吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 1396-1404.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200431
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于多尺度注意力融合和卷积神经网络的水下图像恢复
- 上海海洋大学 信息学院,上海 201306
Underwater image restoration based on multi-scale attention fusion and convolutional neural network
De-xing WANG( ),Ruo-you WU,Hong-chun YUAN(
),Ruo-you WU,Hong-chun YUAN( ),Peng GONG,Yue WANG
),Peng GONG,Yue WANG
- School of Information,Shanghai Ocean University,Shanghai 201306,China
摘要:
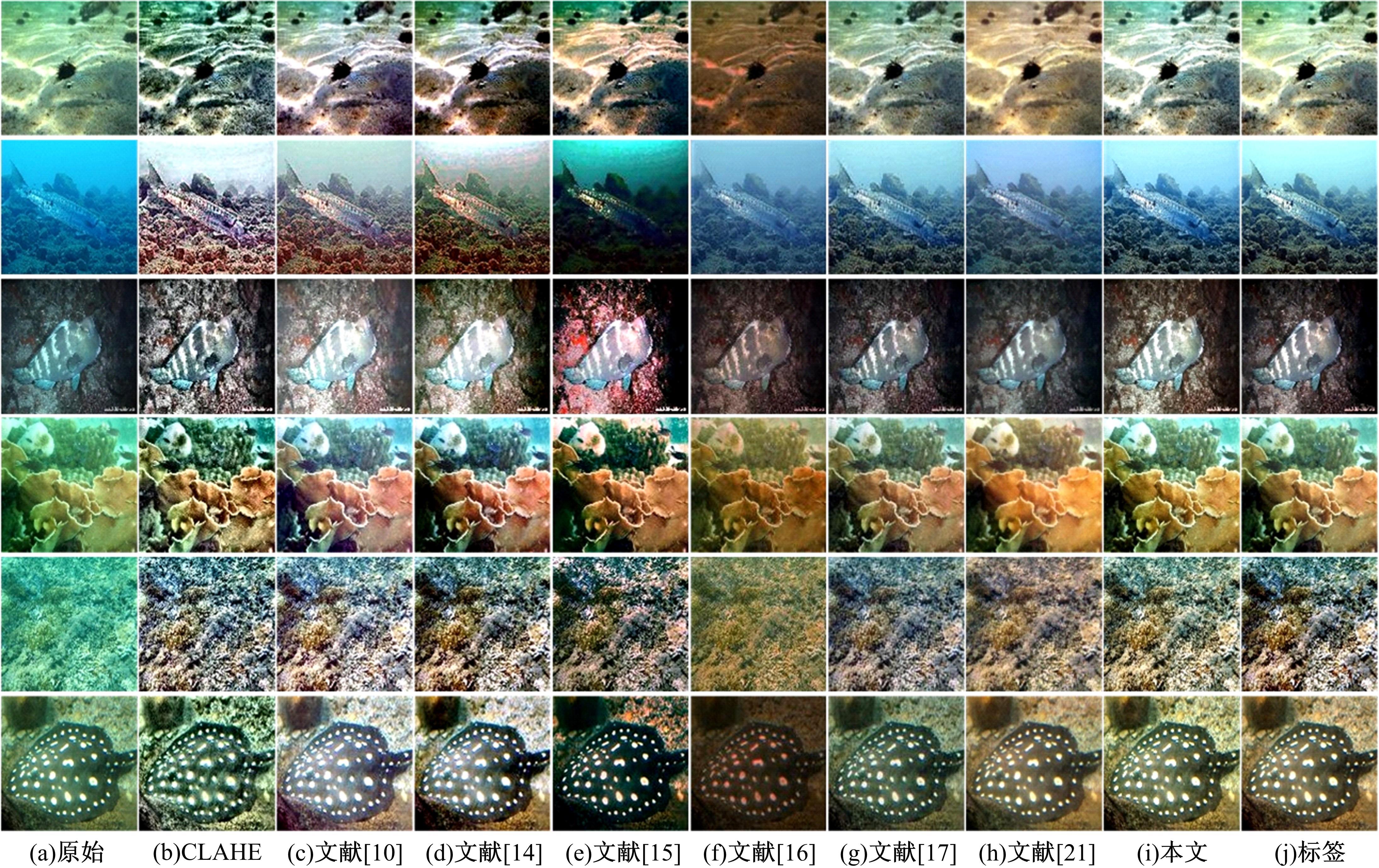
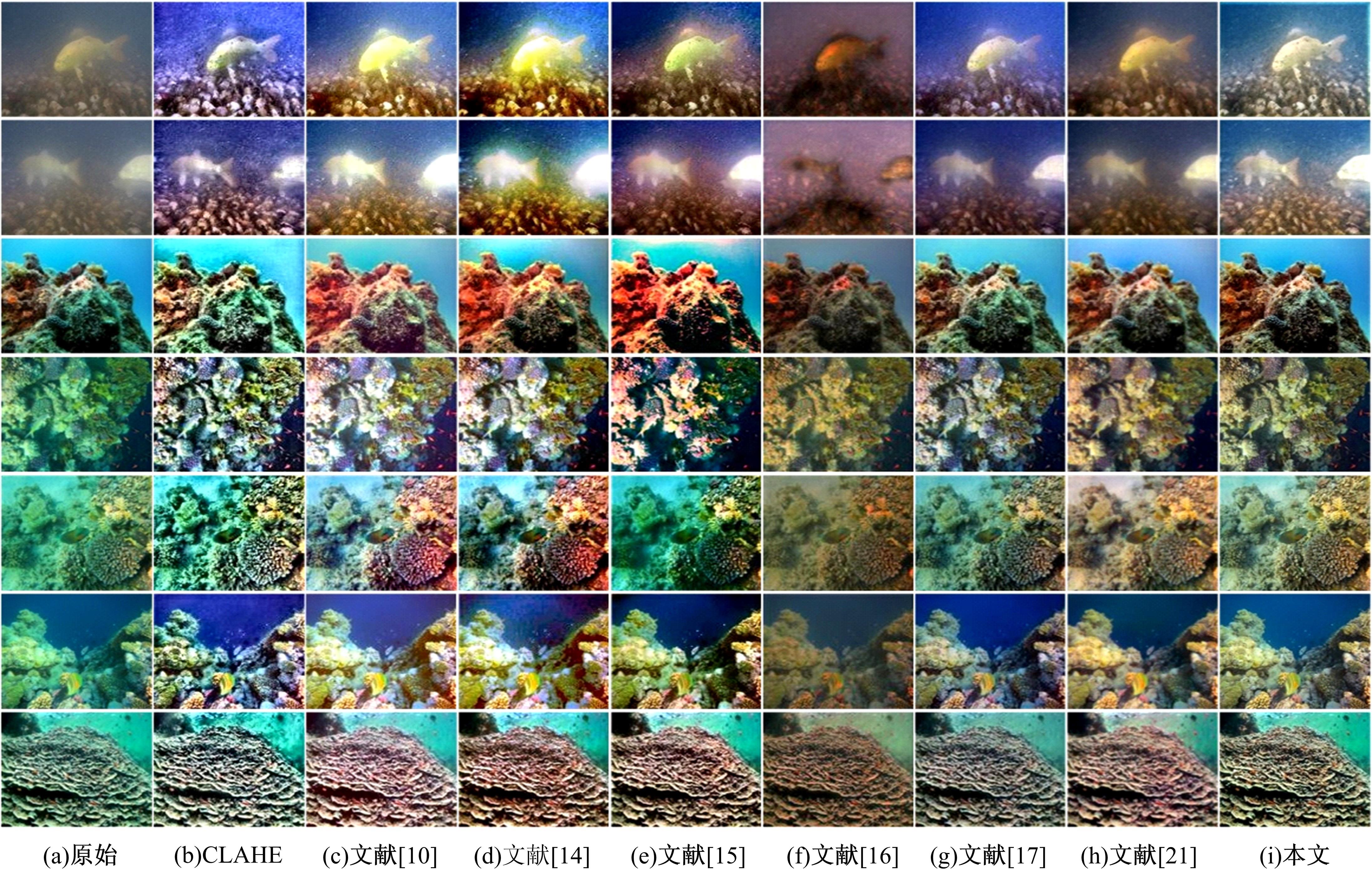
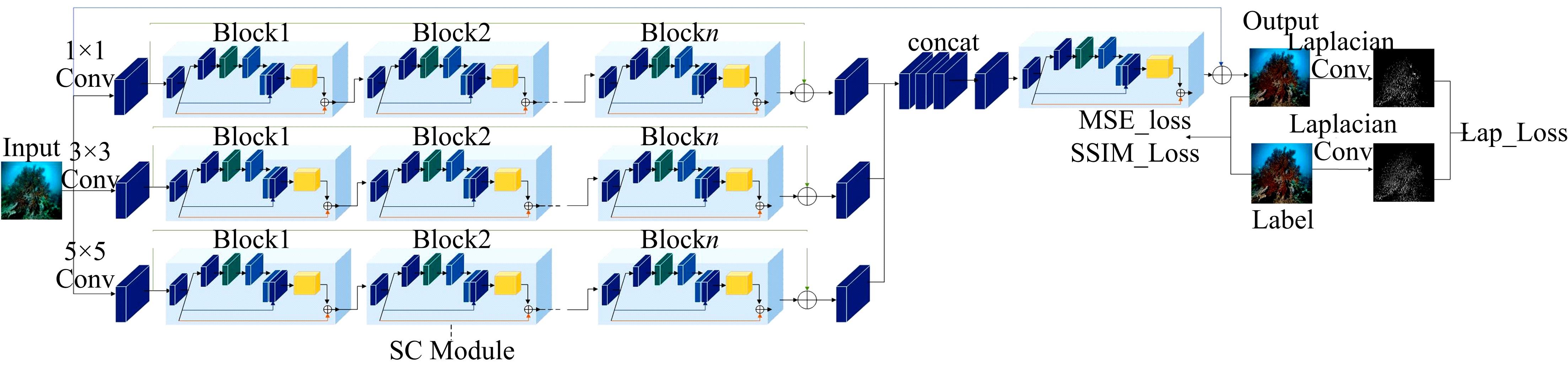
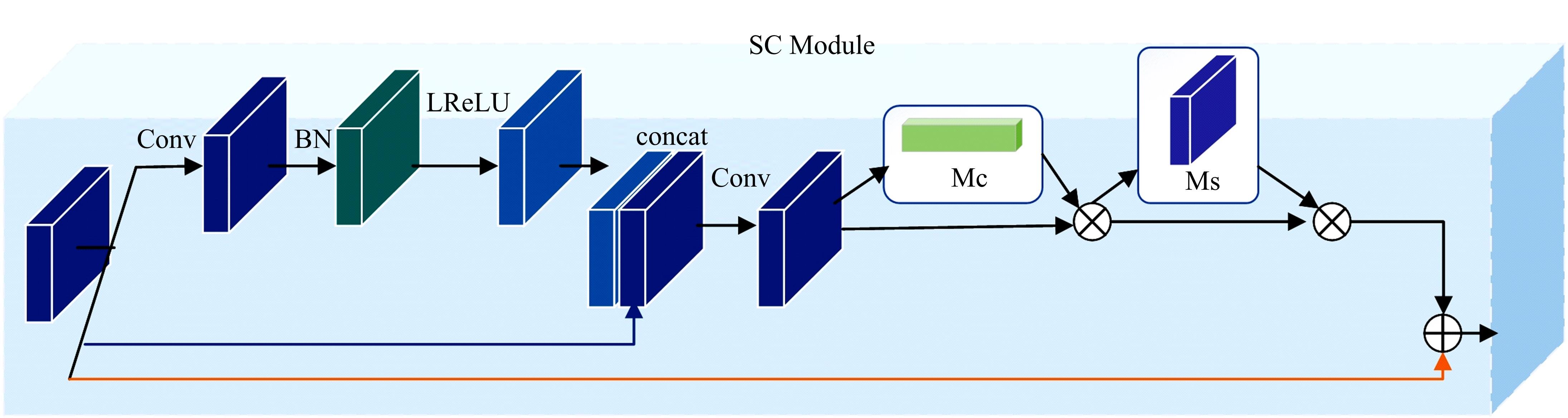
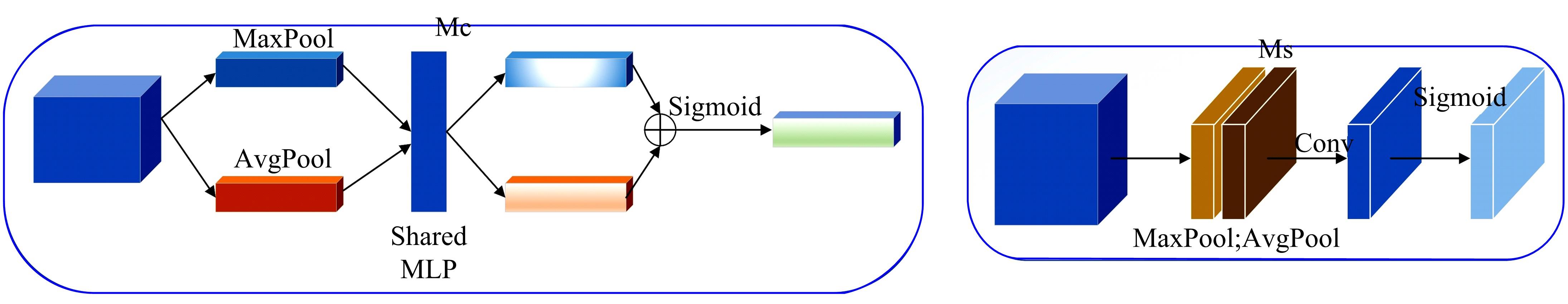
由于水中悬浮粒子对光的吸收和散射,导致原始水下图像清晰度低、细节模糊和颜色失真,针对这些问题,提出了一种基于多尺度注意力融合和卷积神经网络CNN的水下图像恢复方法。利用注意力机制构造SC(Space channel)模块,通过在多尺度特征提取中加入SC模块,可以有效地提取图像中的信息,实现图像清晰度的提高和颜色校正。利用拉普拉斯算子构造多项损失函数,进一步增强图像细节特征,使得恢复后的图像质量得到显著提升。将本文方法与其他方法在两个测试集上进行定性和定量的对比,实验结果表明,本文方法恢复后的图像在图像清晰度、细节增强和颜色校正方面都优于其他方法。
中图分类号:
- TP391.4
| 1 | Meline A, Triboulet J, Jouvencel B. Comparative study of two 3D reconstruction methods for underwater archaeology[C]∥IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Vilamoura, Portugal, 2012: 740-745. |
| 2 | Skarlatos D, Agrafifiotis P, Menna F, et al. Ground control networks for underwater photogrammetry in archaeological excavations[C]∥Proceedings of the 3rd IMEKO International Conference on Metrology for Archaeology and Cultural Heritage,Lecce, Italy, 2017: 23-25. |
| 3 | Chuang M C, Hwang J N, Williams K. A feature learning and object recognition framework for underwater fish images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(4): 1862-1872. |
| 4 | Shkurti F, Xu A, Meghjani M, et al. Multi-domain monitoring of marine environments using a heterogeneous robot team[C]∥IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems,Vilamoura, Portugal, 2012: 1747-1753. |
| 5 | Wang X, Li Q, Yin J, et al. An adaptive denoising and detection approach for underwater sonar image[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(4): No.396. |
| 6 | Zeng L, Sun B, Zhang W, et al. Underwater Image Target Detection with Cascade Classifier and Image Preprocessing Method[C]∥International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Applications, Shenyang, China, 2019: 195-205. |
| 7 | Güraksin G E, Köse U, Deperlioğlu Ö. Underwater image enhancement based on contrast adjustment via differential evolution algorithm[C]∥International Symposium on Innovations in Intelligent Systems and Applications, Sinaia, Romania, 2016: 1-5. |
| 8 | Henke B, Vahl M, Zhou Z. Removing color cast of underwater images through non-constant color constancy hypothesis[C]∥The 8th International Symposium on Image and Signal Processing and Analysis, Trieste, Italy, 2013: 20-24. |
| 9 | Ancuti C O, Ancuti C, de Vleeschouwer C, et al. Locally adaptive color correction for underwater image dehazing and matching[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 1-9. |
| 10 | Zhang W, Li G, Ying Z. A New Underwater Image Enhancing Method via Color Correction and Illumination Adjustment[C]∥IEEE Visual Communications and Image Processing, USA: IEEE, 2017: 1-4. |
| 11 | Zou W, Wang X, Li K, et al. Self-tuning underwater image fusion method based on dark channel prior[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, Qingdao, China, 2016: 788-793. |
| 12 | Chiang J Y, Chen Y C. Underwater image enhancement by wavelength compensation and dehazing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2011, 21(4): 1756-1769. |
| 13 | Akkaynak D, Treibitz T. A revised underwater image formation model[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 6723-6732. |
| 14 | Li C Y, Guo J C, Cong R M, et al. Underwater image enhancement by dehazing with minimum information loss and histogram distribution prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(12): 5664-5677. |
| 15 | Berman D, Levy D, Avidan S, et al. Underwater Single Image Color Restoration Using Haze-Lines and a New Quantitative Dataset [EB/OL]∥[2020-06-13]. . |
| 16 | Li C, Anwar S, Porikli F. Underwater scenes prior inspired deep underwater image and video enhancement[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2020, 98: 107038. |
| 17 | Li C, Guo C, Ren W, et al. An Underwater Image Enhancement Benchmark Dataset and Beyond [EB/OL]. [2020-06-13]. . |
| 18 | 徐岩, 孙美双. 基于卷积神经网络的水下图像增强方法[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2018, 48(6): 1895-1903. |
| Xu Yan, Sun Mei-shuang. Underwater image enhancement method based on convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(6): 1895-1903. | |
| 19 | Li J, Skinner K A, Eustice R M, et al. WaterGAN: Unsupervised generative network to enable real-time color correction of monocular underwater images[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2017, 3(1): 387-394. |
| 20 | Lu J, Li N, Zhang S, et al. Multi-scale adversarial network for underwater image restoration[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2019, 110: 105-113. |
| 21 | Islam M J, Xia Y, Sattar J. Fast underwater image enhancement for improved visual perception[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2020, 5(2): 3227-3234. |
| 22 | Zhang B, Jin S, Xia Y, et al. Attention Mechanism Enhanced Kernel Prediction Networks for Denoising of Burst Images[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 2020: 2083-2087. |
| 23 | Chen D, He Z, Cao Y, et al. Deep neural network for fast and accurate single image super-resolution via channel-attention-based fusion of orientation-aware features [EB/OL].[2020-06-13]. . |
| 24 | Li H, Qiu K, Chen L, et al. SCAttNet: semantic segmentation network with spatial and channel attention mechanism for high-resolution remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020,18(5):905-909. |
| 25 | Woo S, Park J, Lee J Y, et al. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 2018: 3-19. |
| 26 | Hautière N, Tarel J P, Aubert D, et al. Blind contrast enhancement assessment by gradient ratioing at visible edges[J]. Image Analysis & Stereology, 2008, 27(2): 87-95. |
| 27 | Liu L, Liu B, Huang H, et al. No-reference image quality assessment based on spatial and spectral entropies[J]. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2014, 29(8): 856-863. |
| 28 | Mittal A, Soundararajan R, Bovik A C. Making a "completely blind" image quality analyzer[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2012, 20(3): 209-212. |
| 29 | Liu L, Hua Y, Zhao Q, et al. Blind image quality assessment by relative gradient statistics and adaboosting neural network[J]. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2016, 40: 1-15. |
| 30 | Panetta K, Gao C, Agaian S. Human-visual-system-inspired underwater image quality measures[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2015, 41(3): 1-11. |
| [1] | 赵亚慧,杨飞扬,张振国,崔荣一. 基于强化学习和注意力机制的朝鲜语文本结构发现[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1387-1395. |
| [2] | 李厚杰,王法胜,贺建军,周瑜,李威,窦宇轩. 基于伪样本正则化Faster R⁃CNN的交通标志检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1251-1260. |
| [3] | 蒋华伟,杨震,张鑫,董前林. 图像去雾算法研究进展[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1169-1181. |
| [4] | 金静,党建武,王阳萍,申东. 融合模糊统计纹理特征的多线索粒子滤波跟踪[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1111-1120. |
| [5] | 刘元宁,吴迪,朱晓冬,张齐贤,李双双,郭书君,王超. 基于YOLOv3改进的用户界面组件检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1026-1033. |
| [6] | 郭继昌,乔珊珊. 基于深度图的水下图像复原[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 677-684. |
| [7] | 赵海英,周伟,侯小刚,张小利. 基于多任务学习的传统服饰图像双层标注[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 293-302. |
| [8] | 李志军,杨楚皙,刘丹,孙大洋. 基于深度卷积神经网络的信息流增强图像压缩方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1788-1795. |
| [9] | 赵宏伟,刘晓涵,张媛,范丽丽,龙曼丽,臧雪柏. 基于关键点注意力和通道注意力的服装分类算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1765-1770. |
| [10] | 刘国华,周文斌. 基于卷积神经网络的脉搏波时频域特征混叠分类[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1818-1825. |
| [11] | 王柯俨,王迪,赵熹,陈静怡,李云松. 基于卷积神经网络的联合估计图像去雾算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1771-1777. |
| [12] | 史再峰,李金卓,曹清洁,李慧龙,胡起星. 基于生成对抗网络的低剂量能谱层析成像去噪算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1755-1764. |
| [13] | 车翔玖,董有政. 基于多尺度信息融合的图像识别改进算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1747-1754. |
| [14] | 谌华,郭伟,闫敬文,卓文浩,吴良斌. 基于深度学习的SAR图像道路识别新方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1778-1787. |
| [15] | 张薇,韩勇,金铭,乔晓林. 基于托普利兹矩阵集重构的相干信源波达方向估计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 703-710. |
|
||