吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 1496-1505.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200334
• 通信与控制工程 • 上一篇
基于地形聚类分析的移动机器人速度自适应控制
刘明1,2( ),荣学文1(
),荣学文1( ),李贻斌1,张帅帅2,尹燕芳2,阮久宏3
),李贻斌1,张帅帅2,尹燕芳2,阮久宏3
- 1.山东大学 控制科学与工程学院,济南 250061
2.山东科技大学 电气与自动化学院,济南 250031
3.山东交通学院 轨道交通学院,济南 250351
Speed adaptive control of mobile robot based on terrain clustering analysis
Ming LIU1,2( ),Xue-wen RONG1(
),Xue-wen RONG1( ),Yi-bin LI1,Shuai-shuai ZHANG2,Yan-fang YIN2,Jiu-hong RUAN3
),Yi-bin LI1,Shuai-shuai ZHANG2,Yan-fang YIN2,Jiu-hong RUAN3
- 1.College of Control Science and Engineering,Shandong University,Jinan 250061,China
2.College of Electrical Engineering and Automation,Shandong University of Science and Technology,Jinan 250031,China
3.School of Rail Transportation,Shandong Jiaotong University,Jinan 250351,China
摘要:
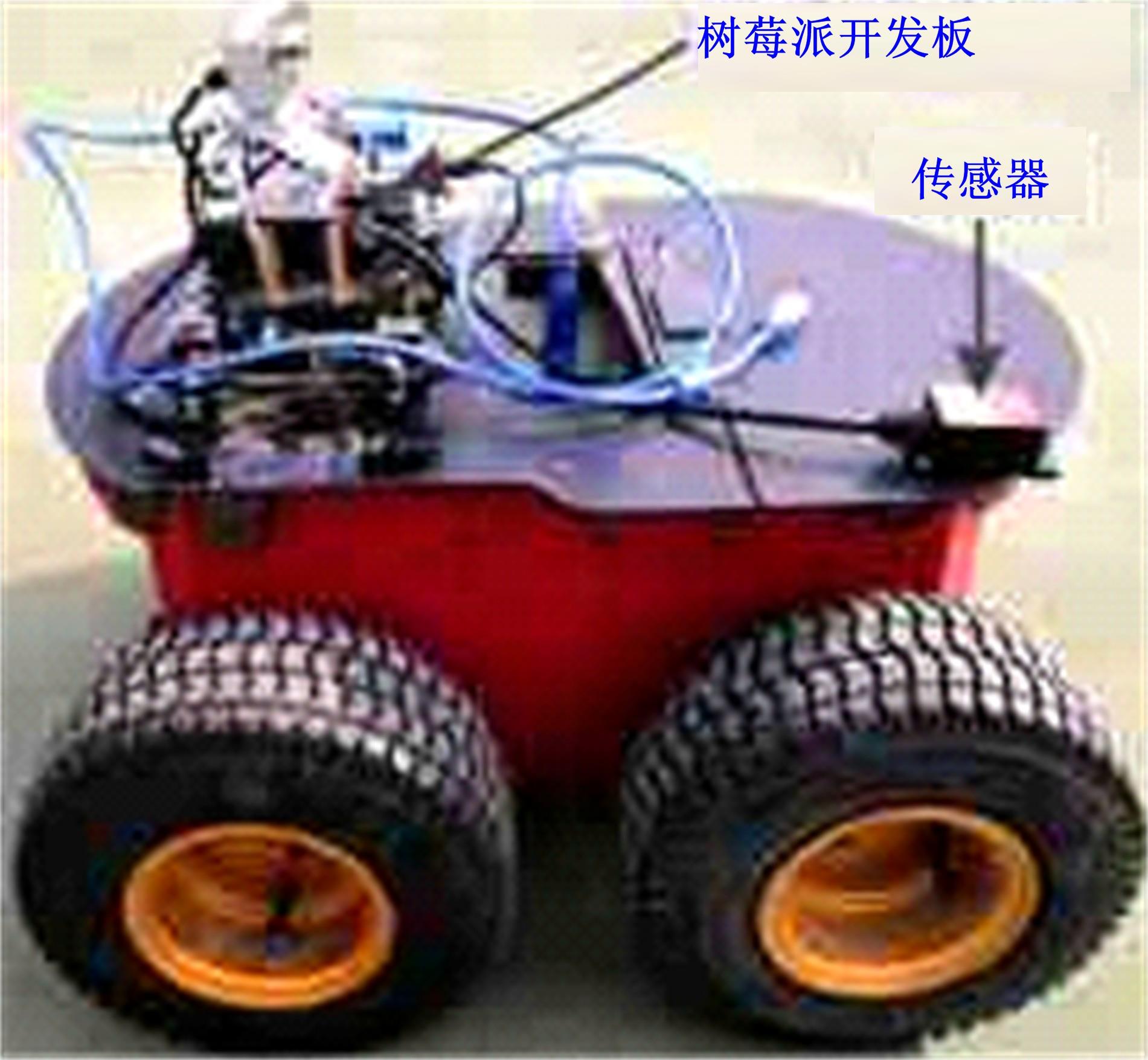
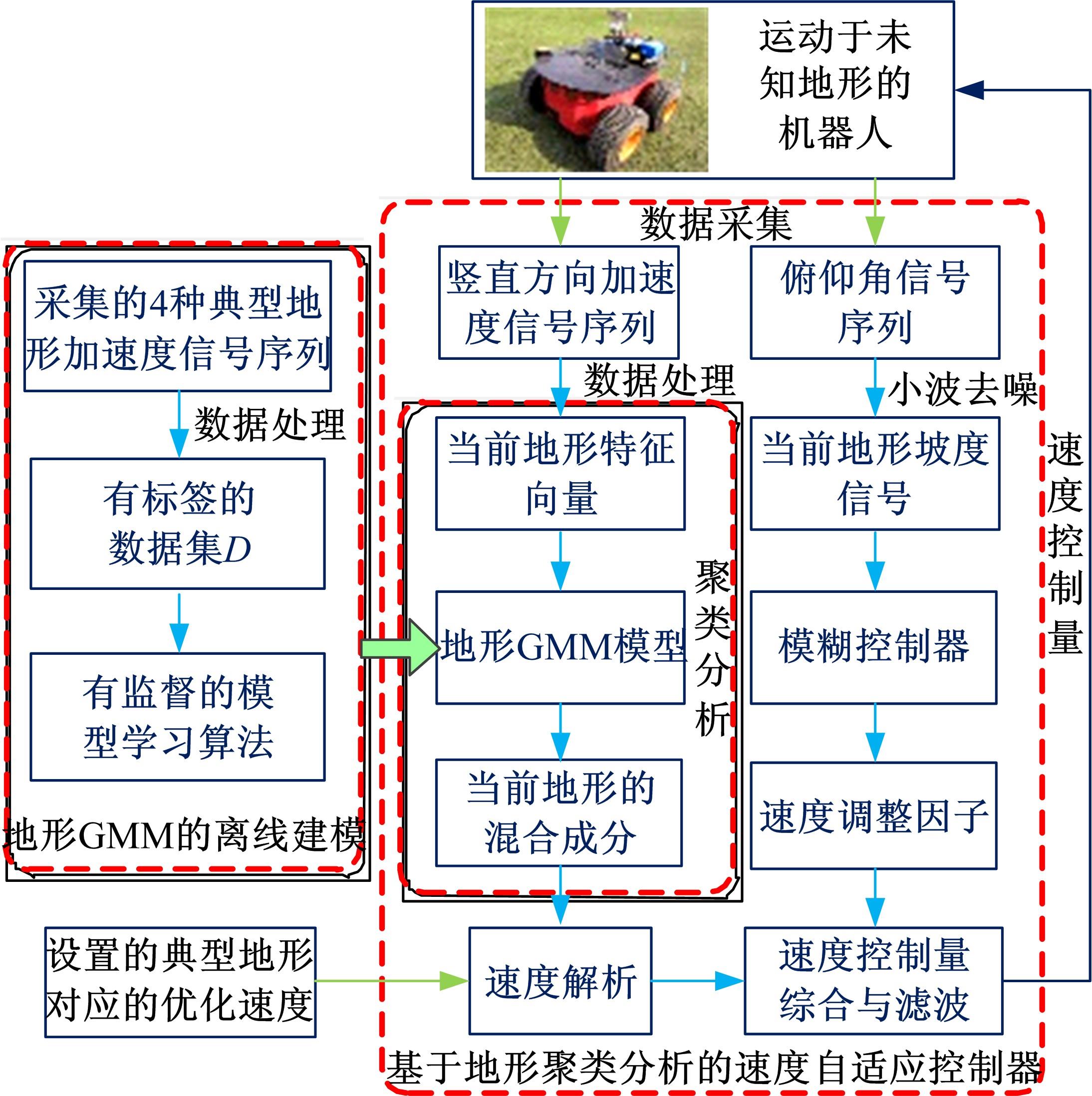
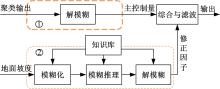
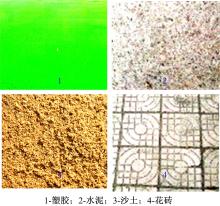
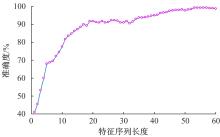
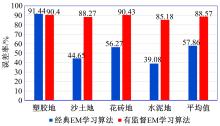
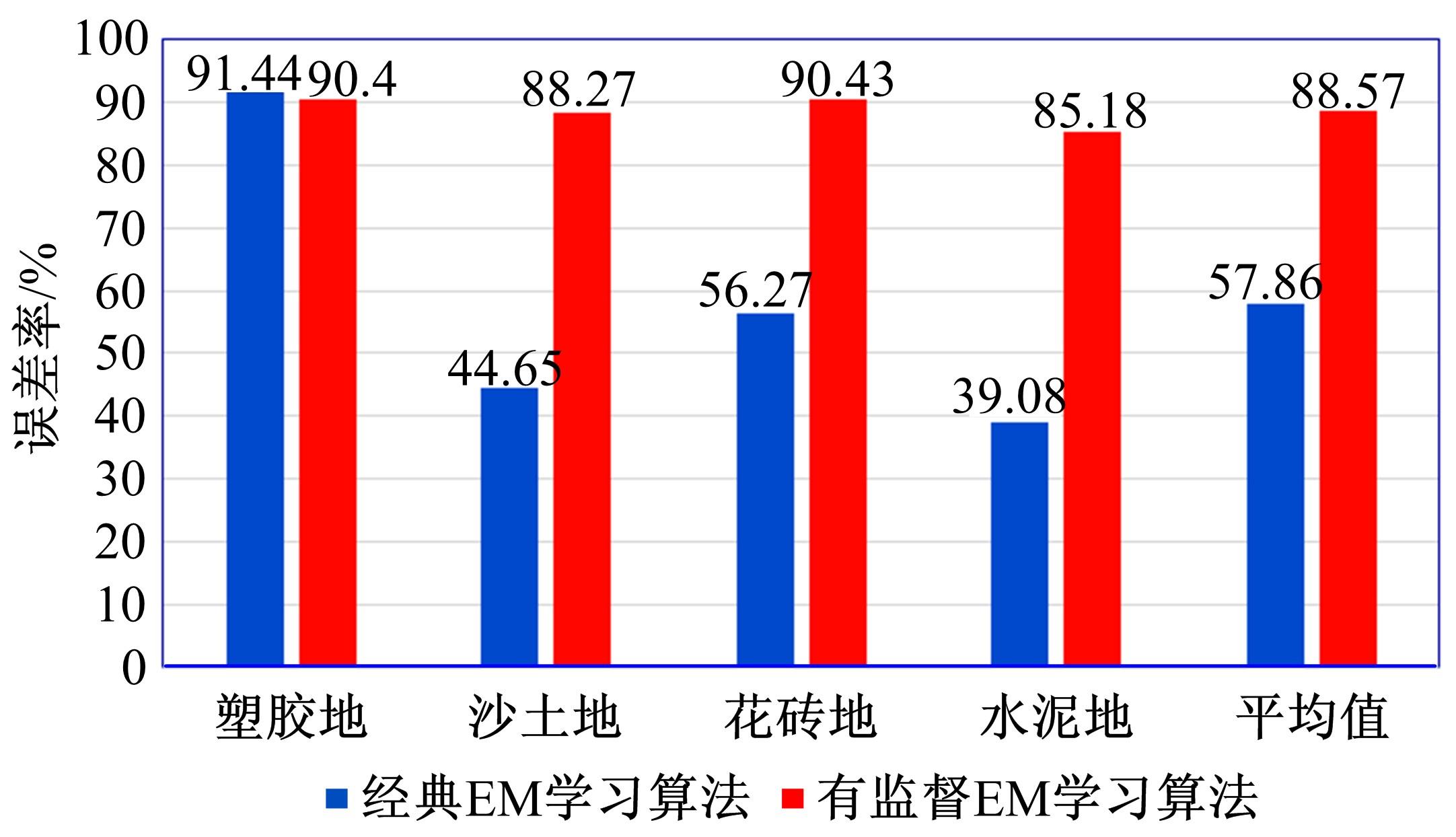
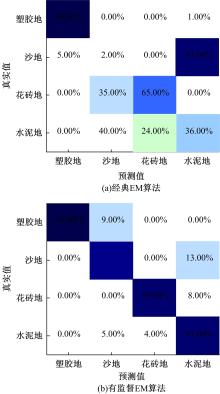
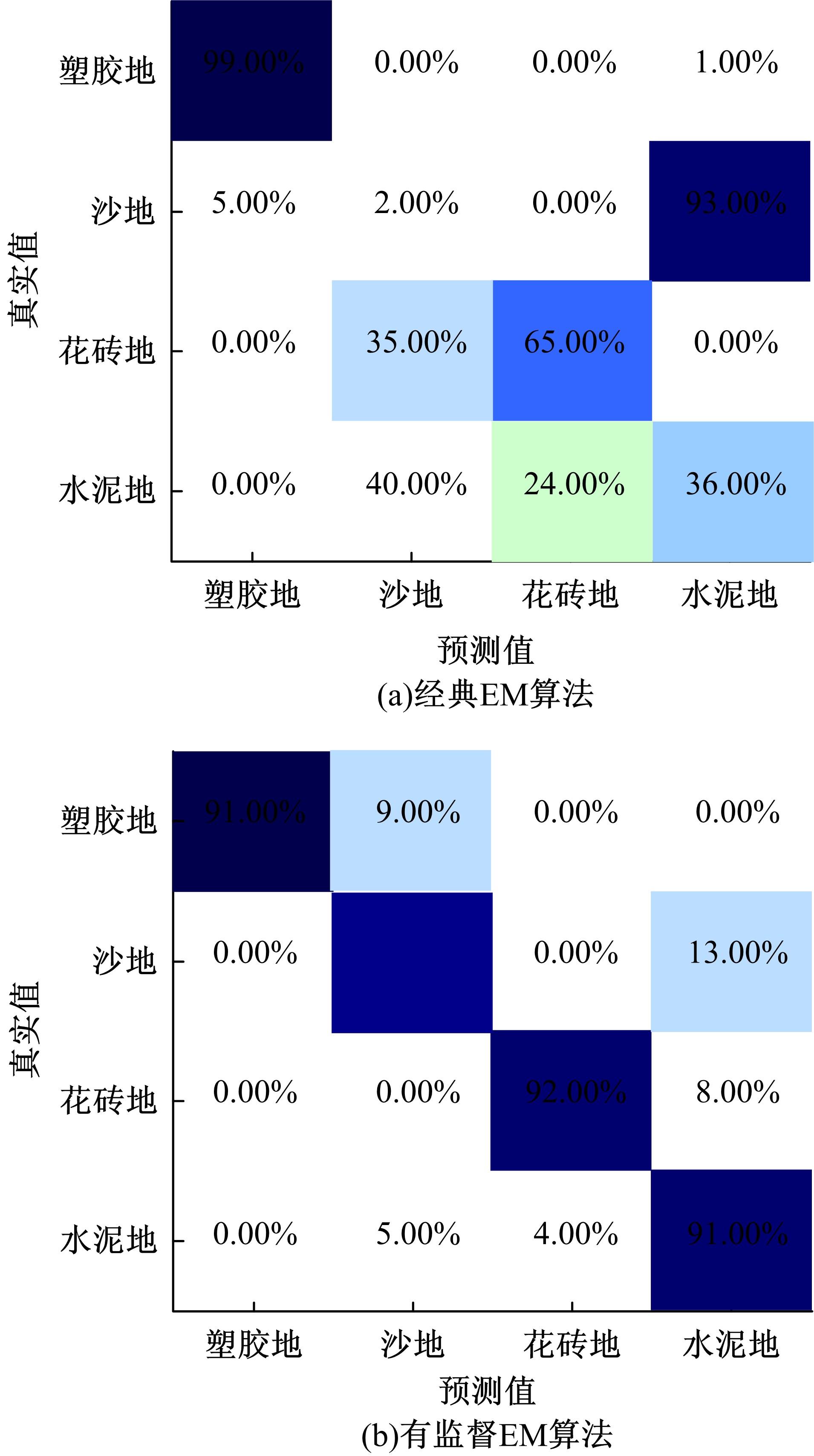
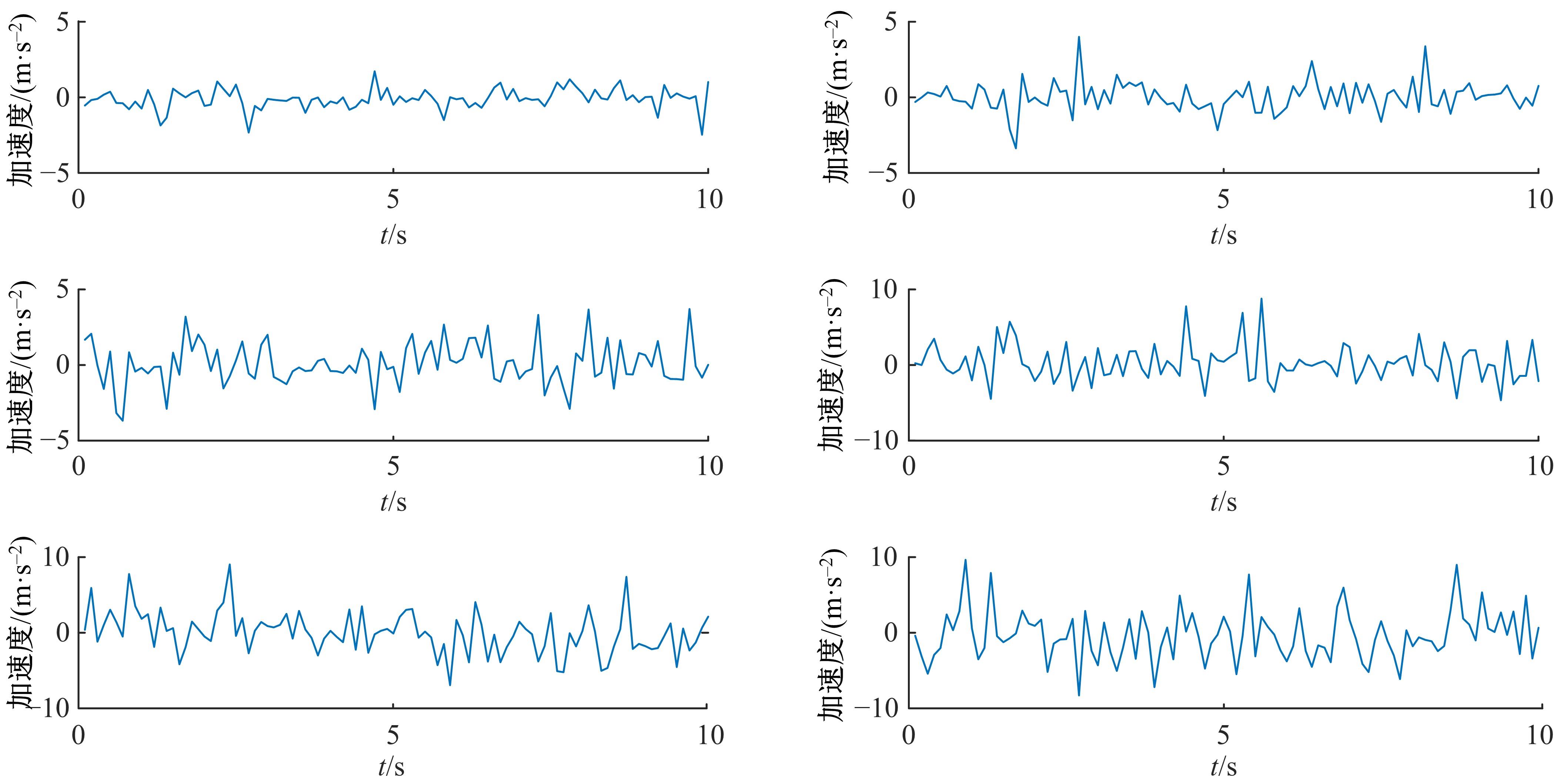
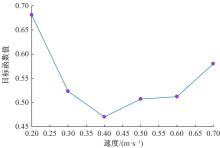
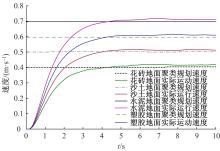
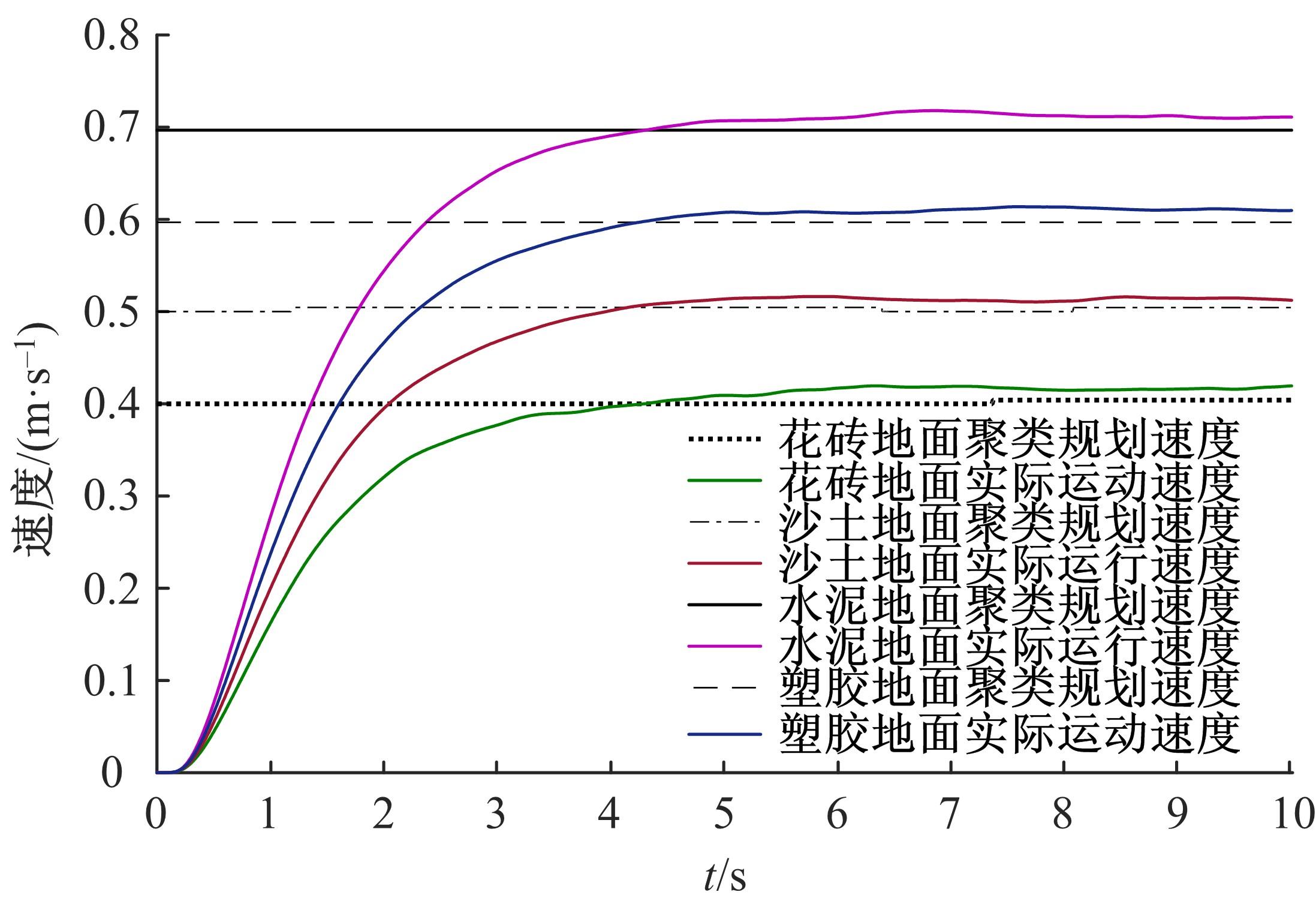
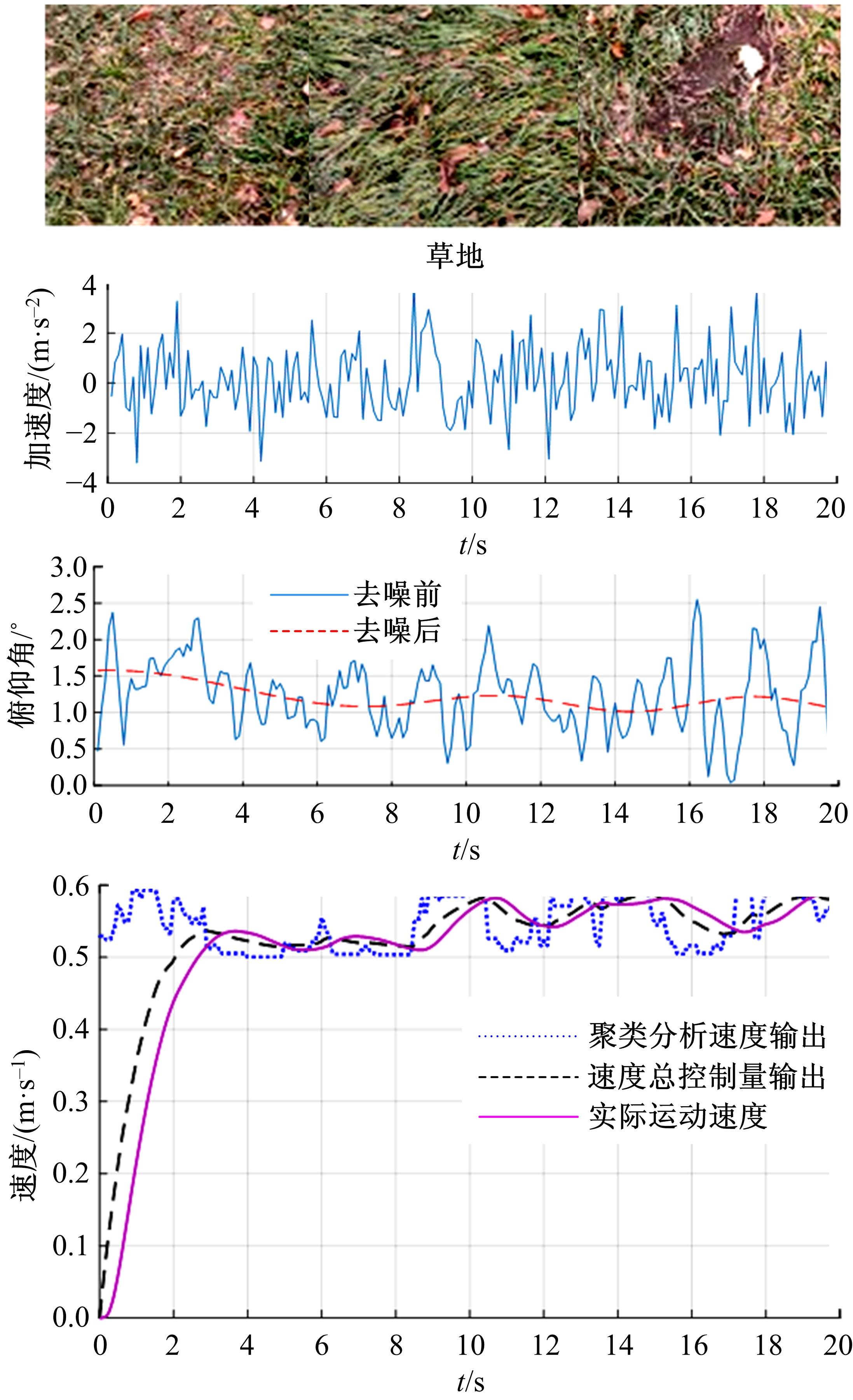
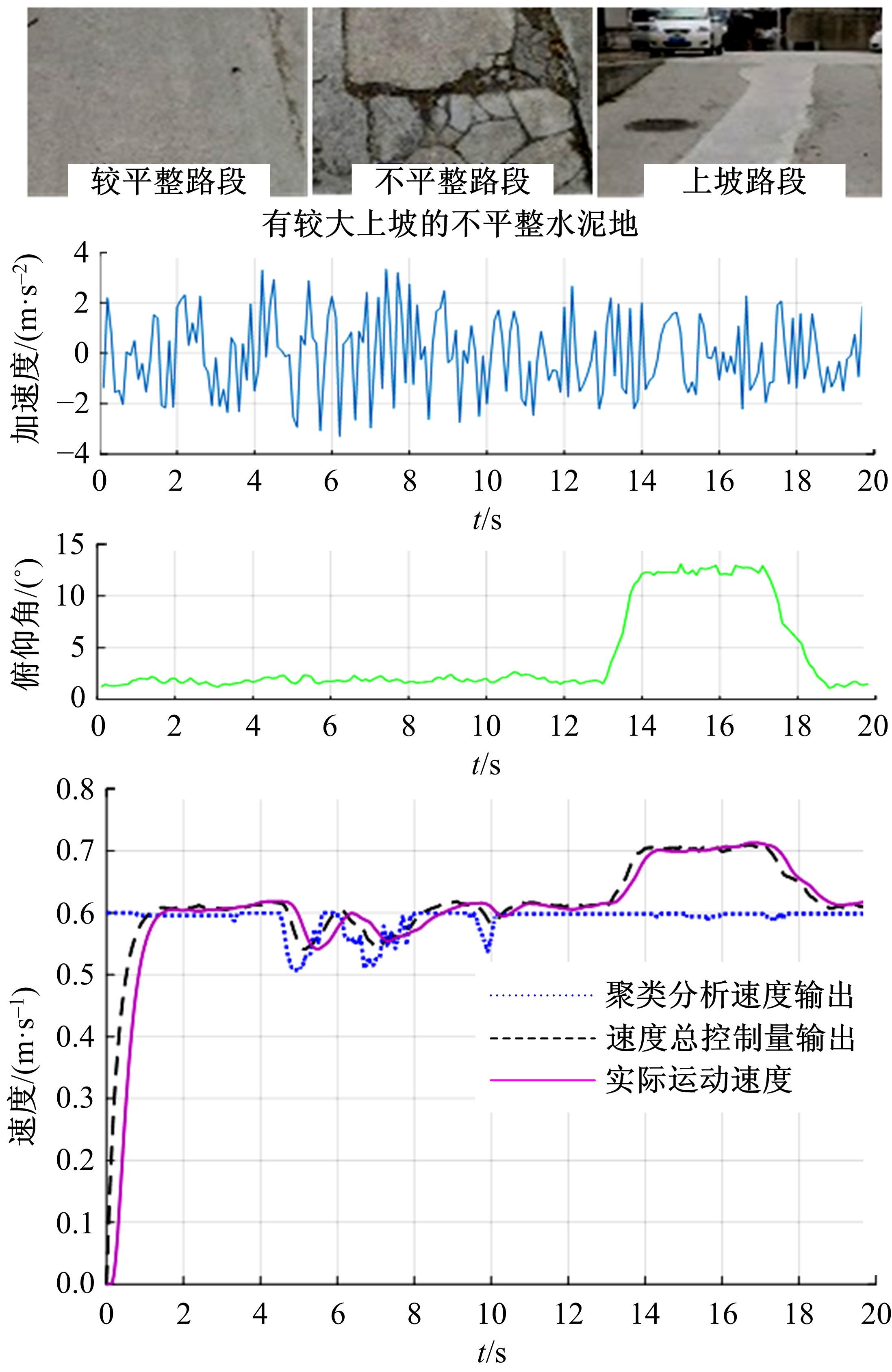
为实现移动机器人在不同地形环境中的速度自适应调整,提出一种利用机器人自身振动信息进行地形聚类分析并根据聚类结果进行运动速度自适应调整的方法。该方法基于机器人在运动过程中竖直方向的加速度信息及俯仰角信息,采用改进的高斯混合模型进行聚类分析,获得该地形相对于典型地形的隶属度,并结合地面的坡度起伏信息,通过模糊控制策略实现了机器人运动速度的自适应控制。为验证本文方法的正确性和实用性,利用Pioneer 3-AT四轮驱动全地形机器人平台进行了相关实验,实验结果表明,本文方法可使机器人准确地对不同地形进行聚类分析并实现了其在不同地形环境下的速度自适应调整,有效增强了机器人的地形适应性。
中图分类号:
- TP242
| 1 | Matos-Carvalho J P, Fonseca J M, Mora A, et al. UAV downwash dynamic texture features for terrain classification on autonomous navigation[C]∥Proceedings of the Federated Conference on Computer Science and Information Systems,Poznan,Poland,2018: 1079-1083. |
| 2 | Chen Y, Zhang P F, Wang S F, et al. Image feature based machine learning approach for road terrain classification[C]∥Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation,Changchun, China, 2018: 2097-2102. |
| 3 | Vandapel N, Huber D F, Kapuria A, et al. Natural terrain classification using 3-D ladar data[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation(ICRA), Piscataway, USA, 2004: 5117-5122. |
| 4 | Yan W Y, Shaker A, El-Ashmawy N. Urban land cover classification using airborne LiDAR data: a review [J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2015, 158: 295-310. |
| 5 | Libby J, Stentz A J. Using sound to classify vehicle-terrain interactions in outdoor environments[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Piscataway, USA, 2012: 3559-3566. |
| 6 | Riopelle N, Caspers P, Sofge D. Terrain classification for autonomous vehicles using Bat-Inspired echolocation[C]∥ Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2018. |
| 7 | Iagnemma K, Dubowsky S. Terrain estimation for high-speed rough-terrain autonomous vehicle navigation[C]∥Proc of the International Society for Optical Engineering, Orlando, USA, 2002, 4715: 256-266. |
| 8 | Brooks C A, Iagnemma K. Vibration-based terrain classification for planetary exploration rovers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2005, 21(6): 1185-1190. |
| 9 | Brooks C A, Iagnemma K. Self-supervised terrain classification for planetary surface exploration rovers [J]. Journal of Field Robotics, 2012, 29(3): 445-468. |
| 10 | du Pont E M, Moore C A, Collins J E G, et al. Frequency response method for terrain classification in autonomous ground vehicles[J]. Autonomous Robots2008, 24(4): 337-347. |
| 11 | Jitpakdee R, Maneewarn T. Neural networks terrain classification using inertial measurement unit for an autonomous vehicle[C]∥Proceedings of International Conference on Instrumentation, Control and Information Technology, Tokyo, Japan, 2008: 554-558. |
| 12 | Weiss C, Fröhlich H, Zell A. Vibration-based terrain classification using support vector machines[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Piscataway, USA, 2006: 4429-4434. |
| 13 | Weiss C, Stark M, Zell A. SVMs for vibration-based terrain classification[C]∥Proceedings of the Autonome Mobile Systeme, Kaiserslautern, Germany, 2007: 1-7. |
| 14 | 魏健,张和明,田雷. 基于车轮力信号的地面类型分类算法研究[J].小型内燃机与车辆技术,2016,45(5): 40-47. |
| Wei Jian, Zhang He-ming, Tian Lei. Research of ground type classification algorithm based on wheel force signal [J]. Small Internal Combustion Engine and Vehicle Technique, 2016, 45(5):40-47. | |
| 15 | Weiss C, Tamimi H, Zell A. A combination of vision- and vibration-based terrain classification[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Piscataway, USA, 2008: 2204-2209. |
| 16 | 李强, 薛开, 徐贺,等.基于振动采用支持向量机方法的移动机器人地形分类[J]. 机器人, 2012,34(6): 660-667. |
| Li Qiang, Xue Kai, Xu He, et al. Vibration-based terrain classification for mobile robots using support vector machine[J]. Robot, 2012, 34(6):660-667. | |
| 17 | Ojeda L, Borenstein J, Witus G, et al. Terrain characterization and classification with a mobile robot[J]. Journal of Field Robotics, 2006, 23(2): 103-122. |
| 18 | 周志华. 机器学习[M]. 北京:清华大学出版社,2016. |
| [1] | 于树友,常欢,孟凌宇,郭洋,曲婷. 基于扰动观测器的轮式移动机器人滚动时域路径跟踪控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1097-1105. |
| [2] | 朱才华,孙晓黎,李岩. 站点分类下的城市公共自行车交通需求预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 531-540. |
| [3] | 吴爱国,韩俊庆,董娜. 基于极局部模型的机械臂自适应滑模控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1905-1912. |
| [4] | 王伟,赵健廷,胡宽荣,郭永仓. 基于快速非奇异终端滑模的机械臂轨迹跟踪方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 464-471. |
| [5] | 刘富,安毅,董博,李元春. 基于ADP的可重构机械臂能耗保代价分散最优控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 342-350. |
| [6] | 曲兴田,王学旭,孙慧超,张昆,闫龙威,王宏一. 熔融沉积成型技术3D打印机加热系统的模糊自适应PID控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 77-83. |
| [7] | 马常友, 高海波, 丁亮, 于海涛, 邢宏军, 邓宗全. 机器人末端执行器自更换机构设计及对接策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2027-2037. |
| [8] | 马苗苗,潘军军,刘向杰. 含电动汽车的微电网模型预测负荷频率控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1644-1652. |
| [9] | 于树友,谭雷,王伍洋,陈虹. 基于三步法的汽车主动四轮转向控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 934-942. |
| [10] | 温海营,任翔,徐卫良,丛明,秦文龙,胡书海. 咀嚼机器人颞下颌关节仿生设计及试验测试[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 943-952. |
| [11] | 顾万里,王萍,胡云峰,蔡硕,陈虹. 具有H∞性能的轮式移动机器人非线性控制器设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1811-1819. |
| [12] | 李战东,陶建国,罗阳,孙浩,丁亮,邓宗全. 核电水池推力附着机器人系统设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1820-1826. |
| [13] | 赵爽,沈继红,张刘,赵晗,陈柯帆. 微细电火花加工表面粗糙度快速高斯评定[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1838-1843. |
| [14] | 王德军, 魏薇郦, 鲍亚新. 考虑侧风干扰的电子稳定控制系统执行器故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1548-1555. |
| [15] | 闫冬梅, 钟辉, 任丽莉, 王若琳, 李红梅. 具有区间时变时滞的线性系统稳定性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1556-1562. |
|
||