吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (2): 557-564.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20190082
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
基于生存分析的城市桥梁使用性能衰变模型
- 同济大学 道路与交通工程教育部重点实验室,上海 201804
Urban bridge performance decay model based on survival analysis
- The Key Laboratory of Road and Traffic Engineering, Ministry of Education, Tongji University, Shanghai 201804, China
摘要:
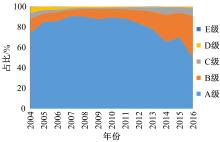
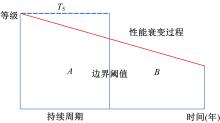
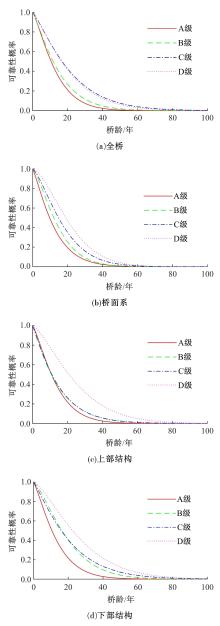
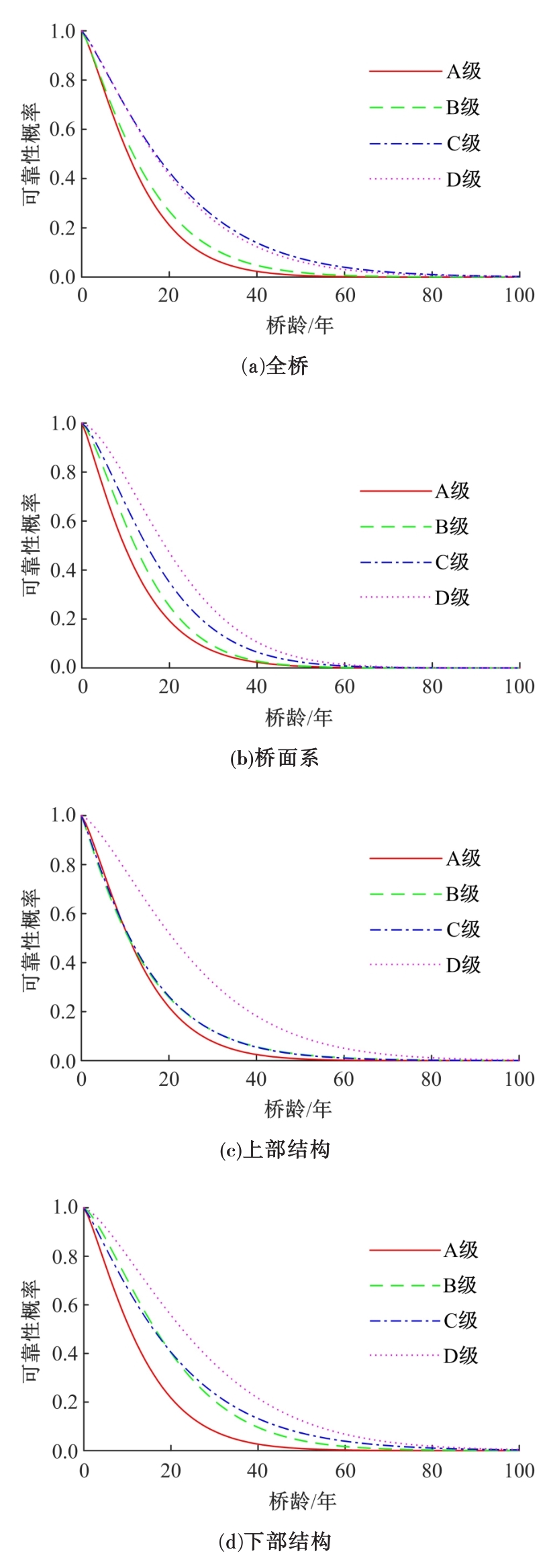
使用上海市城市桥梁的历年常规检测数据,基于生存分析理论建立了桥梁使用性能衰变的概率性预测模型。同时,利用韦伯分布的可靠性函数深入描述了不同等级内桥梁各部位的性能衰变行为,研究表明:当前上海市城市桥梁在状态等级为A级和B级时持续周期相对较短;且相比于下部结构,桥梁的桥面系和上部结构的性能衰变速率更快。最后,根据2016年~2018年网级桥梁衰变预测的实际算例,对比了生存分析与回归分析、马尔科夫链的预测效果差异,验证了生存分析模型具有较高的预测精度。
中图分类号:
- U418
| 1 | 孙立军. 道路与机场设施管理学[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2009. |
| 2 | 周志星. 混凝土梁桥结构技术状况退化预测研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学土木工程学院, 2016. |
| Zhou Zhi-xing. Research on degradation prediction of structural status of concrete beam bridges[D]. Chongqing: College of Civil Engineering, Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2016. | |
| 3 | Mishalani R G, Madanat S M. Computation of infrastructure transition probabilities using stochastic duration models[J]. Journal of Infrastructure Systems, 2002, 8(4): 139-148. |
| 4 | 吉婉欣. 城市桥梁使用性能衰变分析与预测研究[D]. 上海: 同济大学交通运输工程学院, 2014. |
| Ji Wan-xin. Deterioration analysis and forecasting model of urban bridges[D]. Shanghai: School of Transportation Engineering, Tongji University, 2014. | |
| 5 | 杨良, 孙立军. 钢筋混凝土桥梁使用性能衰变特征分析[J]. 武汉理工大学学报: 交通科学与工程版, 2014, 38(5): 989-992. |
| Yang Liang, Sun Li-jun. Analysis of service performance decay characteristic of reinforced concrete bridge[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology (Transportation Science and Engineering), 2014, 38(5): 989-992. | |
| 6 | 陈长. 交通基础设施管理系统技术结构研究[D]. 上海: 同济大学交通运输工程学院, 2005. |
| Chen Zhang. Research on technical structure of transportation infrastructure management system[D]. Shanghai: School of Transportation Engineering, Tongji University, 2005. | |
| 7 | Roelfstra G, Hajdin R, Adey B, et al. Condition evolution in bridge management systems and corrosion-induced deterioration[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2004, 9(3): 268-277. |
| 8 | 肖萍. 桥梁技术状况评价与预测[D]. 西安: 长安大学土木工程学院, 2003. |
| Xiao Ping. Evaluation and prediction of bridge technology status[D]. Xi'an: College of Civil Engineering, Chang'an University, 2003. | |
| 9 | Su D, Nassif H, Hwang E S. Probabilistic approach for forecasting long term performance of girder bridges[R]. TRB Committee AHD35 Bridge Management, Washington DC, United States, 2015. |
| 10 | Li L, Sun L, Ning G. Deterioration prediction of urban bridges on network level using markov-chain model[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2014(7): 1-10. |
| 11 | 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. CJJ 99-2017城市桥梁养护技术标准[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2017. |
| 12 | 曾胜男, 孙立军. 基于构件的桥梁缺损状况分层加权评价方法[J]. 同济大学学报: 自然科学版, 2006, 34(11): 1475-1478, 1498. |
| Zeng Sheng-nan, Sun Li-jun. A hierarchy-weight evaluation method of bridge distress condition[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2006, 34(11): 1475-1478, 1498. | |
| 13 | Morcous G. Performance prediction of bridge deck systems using Markov chains[J]. Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities, 2006, 20(2): 146-155. |
| 14 | Veshosky D, Beidleman C R, Buetow G W, et al. Comparative analysis of bridge superstructure deterioration[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 1994, 120(7): 2123-2136. |
| 15 | Agrawal A K, Kawaguchi A, Chen Z. Deterioration rates of typical bridge elements in New York[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2010, 15(4): 419-429. |
| 16 | van Casteren J. Power system reliability assessment using the weibull-markov model[D]. Sweden: Licentiate Thesis, Electric Power Engineering Department, Chalmers University of Technology, 2001. |
| 17 | Fang Y, Li L, Chen Z, et al. Prediction model of concrete girder bridge deterioration in Shanghai using weibull-distribution method[C]∥Transportation Research Board 96th Annual Meeting, Washington DC, United States, 2017: 202-217. |
| 18 | Madanat S M, Karlaftis M G, Mccarthy P S. Probabilistic infrastructure deterioration models with panel data[J]. Journal of Infrastructure Systems, 1997, 3(1): 4-9. |
| 19 | Lu P, Pei S, Tolliver D, et al. Data-based evaluation of regression models for bridge component deterioration[C]∥Transportation Research Board 94th Annual Meeting, Washington DC, United States, 2015. |
| 20 | Winn E, Burgueno R, Haider S W. Project-and network-level bridge deck degradation models via neural networks trained on empirical data[C]∥Transportation Research Board Meeting, Washington DC, 2013. |
| 21 | 马泽欣, 刘黎萍, 孙立军. 基于加速加载的在役沥青混合料损伤与疲劳性能[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(2): 384-391. |
| Ma Ze-xin, Liu Li-ping, Sun Li-jun. Damage and fatigue performance of in service asphalt mixtures based on accelerated loading test[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(2): 384-391. | |
| 22 | 郭学东, 张立业, 董丽娟, 等. 桥梁系统可靠性评估方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2012, 42(3): 634-638. |
| Guo Xue-dong, Zhang Li-ye, Dong Li-juan, et al. Bridge system reliability evaluation method[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2012, 42(3): 634-638. |
| [1] | 王芳,李晓光,郭慧,胡佳. 基于驾驶员视觉兴趣区的沙漠草原公路曲线间直线段线形指标优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 114-120. |
| [2] | 王鹏辉,乔宏霞,冯琼,曹辉,温少勇. 氯氧镁涂层钢筋混凝土两重因素耦合作用下的耐久性模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 191-201. |
| [3] | 王英,李萍,念腾飞,姜继斌. 基于动水冲刷作用的沥青混合料短期水损害特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 174-182. |
| [4] | 万平,吴超仲,马晓凤. 基于ROC曲线和驾驶行为特征的驾驶愤怒强度判别阈值[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 121-131. |
| [5] | 熊锐,乔宁,褚辞,杨发,关博文,盛燕萍,牛冬瑜. 掺盐沥青胶浆低温流变及粘附特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 183-190. |
| [6] | 朱春凤,程永春,梁春雨,肖波. 硅藻土⁃玄武岩纤维复合改性沥青混合料路用性能试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 165-173. |
| [7] | 狄胜同,贾超,乔卫国,李康,童凯. 橡胶集料混凝土细观损伤特性的加载速率效应[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1900-1910. |
| [8] | 张云龙,周刘光,王静,吴春利,吕翔. 冻融对粉砂土力学特性及路堤边坡稳定性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1531-1538. |
| [9] | 彭勇,高华,万蕾,刘贵应. 沥青混合料劈裂强度影响因素数值模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1521-1530. |
| [10] | 李晓珍,柳俊哲,戴燕华,贺智敏,巴明芳,李玉顺. 碳化作用下水泥浆内亚硝酸根离子的含量分布[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1162-1168. |
| [11] | 徐戊矫,刘承尚,鲁鑫垚. 喷丸处理后6061铝合金工件表面粗糙度的模拟计算及预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1280-1287. |
| [12] | 于天来,李海生,黄巍,王思佳. 预应力钢丝绳加固钢筋混凝土梁桥抗剪性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1134-1143. |
| [13] | 黄晓明,曹青青,刘修宇,陈嘉颖,周兴林. 基于路表分形摩擦理论的整车雨天制动性能模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 757-765. |
| [14] | 王静,吕翔,曲肖龙,钟春玲,张云龙. 路基土抗剪强度与化学及矿物成分的关系[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 766-772. |
| [15] | 李伊,刘黎萍,孙立军. 沥青面层不同深度车辙等效温度预估模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1703-1711. |
|
||