吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (2): 454-463.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20181152
• 车辆工程·机械工程 • 上一篇
纯电动铲运机弓网续能系统设计与动态特性仿真
- 北京科技大学 机械工程学院, 北京 100083
Design and dynamic characteristic simulation of pantograph⁃catenary continuous energy system for pure electric LHD
Yin-ping LI( ),Tian-xu JIN(
),Tian-xu JIN( ),Li LIU
),Li LIU
- School of Mechanical Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China
摘要:
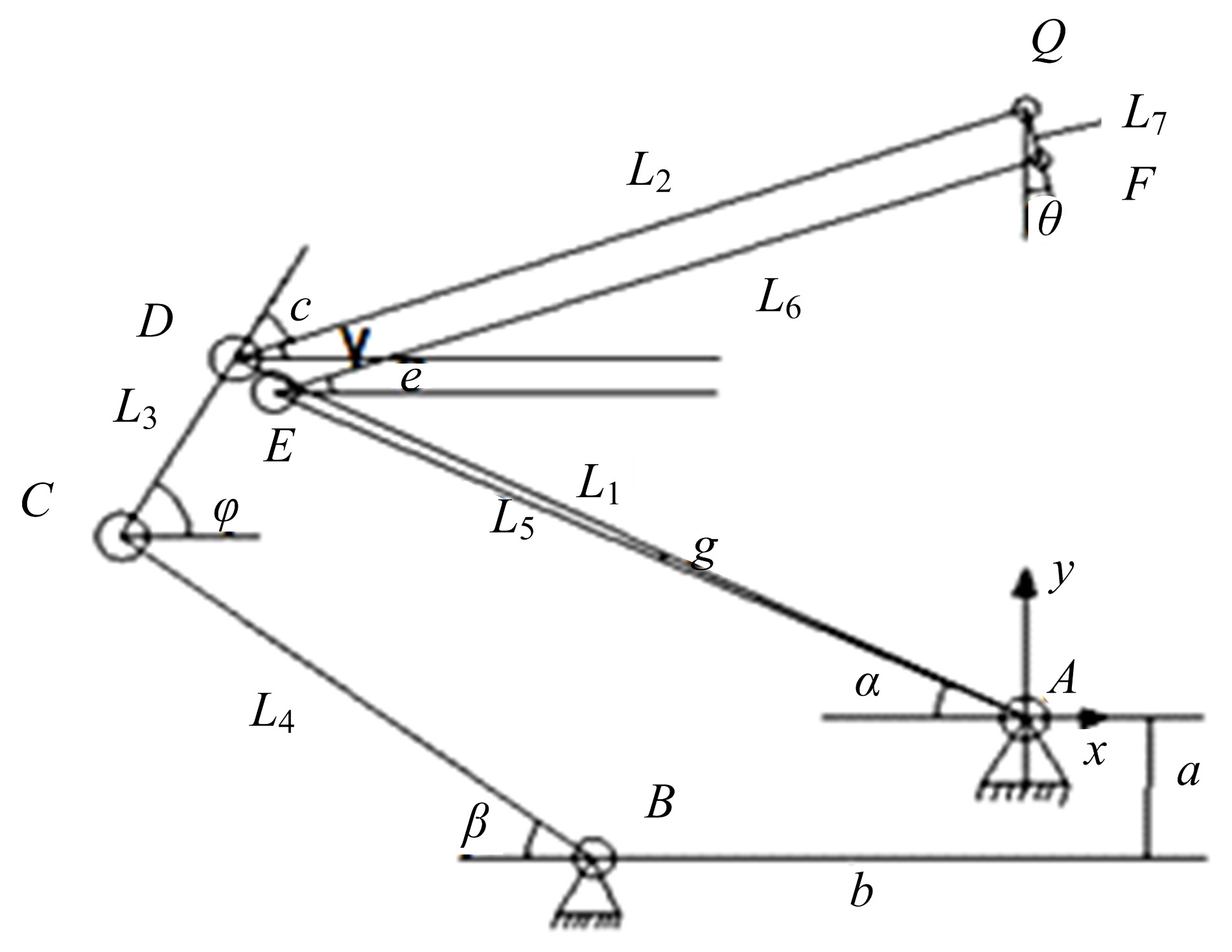
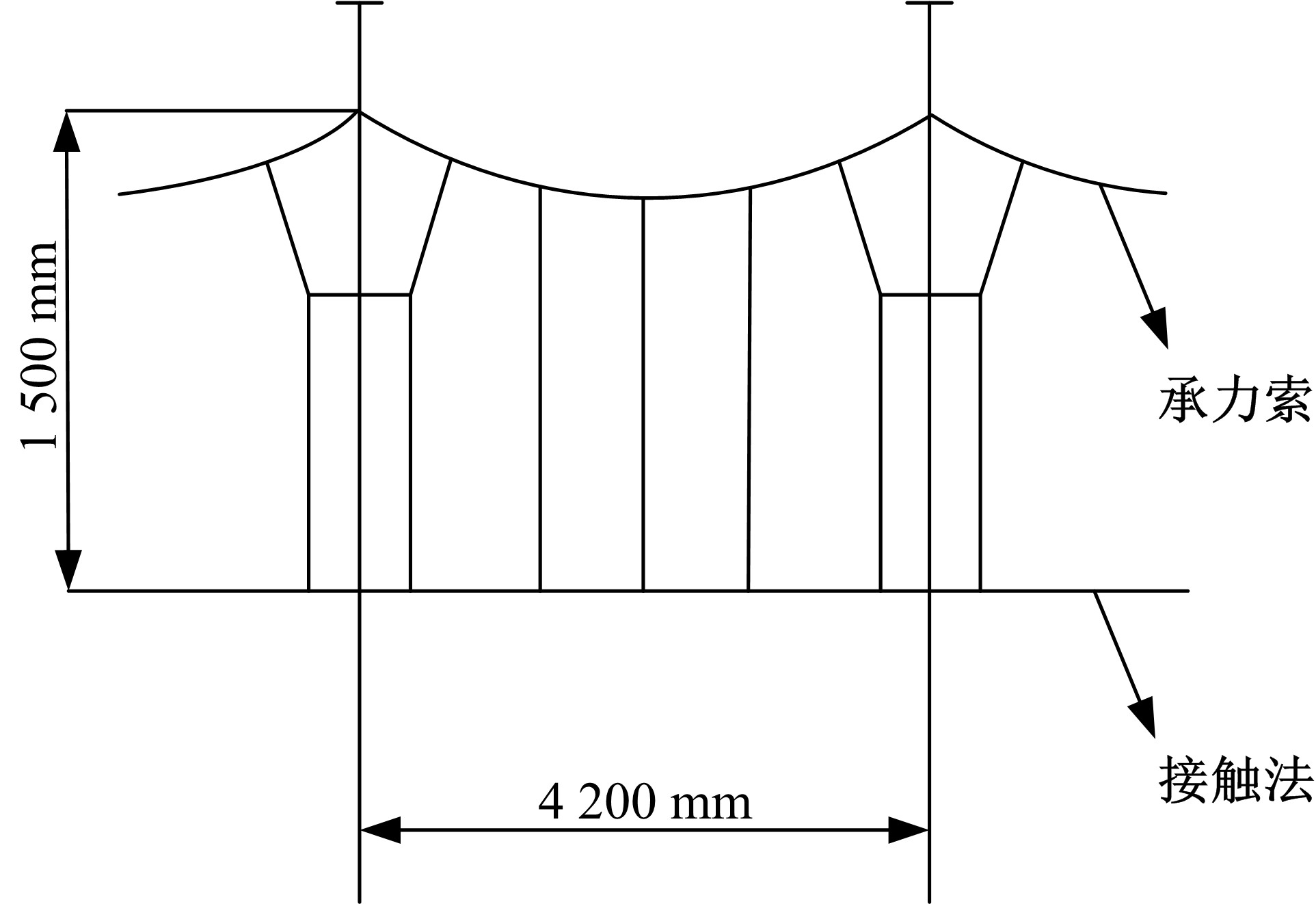
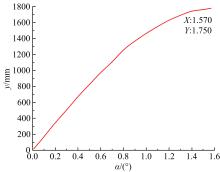
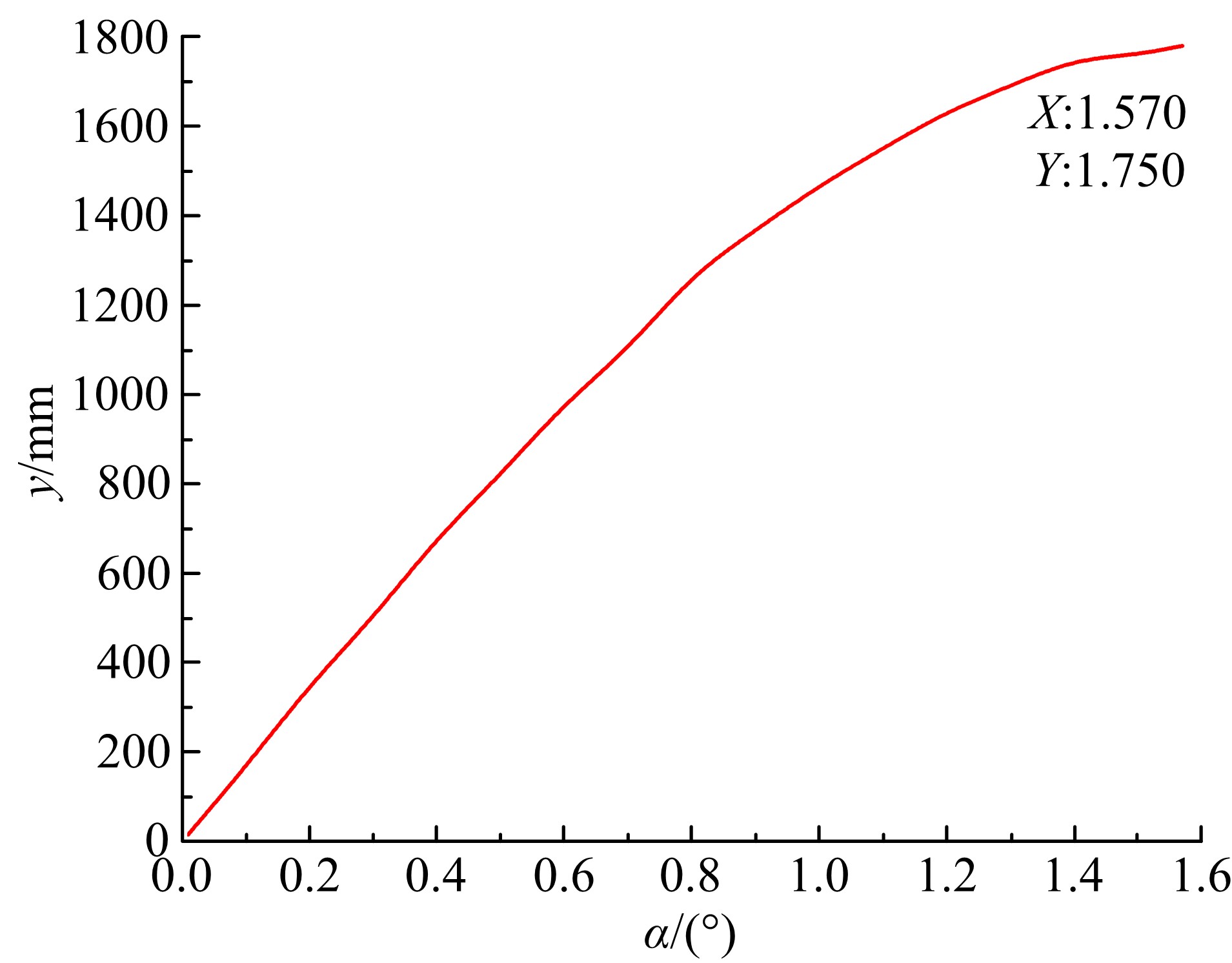
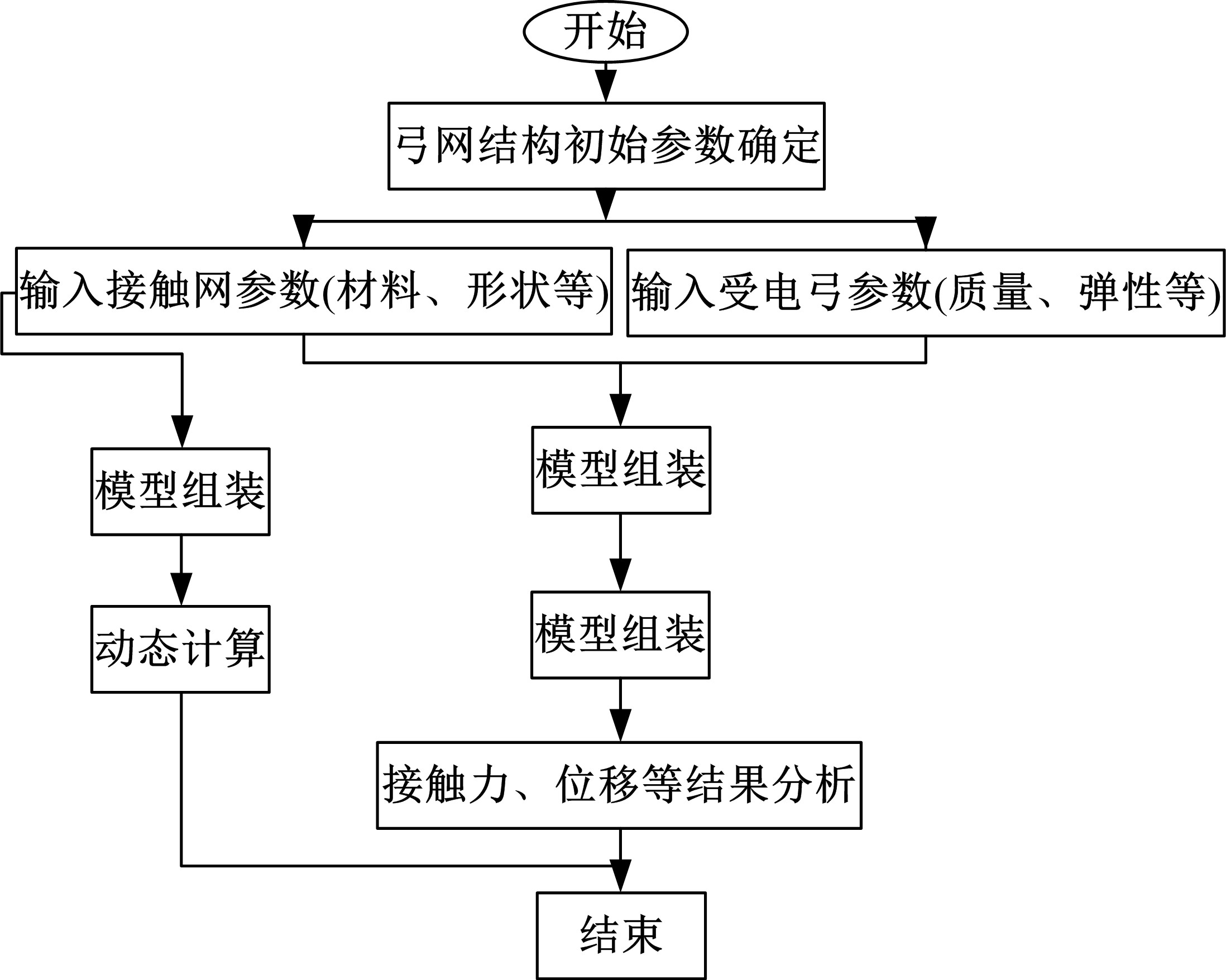
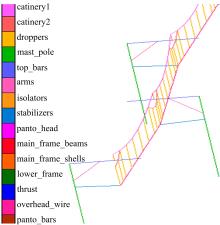
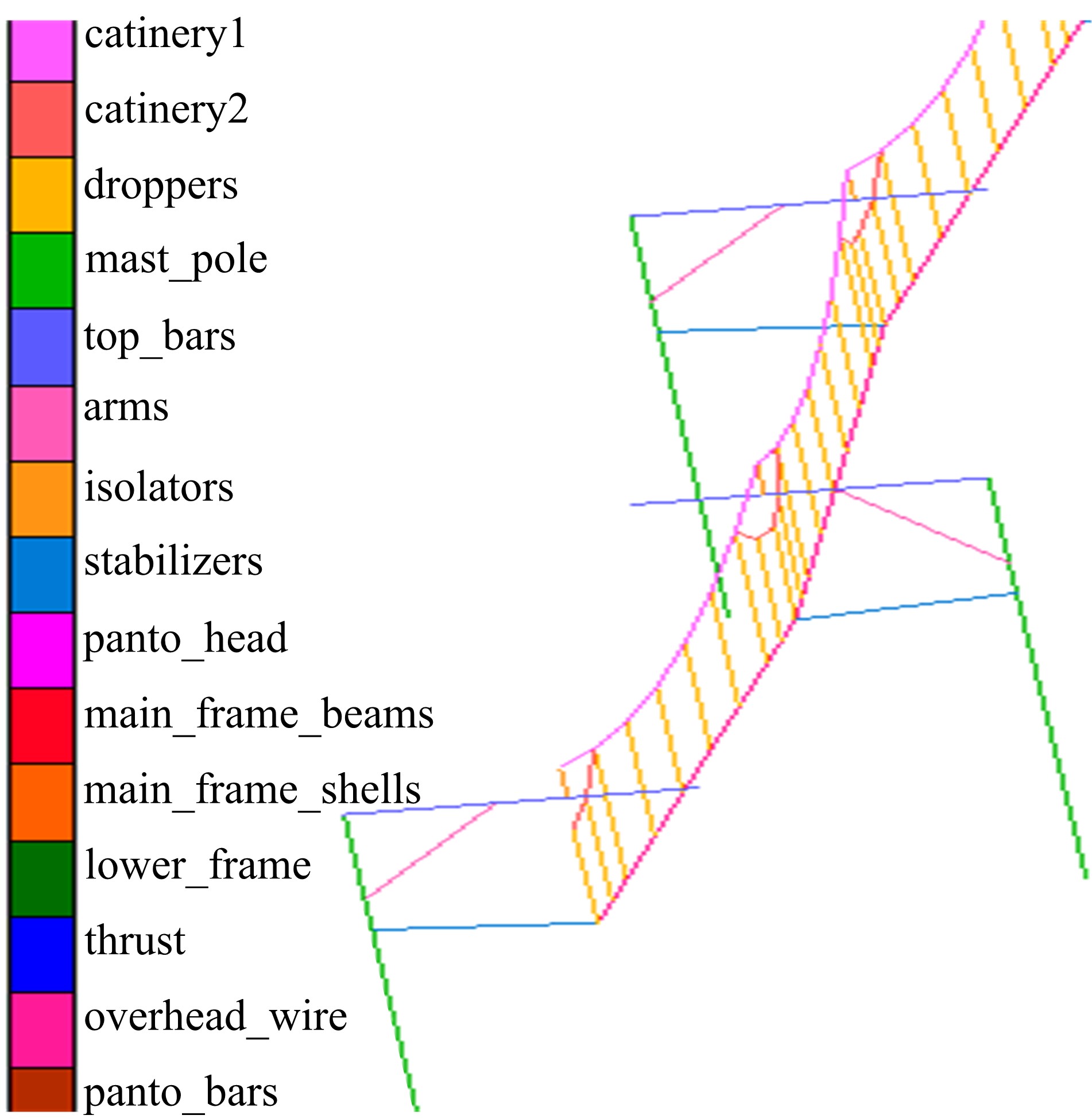
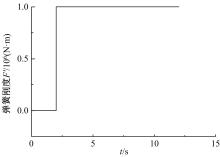
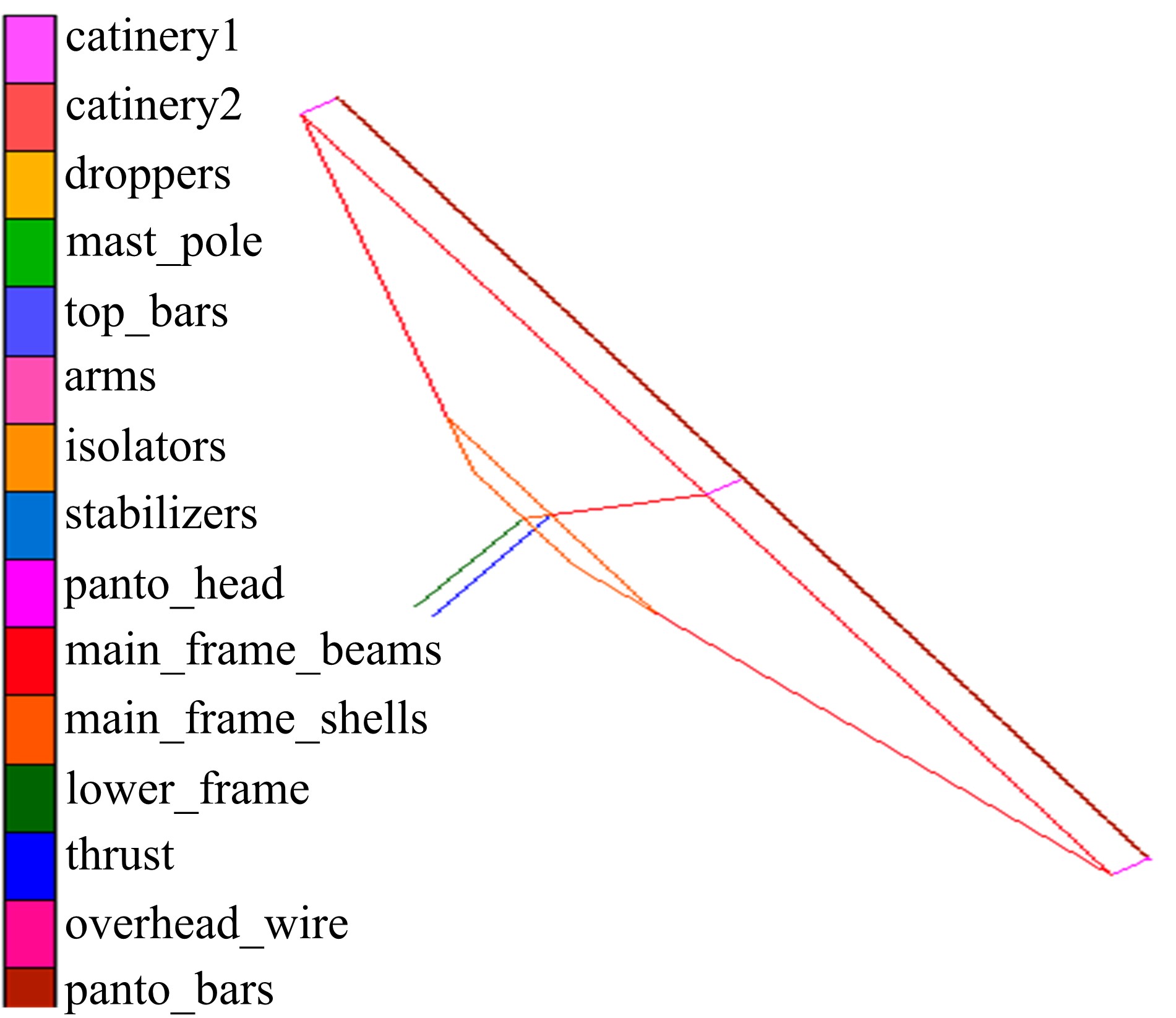
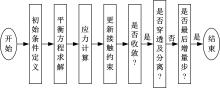
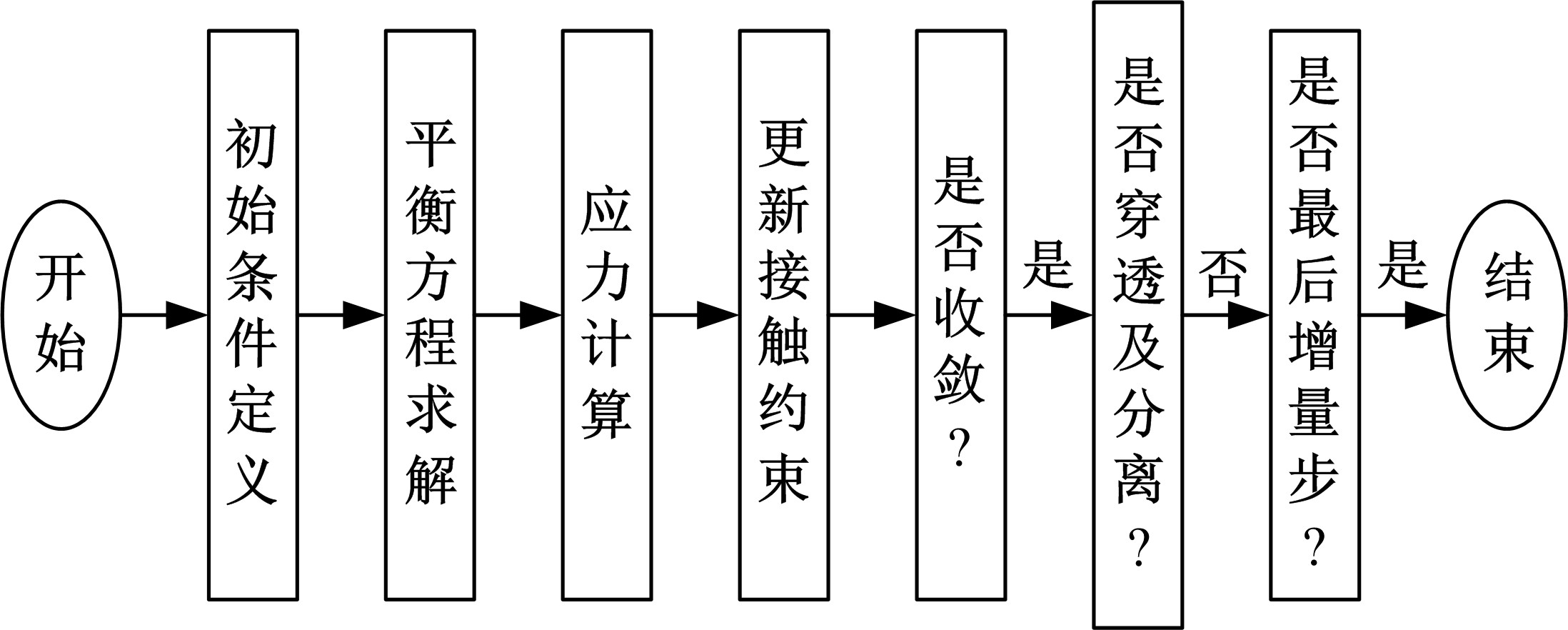
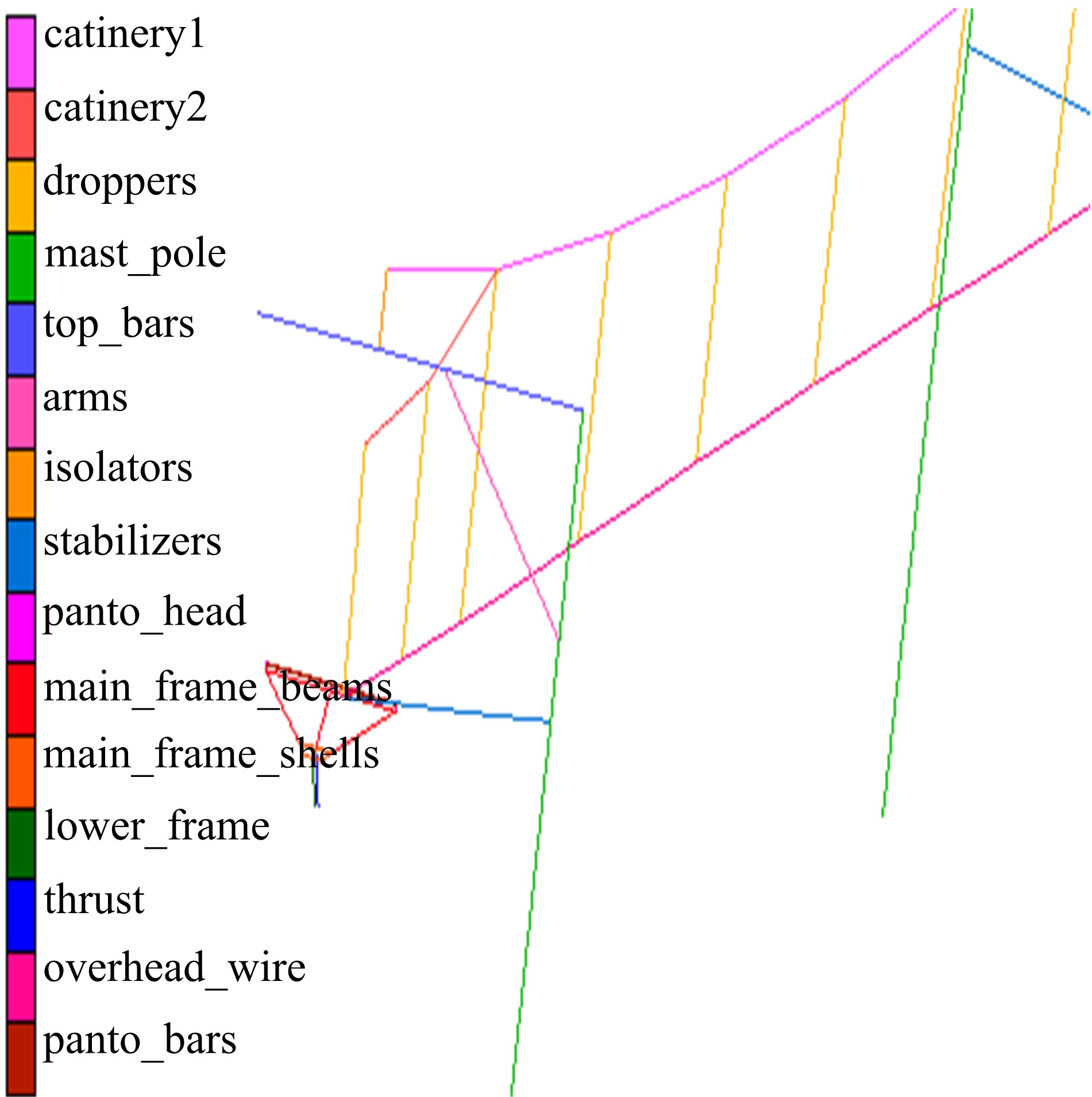
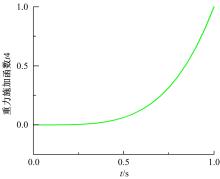
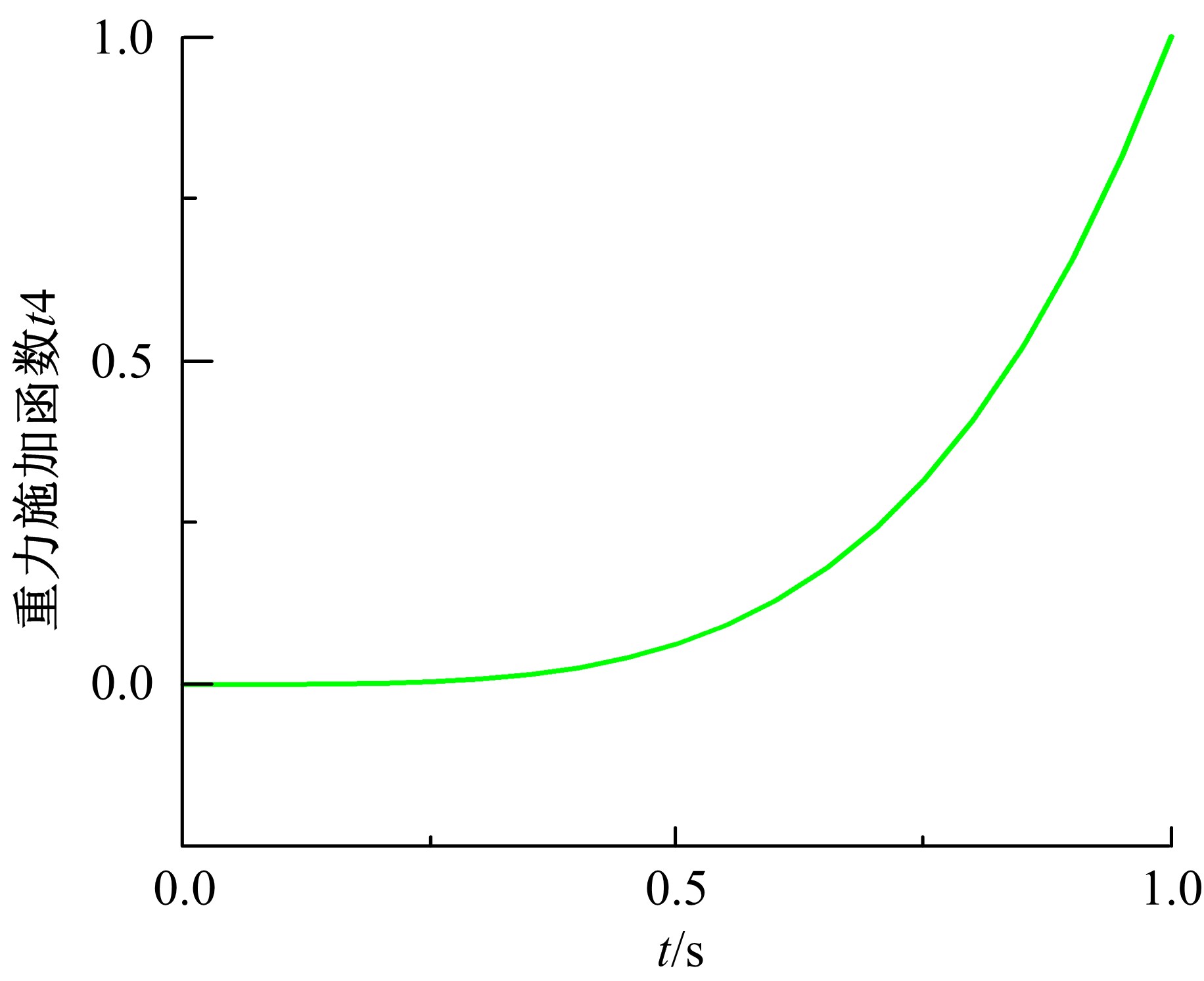
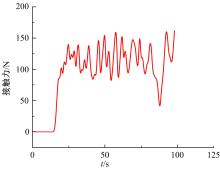
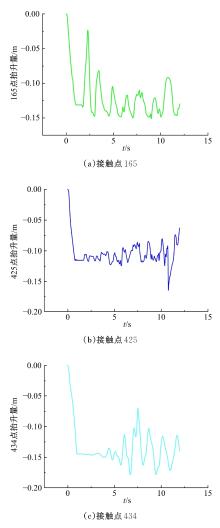
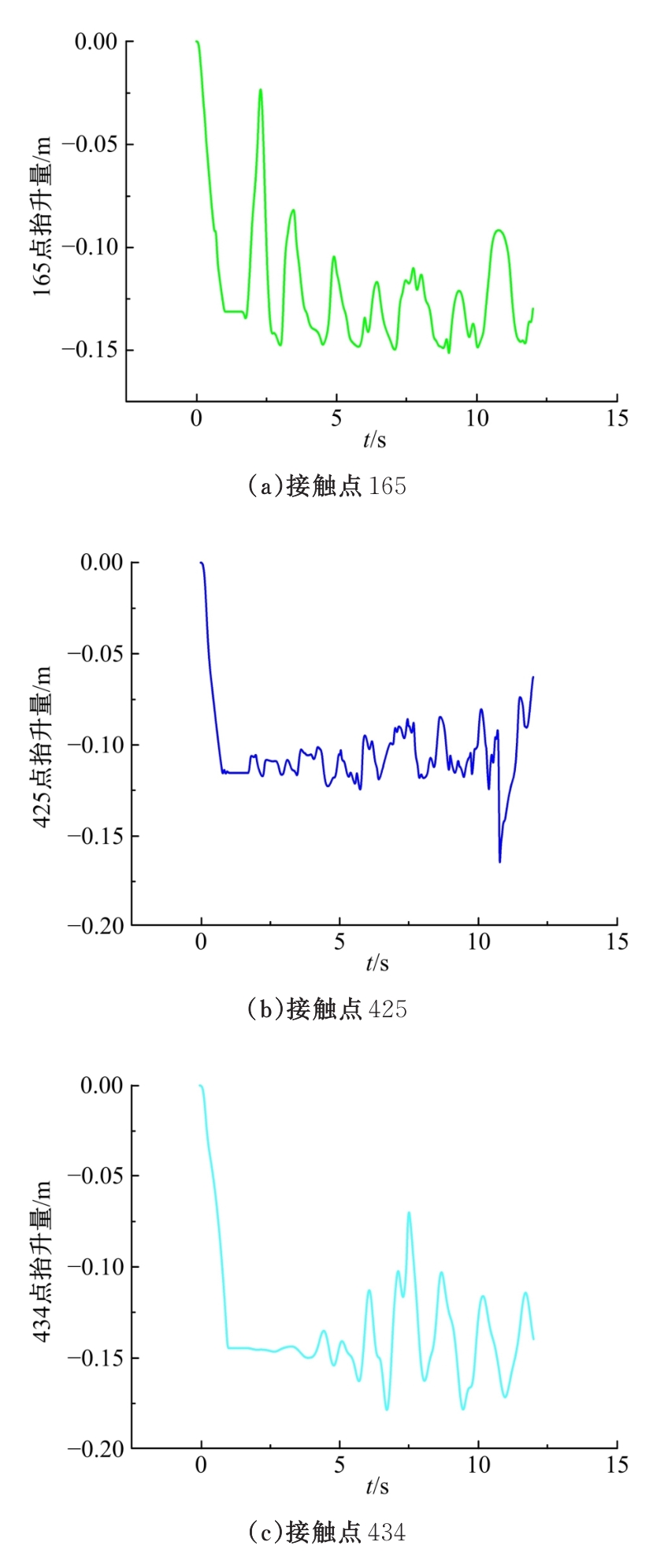
为能给纯电动铲运机充电续能,提出了一种弓网续能充电系统。根据10 t级纯电动铲运机受电弓动力学特征及受电弓与巷道之间的工作条件设计了包括弓网各部件结构、弓头运动轨迹、升弓角及平衡杆转角等弓网续能系统参数。基于建立的受电弓动力学计算模型,结合多目标优化算法设计出纯电动铲运机专用受电弓,基于非线性有限元理论建立了纯电动铲运机弓网续能系统有限元模型,通过MARC软件对弓网续能系统受流情况进行了动态特性仿真和验证分析。结果表明:本弓网续能系统能在保证纯电动铲运机安全运行的前提下仅需12.5 s完成纯电动铲运机续能充电,提高了纯电动铲运机运行作业效率,具有很强的推广性。
中图分类号:
- U469.72
| 1 | 古德生. 地下金属矿采矿科学技术的发展趋势[J]. 采矿工程, 2004, 25( 1): 18- 22. |
| Gu De-sheng. The development of mining science and technology of underground metal mine[J]. Mining Engineering, 2004, 25( 1): 18- 22. | |
| 2 | 王荣祥, 任效乾, 张晶晶. 地下矿山无轨采矿设备的发展与创新[J]. 矿业装备, 2012, 2( 4): 42- 47. |
| Wang Rong-xiang, Ren Xiao-qian, Zhang Jing-jing. Development and innovation of trackless mining equipment in underground mines[J]. Mining Equipment, 2012, 2( 4): 42- 47. | |
| 3 | 侯林帅. 新能源工程机械特点研究[J]. 中国设备工程, 2017, 33( 3): 133- 134. |
| Hou Lin-shuai. Research on the characteristics of new energy engineering machinery[J]. China Plant Engineering, 2017, 33( 3): 133- 134. | |
| 4 | 战凯. 我国地下矿山无轨采矿设备现状及发展动态[J]. 世界有色金属, 2004, 19( 6): 20- 25. |
| Zhan Kai. Current status and development of mineless mining equipment in underground mines in China[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 19( 6): 20- 25. | |
| 5 | Vo V O, Massat J P, Laurent C, et al. Introduction of variability into pantograph-catenary dynamic simulations[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2014, 52( 10): 1254- 1269. |
| 6 | Sanchez-Rebollo C, Jimenez-Octavio J R, Carnicero A. Active control strategy on a catenary-pantograph validated model[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2013, 51( 4): 554- 569. |
| 7 | Yang G, Dai Z M, Li F, et al. Active control of fuzzy for high-speed pantograph[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2013, 251( 12): 158- 163. |
| 8 | Alberto A, Benet J, Arias E, et al. A high performance tool for the simulation of the dynamic pantograph-catenary interaction[J]. Mathematics and Computers in Simulation, 2008, 79( 3): 652- 667. |
| 9 | Shimanovsky A, Yakubovich V, Kapliuk I. Modeling of the pantograph-catenary wire contact interaction[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2016, 134( 1): 284- 290. |
| 10 | Collina A, Bruni S. Numeriacal simulation of pantograph overhead experimental interaction[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2002, 38( 4): 261- 291. |
| 11 | Farhangdoust S, Farahbakhsh M, Shahravi M. Modeling of pantograph-catenary dynamic stability[J]. Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences, 2013, 3( 14): 1486- 1491. |
| 12 | Kusumi S, Fukutani T, Nezu K. Diagnosis of overhead contact line based on contact force[J]. Railway Technical Research Institute, 2006, 47( 1): 39- 45. |
| 13 | Ambrosio J, Pombo J, Pereira M. Optimization of high speed railway pantographs for improving pantograph-catenary contact[J]. Theoretical and Applied Mechanics Letters, 2013, 3( 1): 51- 55. |
| 14 | 刘坤, 叶明, 李超, 等. 臂式站起运动康复训练机械结构设计及分析[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2016, 46( 5): 1532- 1539. |
| Liu Kun, Ye Ming, Li Chao, et al. Design and analysis of an arm mechanical structure for sit-to-stand rehabilitation training[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2016, 46( 5): 1532- 1539. | |
| 15 | 刘坤, 吉硕, 孙震源, 等. 多功能坐站辅助型如厕轮椅机械结构设计与优化[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49( 3): 872- 880. |
| Liu Kun, Ji Shuo, Sun Zhen-yuan, et al. Mechanical structure design and optimization of multifunctional auxiliary toilet wheelchair[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49( 3): 872- 880. | |
| 16 | Naz R, Mahomed F M. Dynamic euler-bernoulli beam equation: classification and reductions[J/OL].( 2015-08-23)[ 2018-11-20]. |
| 17 | 董志波, 刘雪松, 马瑞, 等. MSC.Marc工程实例详解[M]. 1版 . 北京: 人民邮电出版社, 2014. |
| 18 | Pappalardo C M, Patel M D, Tinsley B, et al. Contact force control in multibody pantograph/catenary systems[J]. Journal of Multi-Body Dynamics, 2016, 230( 4): 307- 328. |
| 19 | 吴燕, 吴俊勇, 郑积浩. 高速受电弓-接触网系统动态受流性能的仿真分析[J]. 北京交通大学学报, 2009, 33( 5): 60- 64. |
| Wu Yan, Wu Jun-yong, Zheng Ji-hao. A simulation study on current collection of high-speed pantograph-catenary[J]. Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University, 2009, 33( 5): 60- 64. |
| [1] | 赖晨光,王擎宇,胡博,文凯平,陈彦宇. 静气动弹性影响下带小翼汽车尾翼的设计与优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 399-407. |
| [2] | 叶辉,刘畅,闫康康. 纤维增强复合材料在汽车覆盖件中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 417-425. |
| [3] | 陈鑫,王宁,沈传亮,冯晓,杨昌海. 后视镜造型对前侧窗气动噪声的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 426-436. |
| [4] | 李小雨,许男,仇韬,郭孔辉. 各向异性刚度对轮胎力学特性及车辆操纵性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 389-398. |
| [5] | 马芳武,梁鸿宇,赵颖,杨猛,蒲永锋. 内凹三角形负泊松比结构耐撞性多目标优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 29-35. |
| [6] | 郭孔辉,黄世庆,吴海东. 适用于高频激励的面内轮胎动态模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 19-28. |
| [7] | 王哲,谢怡,臧鹏飞,王耀. 基于极小值原理的燃料电池客车能量管理策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 36-43. |
| [8] | 史文库,陈龙,张贵辉,陈志勇. 多级刚度双质量飞轮扭转特性建模与试验验证[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 44-52. |
| [9] | 管欣,金号,段春光,卢萍萍. 汽车行驶道路侧向坡度估计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1802-1809. |
| [10] | 陈鑫,阮新建,李铭,王宁,王佳宁,潘凯旋. 基于大涡模拟的离散格式改进方法及应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1756-1763. |
| [11] | 马芳武,倪利伟,吴量,聂家弘,徐广健. 轮腿式全地形移动机器人位姿闭环控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1745-1755. |
| [12] | 靳立强, 田端洋, 田浩, 刘蒙蒙. 汽车电子稳定系统制动增力辅助技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1764-1776. |
| [13] | 王杨,宋占帅,郭孔辉,庄晔. 转动惯量试验台的惯性参数测量[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1795-1801. |
| [14] | 庄蔚敏,刘洋,王鹏跃,施宏达,徐纪栓. 钢铝异质自冲铆接头剥离失效仿真[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1826-1835. |
| [15] | 何仁,涂琨. 基于温度补偿气隙宽度的电磁制动器[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1777-1785. |
|
||