吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1): 183-190.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20180882
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
掺盐沥青胶浆低温流变及粘附特性
熊锐1,2( ),乔宁1,褚辞1,杨发3,关博文1,2,盛燕萍1,2,牛冬瑜1,2
),乔宁1,褚辞1,杨发3,关博文1,2,盛燕萍1,2,牛冬瑜1,2
- 1. 长安大学 材料科学与工程学院,西安 710061
2. 交通铺面材料教育部工程研究中心,西安 710061
3. 云南省交通投资建设集团有限公司,昆明 650228
Investigation on low-temperature rheology and adhesion properties of salt-doped asphalt mortars
Rui XIONG1,2( ),Ning QIAO1,Ci CHU1,Fa YANG3,Bo-wen GUAN1,2,Yan-ping SHENG1,2,Dong-yu NIU1,2
),Ning QIAO1,Ci CHU1,Fa YANG3,Bo-wen GUAN1,2,Yan-ping SHENG1,2,Dong-yu NIU1,2
- 1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Chang′an University, Xi′an 710061, China
2. Engineering Research Center of Transportation Materials of Ministry of Education, Xi′an 710061, China
3. Yunnan Communications Investment and Construction Group Co. , Ltd. , Kunming 650228, China
摘要:
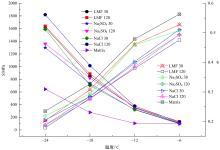
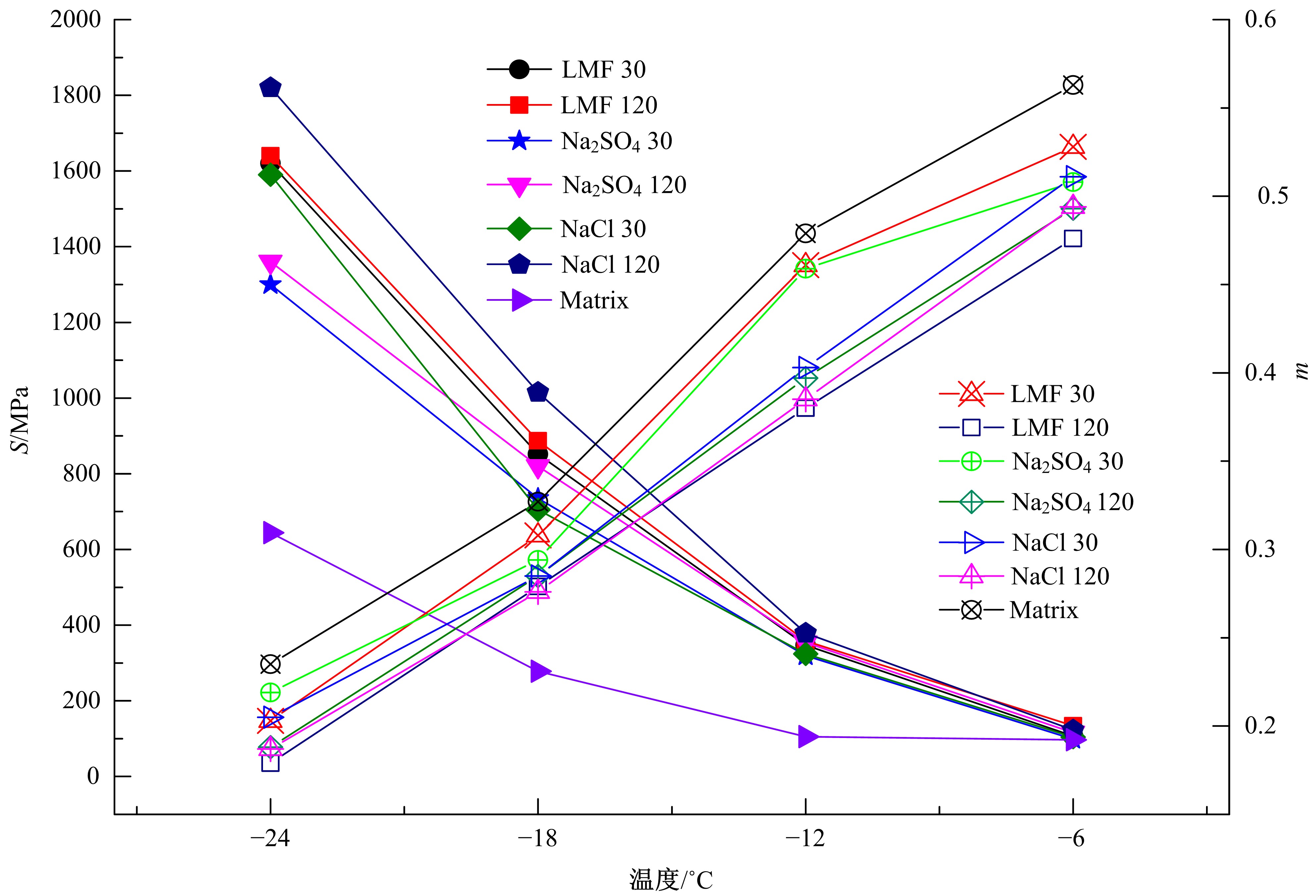
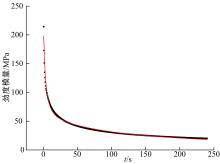
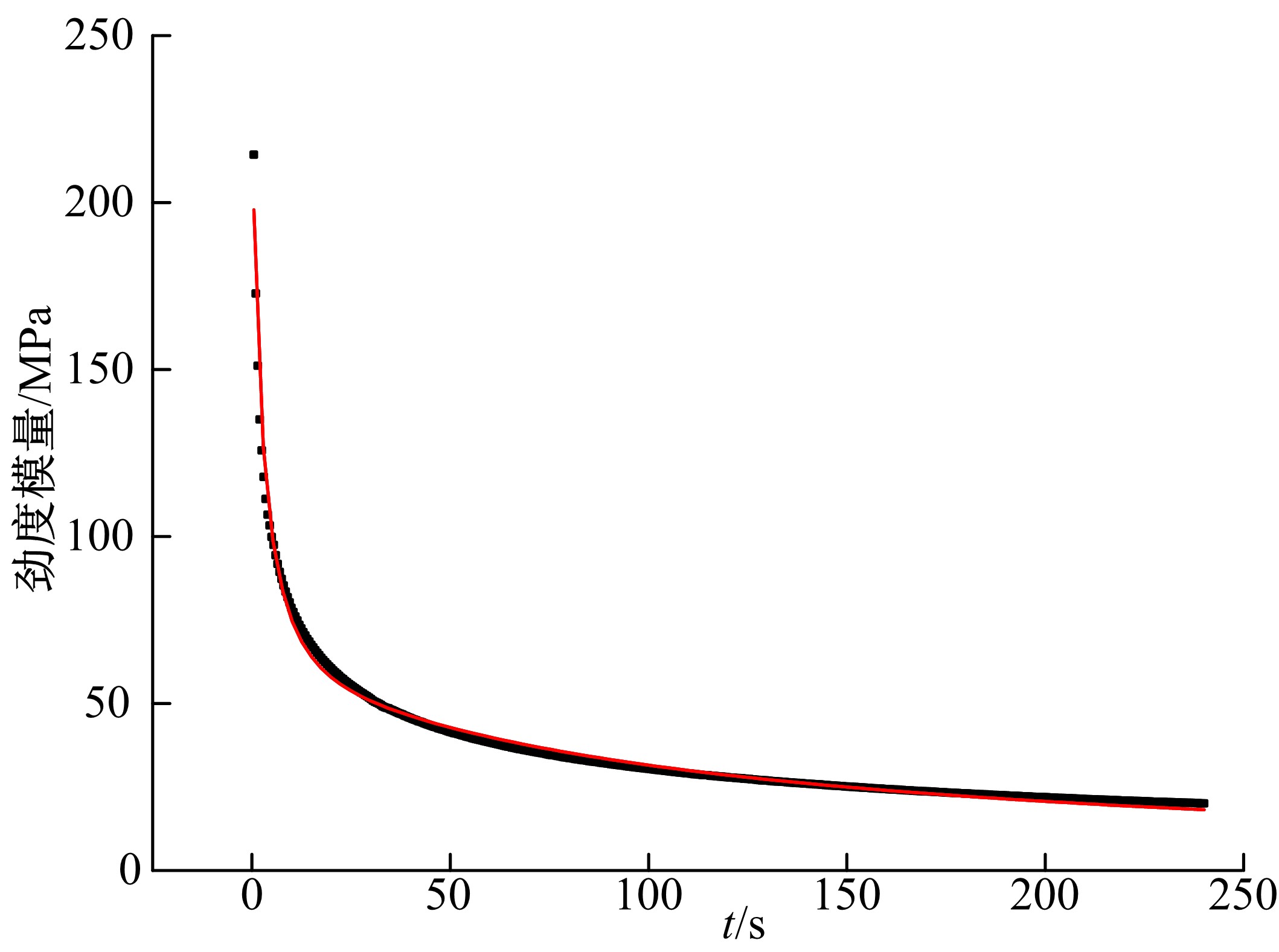
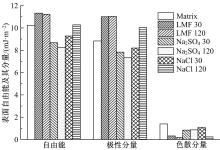
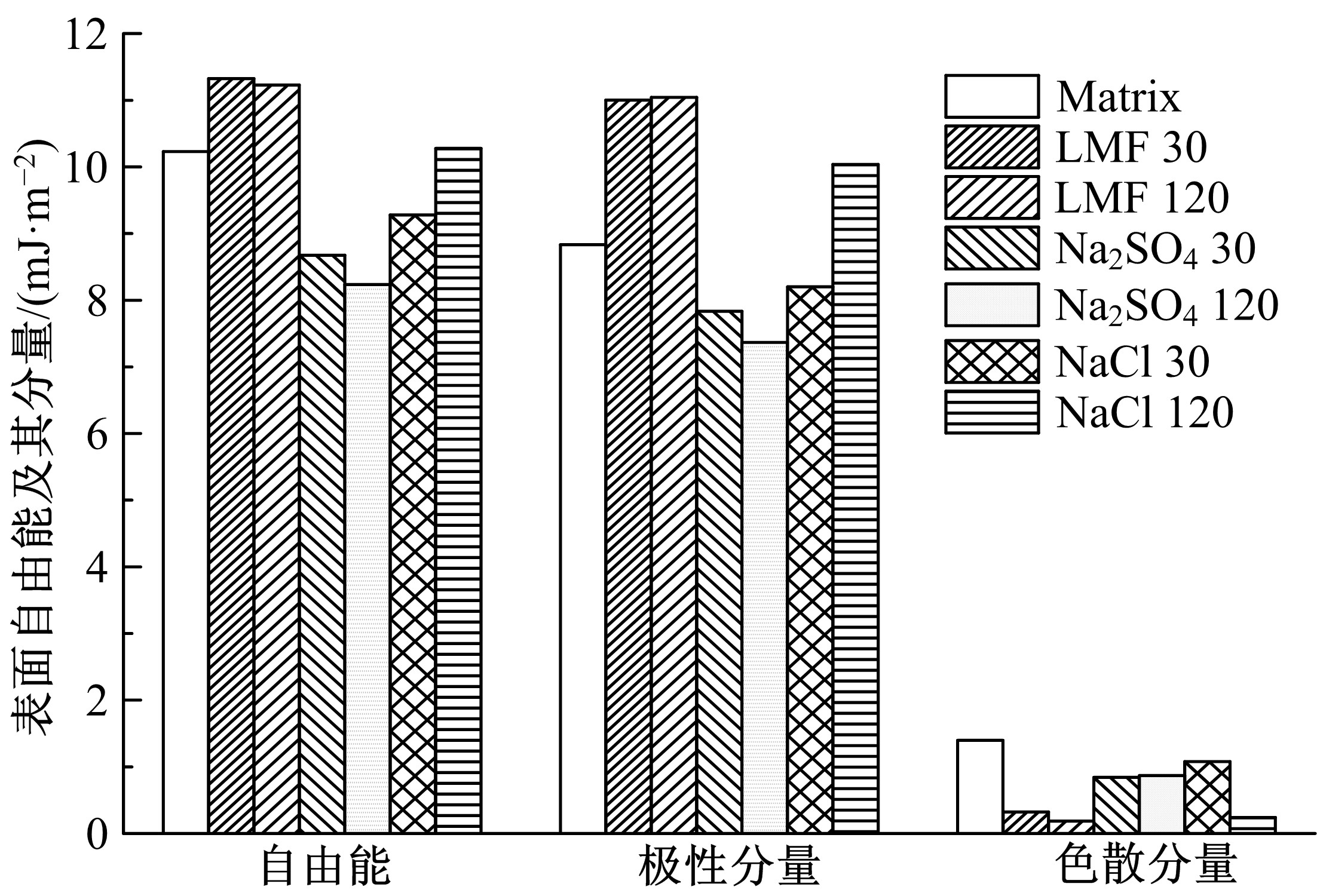
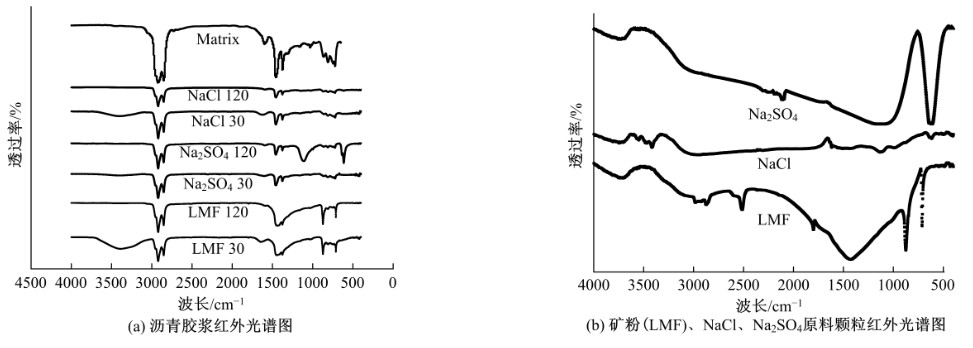
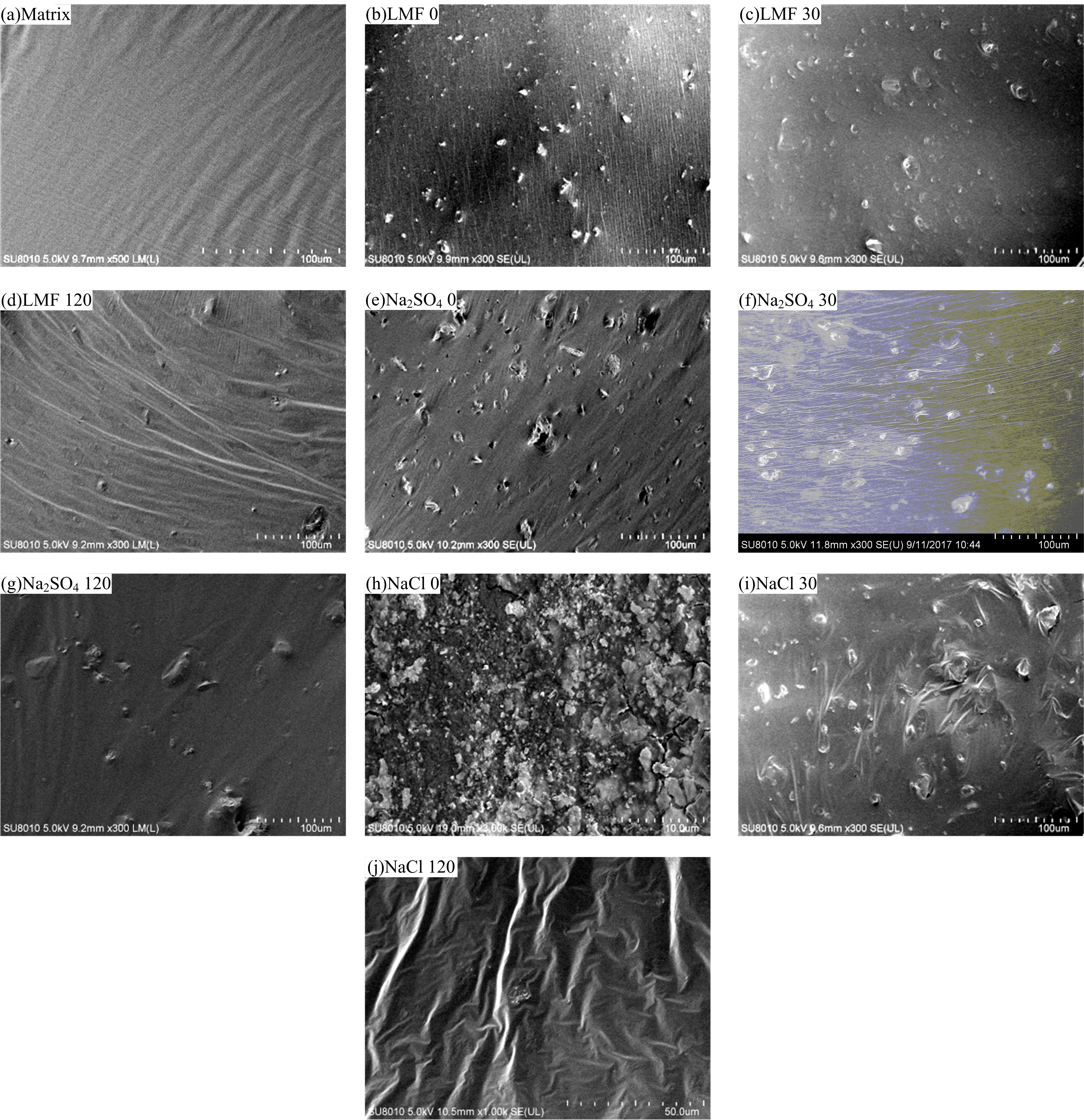
为探究盐分对沥青胶浆低温流变及粘附特性的影响规律,采用盐颗粒以体积比1∶1替代矿粉的沥青胶浆制备方法,通过弯曲梁流变试验(BBR)研究不同掺盐沥青胶浆在30 d与120 d龄期下的低温流变特性,并构建相应的Burgers模型,分析盐分对沥青低温粘弹特性的影响;通过接触角试验,得出沥青表面能参数,评价不同沥青胶浆粘附特性;借助扫描电镜(SEM)和红外光谱(FTIR)手段,探究掺盐沥青胶浆微观作用机理。结果表明:相较于基质沥青,不同种类掺盐沥青胶浆随着龄期的增加,低温流变性能不断降低;经120 d龄期后,沥青接触角明显增大,掺盐沥青胶浆表面能降低,粘附性劣化;盐分颗粒溶析及其盐老化效应,是导致掺盐沥青胶浆性能劣化的主要诱因。
中图分类号:
- U416.217
| 1 | Xiong R , Wang L , Guan B W , et al . Durability prediction of asphalt mixture exposed to sulfate and dry-wet circle erosion environment[J]. International Journal of Pavement Research and Technology, 2015, 8(1): 53-57. |
| 2 | 韩吉伟,崔亚楠,李嘉迪,等 . 盐冻循环条件下改性沥青的细观结构及低温流变性能[J]. 复合材料学报,2016,33(8):1718-1724. |
| Han Ji-wei , Cui Ya-nan , Li Jia-di , et al . Microstructure and rheological properties at lowtemperature of modified asphalt under salt freezing cycle[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2016, 33(8): 1718-1724. | |
| 3 | Feng D C , Yi J Y , Wang D S , et al . Impact of salt and freeze-thaw cycles on performance of asphalt mixtures in coastal frozen region of China[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2010, 62(1): 34-41. |
| 4 | Han J W , Cui Y N , Li Z , et al . Research on the microstructure and performance of asphalt after the salt Freezing cycle[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2014, 575: 238-244. |
| 5 | 马慧莉 . 无机填料对沥青胶浆力学性能影响的细观力学分析[D]. 长春:吉林大学交通学院,2013. |
| Ma Hui-li . Research of inorganic filler on the properties of asphalt mastic by meso-mechanical method[D]. Changchun:College of Transportation, Jilin University, 2013. | |
| 6 | Guo Meng , Tan Yi-qiu , Hou Yue , et al . Improvement of evaluation indicator of interfacial interaction between asphalt binder and mineral fillers[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 151: 236-245. |
| 7 | 熊锐,关博文,盛燕萍 . 硫酸盐-干湿循环侵蚀环境下水镁石纤维沥青混合料抗疲劳性能[J]. 武汉理工大学学报,2014,36(10):45-51. |
| Xiong Rui , Guan Bo-wen , Sheng Yan-ping . Anti-fatigue property of brucite fiber reinforced asphalt mixture under sulfate and dry-wet circle corrosion environment[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2014, 36(10): 45-51. | |
| 8 | 黄新颜,沙爱民,蒋玮,等 . 盐分侵蚀对沥青和沥青混合料性能影响及作用机理[J]. 长安大学学报:自然科学版,2017,37(3):33-38,46. |
| Huang Xin-yan , Sha Ai-min , Jiang Wei , et al . Effect and mechanism of salt erosion on performance of bitumen and asphalt mixtures[J]. Journal of Chang'an University(Natural Science Edition), 2017, 37(3): 33-38, 46. | |
| 9 | Liu Z Z , Sha A M , Xing M L , et al . Low temperature property and salt releasing characteristics of antifreeze asphalt concrete under static and dynamic conditions[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2015, 114: 9-14. |
| 10 | 陈拴发,刘状壮,邢明亮,等 . 融雪抑冰材料疏水性能影响因素研究[J]. 建筑材料学报,2013,16(6):1053-1057,1071. |
| Chen Shuan-fa , Liu Zhuang-zhuang , Xing Ming-liang , et al . Research on the factors influencing hydrophobic properties of anti-freezing material[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2013, 16(6): 1053-1057, 1071. | |
| 11 | 李海莲,李波,王起才,等 . 基于表面能理论的老化温拌SBS改性沥青结合料的粘附性[J].材料导报,2017,31(16):129-133,149. |
| Li Hai-lian , Li Bo , Wang Qi-cai , et al . Adhesion of aged SBS modified asphalt binder containing warm mix additive based on surface free energy[J]. Materials Review, 2017, 31(16): 129-133, 149. | |
| 12 | 张恺,罗蓉,张德润 . 基于表面自由能理论的彩色树脂类沥青材料润湿性分析[J]. 中国公路学报,2016,29(5):34-40. |
| Zhang Kai , Luo Rong , Zhang De-run . Wettability analysis on colored resin asphalt binder based on surface free energy theory[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2016, 29(5): 34-40. | |
| 13 | Liu S T , Cao W D , Shang S J , et al . Analysis and application of relationships between low-temperature rheological performance parameters of asphalt binders[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2010, 24(4): 471-478. |
| [1] | 王芳,李晓光,郭慧,胡佳. 基于驾驶员视觉兴趣区的沙漠草原公路曲线间直线段线形指标优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 114-120. |
| [2] | 王英,李萍,念腾飞,姜继斌. 基于动水冲刷作用的沥青混合料短期水损害特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 174-182. |
| [3] | 万平,吴超仲,马晓凤. 基于ROC曲线和驾驶行为特征的驾驶愤怒强度判别阈值[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 121-131. |
| [4] | 朱春凤,程永春,梁春雨,肖波. 硅藻土⁃玄武岩纤维复合改性沥青混合料路用性能试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 165-173. |
| [5] | 狄胜同,贾超,乔卫国,李康,童凯. 橡胶集料混凝土细观损伤特性的加载速率效应[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1900-1910. |
| [6] | 张云龙,周刘光,王静,吴春利,吕翔. 冻融对粉砂土力学特性及路堤边坡稳定性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1531-1538. |
| [7] | 彭勇,高华,万蕾,刘贵应. 沥青混合料劈裂强度影响因素数值模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1521-1530. |
| [8] | 李晓珍,柳俊哲,戴燕华,贺智敏,巴明芳,李玉顺. 碳化作用下水泥浆内亚硝酸根离子的含量分布[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1162-1168. |
| [9] | 于天来,李海生,黄巍,王思佳. 预应力钢丝绳加固钢筋混凝土梁桥抗剪性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1134-1143. |
| [10] | 黄晓明,曹青青,刘修宇,陈嘉颖,周兴林. 基于路表分形摩擦理论的整车雨天制动性能模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 757-765. |
| [11] | 王静,吕翔,曲肖龙,钟春玲,张云龙. 路基土抗剪强度与化学及矿物成分的关系[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 766-772. |
| [12] | 李伊,刘黎萍,孙立军. 沥青面层不同深度车辙等效温度预估模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1703-1711. |
| [13] | 念腾飞, 李萍, 林梅. 冻融循环下沥青特征官能团含量与流变参数灰熵分析及微观形貌[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1045-1054. |
| [14] | 臧国帅, 孙立军. 基于惰性弯沉点的刚性下卧层深度设置方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1037-1044. |
| [15] | 宫亚峰, 申杨凡, 谭国金, 韩春鹏, 何钰龙. 不同孔隙率下纤维土无侧限抗压强度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 712-719. |
|
||