吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 303-313.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20190939
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
结合残差网络及目标掩膜的人脸微表情识别
- 1.长春理工大学 计算机科学技术学院,长春 130022
2.长春理工大学 人工智能学院,长春 130022
Face micro-expression recognition based on ResNet with object mask
Ming FANG1,2( ),Wen-qiang CHEN1
),Wen-qiang CHEN1
- 1.College of Computer Science and Technology,Changchun University of Science and Technology,Changchun 130022,China
2.College of Artificial Intelligence,Changchun University of Science and Technology,Changchun 130022,China
摘要:
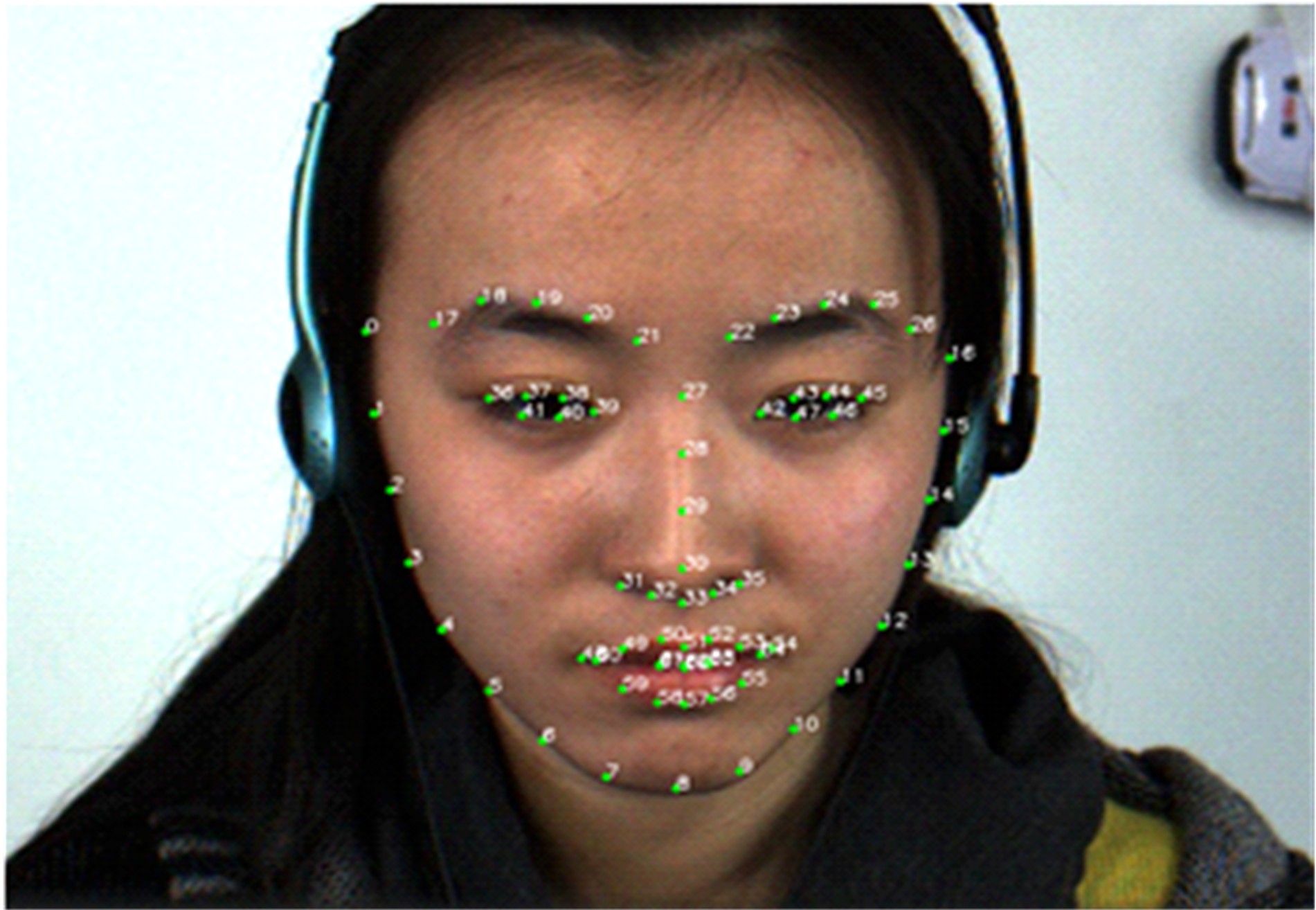
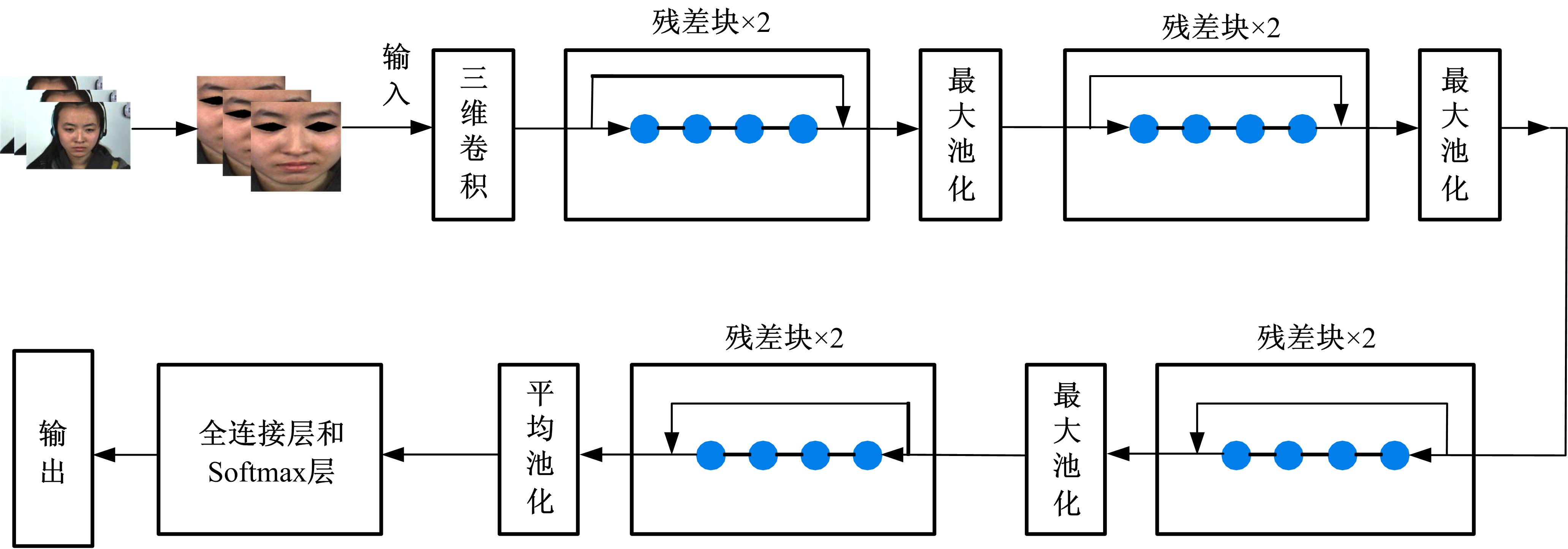
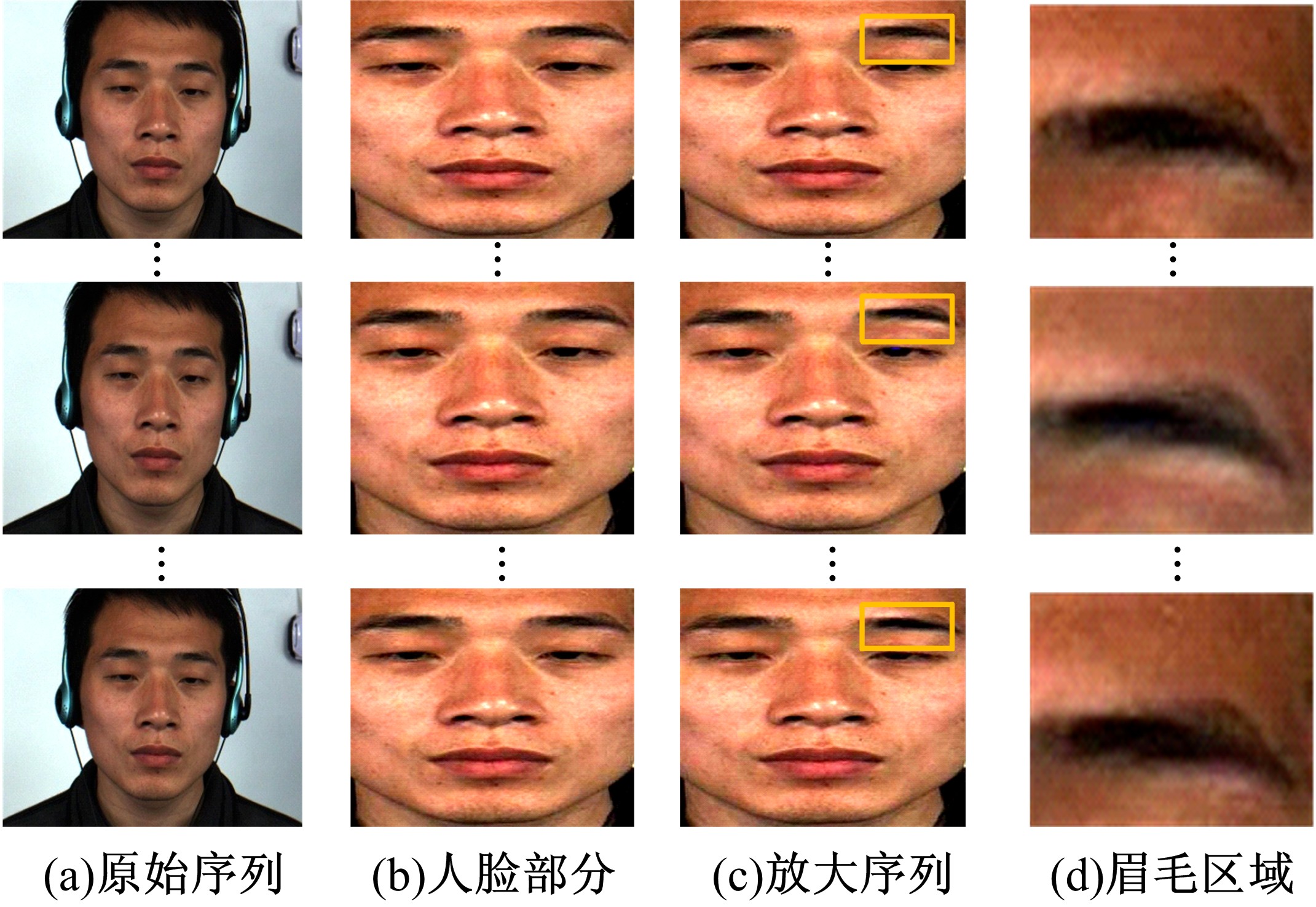
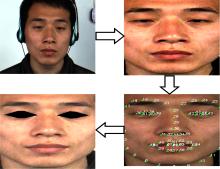
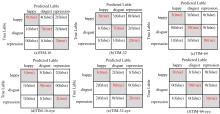
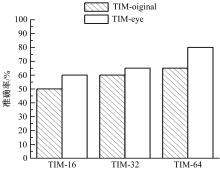
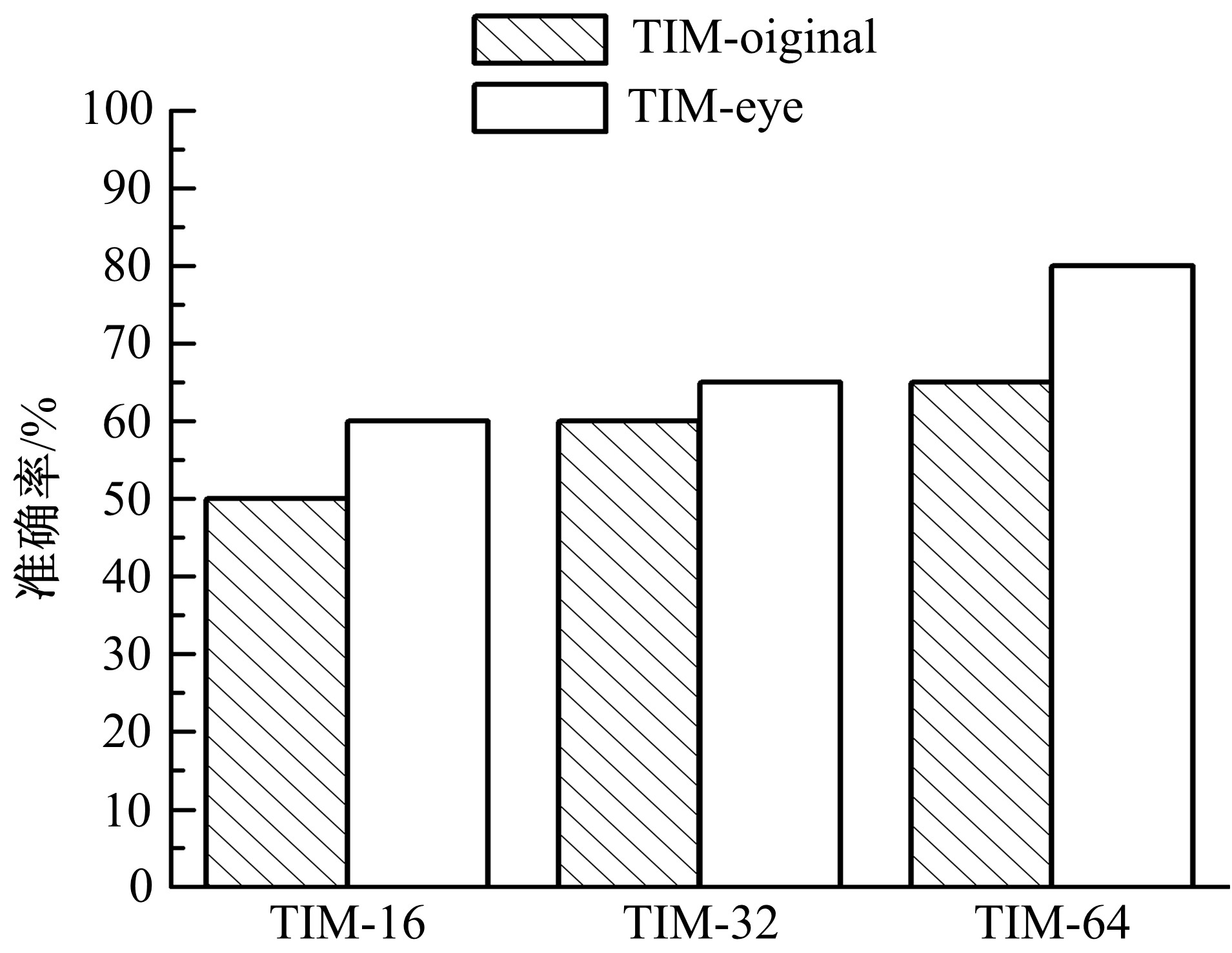
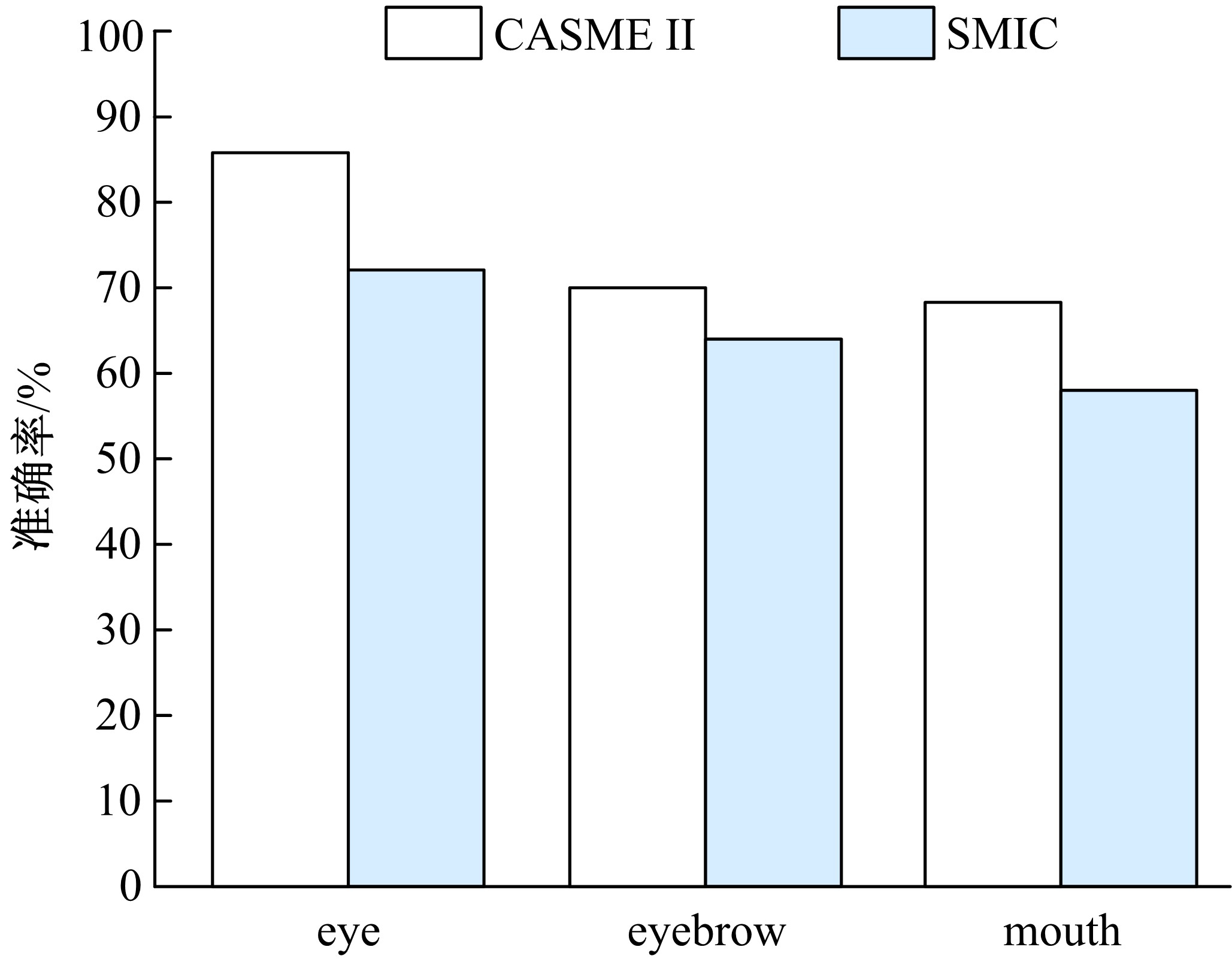
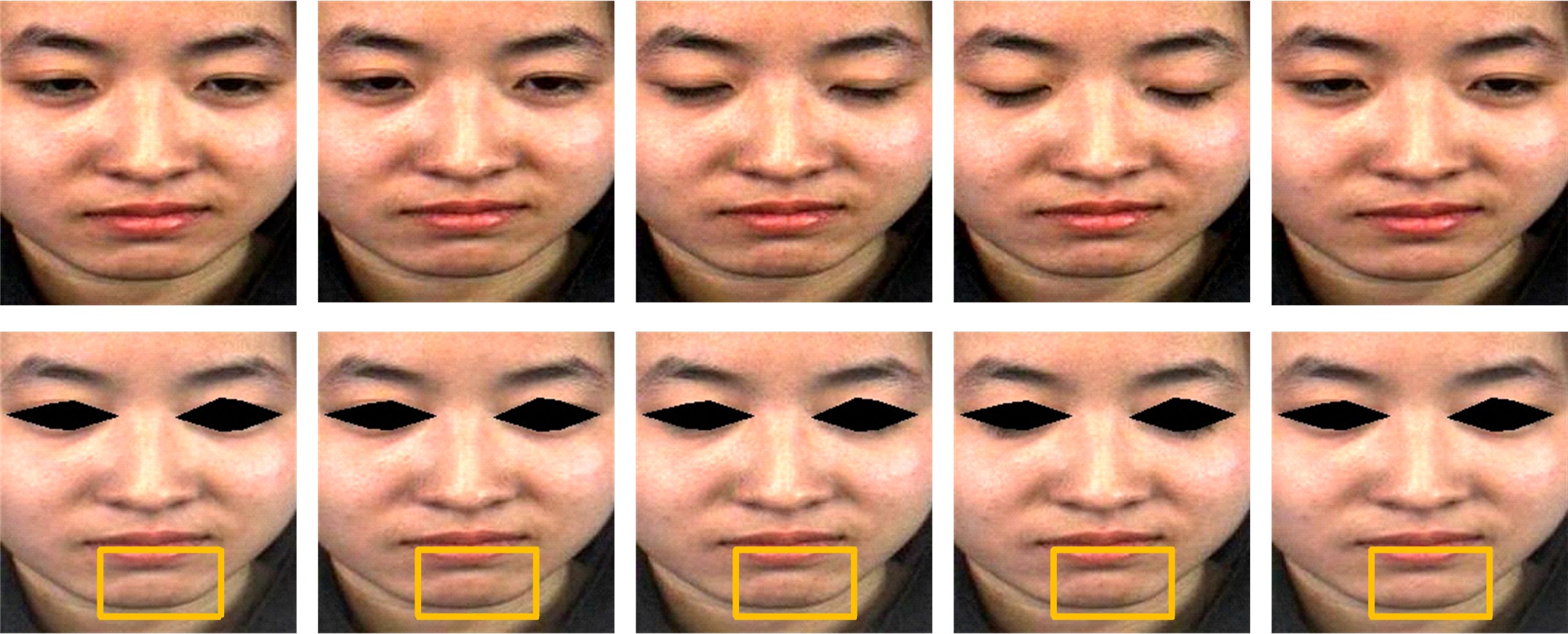
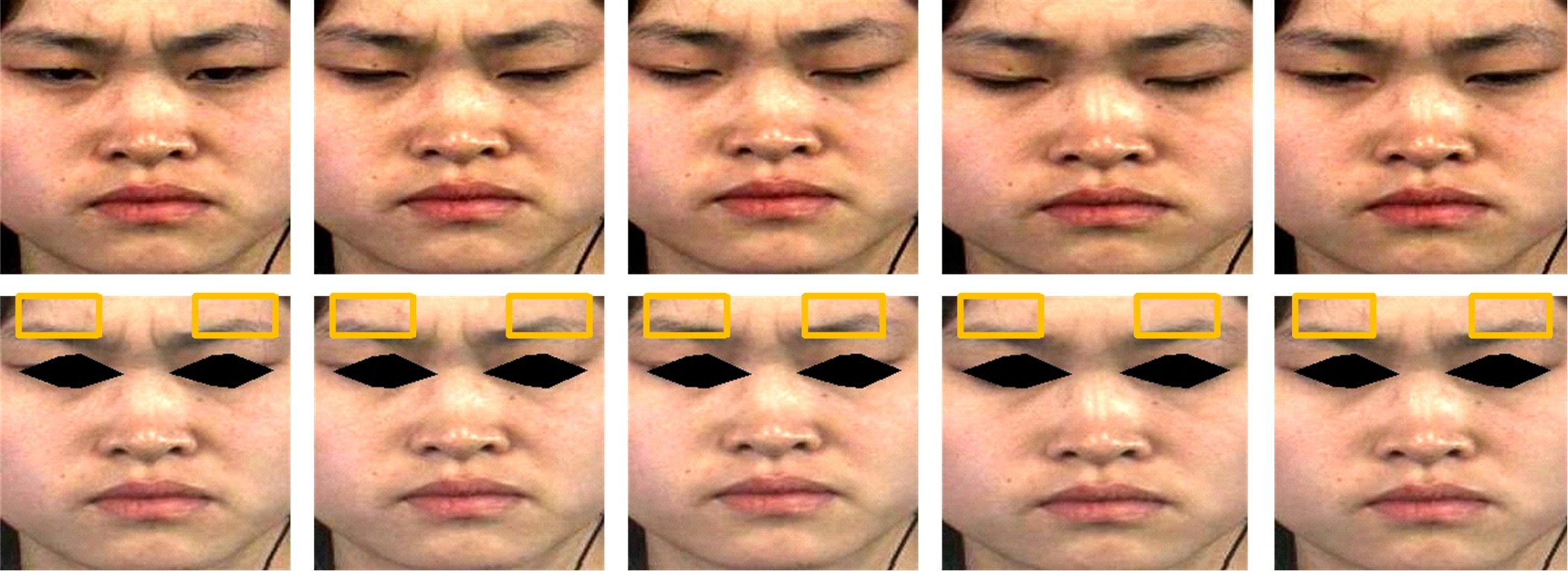
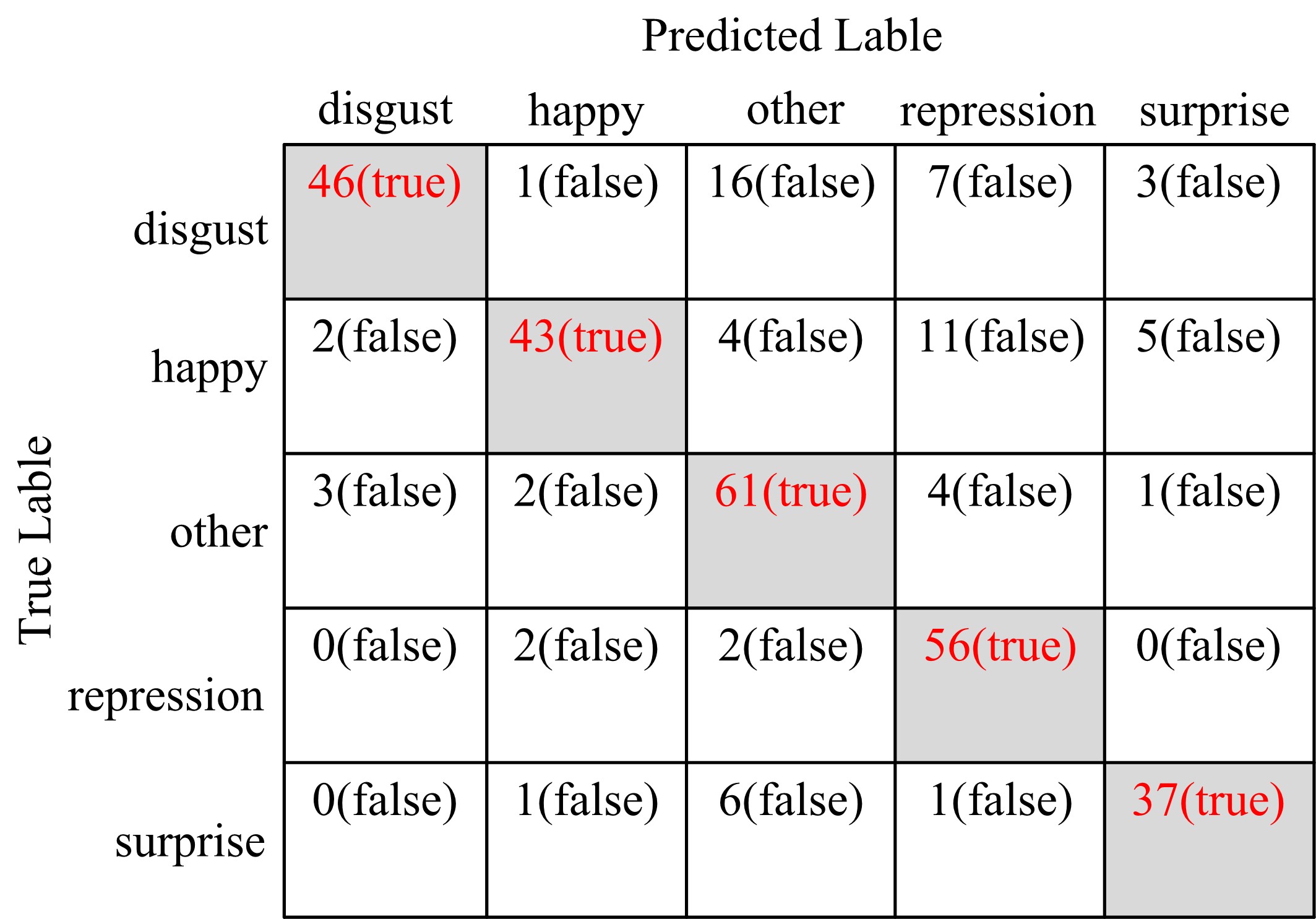
微表情是一种能反映隐藏在人内心最真实情感状态的面部特征,现有的微表情识别技术经常会提取一些与微表情无关的运动特征信息干扰情感的真实性识别。为解决上述问题,提出一种结合残差网络及目标掩膜的特征提取方法。本文首先对原始的微表情序列进行一系列预处理,定位人眼的关键区域,对眼部区域进行图像掩膜,进而减少眨眼动作对微表情特征提取造成的干扰,然后使用欧拉视频放大算法对人脸微表情变化的关键区域进行放大,使得微表情变化更为明显,最后通过3D ResNet网络对连续的微表情序列进行训练和识别。本文方法在CASME II和SMIC数据集上进行了测试,准确率分别达到77.3%和72.4%,与最新方法DSSN、CNN+LSTM等相比,准确率至少提高5%。
中图分类号:
- TP391.4
| 1 | Wu Q, Shen X, Fu X. Micro-expression and its applications[J]. Advances in Psychological Science, 2010, 18(9): 1359-1368. |
| 2 | Pfister T, Li X, Zhao G, et al. Recognising spontaneous facial micro-expressions[C]∥International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 2011: 1449-1456. |
| 3 | Shen X B, Wu Q, Fu X L. Effects of the duration of expressions on the recognition of micro-expressions[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University Science B:Biomedicine & Biotechnology, 2012, 13(3): 221-230. |
| 4 | Yan W J, Wu Q, Liang J, et al. How fast are the leaked facial expressions: the duration of micro-expressions[J]. Journal of Nonverbal Behavior, 2013, 37(4): 217-230. |
| 5 | Russell T A, Chu E, Phillips M L. A pilot study to investigate the effectiveness of emotion recognition remediation in schizophrenia using the micro-expression training tool[J]. British Journal of Clinical Psychology, 2006, 45(4): 579-583. |
| 6 | 贲晛烨, 杨明强, 张鹏, 等. 微表情自动识别综述[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2014, 26(9): 1385-1395. |
| Xian-ye Ben, Yang Ming-qiang, Zhang Peng, et al. Survey on automatic micro expression recognition methods[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2014, 26(9): 1385-1395. | |
| 7 | Zhao G, Pietikainen M. Dynamic texture recognition using local binary patterns with an application to facial expressions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2007, 29(6): 915-928. |
| 8 | Wang Y, See J, Phan W, et al. LBP with six intersection points: Reducing redundant information in LBP-TOP for micro-expression recognition[C]∥Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Singapore, 2015: 525-537. |
| 9 | Huang X H, Wang S J, Zhao G Y, et al. Facial micro-expression recognition using spatiotemporal local binary pattern with integral projection[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops(ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1-9. |
| 10 | Li X, Hong X, Moilanen A, et al. Towards reading hidden emotions: a comparative study of spontaneous micro-expression spotting and recognition methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2018, 9(4): 563-577. |
| 11 | Ben X, Zhang P, Yan R, et al. Gait recognition and micro-expression recognition based on maximum margin projection with tensor representation[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2016, 27(8): 2629-2646. |
| 12 | Liu Y J, Zhang J K, Yan W J, et al. A main directional mean optical flow feature for spontaneous micro-expression recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2016, 7(4): 299-310. |
| 13 | Happy S L, Routray A. Fuzzy histogram of optical flow orientations for micro-expression recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2017, 10(3): 394-406. |
| 14 | Kim D H, Baddar W J, Ro Y M. Micro-Expression recognition with expression-state constrained spatio-temporal feature representations[C]∥Proceedings of the ACM on Multimedia Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 382-386. |
| 15 | Li J, Wang Y, See J, et al. Micro-expression recognition based on 3D flow convolutional neural network[J]. Pattern Analysis and Applications, 2019, 22(4): 1331-1339. |
| 16 | Khor H Q, See J, Liong S T, et al. Dual-stream shallow networks for facial Micro-expression recognition[C]∥ IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Taipei,China, 2019: 36-40. |
| 17 | Zhou Z, Zhao G, Guo Y, et al. An image-based visual speech animation system[J]. IEEE Trans on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2012, 22(10): 1420-1432. |
| 18 | Wu H Y, Rubinstein M, Shih E, et al. Eulerian video magnification for revealing subtle changes in the world[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2012, 31(4): 1-8. |
| 19 | Cohn J F, Ambadar Z, Ekman P. Observer-based measurement of facial expression with the facial action coding system[J]. Neuroscience Letters, 2007, 394(3): 203-221. |
| 20 | Kazemi V, Josephine S. One millisecond face alignment with an ensemble of regression trees[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 2014: 1867-1874. |
| 21 | He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016: 770-778. |
| 22 | Li Y, Huang X, Zhao G. Can micro-expression be recognized based on single apex frame?[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Image Processing(ICIP), Athens, Greece, 2018: 3094-3098. |
| 23 | Yan W J, Li X, Wang S J, et al. CASME II: an improved spontaneous micro-expression database and the baseline evaluation[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(1): e86041. |
| 24 | Li X, Pfister T, Huang X, et al. A spontaneous micro-expression database: Inducement, collection and baseline[C]∥IEEE International Conference and Workshops on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG), Shanghai, China, 2013: 1-6. |
| 25 | Pfister T, Li X, Zhao G, et al. Recognising spontaneous facial micro-expressions[C]∥International Computer on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 2011: 1449-1456. |
| 26 | Huang X, Zhao G, Hong X, et al. Spontaneous facial micro-expression analysis using spatiotemporal completed local quantized patterns[J]. Neurocomputing, 2016, 175: 564-578. |
| 27 | Liong S T, See J, Wong K, et al. Less is more: Micro-expression recognition from video using apex frame[J]. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2018, 62: 82-92. |
| 28 | Ben X, Jia X, Yan R, et al. Learning effective binary descriptors for micro-expression recognition transferred by macroinformation[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2018, 107: 50-58. |
| [1] | 王小玉,胡鑫豪,韩昌林. 基于生成对抗网络的人脸铅笔画算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 285-292. |
| [2] | 车翔玖,董有政. 基于多尺度信息融合的图像识别改进算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1747-1754. |
| [3] | 周炳海,何朝旭. 基于线边集成超市的混流装配线动态物料配送调度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1809-1817. |
| [4] | 蒋磊,管仁初. 基于多目标进化算法的人才质量模糊综合评价系统设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1856-1861. |
| [5] | 李阳,李硕,井丽巍. 基于贝叶斯模型与机器学习算法的金融风险网络评估模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1862-1869. |
| [6] | 赵宏伟,刘晓涵,张媛,范丽丽,龙曼丽,臧雪柏. 基于关键点注意力和通道注意力的服装分类算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1765-1770. |
| [7] | 管乃彦,郭娟利. 基于姿态估计算法的组件感知自适应模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1850-1855. |
| [8] | 刘洲洲,尹文晓,张倩昀,彭寒. 基于离散优化算法和机器学习的传感云入侵检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 692-702. |
| [9] | 王晓辉,吴禄慎,陈华伟. 基于法向量距离分类的散乱点云数据去噪[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 278-288. |
| [10] | 张笑东,夏筱筠,吕海峰,公绪超,廉梦佳. 大数据网络并行计算环境中生理数据流动态负载均衡[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 247-254. |
| [11] | 金顺福,郄修尘,武海星,霍占强. 基于新型休眠模式的云虚拟机分簇调度策略及性能优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 237-246. |
| [12] | 陈蔓,钟勇,李振东. 隐低秩结合低秩表示的多聚焦图像融合[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 297-305. |
| [13] | 邓钧忆,刘衍珩,冯时,赵荣村,王健. 基于GSPN的Ad⁃hoc网络性能和安全平衡[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 255-261. |
| [14] | 王铁君,王维兰. 基于本体的唐卡图像标注方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 289-296. |
| [15] | 李雄飞,王婧,张小利,范铁虎. 基于SVM和窗口梯度的多焦距图像融合方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 227-236. |
|
||