吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (2): 520-525.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20190012
• 材料科学与工程 • 上一篇
等温热处理温度对超级贝氏体组织与性能的影响
- 1.长春工业大学 先进结构材料省部共建教育部重点实验室,长春 130012
2.吉林农业科技学院 机械与土木工程学院,吉林省 吉林市 132101
Effect of isothermal heat treatment temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of super bainite
Wen-cui XIU1,2( ),Hua WU1(
),Hua WU1( ),Ying HAN1,Yun-xu LIU1
),Ying HAN1,Yun-xu LIU1
- 1.Key Laboratory of Advanced Structural Materials of Ministry of Education,Changchun University of Technology,Changchun 130012, China
2.School of Mechanical and Civil Engineering,Jilin Agricultural Science and Technology University, Jilin 132101, China
摘要:
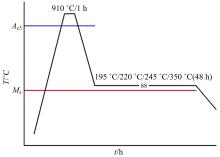
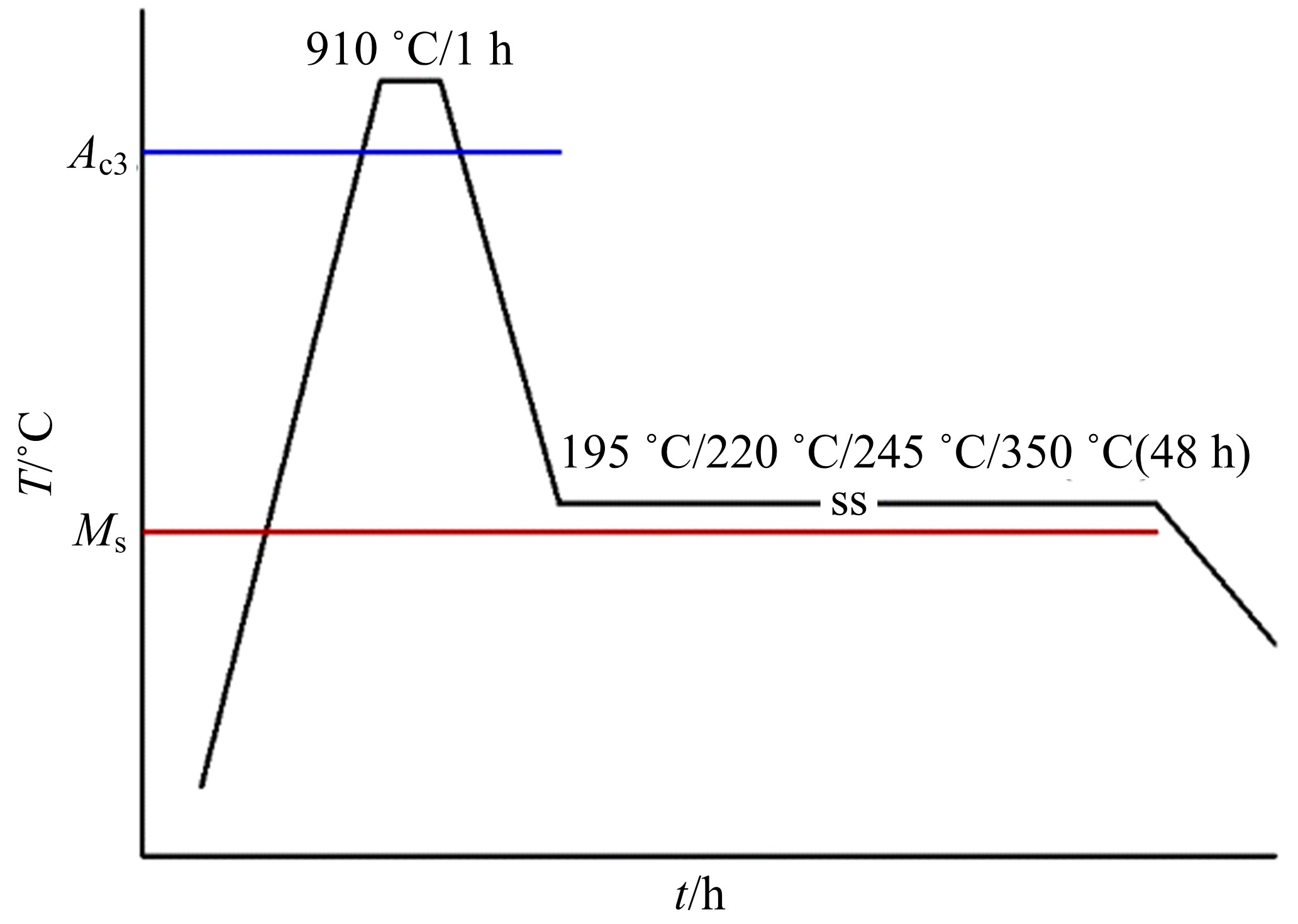
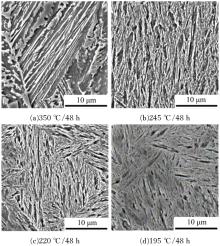
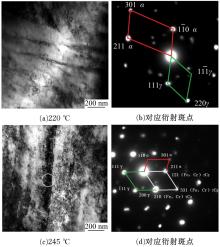
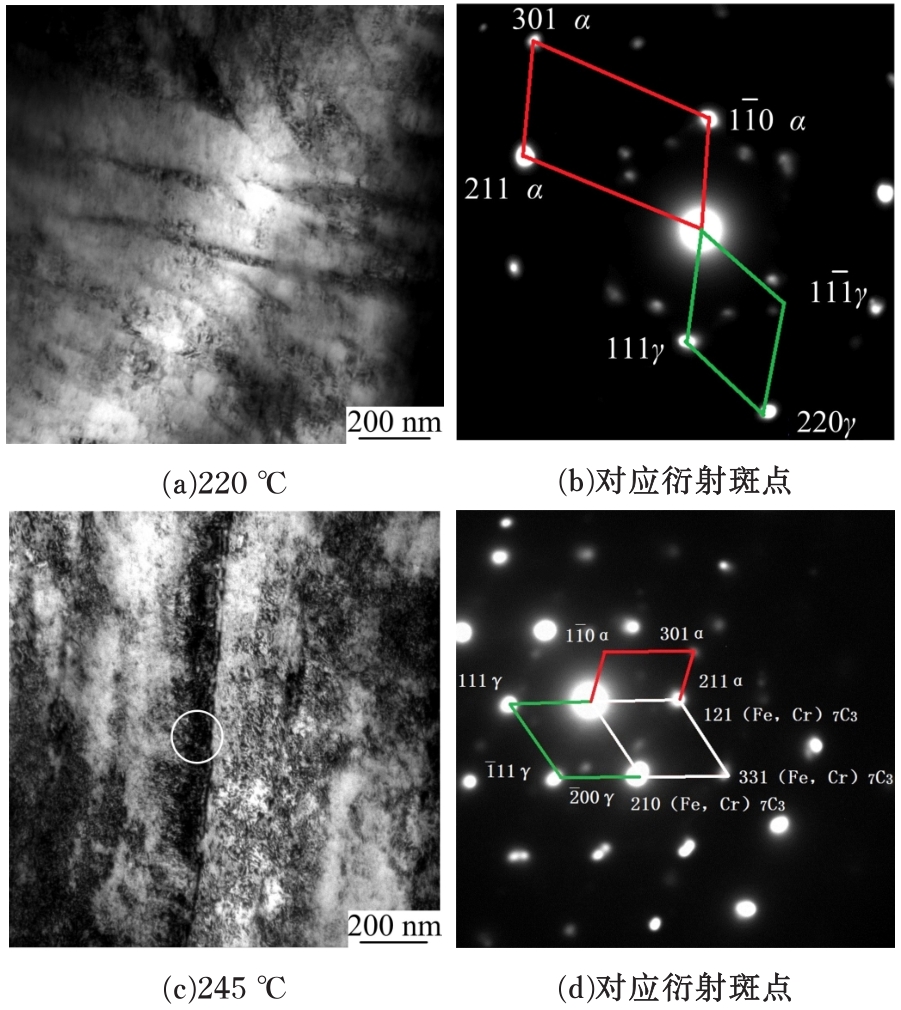
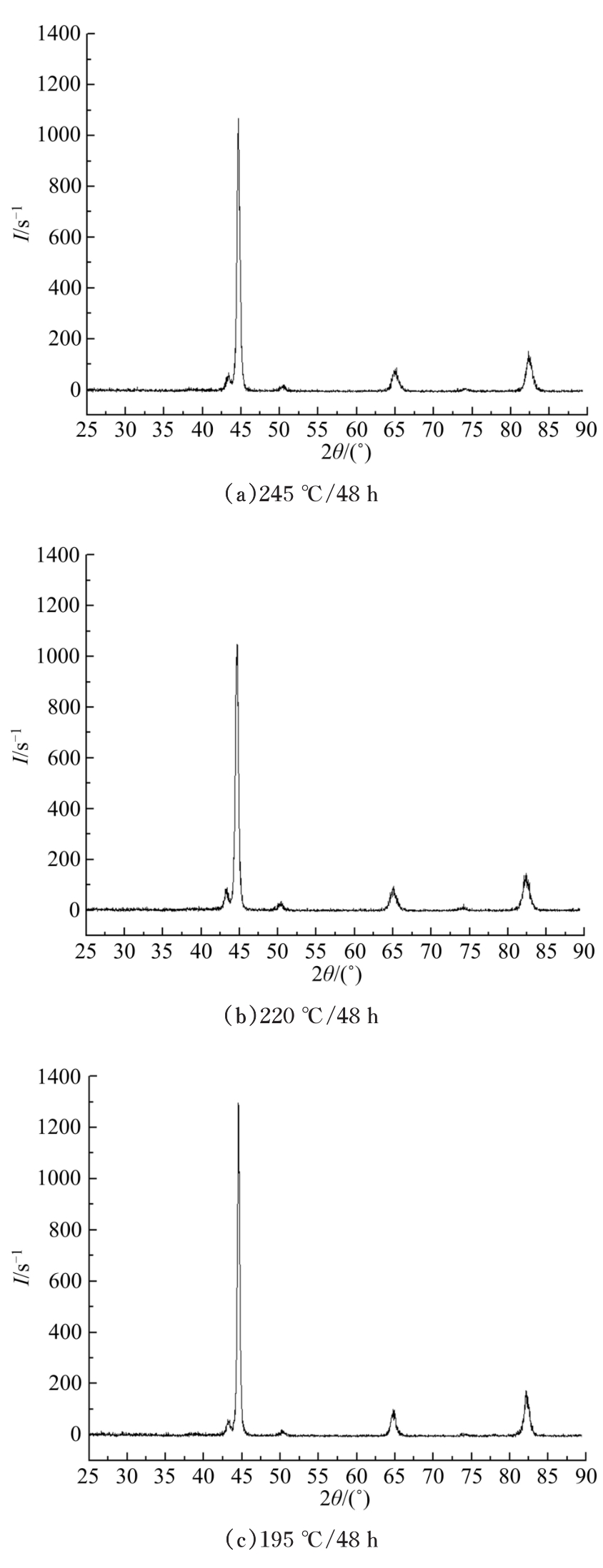
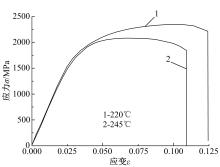
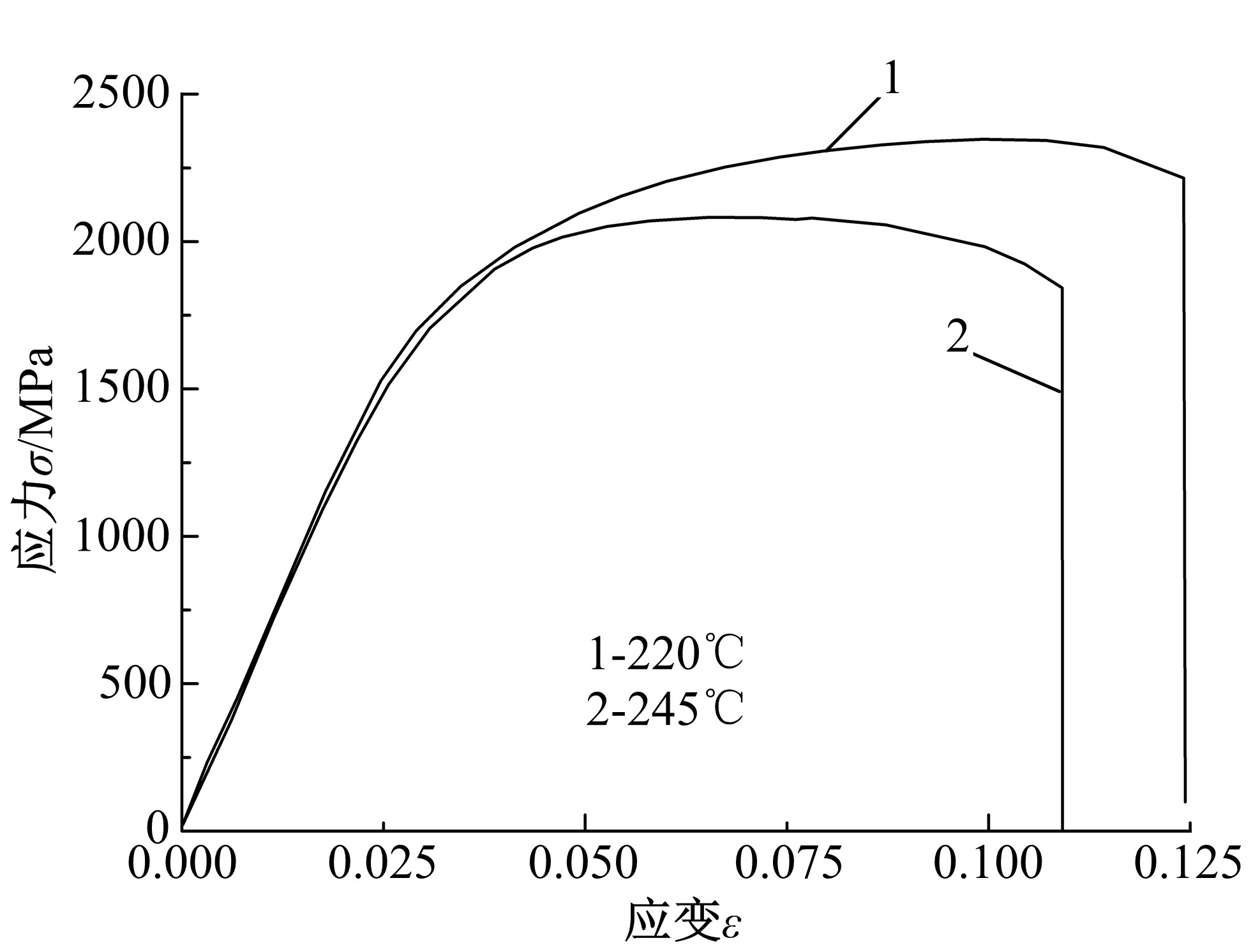
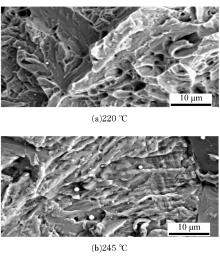
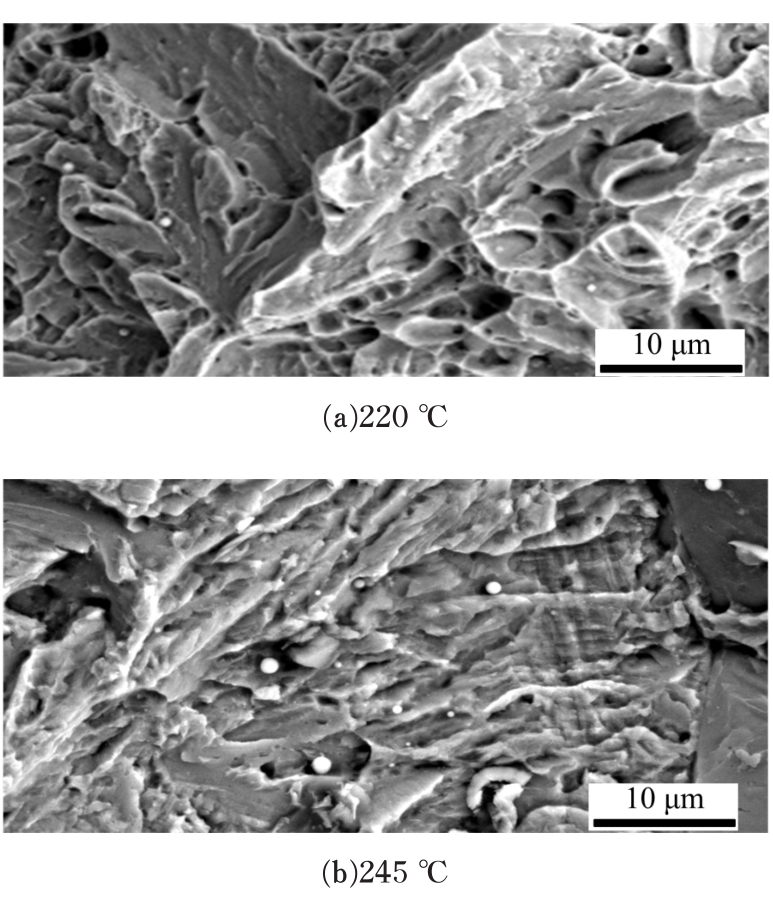
研究了70Si2Mn2CrMo钢经不同温度等温热处理后,产生超级贝氏体组织转变的同时,碳化物析出的情况以及对其力学性能的影响。通过对试样的显微组织和力学性能的检测分析,确定了碳化物析出的温度及类型;同时表明,由于碳化物析出减少了过冷奥氏体中C含量,致使其稳定性下降,超级贝氏体中残余奥氏体质量分数减少。与220 ℃等温热处理没有碳化物析出的样品相比较,245 ℃等温热处理样品的抗拉强度降低11%,强塑积降低16%,疲劳循环断裂次数降低55%。
中图分类号:
- TG142.1
| 1 | Caballero F G, Bhadeshia H K D H. Very strong bainite[J]. Current Opinion in Solid State & Materials Science, 2004, 8(3): 251-257. |
| 2 | Hase K, Garcia-Mateo C, Bhadeshia H K D H. Bimodal size-distribution of bainite plates[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2006, 438-440: 145-148. |
| 3 | Luzginova N V, Zhao L, Sietsma J. Bainite formation kinetics in high carbon alloyed steel[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2008, 481: 766-769. |
| 4 | Han Y, Wu H, Liu C, et al. Microstructures and mechanical characteristics of a medium carbon super-bainitic steel after isothermal transformation[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering & Performance, 2014, 23(12): 4230-4236. |
| 5 | Podder A S, Bhadeshia H K D H. Thermal stability of austenite retained in bainitic steels[J]. Materials Science & Engineering: A, 2010, 527(7/8): 2121-2128. |
| 6 | Wu H, Liu C, Zhao Z B, et al. Design of air-cooled bainitic microalloyed steel for a heavy truck front axle beam[J]. Materials and Design, 2006, 27(8): 651-656. |
| 7 | Soliman M, Mostafa H, El-Sabbagh A S, et al. Low temperature bainite in steel with 0.26 wt% C[J]. Materials Science & Engineering: A, 2010, 527(29/30): 7706-7713. |
| 8 | 吴化. 低合金高强度高塑性复相钢材的成分设计[D]. 上海: 东华大学材料科学与工程学院, 2007. |
| Wu Hua. Composition design of low alloy high strength and plasticity complex phases steels[D]. Shanghai: College of Materials Science and Engineering, Donghua University, 2007. | |
| 9 | 陈连生, 张健杨, 田亚强, 等. 预先Mn配分处理对Q&P钢中C配分及残余奥氏体的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2015, 51(5): 527-536. |
| Chen Lian-sheng, Zhang Jian-yang, Tian Ya-qiang, et al. Effect of Mn pre-partitioning on C partitioning and retained qustenite of Q&P steels[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinice, 2015, 51(5): 527-536. | |
| 10 | Misra A, Sharma S, Sangal S, et al. Critical isothermal temperature and optimum mechanical behaviour of high Si-containing bainitic steels[J]. Materials Science & Engineering: A, 2012, 558: 725-729. |
| 11 | 康沫狂, 朱明, 陈大明, 等. 硅合金钢淬火组织中残留奥氏体的力学稳定性与力学性能[J]. 金属热处理, 2005, 30(1): 14-19. |
| Kang Mo-kuang, Zhu Ming, Chen Da-ming, et al. Mechanical property and mechanical stability of retained austenite in quenching microstructure of an alloy steel containing Si[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2005, 30(1): 14-19. | |
| 12 | Sourmail T, Smanio V. Low temperature kinetics of bainite formation in high carbon steels[J]. Acta Materialia, 2013, 61(7): 2639-2648. |
| 13 | 刘宗昌, 王海燕, 王玉峰, 等. 贝氏体碳化物的形貌及形成机制[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2008, 29(1): 32-37, 46. |
| Liu Zong-chang, Wang Hai-yan,Wang Yu-feng, et al. Morphology and formation mechanism of bainitic carbide[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2008, 29(1): 32-37, 46. | |
| 14 | 蔡珣. 材料科学与工程基础[M]. 上海: 上海交通大学出版社, 2010. |
| 15 | Bhadeshia H K D H. High performance bainitic steels[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2005, 500/501: 63-74. |
| 16 | 范雄. 金属X射线学[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 1981. |
| 17 | 吴万国, 阮玉忠, 黄清明. 残余奥氏体定量分析的特殊方法[J]. 福州大学学报: 自然科学版, 2002, 30(3): 385-386. |
| Wu Wan-guo, Ruan Yu-zhong, Huang Qing-ming. A special method on quantitative analysis of remnant austenite[J]. Journal of Fuzhou University (Natural Science Edition), 2002, 30(3): 385-386. | |
| 18 | Mandal D, Ghosh M, Pal J, et al. Effect of austempering treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of high-Si steel[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2009, 44(4): 1069-1075 |
| 19 | Xiu W C, Han Y, Liu C, et al. Cyclic stress induced phase transformation in super-bainitic microstructure[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2017, 26(3): 545-549. |
| [1] | 宫文彪,朱芮,郄新哲,崔恒,宫明月. 6082铝合金超厚板搅拌摩擦焊接头组织与性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 512-519. |
| [2] | 陈学文,王继业,杨喜晴,皇涛,宋克兴. Cr8合金钢热变形行为及位错密度演变规律[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 91-99. |
| [3] | 王金国,任帅,闫瑞芳,黄恺,王志强. TiC颗粒对铸态球墨铸铁组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2010-2018. |
| [4] | 佟鑫,张雅娇,黄玉山,胡正正,王庆,张志辉. 选区激光熔化304L不锈钢的组织结构及力学性能分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1615-1621. |
| [5] | 李明,王浩然,赵唯坚. 带抗剪键叠合板的力学性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1509-1520. |
| [6] | 徐戊矫,刘承尚,鲁鑫垚. 喷丸处理后6061铝合金工件表面粗糙度的模拟计算及预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1280-1287. |
| [7] | 李于朋,孙大千,宫文彪. 6082⁃T6铝合金薄板双轴肩搅拌摩擦焊温度场[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 836-841. |
| [8] | 关庆丰,张福涛,彭韬,吕鹏,李姚君,许亮,丁佐军. 含硼、钴9%Cr耐热钢的热变形行为[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1799-1805. |
| [9] | 姜秋月,杨海峰,檀财旺. 22MnB5超高强钢焊接接头强化性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1806-1810. |
| [10] | 庄蔚敏, 赵文增, 解东旋, 李兵. 超高强钢/铝合金热铆连接接头性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1016-1022. |
| [11] | 关庆丰, 董书恒, 郑欢欢, 李晨, 张从林, 吕鹏. 强流脉冲电子束作用下45#钢表面Cr合金化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1161-1168. |
| [12] | 赵宇光, 杨雪慧, 徐晓峰, 张阳阳, 宁玉恒. Al-10Sr变质剂状态、变质温度及变质时间对ZL114A合金组织的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 212-220. |
| [13] | 汤华国, 马贤锋, 赵伟, 刘建伟, 赵振业. 高性能金属铝的制备、微观结构及其热稳定性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1542-1547. |
| [14] | 关庆丰, 张远望, 孙潇, 张超仁, 吕鹏, 张从林. 强流脉冲电子束作用下铝钨合金的表面合金化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(4): 1171-1178. |
| [15] | 杨晓红, 杭文先, 秦绍刚, 刘勇兵, 刘利萍. H13钢激光熔覆钴基复合涂层的组织及耐磨性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 891-899. |
|
||