 基于改进 YOLOv3 算法的公路车道线检测方法[J]. 自动化学报, 2022, 45: 1-9. |
| Cui Wen-liang, Wang Yu-jing, Kang Shou-qiang, et al. Road lane line detection method based on improved YOLOv3 algorithm[J]. Journal of Automatica Sinica,2022, 45: 1-9. | |
| 13 | 高明华, 杨璨. 基于改进卷积神经网络的交通目标检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报 :工学版, 2022, 52(6): 1353-1361. |
| Gao Ming-hua, Yang Can. Traffic target detection method based on improved convolution neural network[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1353-1361. | |
| 14 | Tabelini L, Berriel R, Paixao T M, et al. Polylanenet: lane estimation via deep polynomial regression[C]∥2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 2021: 6150-6156. |
| 15 | Sun Y, Wang L, Chen Y, et al. Accurate lane detection with atrous convolution and spatial pyramid pooling for autonomous driving[C]∥2019 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Dali, China, 2019: 642-647. |
| 16 | Neven D, De Brabandere B, Georgoulis S, et al. Towards end-to-end lane detection: an instance segmentation approach[C]∥IEEE intelligent vehicles symposium (IV),Changshu, China, 2018: 286-291. |
| 17 | Tabelini L, Berriel R, Paixao T M, et al. Keep your eyes on the lane: real-time attention-guided lane detection[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Nashville,USA,2021: 294-302. |
| 18 | 汪鹏飞, 沈庆宏, 张维利, 等. 基于多尺度特征图像分割的车道线提取方法[J]. 南京大学学报 :自然科学版, 2022, 58(2): 336-344. |
| Wang Peng-fei, Shen Qing-hong, Zhang Wei-li, et al. Lane extraction method based on multi-scale feature image segmentation[J]. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Science), 2022, 58(2): 336-344. | |
| 19 | Fan R, Wang X, Hou Q, et al. SpinNet: spinning convolutional network for lane boundary detection[J]. Computational Visual Media, 2019, 5(4): 417-428. |
| 20 | Qin Z, Wang H, Li X. Ultra fast structure-aware deep lane detection[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision. Cham: Springer, 2020: 276-291. |
| 21 | Woo S, Park J, Lee J Y, et al. Cbam: convolutional block attention module [C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 3-19. |
| 22 | Wang Q, Wu B, Zhu P, et al. ECA-Net: efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks[C]∥2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle,USA,2020: 11531-11539. |
| 23 | Philion J. Fastdraw: addressing the long tail of lane detection by adapting a sequential prediction network[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA,2019: 11582-11591. |
| 24 | Pan X, Shi J, Luo P, et al. Spatial as deep: spatial cnn for traffic scene understanding[C]∥Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, USA, 2018, 32(1): 7276-7283. |
| 25 | Hou Y, Ma Z, Liu C, et al. Learning lightweight lane detection cnns by self-attention distillation[C]∥Proce-edings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision,Seoul, Korea (South),2019: 1013-1021. |
| 26 | Xu H, Wang S, Cai X, et al. Curvelane-nas: unifying lane-sensitive architecture search and adaptive point blending[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision. Cham:Springer, 2020: 689-704. |
| 27 | Chen L C, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I, et al. DeepLab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(4): 834-848. |
| [1] | 孙铭会,薛浩,金玉波,曲卫东,秦贵和. 联合时空注意力的视频显著性预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1767-1776. |
| [2] | 李延风,刘名扬,胡嘉明,孙华栋,孟婕妤,王奥颖,张涵玥,杨华民,韩开旭. 基于梯度转移和自编码器的红外与可见光图像融合[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1777-1787. |
| [3] | 张丽平,刘斌毓,李松,郝忠孝. 基于稀疏多头自注意力的轨迹kNN查询方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1756-1766. |
| [4] | 梁礼明,周珑颂,尹江,盛校棋. 融合多尺度Transformer的皮肤病变分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 1086-1098. |
| [5] | 张云佐,郭威,李文博. 遥感图像密集小目标全方位精准检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 1105-1113. |
| [6] | 李雄飞,宋紫萱,朱芮,张小利. 基于多尺度融合的遥感图像变化检测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 516-523. |
| [7] | 霍光,林大为,刘元宁,朱晓冬,袁梦,盖迪. 基于多尺度特征和注意力机制的轻量级虹膜分割模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2591-2600. |
| [8] | 何颖,王卓然,周旭,刘衍珩. 融合社交地理信息加权矩阵分解的兴趣点推荐算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2632-2639. |
| [9] | 张云佐,董旭,蔡昭权. 拟合下肢几何特征的多视角步态周期检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2611-2619. |
| [10] | 肖明尧,李雄飞,朱芮. 基于NSST域像素相关分析的医学图像融合[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2640-2648. |
| [11] | 赵亚慧,李飞雨,崔荣一,金国哲,张振国,李德,金小峰. 基于跨语言预训练模型的朝汉翻译质量评估[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2371-2379. |
| [12] | 郭晓新,李佳慧,张宝亮. 基于高分辨率网络的视杯和视盘的联合分割[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2350-2357. |
| [13] | 车翔玖,徐欢,潘明阳,刘全乐. 生物医学命名实体识别的两阶段学习算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2380-2387. |
| [14] | 王连明,吴鑫. 基于姿态估计的物体3D运动参数测量方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2099-2108. |
| [15] | 张则强,梁巍,谢梦柯,郑红斌. 混流双边拆卸线平衡问题的精英差分进化算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1297-1304. |
|
||