吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (5): 1763-1771.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20240906
基于群智能增强核极限学习机的创新人才预测模型
- 1.温州理工学院 创新创业学院,浙江 温州 325035
2.温州大学 计算机与人工智能学院,浙江 温州 325035
Predictive model for identifying innovative university talents based on the swarm intelligence evolution enhanced kernel extreme learning machine
Qing-liang JIN1( ),Xin-sen ZHOU2,Yi CHEN2,Cheng-wen WU2(
),Xin-sen ZHOU2,Yi CHEN2,Cheng-wen WU2( )
)
- 1.Innovation and Entrepreneurship College,Wenzhou University of Technology,Wenzhou 325035,China
2.College of Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence,Wenzhou University,Wenzhou 325035,China
摘要:
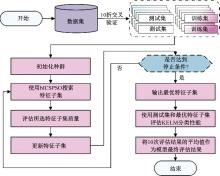
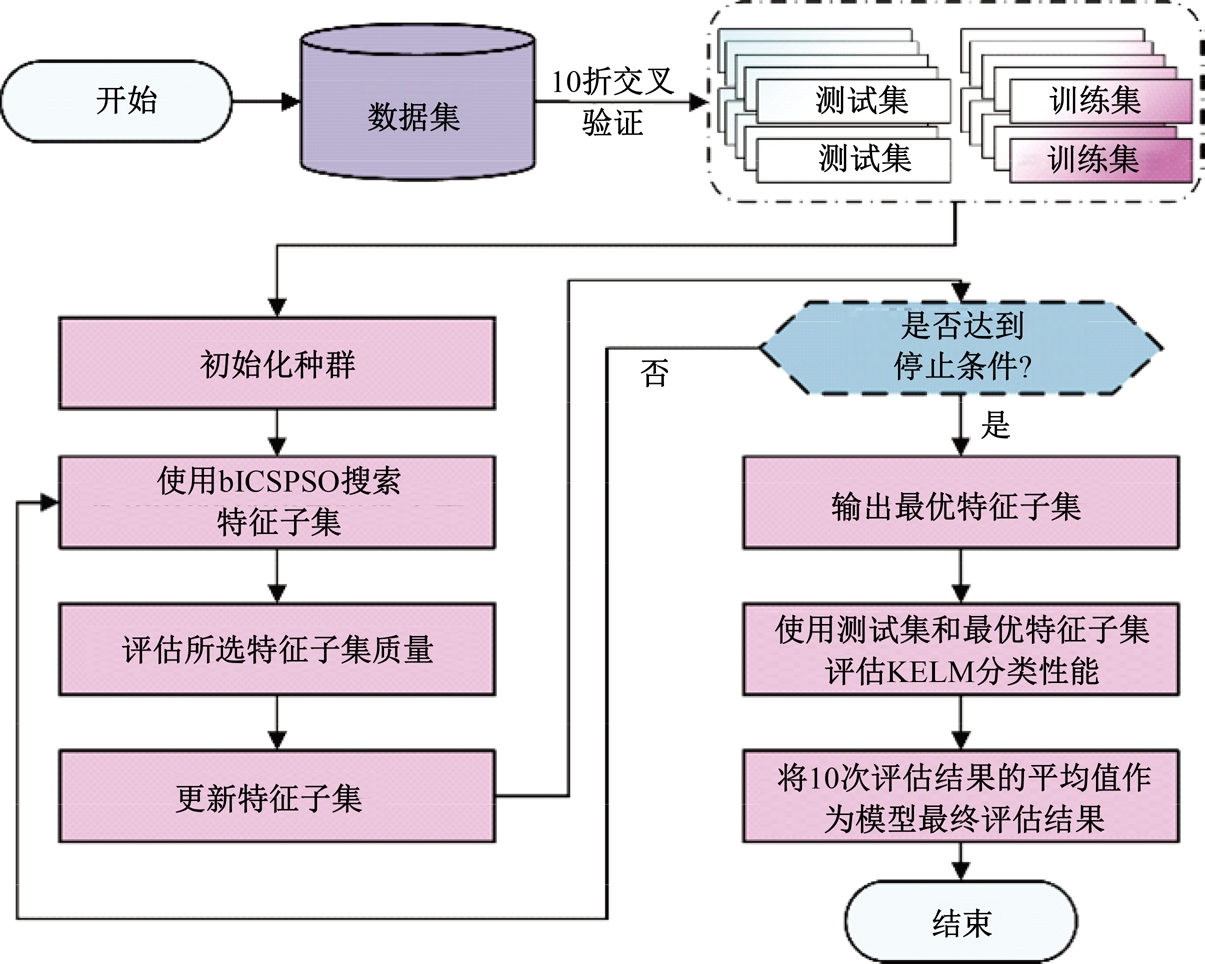
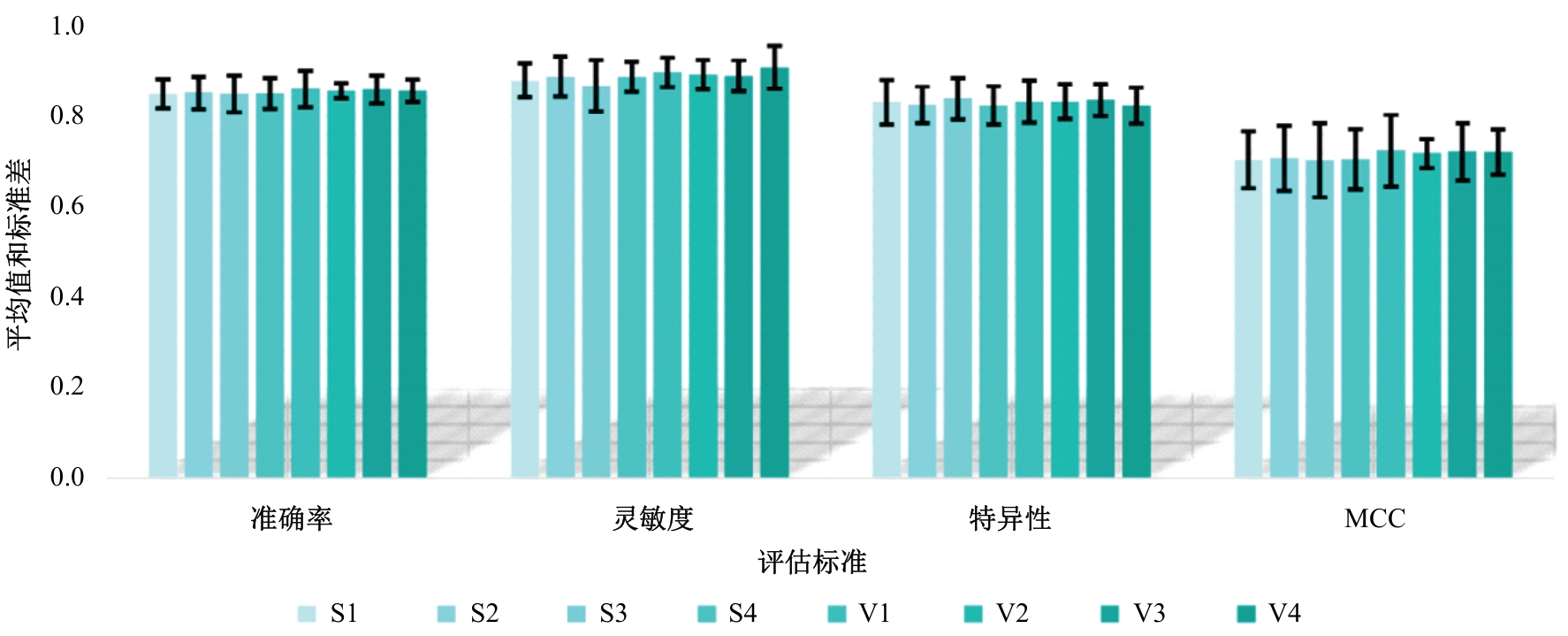
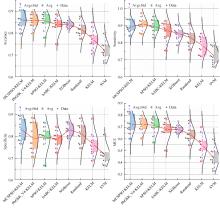
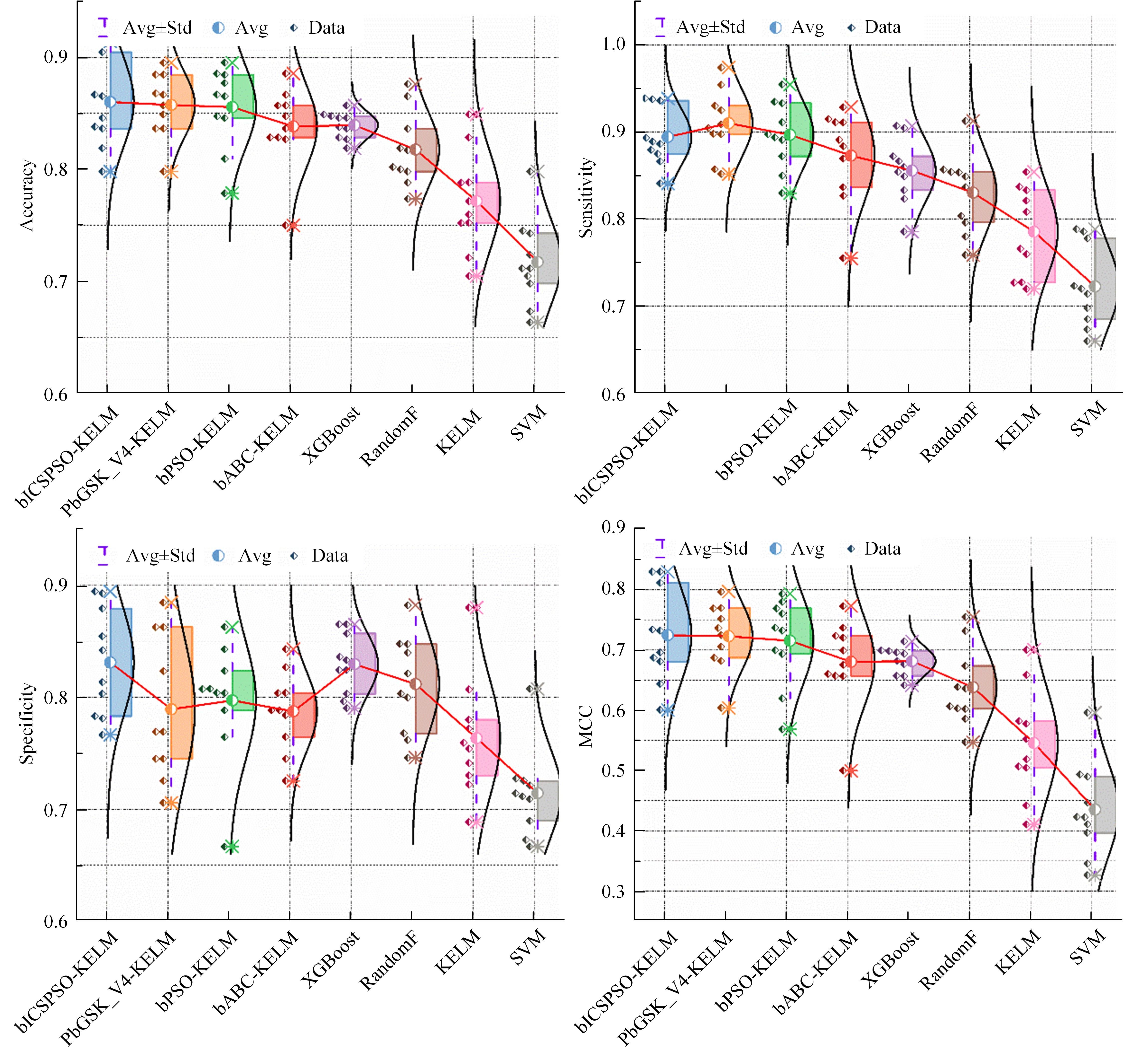
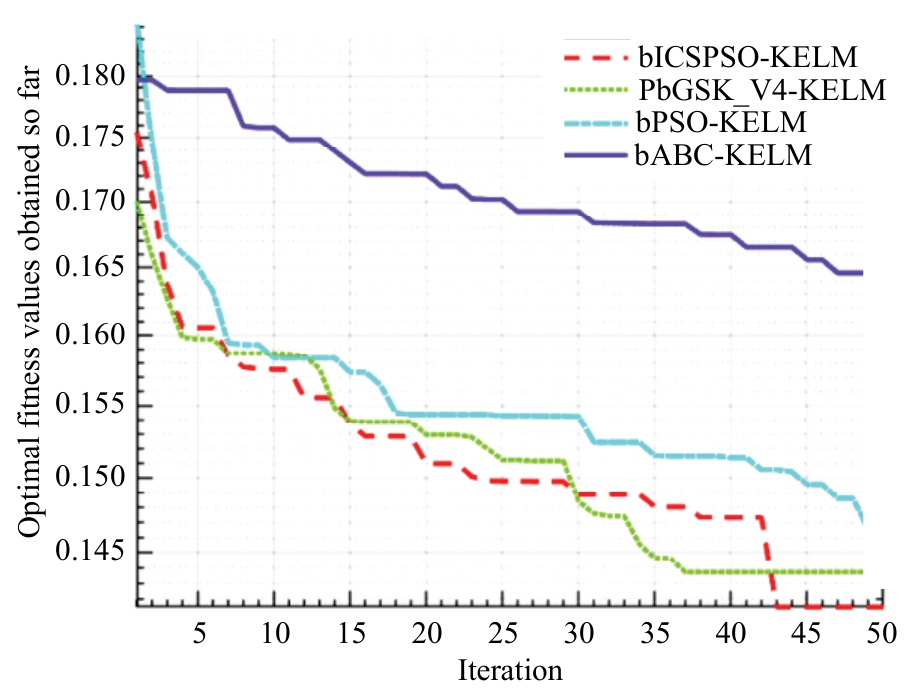
为解决高校创新人才传统预测方法存在主观性强、准确度低等问题,提出了一种融合信息引导交流搜索策略的粒子群优化算法与核极限学习机的高校创新人才智能预测模型。该模型利用改进的粒子群优化算法增强种群多样性与全局寻优能力,以提升核极限学习机的分类性能,旨在更科学、客观地识别与选拔创新人才。为验证模型有效性,通过十折交叉验证在高校创新人才数据集上进行实验,结果表明:本文模型在分类准确率(86.05%)、灵敏度(89.74%)、特异性(83.24%)和马修斯相关系数(72.42%)上均优于多种对比模型 。研究结果证实了该模型在高校创新人才预测方面的显著优势,为人才的科学选拔与培养提供了新的技术手段,具备良好的应用前景。
中图分类号:
- TP391.4
| [1] | Li J, Xue E.How talent cultivation contributes to creating world-class universities in China:a policy discourse analysis[J].Educational Philosophy and Theory, 2022, 54(12): 2008-2017. |
| [2] | 史秋衡, 李瑞. 高校拔尖创新人才培养的价值逻辑、关键要素与路径选择[J]. 中国远程教育, 2024, 44(1): 15-24. |
| Shi Qiu-heng, Li Rui. Value logic, key elements and path selection of top innovative talents training in universities[J]. Distance Education in China, 2024, 44(1): 15-24. | |
| [3] | 李润亚, 张潮, 张珂, 等. 大学生创新创业能力系统构成及其表现研究[J]. 教育理论与实践, 2024, 44(18): 10-15. |
| Li Run-ya, Zhang Chao, Zhang Ke, et al. A study on the system composition and performance of college students' innovation and entrepreneurship ability[J]. Educational Theory and Practice,2024,44(18):10-15. | |
| [4] | Gao H W.Innovation and development of ideological and political education in colleges and universities in the network era[J]. International Journal of Electrical Engineering& Education,2021,60(Sup.2): 489-499. |
| [5] | 李立国, 刘振天, 陈恩伦, 等. 笔谈:大学可持续发展的多维思考[J] .现代大学教育, 2023, 39(6): 41-59. |
| Li Li-guo, Liu Zhen-tian, Chen En-lun, et al. Writing: multi-dimensional thinking on sustainable development of universities [J]. Modern University Education,2023,39(6): 41-59. | |
| [6] | 徐玉成, 王波, 朱萍. 科教融汇赋能职业教育人才培养的时代价值、现实困境及破解对策[J].教育学术月刊, 2023(9): 58-66. |
| Xu Yu-cheng, Wang Bo, Zhu Ping. The times value, realistic dilemma and solutions of talent training in enabling vocational education by integrating science and education[J]. Educational Academic Monthly, 2023(9): 58-66. | |
| [7] | Liu Y. Construction of talent training mechanism for innovation and entrepreneurship education in colleges and universities based on data fusion algorithm[J].Frontiers in Psychology,2022,13: 968023. |
| [8] | 周沂, 陈圆月, 冯皓月. 学科交叉推动拔尖创新人才培养的作用研究——来自S大学书院制的经验证据[J]. 湖南师范大学教育科学学报, 2024, 23(1): 33-43. |
| Zhou Yi, Chen Yuan-Yue, Feng Hao-yue. Research on the role of interdisciplinary interaction in promoting the cultivation of top innovative talents: empirical evidence from the college system of S University[J]. Journal of Education Science, Hunan Normal University, 2024, 23(1): 33-43. | |
| [9] | Sarker I H.Machine learning:algorithms, real-world applications and research directions[J]. SN Computer Science, 2021, 2(3): No.160. |
| [10] | Mishra D K, Shinde V.6 A review of global optimization problems using meta-heuristic algorithm[M]∥Aditya K, Ashish K, Nhu Gia N, et al. Nature-Inspired Optimization Algorithms.Berlin,Boston;De Gruyter, 2021: 87-106. |
| [11] | Storn R, Price K. Differential evolution—a simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces[J]. Journal of Global Optimization,1997, 11(4): 341-359. |
| [12] | Kennedy J, Eberhart R.Particle swarm optimization[C]∥Proceedings of ICNN'95-International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, Australia, 1995:488968. |
| [13] | Dorigo M, Birattari M, Stutzle T. Ant colony optimization[J]. IEEE Computational Intelligence Magazine, 2006, 1(4): 28-39. |
| [14] | Mirjalili S, Mirjalili S M, Lewis A. Grey wolf optimizer[J].Advances in Engineering Software, 2014, 69: 46-61. |
| [15] | Lian J, Hui G, Ma L, et al.Parrot optimizer: algorithm and applications to medical problems[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2024, 172: 108064. |
| [16] | Chauhan S, Vashishtha G, Abualigah L, et al.Boosting salp swarm algorithm by opposition-based learning concept and sine cosine algorithm for engineering design problems[J].Soft Computing, 2023, 27(24):18775-18802. |
| [17] | Gao R, Tao J, Zhang J,et al.NSGA-Ⅲ-SD based fuzzy energy management system optimization for lithium battery/supercapacitor HEV[J].Applied Soft Computing, 2023, 142: 110280. |
| [18] | Dong R, Sun L, Ma L, et al.Boosting kernel search optimizer with slime mould foraging behavior for combined economic emission dispatch problems[J]. Journal of Bionic Engineering, 2023, 20(6): 2863-2895. |
| [19] | Pan X, Zhang G, Lin A,et al.An evaluation model for children's foot& ankle deformity severity using sparse multi-objective feature selection algorithm[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2022, 151: 106229. |
| [20] | Huang G B, Zhou H, Ding X,et al. Extreme learning machine for regression and multiclass classification[J].IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics,Part B(Cybernetics), 2012, 42(2): 513-529. |
| [21] | Huang G B, Zhu Q Y, Siew C K. Extreme learning machine: theory and applications[J]. Neurocomputing, 2006, 70(1): 489-501. |
| [1] | 赵秀芝,谢德红. 基于噪声鲁棒性特征提取的普洱茶品种鲁棒判别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(5): 1756-1762. |
| [2] | 李燕飞,吴加宁. 基于改进RBF神经网络的人体姿态局部特征识别算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(5): 1749-1755. |
| [3] | 梅生启,刘晓东,王兴举,李旭峰,武腾,程相旭. 基于参数相关性分析和机器学习算法的高强混凝土徐变预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(5): 1595-1603. |
| [4] | 郭祎,魏书威,姜涛. 基于区位势能和多源数据的城市客运交通规划算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1328-1335. |
| [5] | 孟祥海,王国锐,张明扬,田毕江. 基于选择集成的山区高速事故预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1298-1306. |
| [6] | 戴银飞,周秀贞,刘玉宝,刘志远. 基于CAN总线数据的车载网络入侵检测系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(3): 857-865. |
| [7] | 张磊,焦晶,李勃昕,周延杰. 融合机器学习和深度学习的大容量半结构化数据抽取算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2631-2637. |
| [8] | 张良力,马晓凤. 基于改进粒子群算法的新能源汽车充电站选址方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2275-2281. |
| [9] | 陈城,史培新,贾鹏蛟,董曼曼. 基于MK-LSTM算法的盾构掘进参数相关性分析及结构变形预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1624-1633. |
| [10] | 巩亚东,丁明祥,李响,田近民. TC4钛合金材料铣削加工分析及参数优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 917-925. |
| [11] | 牛世峰,于士杰,刘彦君,马冲. 基于手环数据的愤怒驾驶行为实时检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(12): 3505-3512. |
| [12] | 戴理朝,王冲,袁平,王磊. 基于可解释机器学习的锈蚀RC构件抗剪承载力预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(11): 3231-3243. |
| [13] | 付忠良,陈晓清,任伟,姚宇. 带学习过程的随机K最近邻算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 209-220. |
| [14] | 耿庆田,刘植,李清亮,于繁华,李晓宁. 基于一种深度学习模型的土壤湿度预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2430-2436. |
| [15] | 谭国金,孔庆雯,何昕,张攀,杨润超,朝阳军,杨忠. 基于动力特性和改进粒子群优化算法的桥梁冲刷深度识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1592-1600. |
|